Abstract
Background
Inflammatory breast cancer (IBC) is a rare and aggressive subtype of breast cancer characterized by rapid progression and early metastasis, often with advanced nodal locations, including the supraclavicular (SCV) nodal basin. Previously considered M1 disease, ipsilateral clinical supraclavicular node involvement (N3c) disease is now considered locally advanced disease and warrants treatment with intent to cure. The objective of this study was to evaluate the long-term outcomes of patients with IBC and N3c disease.
Patients and Methods
This study was conducted using a prospectively collected database of all patients with IBC treated at a dedicated cancer center from 2007 to 2019. Surgical patients with SCV nodal involvement and complete follow-up were identified. Our primary outcome was 5-year overall survival (OS). Multivariate Cox proportional hazards models were used to determine predictors for survival. Event-free survival (EFS) and OS were calculated using the Kaplan–Meier method.
Results
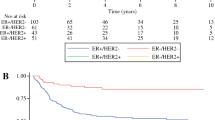
There were 70 patients who met inclusion criteria. All patients underwent comprehensive trimodality therapy. The majority of patients had complete (66.2%) radiologic response in the SCV nodal basins following neoadjuvant therapy. Six patients (8.6%) had a locoregional recurrence, with two (2.9%) occurring in the supraclavicular fossa. The 5-year OS was 60.2% [95% confidence interval (CI) 47.7–72.7%]. Increasing age (hazard ratio 2.7; p = 0.03) and triple-negative subtype (hazard ratio 4.9; p = 0.03) were associated with poor OS. The 5-year EFS was 56.1% (95% CI 40.9–68.8%). The presence of more than ten positive axillary nodes on final surgical pathology (hazard ratio 5.5; p = 0.01) predicted poor EFS.
Conclusions
With comprehensive trimodality therapy and multidisciplinary team approach, patients with IBC with supraclavicular nodal involvement experience excellent locoregional control and favorable survival.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adesoye T, Lucci A. Current surgical management of inflammatory breast cancer. Ann Surg Oncol. 2021;28(10):5461–7.
Brito RA, Valero V, Buzdar AU, Booser DJ, Ames F, Strom E, Ross M, Theriault RL, Frye D, Kau SW, Asmar L. Long-term results of combined-modality therapy for locally advanced breast cancer with ipsilateral supraclavicular metastases: the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center experience. J Clin Oncol. 2001;19(3):628–33.
Fouad TM, Barrera AM, Reuben JM, Lucci A, Woodward WA, Stauder MC, Lim B, DeSnyder SM, Arun B, Gildy B, Valero V. Inflammatory breast cancer: a proposed conceptual shift in the UICC–AJCC TNM staging system. Lancet Oncol. 2017;18(4):e228–32.
National Comprehensive Cancer Network. NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology (NCCN Guidelines). Breast Cancer. Version 5.2021—June 28, 2021. Available at https://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/pdf/breast.pdf. Accessed 1 July 2021
Bristol IJ, Woodward WA, Strom EA, Cristofanilli M, Domain D, Singletary SE, Perkins GH, Oh JL, Yu TK, Terrefe W, Sahin AA. Locoregional treatment outcomes after multimodality management of inflammatory breast cancer. IJROBP. 2008;72(2):474–84.
Lv M, Li J, Guo H, Wang C, Tian P, Ma Y, Chen X, Luo S. Impact of ipsilateral supraclavicular lymph node dissection (ISLND) for breast cancer patients and a nomogram for predicting ipsilateral supraclavicular pathological complete response (ispCR). Ann Surg Oncol. 2021;28(9):5098–109.
Ai X, Wang M, Li J, Hu Y, Hou L, Zheng X, Yan Y, Pan Q, Jin Y, Liu W, Tan X. Supraclavicular lymph node dissection with radiotherapy versus radiotherapy alone for operable breast cancer with synchronous ipsilateral supraclavicular lymph node metastases: a real-world cohort study. Gland Surg. 2020;9(2):329.
Dominici LS, Negron Gonzalez VM, Buzdar AU, Lucci A, Mittendorf EA, Le-Petross HT, Babiera GV, Meric-Bernstam F, Hunt KK, Kuerer HM. Cytologically proven axillary lymph node metastases are eradicated in patients receiving preoperative chemotherapy with concurrent trastuzumab for HER2-positive breast cancer. Cancer. 2010;116(12):2884–9.
