Abstract
Background
Estradiol is an important marker of ovarian response to ovarian stimulation in ART cycles. The study tries to find the correlation of serum estradiol on the day of HCG trigger to the number of follicles, the number of oocytes retrieved, and the number of mature oocytes, and also, to correlate estradiol per follicle and estradiol per oocyte on the day of HCG, to the number of oocytes retrieved, and to the number of mature oocytes. It is a cross sectional study using retrospective data.
Results
The data of 232 patients were analyzed. Our study showed a positive correlation between estradiol levels and the number of follicles (NF) (r = 0.592, p < 0.001), number of retrieved oocytes (NRO) (r = 0.576, p < 0.001), and number of mature oocytes (NMO) (r = 0.554, p < 0.001). E/follicle ratio did not have a significant correlation with NRO and NMO. E/Oocyte ratio had a strong negative correlation with NMO (r = −0.280, p < 0.001)
Conclusions
Serum estradiol had a positive correlation with NF, NRO, and NMO. But E/O had a strong negative correlation with NMO. These results indicate that estradiol levels can be used as an important clinical tool in the prediction of oocyte and mature oocyte yield in ART cycles. Reproductive outcome in ART cycles is largely dependent on the number of oocytes and mature oocyte yield. Estradiol levels on the day of HCG appear to strongly correlate with the outcome of ART cycles.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Ovarian stimulation is the standard of care for in vitro fertilization. The two important clinical parameters seen during follicular tracking is the follicular size measured by ultrasound and serum estradiol levels.
Estradiol (E2) or 17β E2 is the primary female sex steroid secreted mainly from the granulosa cells of the ovarian follicle. It is secreted in the follicular phase of the menstrual cycle, peaks at the time of ovulation before luteinizing hormone surge, and declines and plateaus thereafter [1]. Measurement of E2 in in vitro fertilization/intracytoplasmic sperm injection (IVF/ICSI) cycles would be helpful to assess the ovarian response and prediction of ovarian hyper stimulation syndrome (OHSS). Several studies have been performed to assess the impact of E2 levels on the day of human chorionic gonadotropin (HCG) on IVF-ICSI outcome. The results of these studies were heterogeneous. Some studies have reported that higher values adversely affected endometrial receptivity, whereas other studies showed no significant effect [2,3,4,5]. Higher E2 level on the day of HCG was found to have a positive impact on embryo quality, but extremely high levels were found to affect embryo quality, implantation, and pregnancy [5, 6]. Medium levels of E2 exposure during ovarian stimulation were found to have significantly higher number of pregnancies than low and high E2 groups [7]. This probably attributes to the higher pregnancy rates reported after frozen-embryo transfer (FET) compared to fresh ET due to lower exposure to hormones, such as E2 [8].
The present study was designed to study the following outcomes:
-
1)
To find the correlation between estradiol levels on the day of HCG trigger and the number of mature follicles (NF), the number of oocytes retrieved (NRO), and the number of mature oocytes M2 (NMO) after oocyte aspiration in ICSI cycles
-
2)
To find the correlation of estradiol/follicle (E2/fol) ratio (defined as estradiol levels (E2) level per mature follicle > 14 mm), to the number of oocytes retrieved (NRO), and to the number of mature oocytes (NMO)
-
3)
To find the correlation of estradiol/oocyte (E2/O) ratio (defined as estradiol level per oocyte retrieved) to the number of mature oocytes (NMO)
Methods
Study population
It was a cross-sectional study using retrospective data of infertile couples who underwent intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI) in the ART clinic at Medical College, Trivandrum, during the period January 2014 to October 2016. The data of all patients who underwent ICSI during this period were analyzed. The cycles were long agonist cycles or antagonist cycles. Women, whose estradiol levels were not recorded, were excluded from the study.
Sample size was calculated using n Master version 2.0 with a power of 80% and significance level of 5%, and the sample size was calculated as 188.
