Abstract
Background
Microwave (MWA) and radiofrequency ablation (RFA) are the most commonly used techniques for ablating colorectal-liver metastases (CRLM). The technical and oncologic differences between these modalities are unclear.
Methods
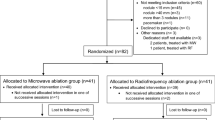
We conducted a matched-cohort analysis of patients undergoing open MWA or RFA for CRLM at a tertiary-care center between 2008 and 2011; the primary endpoint was ablation-site recurrence. Tumors were matched by size, clinical-risk score, and arterial-intrahepatic or systemic chemotherapy use. Outcomes were compared using conditional logistic regression and stratified log-rank test.
Results
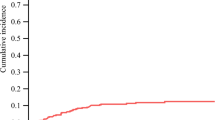
We matched 254 tumors (127 per group) from 134 patients. MWA and RFA groups were comparable by age, gender, median number of tumors treated, proximity to major vessels, and postoperative complication rates. Patients in the MWA group had lower ablation-site recurrence rates (6% vs. 20%; P < 0.01). Median follow-up, however, was significantly shorter in the MWA group (18 months [95% confidence interval 17–20] vs. 31 months [95% confidence interval 28–35]; P < 0.001). Kaplan–Meier estimates of ablation-site recurrence at 2 years were significantly lower for the lesions treated with MWA (7% vs. 18%, P: 0.01).
Conclusions
Ablation-site recurrences of CRLM were lower with MWA compared with RFA in this matched cohort analysis. Longer follow-up time in the MWA may increase the recurrence rate; however, actuarial local failure estimations demonstrated better local control with MWA.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kingham TP, Tanoue M, Eaton A, et al. Patterns of recurrence after ablation of colorectal cancer liver metastases. Ann Surg Oncol. 2012;19:834–41.
Rocha FG, D’Angelica M. Treatment of liver colorectal metastases: role of laparoscopy, radiofrequency ablation, and microwave coagulation. J Surg Oncol. 2010;102:968–74.
Pathak S, Jones R, Tang JM, et al. Ablative therapies for colorectal liver metastases: a systematic review. Colorectal Dis. 2011;13:e252–65.
Martin RC, Scoggins CR, McMasters KM. Safety and efficacy of microwave ablation of hepatic tumors: a prospective review of a 5-year experience. Ann Surg Oncol. 2010;17:171–8.
Fong Y, Fortner J, Sun RL, et al. Clinical score for predicting recurrence after hepatic resection for metastatic colorectal cancer: analysis of 1001 consecutive cases. Ann Surg. 1999;230:309–18; discussion 318–21.
House MG, Ito H, Gonen M, et al. Survival after hepatic resection for metastatic colorectal cancer: trends in outcomes for 1,600 patients during two decades at a single institution. J Am Coll Surg. 2010;210:744–52, 752–5.
Grobmyer SR, Pieracci FM, Allen PJ, et al. Defining morbidity after pancreaticoduodenectomy: use of a prospective complication grading system. J Am Coll Surg. 2007;204:356–64.
Dindo D, Demartines N, Clavien PA. Classification of surgical complications: a new proposal with evaluation in a cohort of 6336 patients and results of a survey. Ann Surg. 2004;240:205–13.
Adam R, Hagopian EJ, Linhares M, et al. A comparison of percutaneous cryosurgery and percutaneous radiofrequency for unresectable hepatic malignancies. Arch Surg. 2002;137:1332–9; discussion 1340.
Izzo F. Other thermal ablation techniques: microwave and interstitial laser ablation of liver tumors. Ann Surg Oncol. 2003;10:491–7.
Simon CJ, Dupuy DE, Mayo-Smith WW. Microwave ablation: principles and applications. Radiographics. 2005;25(Suppl 1):S69–83.
Carrafiello G, Lagana D, Mangini M, et al. Microwave tumors ablation: principles, clinical applications and review of preliminary experiences. Int J Surg. 2008;6(Suppl 1):S65–9.
Carpizo DR, Are C, Jarnagin W, et al. Liver resection for metastatic colorectal cancer in patients with concurrent extrahepatic disease: results in 127 patients treated at a single center. Ann Surg Oncol. 2009;16:2138–46.
Iannitti DA, Martin RC, Simon CJ, et al. Hepatic tumor ablation with clustered microwave antennae: the US Phase II trial. HPB (Oxford). 2007;9:120–4.
Clark PE, Woodruff RD, Zagoria RJ, et al. Microwave ablation of renal parenchymal tumors before nephrectomy: phase I study. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2007;188:1212–4.
Sun Y, Cheng Z, Dong L, et al. Comparison of temperature curve and ablation zone between 915- and 2450-MHz cooled-shaft microwave antenna: results in ex vivo porcine livers. Eur J Radiol. 2012; 81:553–7.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Correa-Gallego, C., Fong, Y., Gonen, M. et al. A Retrospective Comparison of Microwave Ablation vs. Radiofrequency Ablation for Colorectal Cancer Hepatic Metastases. Ann Surg Oncol 21, 4278–4283 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-014-3817-0
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-014-3817-0