Abstract
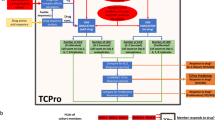
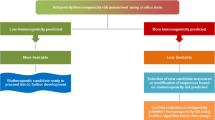
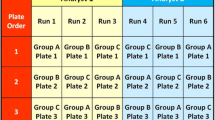
In silico HLA-binding algorithms and in vitro T cell-based assays as predictive tools for human immunogenicity risk have made inroads in the biotherapeutic drug discovery and development process. Currently, these tools are being used only for candidate selection or characterization and not for making a go/no-go decision for further development. A clear limitation for a broader implementation is the lack of correlation between the predicted T cell epitope content/immune reactivity potential of a biotherapeutic and the subsequent ADA-related clinical immunogenicity outcome. The current state of technologies and their pros and cons were discussed as a part of the 2016 AAPS National Biotechnology Conference in a themed session. A review of the advances in the area and the session talks along with the ensuing discussions are summarized in this commentary.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Shankar G, Arkin S, Cocea L, Devanarayan V, Kirshner S, Kromminga A, et al. Assessment and reporting of the clinical immunogenicity of therapeutic proteins and peptides-harmonized terminology and tactical recommendations. AAPS J. 2014;16(4):658–73.
Jawa V, Cousens LP, Awwad M, Wakshull E, Kropshofer H, De Groot AS. T cell dependent immunogenicity of protein therapeutics: preclinical assessment and mitigation. Clin Immunol. 2013;149(3):534–55.
Karle A, Spindeldreher S, Kolbinger F. Secukinumab, a novel anti-IL-17A antibody, shows low immunogenicity potential in human in vitro assays comparable to other marketed biotherapeutics with low clinical immunogenicity. MAbs. 2016;8(3):536–50.
Xue L, Hickling T, Song R, Nowak J, Rup B. Contribution of enhanced engagement of antigen presentation machinery to the clinical immunogenicity of a human interleukin (IL)-21 receptor-blocking therapeutic antibody. Clin Exp Immunol. 2016;183(1):102–13.
Lamberth K, Reedtz-Runge SL, Simon J, Klementyeva K, Pandey GS, Padkjaer SB, et al. Post hoc assessment of the immunogenicity of bioengineered factor VIIa demonstrates the use of preclinical tools. Sci Transl Med. 2017;9(372):eaag1286.
Mazor R, Onda M, Pastan I. Immunogenicity of therapeutic recombinant immunotoxins. Immunol Rev. 2016;270(1):152–64.
Mazor R, Zhang J, Xiang L, Addissie S, Awuah P, Beers R, et al. Recombinant immunotoxin with T cell epitope mutations that greatly reduce immunogenicity for treatment of mesothelin-expressing tumors. Mol Cancer Ther. 2015;14(12):2789–96.
Jawa V, Joubert MK, Zhang Q, Deshpande M, Hapuarachchi S, Hall MP, et al. Evaluating immunogenicity risk due to host cell protein impurities in antibody-based biotherapeutics. AAPS J. 2016;18(6):1439–52.
Joubert MK, Deshpande M, Yang J, Reynolds H, Bryson C, Fogg M, et al. Use of in vitro assays to assess immunogenicity risk of antibody-based biotherapeutics. PLoS One. 2016;11(8):e0159328.
Moussa EM, Panchal JP, Moorthy BS, Blum JS, Joubert MK, Narhi LO, et al. Immunogenicity of therapeutic protein aggregates. J Pharm Sci. 2016;105(2):417–30.
Jiskoot W, Kijanka G, Randolph TW, Carpenter JF, Koulov AV, Mahler HC, et al. Mouse models for assessing protein immunogenicity: lessons and challenges. J Pharm Sci. 2016;105(5):1567–75.
De Groot AS, Martin W. Reducing risk, improving outcomes: bioengineering less immunogenic protein therapeutics. Clin Immunol. 2009;131(2):189–201.
Moise L, Gutierrez AH, Bailey-Kellogg C, Terry F, Leng Q, Abdel Hady KM, et al. The two-faced T cell epitope: examining the host-microbe interface with JanusMatrix. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2013;9(7):1577–86.