There were 232 cases of ICSI during the study period from January 2014-October 2016. All cases were taken for analysis. The data of all patients were collected from case records. The quantitative variables are summarized in mean and standard deviation (SD). Qualitative variables are in proportion. Correlation was found by Spearman correlation, and coefficient P value < 0.05 is taken as statistically significant.
Ovarian stimulation was performed using long agonist protocol or antagonist protocol, individualized depending on the patient characteristics. Combined oral contraceptive pill (OCP) was started in the previous cycle and given for a period of 2 weeks. A washout period of 7 days was given before starting gonadotrophins. In long agonist protocol, leuprolide acetate 3.75 mg depot was given 4 days prior to stopping OC pills. In antagonist protocol, OCPs were administered for 2 weeks and a washout period of 5 days. The gonadotropins used were mainly recombinant follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH). Human menopausal gonadotropin (HMG) was added from day 1 or later in case of expected poor response, poor initial response, or tardy follicular growth. The doses of gonadotropins were decided according to the individual patient characteristics, in both the protocols.
Follicular study was done by transvaginal ultrasound with 8 MHz probe, starting from day 5 of ovarian stimulation and every day thereafter. In antagonist protocol, ganirelix (Orgalutran) 0.25 mg was administered by flexible regime, when lead follicle reached 14 mm. Ovulation was triggered by 250 mcg of recombinant HCG when at least 3 follicles reached ≥ 17 mm. Serum E2 was estimated by chemiluminescence assay, on the morning of the day of ovulation trigger. Oocyte retrieval was performed after 34–35 h of ovulation trigger. ICSI was done on the mature oocytes (M2) recovered, within 2-4 h of retrieval.
The study subjects were divided into five groups based on the serum E2 level on the day of ovulation trigger.
Group 1—< 1000 pg/ml; Group 2—1000.1–2000 pg/ml; Group 3—2000.1–3000 pg/ml;
Group 4—3000.1–4000 pg/ml; Group 5—> 4000 pg/ml
The relationship of demographic parameters such as age, body mass index (BMI), AMH levels (anti-Mullerian hormone), and AFC (antral follicle count) with the estradiol values on day of HCG, number of mature follicles (NFO), number of oocytes retrieved (NRO), and the number of mature oocytes (NMO) were analyzed. The outcome parameters, viz., NRO and NMO oocytes were compared among these five groups. The correlation of estradiol/follicle (E2/fol) ratio and the estradiol/oocyte ratio (E2/O) with the NRO and NMO were also analyzed.
Results
Data of 232 patients who underwent ICSI during the study period was analyzed. The demographic parameters were analyzed and then their relationship with estradiol levels.
Ninety-eight women belonged to the age group of 30-35 years (42.2%) as shown in Table 1.
One hundred thirty-nine patients (55.9%) had normal BMI. Thirteen (5.6%) were obese. Forty-one patients (17.7%) had very low AMH < 2.2 pmol/L, while 5.2% had very high AMH. Nine patients (5.2%) had very low AFC of < 5 and 12.5% had very high AFC (Table 2).
Twenty-one patients in the study (9.1%) had estradiol values ≤ 1000 pg/ml. Thirty-six patients (15.5%) belonged to group 2 (1000-2000 pg/ml). Seventy-eight patients (33.6%) had E2 values between 2000 and 4000 pg/ml. Ninety-seven (41.8%) had very high E2 values above 4000 pg/ml as shown in Table 3.
Table 4 shows the significant relation of estradiol values with E2/follicle, E2/oocyte, and E2/M2 ratios. As the estradiol values increased, all the above ratios increased (p < 0.001).
As age increased the mean of the number of follicles, oocytes and mature oocytes decreased, indicating that age is an important ovarian reserve marker (Table 5). However, the relation of age with mature oocytes was not found to be significant. Consequent to this, as age increased the mean estradiol values also decreased (Table 6) indicating diminishing reserves (p = 0.021).
As weight increased, there was a drop in the number of mature oocytes, though not statistically significant, pointing to an adverse reproductive outcome in obese patients (Table 7).