Diao K, Andring LM, Barcenas CH, Singh P, Le-Petross HC, Reed VK, Reddy JP, Bloom ES, Ahmad NR, Mayo LL, Perkins GH. Contemporary outcomes after multimodality therapy in patients with breast cancer presenting with ipsilateral supraclavicular node involvement. IJROBP. 2022;112(1):66–74.
Rosso KJ, Tadros AB, Weiss A, Warneke CL, DeSnyder S, Kuerer H, Ueno NT, Stecklein SR, Woodward WA, Lucci A. Improved locoregional control in a contemporary cohort of nonmetastatic inflammatory breast cancer patients undergoing surgery. Ann Surg Oncol. 2017;24(10):2981–8.
Dawood S, Merajver SD, Viens P, Vermeulen PB, Swain SM, Buchholz TA, Dirix LY, Levine PH, Lucci A, Krishnamurthy S, Robertson FM, Woodward WA, Yang WT, Ueno NT, Cristofanilli M. International expert panel on inflammatory breast cancer: consensus statement for standardized diagnosis and treatment. Ann Oncol. 2011;22(3):515–23. https://doi.org/10.1093/annonc/mdq345.
Huang EH, Tucker SL, Strom EA, McNeese MD, Kuerer HM, Hortobagyi GN, Buzdar AU, Valero V, Perkins GH, Schechter NR, Hunt KK. Predictors of locoregional recurrence in patients with locally advanced breast cancer treated with NACT, mastectomy, and radiotherapy. IJROBP. 2005;62(2):351–7.
Mamounas EP, Anderson SJ, Dignam JJ, Bear HD, Julian TB, Geyer CE Jr, Taghian A, Wickerham DL, Wolmark N. Predictors of locoregional recurrence after NACT: results from combined analysis of National Surgical Adjuvant Breast and Bowel Project B-18 and B-27. J Clin Oncol. 2012;30(32):3960.
Mordenti C, Peris K, Concetta Fargnoli M, Cerroni L, Chimenti S. Cutaneous metastatic breast carcinoma. Acta Dermatovenerol. 2000;9:4. https://doi.org/10.12890/2020_001356
Greenbaum MP, Strom EA, Allen PK, Perkins GH, Oh JL, Tereffe W, Yu TK, Buchholz TA, Woodward WA. Low locoregional recurrence rates in patients treated after 2000 with doxorubicin based chemotherapy, modified radical mastectomy, and post-mastectomy radiation. Radiother Oncol. 2010;95(3):312–6.
Grotenhuis BA, Klem TM, Vrijland WW. Treatment outcome in breast cancer patients with ipsilateral supraclavicular lymph node metastasis at time of diagnosis: a review of the literature. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2013;39(3):207–12.
Olivotto IA, Chua B, Allan SJ, Speers CH, Chia S, Ragaz J. Long-term survival of patients with supraclavicular metastases at diagnosis of breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2003;21(5):851–4.
Fan Y, Xu B, Liao Y, Yao S, Sun Y. A retrospective study of metachronous and synchronous ipsilateral supraclavicular lymph node metastases in breast cancer patients. Breast. 2010;19(5):365–9.
Ogino T, Komoike Y, Ishitobi M, Motomura K, Koyama H, Inaji H. Breast cancer with ipsilateral supraclavicular metastases. Breast J. 2011;17(5):555–7.
Park HJ, Shin KH, Cho KH, Park IH, Lee KS, Ro J, Jung SY, Lee S, Kim SW, Kang HS, Chie EK. Outcomes of positron emission tomography–staged clinical N3 breast cancer treated with NACT, surgery, and radiotherapy. IJROBP. 2011;81(5):e689–95.
Hester RH, Hortobagyi GN, Lim B. Inflammatory breast cancer: early recognition and diagnosis is critical. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2021;225(4):392–6.
Fouad TM, Ueno NT, Yu RK, Ensor JE, Alvarez RH, Krishnamurthy S, Lucci A, Reuben JM, Yang W, Willey JS, Valero V. Distinct epidemiological profiles associated with inflammatory breast cancer (IBC): a comprehensive analysis of the IBC registry at The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center. PLoS ONE. 2018;13(9):e0204372.
