Abstract
Background
Neoadjuvant chemotherapy (NAC) downstages axillary disease in 55 % of node-positive (N1) breast cancer. The feasibility and accuracy of sentinel lymph node biopsy (SLNB) after NAC for percutaneous biopsy-proven N1 patients who are clinically node negative (cN0) by physical examination after NAC is under investigation. ACOSOG Z1071 reported a false-negative rate of <10 % if ≥3 nodes are removed with dual tracer, including excision of the biopsy-proven positive lymph node (BxLN). We report our experience using radioactive seed localization (RSL) to retrieve the BxLN with SLNB (RSL/SLNB) for cN0 patients after NAC.
Methods
We performed a retrospective review of a single-institution, prospectively maintained registry for the years 2013 to 2014. Patients with BxLN who received NAC and had RSL/SLNB were identified. All BxLNs were marked with a radiopaque clip before NAC to facilitate RSL.
Results
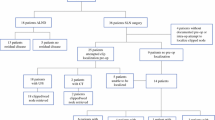
Thirty patients with BxLN before NAC were cN0 after NAC and underwent RSL/SLNB. Median age was 55 years. Disease stage was IIA–IIIB. Twenty-nine of 30 had ductal cancer (12 triple negative and 16 HER-2 positive). One to 11 nodes were retrieved. Twenty-nine of 30 BxLN were successfully localized with RSL. Note was made of the BxLN-containing isotope and/or dye in 22 of 30. Nineteen patients had no residual axillary disease; 11 had persistent disease. All who remained node positive had disease in the BxLN.
Conclusions
RSL/SLNB is a promising approach for axillary staging after NAC in patients whose disease becomes cN0. The status of the BxLN after NAC predicted nodal status, suggesting that localization of the BxLN may be more accurate than SLNB alone for staging the axilla in the cN0 patient after NAC.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Krag DN, Anderson SJ, Julian TB, et al. Technical outcomes of sentinel-lymph-node resection and conventional axillary-lymph-node dissection in patients with clinically node-negative breast cancer: results from the NSABP B-32 randomised phase III trial. Lancet Oncol. 2007;8:881–8.
Krag DN, Anderson SJ, Julian TB, et al. Sentinel-lymph-node resection compared with conventional axillary-lymph-node dissection in clinically node-negative patients with breast cancer: overall survival findings from the NSABP B-32 randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2010;11:927–33.
Lyman GH, Temin S, Edge SB, et al. Sentinel lymph node biopsy for patients with early-stage breast cancer: American Society of Clinical Oncology clinical practice guideline update. J Clin Oncol. 2014;32:1365–83.
Boughey JC, Suman VJ, Mittendorf EA, et al. Sentinel lymph node surgery after neoadjuvant chemotherapy in patients with node-positive breast cancer: the ACOSOG Z1071 (Alliance) clinical trial. JAMA. 2013;310:1455–61.
Giuliano AE, Hunt KK, Ballman KV, et al. Axillary dissection vs. no axillary dissection in women with invasive breast cancer and sentinel node metastasis: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA. 2011;305:569–75.
Galimberti V, Cole BF, Zurrida S, et al. Axillary dissection versus no axillary dissection in patients with sentinel-node micrometastases (IBCSG 23-01): a phase 3 randomised controlled trial. Lancet Oncol. 2013;14:297–305.
Donker M, van Tienhoven G, Straver ME, et al. Radiotherapy or surgery of the axilla after a positive sentinel node in breast cancer (EORTC 10981-22023 AMAROS): a randomised, multicentre, open-label, phase 3 non-inferiority trial. Lancet Oncol. 2014;15:1303–10.
Kuerer HM, Sahin AA, Hunt KK, et al. Incidence and impact of documented eradication of breast cancer axillary lymph node metastases before surgery in patients treated with neoadjuvant chemotherapy. Ann Surg. 1999;230:72–8.
Erdahl LM, Boughey JC. Use of sentinel lymph node biopsy to select patients for local-regional therapy after neoadjuvant chemotherapy. Curr Breast Cancer Rep. 2014;6:10–6.
Rastogi P, Anderson SJ, Bear HD, et al. Preoperative chemotherapy: updates of National Surgical Adjuvant Breast and Bowel Project Protocols B-18 and B-27. J Clin Oncol. 2008;26:778–85.
