Abstract
Purpose
Repeat sentinel node biopsy (SNB) is an alternative to axillary lymph node dissection (ALND) for axillary staging in recurrent breast cancer. This study was conducted to determine factors associated with technical success of repeat SNB.
Methods
A total of 536 patients with locally recurrent nonmetastatic breast cancer underwent lymphatic mapping (LM) and repeat SNB in 29 Dutch hospitals.
Results
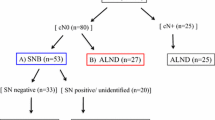
A total of 179 patients previously underwent breast-conserving surgery (BCS) with SNB, 262 patients BCS with ALND and 61 patients mastectomy, 35 with SNB and 26 with ALND. Another 34 patients underwent breast surgery without axillary interventions. A repeat sentinel node (SN) was identified in 333 patients (62.1 %) and was successfully removed in 235 (53.5 %). The overall repeat SN identification rate was 62.1 %, varying from 35 to 100 % in the participating hospitals. Previous radiotherapy of the breast [odds ratio (OR) 0.16; 95 % confidence interval (CI) 0.03–0.84], subareolar tracer injection (OR 0.34; 95 % CI 0.16–0.73), and a 2-day LM protocol (OR 0.57; 95 % CI 0.33–0.97) after previous BCS were independently associated with failure of SN identification. Injection of a larger amount of tracer (>180 MBq) led to a higher identification rate (OR 4.40; 95 % CI 1.45–13.32).
Conclusions
Repeat SNB is a technically feasible procedure for axillary staging in recurrent breast cancer patients. Previous radiotherapy appears to be associated with failure of SN identification. Injection with a larger amount of tracer (>180 MBq) leads to a higher identification rate; subareolar injection and a 2-day LM protocol after previous BCS appear to be less adequate.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
NABON. Richtlijn behandeling van het mammacarcinoom. 2012. http://www.oncoline.nl/. Accessed 1 May 2015.
Kim T, Giuliano AE, Lyman GH. Lymphatic mapping and sentinel lymph node biopsy in early-stage breast carcinoma: a metaanalysis. Cancer. 2006;106:4–16.
Burger AE, Pain SJ, Peley G. Treatment of recurrent breast cancer following breast conserving surgery. Breast J. 2013;19:310–8.
Maaskant-Braat AJ, Voogd AC, Roumen RM, Nieuwenhuijzen GA. Repeat sentinel node biopsy in patients with locally recurrent breast cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis of the literature. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2013;138:13–20.
Maaskant-Braat AJ, Roumen RM, Voogd AC, Pijpers R, Luiten EJ, Rutgers EJ, et al. Sentinel Node and Recurrent Breast Cancer (SNARB): results of a nationwide registration study. Ann Surg Oncol. 2013;20:620–6.
Intra M, Viale G, Vila J, Grana CM, Toesca A, Gentilini O, et al. Second axillary sentinel lymph node biopsy for breast tumor recurrence: experience of the European Institute of Oncology. Ann Surg Oncol. 2015;22:2372–7.
Roumen RM, Kuijt GP, Liem IH. Lymphatic mapping and sentinel node harvesting in patients with recurrent breast cancer. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2006;32:1076–81.
Lyman GH, Giuliano AE, Somerfield MR, Benson AB 3rd, Bodurka DC, Burstein HJ, et al. American Society of Clinical Oncology guideline recommendations for sentinel lymph node biopsy in early-stage breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2005;23:7703–20.
Donker M, van Tienhoven G, Straver ME, Meijnen P, van de Velde CJ, Mansel RE, et al. Radiotherapy or surgery of the axilla after a positive sentinel node in breast cancer (EORTC 10981-22023 AMAROS): a randomised, multicentre, open-label, phase 3 non-inferiority trial. Lancet Oncol. 2014;15:1303–10.
Valdes-Olmos RA, Jansen L, Hoefnagel CA, Nieweg OE, Muller SH, Rutgers EJ, et al. Evaluation of mammary lymphoscintigraphy by a single intratumoral injection for sentinel node identification. J Nucl Med. 2000;41:1500–6.
Heuts EM, van der Ent FW, van der Pol HA, von Meyenfeldt MF, Voogd AC. Additional tracer injection to improve the technical success rate of lymphoscintigraphy for sentinel node biopsy in breast cancer. Ann Surg Oncol. 2009;16:1156–63.
Tanis PJ, van Sandick JW, Nieweg OE, Valdes Olmos RA, Rutgers EJ, Hoefnagel CA, et al. The hidden sentinel node in breast cancer. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2002;29:305–11.
Pelosi E, Bello M, Giors M, Ala A, Giani R, Bussone R, et al. Sentinel lymph node detection in patients with early-stage breast cancer: comparison of periareolar and subdermal/peritumoral injection techniques. J Nucl Med. 2004;45:220–5.
Chakera AH, Friis E, Hesse U, Al-Suliman N, Zerahn B, Hesse B. Factors of importance for scintigraphic non-visualisation of sentinel nodes in breast cancer. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2005;32:286–93.