Viale G, Hanlon Newell AE, Walker E, Harlow G, Bai I, Russo L, Dell’Orto P, Maisonneuve P. Ki-67 (30–9) scoring and differentiation of luminal A-and luminal B-like breast cancer subtypes. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2019;178(2):451–8.
Çakar B, Sürmeli Z, Öner PG, Yelim ES, Karabulut B, Uslu R. The impact of subtype distribution in inflammatory breast cancer outcome. Eur J Breast Health. 2018;14(4):211.
Postlewait LM, Teshome M, DeSnyder SM, Lim B, Kuerer HM, Bedrosian I, Woodward WA, Ueno NT, Lucci A. Factors associated with pathological node negativity in inflammatory breast cancer: are there patients who may be candidates for a de-escalation of axillary surgery? Ann Surg Oncol. 2020;27(12):4603–12.
Hieken TJ, Murphy BL, Boughey JC, Degnim AC, Glazebrook KN, Hoskin TL. Influence of biologic subtype of inflammatory breast cancer on response to neoadjuvant therapy and cancer outcomes. Clin Breast Cancer. 2018;18(4):e501–6.
Woodward WA, Buchholz TA. The role of locoregional therapy in inflammatory breast cancer. Semin Oncol. 2008;35(1):78–86.
Ueno NT, Espinosa Fernandez JR, Cristofanilli M, Overmoyer B, Rea D, Berdichevski F, El-Shinawi M, Bellon J, Le-Petross HT, Lucci A, Babiera G, DeSnyder SM, Teshome M, Chang E, Lim B, Krishnamurthy S, Stauder MC, Parmar S, Mohamed MM, Alexander A, Valero V, Woodward WA. International consensus on the clinical management of inflammatory breast cancer from the Morgan Welch Inflammatory Breast Cancer Research Program 10th Anniversary Conference. J Cancer. 2018;9(8):1437–47. https://doi.org/10.7150/jca.23969.PMID:29721054;PMCID:PMC5929089.
Brzezinska M, Williams LJ, Thomas J, Michael Dixon J. Outcomes of patients with inflammatory breast cancer treated by breast-conserving surgery. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2016;160(3):387–91. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-016-4017-3 (Epub 2016 Oct 18 PMID: 27757718).
Cortazar P, Zhang L, Untch M, Mehta K, Costantino JP, Wolmark N, Bonnefoi H, Cameron D, Gianni L, Valagussa P, Swain SM. Pathological complete response and long-term clinical benefit in breast cancer: the CTNeoBC pooled analysis. Lancet. 2014;384(9938):164–72.
Nakhlis F, Regan MM, Warren LE, Bellon JR, Hirshfield-Bartek J, Duggan MM, Dominici LS, Golshan M, Jacene HA, Yeh ED, Mullaney EE. The impact of residual disease after preoperative systemic therapy on clinical outcomes in patients with inflammatory breast cancer. Ann Surg Oncol. 2017;24(9):2563–9.
Kuru B. Prognostic significance of total number of nodes removed, negative nodes removed, and ratio of positive nodes to removed nodes in node positive breast carcinoma. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2006;32(10):1082–8.
Neal CH, Daly CP, Nees AV, Helvie MA. Can preoperative axillary US help exclude N2 and N3 metastatic breast cancer? Radiology. 2010;257(2):335–41.
Aukema TS, Straver ME, Peeters MJ, Russell NS, Gilhuijs KG, Vogel WV, Rutgers EJ, Olmos RA. Detection of extra-axillary lymph node involvement with FDG PET/CT in patients with stage II–III breast cancer. Eur J Cancer. 2010;46(18):3205–10.
Acknowledgement
Institutional database supported by Morgan Welch Inflammatory Breast Cancer Research Program and the State of Texas Rare and Aggressive Breast Cancer Research Program Grant.
Funding
Wendy Woodward, Epic Science (honorarium), Exact Science (honorarium), Physicians Education Resource (honorarium).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Disclosure
Wendy Woodward, Epic Science (honorarium), Exact Science (honorarium), Physicians Education Resource (honorarium).
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cobb, A.N., Diao, K., Teshome, M. et al. Long-term Oncologic Outcomes in Patients with Inflammatory Breast Cancer with Supraclavicular Nodal Involvement. Ann Surg Oncol 29, 6381–6392 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-022-12144-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-022-12144-5