Hicks M, Macrae ER, Abdel-Rasoul M, et al. Neoadjuvant dual HER2-targeted therapy with lapatinib and trastuzumab improves pathologic complete response in patients with early stage HER2-positive breast cancer: a meta-analysis of randomized prospective clinical trials. Oncologist. 2015;20:337–43.
Denkert C, von Minckwitz G, Brase JC, et al. Tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes and response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy with or without carboplatin in human epidermal growth factor receptor 2–positive and triple-negative primary breast cancers. J Clin Oncol. 2015;33:983–91.
Lips EH, Mukhtar RA, Yau C, et al. Lobular histology and response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in invasive breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2012;136:35–43.
Kang SH, Kang JH, Choi EA, Lee ES. Sentinel lymph node biopsy after neoadjuvant chemotherapy. Breast Cancer. 2004;11:233–41.
Canavese G, Dozin B, Vecchio C, et al. Accuracy of sentinel lymph node biopsy after neo-adjuvant chemotherapy in patients with locally advanced breast cancer and clinically positive axillary nodes. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2011;37:688–94.
Kuehn T, Bauerfeind I, Fehm T, et al. Sentinel-lymph-node biopsy in patients with breast cancer before and after neoadjuvant chemotherapy (SENTINA): a prospective, multicentre cohort study. Lancet Oncol. 2013;14:609–18.
Boughey JC, Suman VJ, Mittendorf EA, et al. Factors affecting sentinel lymph node identification rate after neoadjuvant chemotherapy for breast cancer patients enrolled in ACOSOG Z1071 (Alliance). Ann Surg. 2015;261:547–52.
National Comprehensive Cancer Network. Breast cancer, version 2.2015. http://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/pdf/breast.pdf. Accessed 12 Apr 2015.
DiSipio T, Rye S, Newman B, Hayes S. Incidence of unilateral arm lymphoedema after breast cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Oncol. 2013;14:500–15.
McLaughlin SA, Wright MJ, Morris KT, et al. Prevalence of lymphedema in women with breast cancer 5 years after sentinel lymph node biopsy or axillary dissection: objective measurements. J Clin Oncol. 10 2008;26:5213–9.
Norman SA, Localio AR, Kallan MJ, et al. Risk factors for lymphedema after breast cancer treatment. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2010;19:2734–46.
Sagen A, Kaaresen R, Sandvik L, Thune I, Risberg MA. Upper limb physical function and adverse effects after breast cancer surgery: a prospective 2.5-year follow-up study and preoperative measures. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2014;95:875–81.
Wernicke AG, Shamis M, Sidhu KK, et al. Complication rates in patients with negative axillary nodes 10 years after local breast radiotherapy after either sentinel lymph node dissection or axillary clearance. Am J Clin Oncol. 2013;36:12–9.
Yen TW, Fan X, Sparapani R, Laud PW, Walker AP, Nattinger AB. A contemporary, population-based study of lymphedema risk factors in older women with breast cancer. Ann Surg Oncol. 2009;16:979–88.
Caudle AS, Yang WT, Mittendorf EA, et al. Selective surgical localization of axillary lymph nodes containing metastases in patients with breast cancer: a prospective feasibility trial. JAMA Surg. 2015;150:137–43.
Donker M, Straver ME, Wesseling J, et al. Marking axillary lymph nodes with radioactive iodine seeds for axillary staging after neoadjuvant systemic treatment in breast cancer patients: the MARI procedure. Ann Surg. 2015;261:378–82.
Caudle AS, Yang WT, Mittendorf EA, et al. Targeted axillary dissection improves axillary evaluation following neoadjuvant chemotherapy in node positive breast cancer. Paper presented at: 68th SSO Annual Cancer Symposium; March 25–28, 2015; Houston, TX.
Disclosure
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Diego, E.J., McAuliffe, P.F., Soran, A. et al. Axillary Staging After Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy for Breast Cancer: A Pilot Study Combining Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy with Radioactive Seed Localization of Pre-treatment Positive Axillary Lymph Nodes. Ann Surg Oncol 23, 1549–1553 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-015-5052-8
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-015-5052-8