Shen P, Glass EC, DiFronzo LA, Giuliano AE. Dermal versus intraparenchymal lymphoscintigraphy of the breast. Ann Surg Oncol. 2001;8:241–8.
Cody HS 3rd, Fey J, Akhurst T, Fazzari M, Mazumdar M, Yeung H, et al. Complementarity of blue dye and isotope in sentinel node localization for breast cancer: univariate and multivariate analysis of 966 procedures. Ann Surg Oncol. 2001;8:13–9.
Pelosi E, Ala A, Bello M, Douroukas A, Migliaretti G, Berardengo E, et al. Impact of axillary nodal metastases on lymphatic mapping and sentinel lymph node identification rate in patients with early stage breast cancer. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2005;32:937–42.
Cox CE, Furman BT, Kiluk JV, Jara J, Koeppel W, Meade T, et al. Use of reoperative sentinel lymph node biopsy in breast cancer patients. J Am Coll Surg. 2008;207:57–61.
Port ER, Garcia-Etienne CA, Park J, Fey J, Borgen PI, Cody HS 3rd. Reoperative sentinel lymph node biopsy: a new frontier in the management of ipsilateral breast tumor recurrence. Ann Surg Oncol. 2007;14:2209–14.
van der Ploeg IM, Russell NS, Nieweg OE, Oldenburg HS, Kroon BB, Olmos RA, et al. Lymphatic drainage patterns in breast cancer patients who previously underwent mantle field radiation. Ann Surg Oncol. 2009;16:2295–9.
Gray RJ, Pockaj BA, Roarke MC. Injection of (99m)Tc-labeled sulfur colloid the day before operation for breast cancer sentinel lymph node mapping is as successful as injection the day of operation. Am J Surg. 2004;188:685–9.
Giammarile F, Alazraki N, Aarsvold JN, Audisio RA, Glass E, Grant SF, et al. The EANM and SNMMI practice guideline for lymphoscintigraphy and sentinel node localization in breast cancer. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2013;40:1932–47.
Nieweg OE, Estourgie SH, van Rijk MC, Kroon BB. Rationale for superficial injection techniques in lymphatic mapping in breast cancer patients. J Surg Oncol. 2004;87:153–6.
Noguchi M, Inokuchi M, Zen Y. Complement of peritumoral and subareolar injection in breast cancer sentinel lymph node biopsy. J Surg Oncol. 2009;100:100–5.
Linehan DC, Hill AD, Akhurst T, Yeung H, Yeh SD, Tran KN, et al. Intradermal radiocolloid and intraparenchymal blue dye injection optimize sentinel node identification in breast cancer patients. Ann Surg Oncol. 1999;6:450–4.
Klimberg VS, Rubio IT, Henry R, Cowan C, Colvert M, Korourian S. Subareolar versus peritumoral injection for location of the sentinel lymph node. Ann Surg. 1999;229:860–4.
Acknowledgment
The authors thank the following clinicians for patient recruitment and providing the study data: Mw. Dr. M. Bessems, Mw. Dr. M. F. Ernst, Dr. J. M. Klaase, Dr. F. C. Den Boer, Mw. Drs. S. Muller, Dr. J. E. De Vries, Mw. Dr. A. B. Francken, Mw. J. P. J. Burgmans, Dr. T. Van Dalen, Mw. Dr. L. Jansen, Mw. Drs. C. I.E. Scheeren, Dr. S. A. Koopal, Dr. F. W. C. van der Ent, Mw. Dr. Y. L. J. Vissers, Mw. Dr. M. L. Smidt, Dr. J. W. S. Merkus, Mw. Dr. C. M. E. Contant, Dr. P. H. J. M. Veldman, Dr. R. F. Schmitz, Mw. Dr. E. Linthorst-Niers, Dr. J. R. M. van der Sijp, Dr. O. R. Guicherit, Mw. Dr. M. B. E. Menke-Pluymers, Mw. Dr. L. B. Koppert, Mw. Dr. A. M. Bosch, Dr. L. J. A. Strobbe, Prof. Dr. H. De Wilt, Mw. Drs. M. S. Schlooz-Vries, Mw. Dr. P. G. Boelens, Dr. H. W. P. M. Kemperman, Dr. J. A. van Essen, Dr. J. W. D. de Waard, Dr. B. C. Vrouenraets, and Dr. B. van Ooijen. The authors thank the Dutch Breast Cancer Trialists’ Group (BOOG) for their support in promoting, coordinating, and facilitating the SNARB study. This study was supported by a Grant from the Dutch Cancer Society—KWF (Grant 2009-4466) for data registration and management.
Disclosure
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
On behalf of the Sentinel Node and Recurrent Breast Cancer (SNARB) study group.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vugts, G., Maaskant-Braat, A.J.G., Voogd, A.C. et al. Improving the Success Rate of Repeat Sentinel Node Biopsy in Recurrent Breast Cancer. Ann Surg Oncol 22 (Suppl 3), 529–535 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-015-4787-6
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-015-4787-6