AMH had a significant positive relation with number of follicles, oocytes, and mature oocytes (Table 8). Very low AMH was associated with significantly reduced follicles, oocytes, and mature follicles and vice versa. Very high AMH was significantly associated with very high estradiol values and vice versa, thus a predictive value for OHSS in hyper responders (Table 9).
AFC again showed a significant positive relation (p <0.001) with NFO, NRO, and NMO. This highlights the significance of AFC as an important determinant of oocyte and mature oocyte yield in ART (Table 10). As AFC increased the mean of estradiol values increased, which was found to be significant as shown in Table 11.
As estradiol levels increased the number of follicles, oocytes retrieved, and mature follicles increased, which was statistically significant (p < 0.001) (Table 12).
Correlation
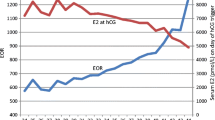
Since normality assumption was not satisfied, Spearman correlation coefficient was used for finding the correlation between estradiol (E2) values and the NFO, NRO, and NMO (Table 13). The analysis showed that there was a strong positive correlation between E2 levels and the said parameters. No. of follicles (r = 0.592, p < 0.001); no. of oocytes (r = 0.576, p < 0.001); no. of mature oocytes (r = 0.554, p < 0.001). As the estradiol level increased, all the other said variables significantly increased, indicating the prognostic predictive value of estradiol (Figs. 1, 2, 3).
E2/follicle ratio and E2/oocyte ratios were analyzed in relation to NRO and NMO (Table 14). E2/follicle ratio had a negative correlation with NRO and NMO, but was not statistically significant (Figs. 4, 5).
On the other hand, E2/oocyte had a very significant negative correlation with the number of mature oocytes (p < 0.001) (Fig. 6) (Table 15).
Discussion
The number and quality of oocytes and embryos are important determinants of success of any ART cycle. Serum estradiol as a factor affecting these parameters has been studied and published in few instances, with conflicting results. In this study, we tried to find a correlation between the serum estradiol levels on day of trigger with mature follicles, oocytes, and mature follicles, with the aim of finding out whether estradiol levels can be a clinical tool is assessing oocyte and mature oocyte yield.
Age had a negative relation with the number of follicles (p = 0.015) and number of oocytes retrieved (p = 0.041) (Table 5). Similarly, age had a significant negative correlation with estradiol values (p = 0.021) (Table 6), both indicating diminished ovarian reserves with aging. Similar finding was seen in the study by Vaughan et al. [9], where E2 levels on day of HCG was found to be inversely proportional to patient’s age and the quantity of oocytes retrieved also declined. As maternal age increased, a linear increase in E/O ratio was observed since the number of oocytes retrieved declined. A simple estradiol level measured on day of HCG would not have brought out this finding. Study by Kara et al. [10] also showed NRO higher in age group < 36 years, so as also pregnancy. Mitwally et al. [7] commented in their study that women above 35 years are more vulnerable to high E2 levels; and also had significantly lower pregnancy rates. The negative correlation started at lower E2 levels in women above 35 years.
Obesity was associated with decreased number of mature oocytes in the present study, though not statistically significant (Table 7). This was similar to the observation in the study by Siddhartha et al. [11], where overweight women with BMI > 26 kg/m2 had significantly decreased E2 values on day of HCG. AMH had a very significant positive relation with the number of follicles, number of oocytes, and the number of mature follicles (p < 0.001). It also has a strong positive relation with the estradiol values on day of HCG (p =0.002). AFC, the other parameter analyzed had a very strong positive relation with all the three parameters—number of follicles, oocytes, and mature oocytes (p < 0.001), also, with the estradiol values (p < 0.001).
Estradiol vs NF, NRO, NMO
As estradiol increased, estradiol per follicle, oocyte, and mature oocyte increased. As estradiol increased, there was a significant increase in the number of follicles—NF (p < 0.001), number of oocytes retrieved—NRO (p < 0.001), and the number of mature oocytes—NMO (p < 0.001). Similar findings were noted in the study by Xin Li et al. [12], where NRO, NMO, and CPR increased as E2 level increased. But beyond a level of 5000 pg/ml, all these decreased. Their study revealed that E2 levels < 1000 pg/ml and > 5000 pg/ml had a negative impact on IVF outcome.