De Groot AS, Moise L, McMurry JA, Wambre E, Van Overtvelt L, Moingeon P, et al. Activation of natural regulatory T cells by IgG Fc-derived peptide “Tregitopes”. Blood. 2008;112(8):3303–11.
Kim Y, Sette A, Peters B. Applications for T cell epitope queries and tools in the immune epitope database and analysis resource. J Immunol Methods. 2011;374(1–2):62–9.
Haile LA, Puig M, Kelley-Baker L, Verthelyi D. Detection of innate immune response modulating impurities in therapeutic proteins. PLoS One. 2015;10(4):e0125078.
Rosenberg AS, Verthelyi D, Cherney BW. Managing uncertainty: a perspective on risk pertaining to product quality attributes as they bear on immunogenicity of therapeutic proteins. J Pharm Sci. 2012;101(10):3560–7.
Verthelyi D, Wang V. Trace levels of innate immune response modulating impurities (IIRMIs) synergize to break tolerance to therapeutic proteins. PLoS One. 2010;5(12):e15252.
Baker MP, Reynolds HM, Lumicisi B, Bryson CJ. Immunogenicity of protein therapeutics: the key causes, consequences and challenges. Self Nonself. 2010;1(4):314–22.
Harding FA, Stickler MM, Razo J, DuBridge RB. The immunogenicity of humanized and fully human antibodies: residual immunogenicity resides in the CDR regions. MAbs. 2010;2(3):256–65.
Joubert MK, Hokom M, Eakin C, Zhou L, Deshpande M, Baker MP, et al. Highly aggregated antibody therapeutics can enhance the in vitro innate and late-stage T cell immune responses. J Biol Chem. 2012;287(30):25266–79.
Davies V, Vaughan K, Damle R, Peters B, Sette A. Classification of the universe of immune epitope literature: representation and knowledge gaps. PLoS One. 2009;4(9):e6948.
Paul S, Lindestam Arlehamn CS, Scriba TJ, Dillon MB, Oseroff C, Hinz D, et al. Development and validation of a broad scheme for prediction of HLA class II restricted T cell epitopes. J Immunol Methods. 2015;422:28–34.
Bryson CJ, Jones TD, Baker MP. Prediction of immunogenicity of therapeutic proteins: validity of computational tools. BioDrugs. 2010;24(1):1–8.
Rombach-Riegraf V, Karle AC, Wolf B, Sorde L, Koepke S, Gottlieb S, et al. Aggregation of human recombinant monoclonal antibodies influences the capacity of dendritic cells to stimulate adaptive T cell responses in vitro. PLoS One. 2014;9(1):e86322.
Koren E, De Groot AS, Jawa V, Beck KD, Boone T, Rivera D, et al. Clinical validation of the “in silico” prediction of immunogenicity of a human recombinant therapeutic protein. Clin Immunol. 2007;124(1):26–32.
Dhir V, Fort M, Mahmood A, Higbee R, Warren W, Narayanan P, et al. A predictive biomimetic model of cytokine release induced by TGN1412 and other therapeutic monoclonal antibodies. J Immunotoxicol. 2012;9(1):34–42.
Hamze M, Meunier S, Karle A, Gdoura A, Goudet A, Szely N, et al. Characterization of CD4 T cell epitopes of infliximab and rituximab identified from healthy donors. Front Immunol. 2017;8:500.
Schultz HS, Reedtz-Runge SL, Backstrom BT, Lamberth K, Pedersen CR, Kvarnhammar AM, et al. Quantitative analysis of the CD4+ T cell response to therapeutic antibodies in healthy donors using a novel T cell: PBMC assay. PLoS One. 2017;12(5):e0178544.
Ing M, Gupta N, Teyssandier M, Maillere B, Pallardy M, Delignat S, et al. Immunogenicity of long-lasting recombinant factor VIII products. Cell Immunol. 2016;301:40–8.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gokemeijer, J., Jawa, V. & Mitra-Kaushik, S. How Close Are We to Profiling Immunogenicity Risk Using In Silico Algorithms and In Vitro Methods?: an Industry Perspective. AAPS J 19, 1587–1592 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1208/s12248-017-0143-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1208/s12248-017-0143-z