Abstract
Background
Bone disease is common in patients undergoing hemodialysis. It is the result of bone turnover abnormalities and the decrease of bone mineral density (BMD). We aimed to determine the usefulness of serum bone turnover markers and BMD measurement by dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry (DXA) in hemodialysis patients.
Methods
We conducted a cross-sectional study including 90 hemodialysis for more than 12 months. Bone mineral density was assessed by DXA. Peripheral blood samples were obtained from each patient before dialysis in a fasting state within a week of the DXA. Biochemical variables of calcium and phosphate were measured. One bone formation marker (bone-specific alkaline phosphatase (bAP), one bone resorption marker (carboxy-terminal telopeptides of type 1 collagen (CTX)) were measured. Total alkaline phosphatase (TAP), intact parathyroid hormone (PTH) and fibroblast growth factor 23 (FGF23) which is a bone-derived hormone were also measured.
Results
CTX values were 6.25 times higher than the normal limit of the assay. Bone alkaline phosphatase levels were less than 10 ng/mL in 28.8% of cases. 23% of patients have osteoporosis and 45% have osteopenia. Femoral BMD had negative correlations with age and PTH levels. FGF23 levels were significantly increased in patients with osteoporosis affecting the lumbar. The levels of bAP and CTX showed a positive correlation. Both circulating bAP and CTX levels showed also positive correlations with PTH levels. Fractures, observed in 12.2% of cases, were associated with low PTH values and the existence of osteoporosis.
Conclusions
Our study showed that osteoporosis and fracture are common in dialysis patients. The reduced BMD was associated with advanced age and elevated levels of PTH. Markers of bone turnover and FGF23 may play a role in the diagnosis of bone disease in hemodialysis patients. DXA measurement is necessary for the monitoring for bone loss.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Bone disease is highly prevalent in patients with chronic kidney disease on dialysis (CKD-5D) [1]. It can induce serious bone health problems, especially fragility fractures. Bone disease in patients with CKD-5D is the result of bone turnover abnormalities and the decrease of bone mineral density (BMD). Bone biopsy remains the gold standard for the diagnosis of bone turnover abnormalities. However, it is an invasive method and repetitive assessment of bone status cannot be possible. Measurements of serum bone turnover markers are not common practice in the management of CKD-5D patients [1]. Fibroblast growth factor-23 (FGF23) is a circulating factor produced by osteocytes. This hormone inhibits phosphate reabsorption and renal production of 1,25(OH) vitamin D. FGF23 regulates phosphate and vitamin D. This hormone plays an important role in bone metabolism of patients with chronic kidney disease [2]. Moreover, the assessment of bone mass in patients under dialysis is not yet codified. Both bone resorption and bone formation markers in patients with CKD-5D may be up- or down-regulated by systemic hormones such as parathormone. The measurement of BMD by dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry (DXA) is recommended only in patients with a history of fractures. Multiple factors are associated with reduced BMD and may affect bone health [3].
This study aimed to determine the usefulness of serum bone turnover markers by measuring one bone formation marker (bone-specific alkaline phosphatase) and one bone resorption marker (carboxy-terminal telopeptides of type 1 collagen) and the usefulness of the BMD by DXA in patients with CKD-5D. We aimed also to assess the frequency and risk factors of osteoporosis and osteoporotic fracture in hemodialysis patients.
Methods
Patients
We conducted a cross-sectional study including patients in maintenance hemodialysis three times weekly for more than 12 months.
Exclusion criteria included patients younger than 20 years, premature menopause (occurring before the age of 40), prolonged immobilization and patients receiving treatments related to mineral metabolism (long-term steroids, hormone replacement therapy, and bisphosphonate). Patients with a history of gastrectomy, parathyroidectomy, neoplasia or hysterectomy were excluded from this study. Patients with disease that may affect bone such as chronic inflammatory bowel disease, cirrhosis, and endocrinopathies except diabetes were also excluded.
Demographic and clinical data, including age, gender, anthropometric measurements, body mass index (weight/height2), comorbidities, menopausal status, etiology of kidney disease, and duration of dialysis were collected. We inquired also about low trauma fractures since starting dialysis.