Erzincan et al. [13] also made similar observations in their study, where the NRO increased parallel to E2 levels, with no significant differences in clinical pregnancy rates (CPR) between various E2 levels. In the study by Siddharth et al. [11], the NRO and NMO were highest when estradiol was > 4000 pg/ml, as in the present study. CPR was highest in the group with estradiol between 3000 and 4000 pg/ml, suggesting that very high levels of estradiol may be detrimental for implantation. Reduced implantation and pregnancy rates when E2 > 90th centile was shown in the study by Arslan et al. [4], even when the NRO, NMO, and embryo scores were similar in various E2 groups. Similar positive correlation of E2 levels with NRO, NMO was noted in the study by Mittal et al. [14] also. The study by Kara et al. [10] also mirrored similar results with NRO parallel to E2 levels, maximum at > 4000 pg/ml. The findings of Anifandis et al. [6] observed that very low and very high E2 levels on day of HCG yielded very low and very high number of oocytes respectively, again suggesting a linear correlation. The study by Yu Ng EH et al. [3] concluded that high E2 levels in IVF cycles adversely affected implantation and pregnancy rates. They observed that embryo quality was unaffected by E2 levels and it was the adverse endometrial milieu associated with very high E2 levels that affected implantation. Frozen thawed embryos from same cycle implanted well. Almost similar observation was made by Kolibianakis et al. [2] who observed that high E2 adversely affects endometrium and therefore implantation, but had little impact on M2 oocytes and embryo quality.
However, a systematic review by Kosmas et al. [15] did not find any high-quality evidence to support or deny the value of E2 on day of HCG administration for IVF outcome. They found no positive correlation on retrospective evaluation of studies.
The finding by Kyrou et al. [5] was similar to that by Yu Ng et al. [3], the NRO, NMO, and good quality embryos increased with E2, but not pregnancy, probably due to the deleterious effect on endometrial receptivity. The results of the study by Mitwally et al. [7] mirrored that by Anifandis [6]. They found that cycles with low and high AUC-E2 values had significantly lower pregnancy rates particularly if the patient was > 35years. The study inferred that women above 35 years of age are more vulnerable to high E2 levels. Present study did not include the reproductive outcome. NRO and NMO increased parallel to estradiol levels as was found in the many of the mentioned studies.
The ESHRE guidelines for ovarian stimulation state that the addition of estradiol measurements to ultrasound monitoring was neither found superior to ultrasound monitoring alone nor does it recommend the timing of final oocyte maturation trigger based on estradiol or estradiol/follicle ratio as it was not found superior in terms of efficacy and safety than ultrasound monitoring alone [16].The present study found that as estradiol values increased, you could expect more oocytes and mature oocytes, in turn leading to a probably better ART outcome. So also as estradiol/oocyte increased, the outcome in terms of mature oocytes was poor. The present study aimed at predicting ART outcomes in term of oocyte and mature oocyte yield rather than using estradiol values as means of follicular monitoring during ART stimulation.
E2/follicle vs NRO and NMO
E2/follicle was not found to have a significant correlation with the NRO and NMO in the present study. In the study by Mittal et al. [14], however, a positive correlation was seen between E2/fol and NRO NMO, fertilized oocytes, and embryo quality. Study by Ozdegirmenci et al. [17] also showed that E2/follicle correlated positively with NRO, NMO.
