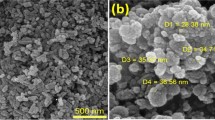
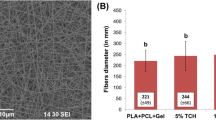
Abstract
Periodontitis is a common microbial infection that involves pocket formation due to the destruction of periodontal ligament. The present work is oriented to provide a holistic approach for the treatment of periodontitis comprising localized delivery of nanometric hydroxyapatite as a reinforcing filler and silver–metronidazole as periodontal pocket disinfectant adjunct to current periodontal therapy because of its broad-spectrum antimicrobial activity and low systemic toxicity. In the present work, electrospinning technique was used to prepare medicated nanofiber enriched with antibacterial-hydroxyapatite layers for dental application. The optimized formulation was characterized by SEM, FTIR, DSC, XRD, etc. Safety assessment and therapeutic potential of optimized formulation was evaluated in both in vitro and in vivo animal models. The newly synthesized complex (silver–metronidazole) exhibited higher antibacterial activity against the selected strain over the referenced silver and metronidazole. Results of in vitro studies suggested good compatibility of the metal complex with the polymer matrix. The drug release behavior from optimized formulation shows constant in vitro release behavior. Both in vitro and in vivo studies show broad-spectrum antimicrobial activity of the metal complex and demonstrate the potential of biomimetic nano-hydroxyapatite for filling periodontal defects. All these observations indicated that the above formulation could play a useful role in the treatment of periodontitis.

ᅟ








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brogden KA, Guthmiller JM. Polymicrobial diseases. ASM press; 2002.
Albandar JM, Streckfus CF, Adesanya MR, Winn DM. Cigar, pipe, and cigarette smoking as risk factors for periodontal disease and tooth loss. J Periodontol. 2000;71(12):1874–81.
Bergström J. Cigarette smoking as risk factor in chronic periodontal disease. Community Dent Oral Epidemiol. 1989;17(5):245–7.
H Zhang, Y. Mao, F. Zhang, C. Ye, H. Tong, Y. Su, Zhu J. The inhibitory effect of a new scFv/tP protein as siRNA delivery system to target hWAPL in cervical carcinoma. Mol Cell Biochem. 2014.
Lalla E, Papapanou PN. Diabetes mellitus and periodontitis: a tale of two common interrelated diseases. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2011;7(12):738–48.
Santos VR, Lima JA, Miranda TS, Feres M, Zimmermann GS, da Rocha Nogueira-Filho G, et al. Relationship between glycemic subsets and generalized chronic periodontitis in type 2 diabetic Brazilian subjects. Arch Oral Biol. 2012;57(3):293–9.
Guiglia R, Di Fede O, Lo Russo L, Sprini D, Rini GB, Campisi G. Osteoporosis, jawbones and periodontal disease. 2013.
Esfahanian V, Shamami MS, Shamami MS. Relationship between osteoporosis and periodontal disease: review of the literature. J Dent Tehran Univ Med Sci. 2012;9(4):256–64.
Van Dyke TE, Dave S. Risk factors for periodontitis. J Int Acad Periodontol. 2005;7(1):3.
Joshi D, Garg T, Goyal AK, Rath G. Advanced drug delivery approaches against periodontitis. Drug Deliv. 2016;23(2):363–77.
Tariq M, Iqbal Z, Ali J, Baboota S, Talegaonkar S, Ahmad Z, et al. Treatment modalities and evaluation models for periodontitis. Int J Pharm Investig. 2012;2(3):106.
Sanz I, Alonso B, Carasol M, Herrera D, Sanz M. Nonsurgical treatment of periodontitis. J Evid Based Dent Pract. 2012;12(3):76–86.
Herrera D, Matesanz P, Bascones-Martínez A, Sanz M. Local and systemic antimicrobial therapy in periodontics. J Evid Based Dent Pract. 2012;12(3):50–60.
Malik R, Garg T, Goyal AK, Rath G. Diacerein-loaded novel gastroretentive nanofiber system using PLLA: development and in vitro characterization. Artif Cells, Nanomed, Biotechnol. 2016;44(3):928–36.
Modgill V, Garg T, Goyal AK, Rath G. Permeability study of ciprofloxacin from ultra-thin nanofibrous film through various mucosal membranes. Artif Cells, Nanomed, Biotechnol. 2016;44(1):122–7.
Pinheiro ALB, Gerbi MEM, de Assis Limeira F Jr, Ponzi EAC, Marques AM, Carvalho CM, et al. Bone repair following bone grafting hydroxyapatite guided bone regeneration and infra-red laser photobiomodulation: a histological study in a rodent model. Lasers Med Sci. 2009;24(2):234–40.
Yar M, Farooq A, Shahzadi L, Khan AS, Mahmood N, Rauf A, et al. Novel meloxicam releasing electrospun polymer/ceramic reinforced biodegradable membranes for periodontal regeneration applications. Mater Sci Eng C. 2016;64:148–56.
Kalinowska-Lis U, Felczak A, Chęcińska L, Zawadzka K, Patyna E, Lisowska K, et al. Synthesis, characterization and antimicrobial activity of water-soluble silver (I) complexes of metronidazole drug and selected counter-ions. Dalton Trans. 2015;44(17):8178–89.
Bouyer E, Gitzhofer F, Boulos M. Morphological study of hydroxyapatite nanocrystal suspension. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2000;11(8):523–31.
Rath G, Hussain T, Chauhan G, Garg T, Kumar GA. Fabrication and characterization of cefazolin-loaded nanofibrous mats for the recovery of post-surgical wound. Artif Cells, Nanomed, Biotechnol. 2016;44(8):1783–92.
Aggarwal U, Goyal AK, Rath G. Development and characterization of the cisplatin loaded nanofibers for the treatment of cervical cancer. Mater Sci Eng C. 2017;75:125–32.
Rath G, Johal E, Goyal AK. Development of serratiopeptidase and metronidazole based alginate microspheres for wound healing. Artif Cells, Blood Substit Biotechnol. 2011;39(1):44–50.
Singh B, Garg T, Goyal AK, Rath G. Development, optimization, and characterization of polymeric electrospun nanofiber: a new attempt in sublingual delivery of nicorandil for the management of angina pectoris. Artif Cells, Nanomed, Biotechnol. 2016;44(6):1498–507.
Struillou X, Boutigny H, Soueidan A, Layrolle P. Experimental animal models in periodontology: a review. Open Dent J. 2010;4(1).
Joshi D, Garg T, Goyal AK, Rath G. Development and characterization of novel medicated nanofibers against periodontitis. Curr Drug Deliv. 2015;12(5):564–77.
Greenberg J, Laster L, Listgarten M. Transgingival probing as a potential estimator of alveolar bone level. J Periodontol 1976;47(9):514–517.
Clogston JD, Patri AK. Zeta potential measurement. Methods Mol Biol. 2011;697:63–70.
Modgill V, Garg T, Goyal AK, Rath G. Transmucosal delivery of linagliptin for the treatment of type-2 diabetes mellitus by ultra-thin nanofibers. Curr Drug Deliv. 2015;12(3):323–32.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Deepak, A., Goyal, A.K. & Rath, G. Development and Characterization of Novel Medicated Nanofiber for the Treatment of Periodontitis. AAPS PharmSciTech 19, 3687–3697 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1208/s12249-018-1177-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1208/s12249-018-1177-y