E/O vs NMO
Study showed E2/O had a strong negative correlation with the NMO (p value < 0.001). This was observed in many other studies as well, suggesting that raised E2 per oocyte is probably linked with maturation of oocytes. In the study by Vaughan et al. [9], NMO was found to be lowest with E2/O < 250 and was highest when the E/O was > 2000. CPR was highest when E2/O ratio was in the range 250-750 but declined as the ratio increased. Lowest fertilization rates were measured at extremes of ratio (< 250 and > 2000) reflecting negative impact of increasing E/O on reproductive outcome. A negative correlation between E2/O and NMO and number of fertilized oocytes was also found in the study by Ozdegirmenci et al. [17]. They concluded that while E2/follicle had a positive correlation with NRO, NMO, and fertilized oocytes, but E2/O adversely affects these parameters. Mittal et al. [16] showed a similar negative correlation of E2/O and NRO, NMO commenting on the probable negative effect of high E2 levels on maturation of oocytes.
Limitations
It was a retrospective study. The effect of different protocols of IVF on estradiol was not separately considered. The study also did not include the effect of estradiol on quality of embryos and IVF outcome.
Conclusions
Present study showed a positive correlation between estradiol levels and the number of mature follicles, retrieved oocytes, and number of mature oocytes. E/follicle ratio was not found to have a significant correlation with NRO and NMO, but E/O ratio had a strong negative correlation with NMO. These results demonstrate the fact that estradiol levels can be an important clinical tool to reckon with, in the prediction of oocyte and mature oocyte yield in ART cycles. Both being significant landmarks in the path to the final ART outcome, namely, CPR and LBR, estradiol on the day of trigger appears to strongly correlate with the outcome of ART cycles.
Availability of data and materials
The data was obtained from case records of IVF patients treated in our department.
Abbreviations
- ART:
-
Assisted reproductive techniques
- ICSI:
-
Intra cytoplasmic sperm injection
- E2 :
-
Estradiol
- HCG:
-
Human chorionic gonadotrophin
- IVF:
-
In vitro fertilization
- NF:
-
Number of mature follicles
- NRO:
-
Number of retrieved oocytes
- NMO:
-
Number of mature oocytes
- E/fol:
-
Estradiol per follicle
- E/O:
-
Estradiol per oocyte
- OCP:
-
Oral contraceptive pill
References
Speroff’s Clinical Gynaecologic Endocrinology and Infertility. Ninth edition. 2020. Chapter 5. Regulation of menstrual cycle. editors. Pg 361 – 369.
Kolibianakis EM, Albano C, Kahn J, Camus M, Tournaye H, Van Steirteghem AC et al (2003) Exposure to high levels of luteinizing hormone and estradiol in the early follicular phase of gonadotropin-releasing hormone antagonist cycles is associated with a reduced chance of pregnancy. Fertil Steril 79:873–880
Yu Ng EH, Yeung WS, Yee Lan Lau E, So WW, Ho PC (2000) High serum oestradiol concentrations in fresh IVF cycles do not impair implantation and pregnancy rates in subsequent frozen-thawed embryo transfer cycles. Hum Reprod 15(2):250–255. https://doi.org/10.1093/humrep/15.2.250
Arslan M, Bocca S, Arslan EO, Duran HE, Stadtmauer L, Oehninger S (2007) Cumulative exposure to high estradiol levels during the follicular phase of IVF cycles negatively affects implantation. J Assist Reprod Genet 24(4):111–117. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10815-006-9101-x
Kyrou D, Popovic-Todorovic B, Fatemi HM, Bourgain C, Haentjens P, Van Landuyt L et al (2009) Does the estradiol level on the day of human chorionic gonadotrophin administration have an impact on pregnancy rates in patients treated with rec-FSH/GnRH antagonist? Hum Reprod 24(11):2902–2909. https://doi.org/10.1093/humrep/dep290
Anifandis G, Koutselini E, Louridas K, Liakopoulos V, Leivaditis K, Mantzavinos T, Sioutopoulou D, Vamvakopoulos N (2005) Estradiol and leptin as conditional prognostic IVF markers. Reproduction. 129(4):531–534. https://doi.org/10.1530/rep.1.00567
Mitwally MF, Bhakoo HS, Crickard K, Sullivan MW, Batt RE, Yeh J (2006) Estradiol production during controlled ovarian hyperstimulation correlates with treatment outcome in women undergoing invitrofertilization-embryo transfer. Fertil Steril 86(3):588–596. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fertnstert.2006.02.086
Shapiro BS, Daneshmand ST, Garner FC, Aguirre M, Hudson C, Thomas S (2011) Evidence of impaired endometrial receptivity after ovarian stimulation for in vitro fertilization: a prospective randomized trial comparing fresh and frozen-thawed embryo transfer in normal responders. Fertil Steril 96:344–348
Vaughan DA, Harrity C, Sills ES, Mocanu EV (2016) Serum estradiol: oocyte ratio as a predictor of reproductive outcome: an analysis of data from > 9000 IVF cycles in the Republic of Ireland. J Assist Reprod Genet 33:481–488
Kara M, Kutlu T, Sofuoglu K, Devranoglu B, Cetinkaya T (2012) Association between serum estradiol level on the hCG administration in IVF-ICSI patients. IJRM 10(1):53–58
Siddhartha N, Reddy NS, Pandurangi M, Tamizharasi M, Radha V, Kanimozhi K (2016) Correlation of serum estradiol level on the day of ovulation trigger with the reproductive outcome of intracytoplasmic injection. Retrospective observational study. J Hum Reprod Sci 9(1):23–27
Li X, Cheng Z, Shang J, Wang S, Gao X-L, Xue Q (2019) Association between serum estradiol on the human chorionic gonadotrophin administration day and clinical outcome. Chin Med J 132(10):1194–1201. https://doi.org/10.1097/CM9.0000000000000251
Erzincan SG, Esmer AC, Baysal B (2014) Does the estradiol level on the day of human chorionic gonadotropin administration predict the clinical outcome of controlled ovarian hyperstimulation? Clin Exp Obstet Gynecol 41(6):709–712
Mittal S, Gupta P, Malhotra N, Singh N (2014) Serum estradiol as a predictor of success of in vitro fertilization. J Obstet Gynaecol India 64(2):124–129 Epub 2013 Nov 1
Kosmas IP, Kolibianakis EM, Devroey P (2004) Association of estradiol levels on the day of HCG administration and pregnancy achievement in IVF: a systematic review. Hum Reprod 19(11):2446–2453. Epub 2004 Oct 7. https://doi.org/10.1093/humrep/deh473
ESHRE Guidelines on ovarian stimulation for IVF/ICSI October 2019 by the ESHRE Reproductive Endocrinology Guideline Group. 11- (48,49) 13- (54,55)
Ozdegirmenci O, Dilbaz S, Cinar O (2011) Aydin Can serum oestradiol be a predictor of quality of oocytes and embryos, maturation of oocytes and pregnancy rate in ICSI cycles. Gynecol Endocrinol 27(4):279–285. Epub 2010 Jun 14. https://doi.org/10.3109/09513590.2010.491168
Acknowledgements
Dr. Kumari Jayageetha, Associate Professor, Statistics and Demography, Medical College, Trivandrum
Jayakumar P, Junior Lab Assistant, Medical College, Trivandrum
Funding
There was no funding received from the institution.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All the authors have worked in unison in the IVF cycles from which the data was taken. All the authors have read and approved the final manuscript.
Principal investigator: Dr. AM has conceptualized the study, collected the necessary data, and played a key role in the analysis of the data. Co-investigator: Dr. SB has contributed to the work design, drafting of the work, and final revision. Co-investigator: Dr. LBS helped in data analysis and interpretation and also contributed to the final drafting of the article.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Ethical clearance was given by the Institutional Review Board and Ethics Committee. It was a cross sectional study using retrospective data. The data was obtained from case records of ART patients in our department.
Consent for publication
Not applicable
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Malathi, A., Balakrishnan, S. & B. S., L. Correlation between estradiol levels on day of HCG trigger and the number of mature follicles, number of oocytes retrieved, and the number of mature oocytes (M2) after oocyte aspiration in ICSI cycles. Middle East Fertil Soc J 26, 34 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1186/s43043-021-00080-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s43043-021-00080-5