Measurements of biochemical variables
Peripheral blood samples were obtained from each patient before dialysis in a fasting state within a week of the DXA. Biochemical variables of calcium and phosphate were measured using an in vitro photometric assay for automated clinical chemistry analyzers.
Plasma intact PTH (PTH) levels were measured using chemiluminescent microparticle immunoassay. Normal values range from 15-65 pg/mL.
Serum concentrations of 25(OH) vitamin D (25(OH)D) were measured using chemiluminescent immunoassay. Vitamin D deficiency was defined as 25(OH)D values lower than 10 ng/mL, vitamin D insufficiency was defined as 25(OH)D values between 10 and 30 ng/mL [4]. Recommended rates of vitamin D ranged between 30 and 70 ng/mL.
Bone alkaline phosphatase (bAP), a marker of osteoblastic activity, was measured using an immunosorbent enzyme-linked assay.
C-terminal telopeptide of type I collagen (CTX), a marker of osteoclastic activity, was measured by chemiluminescent immunoassay.
Fibroblast growth factor 23 (FGF23) was measured with the ELISA technique. Normal values range from 30 to 176 pg/mL.
Measurements of BMD
Dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA) was performed to assess bone mineral density (BMD). Instrument quality control was performed regularly. Bone mass density, expressed in gm/cm2, was measured at the lumbar spine, total hip, femoral neck, and total body.
In the lack of diagnostic criteria for defining osteoporosis in men and premenopausal women, we used WHO criteria as a cutoff point. Osteopenia corresponded to T-score more than − 2.5 SD but less than − 1 SD. Osteoporosis was defined as T-score less than or equal to − 2.5 SD in at least one of these sites: lumbar spine, femoral neck or total hip [5].
Fragility fractures
Fragility fractures were defined as fractures resulting from low-trauma (fall from standing-height or lower).
Lateral dorsal and lumbar spine X-rays were performed to assess vertebral fracture.
Statistical analysis
Statistical Package for Social Sciences (SPSS) version 19.0 was used to perform statistical analysis. Means and standard errors were calculated. Comparisons were performed using Student’s t-test and analysis of variance (ANOVA) for normally distributed variables. The chi-square test was used to analyze categorical data. The multiple linear regression was performed to identify predictors of low bone mass. The significance level was set at < 0.05. Correlations were reported as either the Pearson correlation coefficient.
Results
Patients’ characteristics
A total of 90 patients were included in the study. All of them were Caucasian. There were 58 men (64%) with a sex ratio of 1.8. The mean age was 53.01 years [20; 89]. Sixty-eight percent of patients were under the age of 50 years. There were 8 post-menopausal women. The duration of hemodialysis was less than 5 years in 61% of patients whereas it was more than 10 years in only two cases. The calcium intake was noted in 97% of cases with a mean dose of 1.89 g daily [0.5; 3]. Only 30% of patients were orally supplemented with 0.5 microg of alfacalcidol daily.
Hyperphosphatemia was noted in 62.22% and hypocalcemia was found also in 62.22%. Fifty-six percent of patients have PTH values between 2 and 9 times the upper normal limit of the assay. However, 19% of patients have PTH values less than 2 times the upper normal limit of the assay. Insufficiency and deficiency of vitamin D were found respectively in 41.11 and 44.44% of cases. CTX values were 6.25 times higher than the normal limit of the assay.
Only 6 patients had CTX levels within the normal range. Bone alkaline phosphatase levels were less than 10 ng/mL in 26 cases and higher than 25 ng/mL in 31 cases. Table 1 summarized the clinical and biological characteristics of patients.
Prevalence of osteoporotic fracture
Osteoporotic fractures were noted in 12.22% of cases (n = 11) and had occurred after the age of 50 years in 9 cases. Vertebral fractures are the most common type of osteoporotic fractures, found in 6 patients, followed by hip fractures noted in 3 cases. For the two other cases, there were wrist fracture and tibial fracture.
Prevalence of osteoporosis
As shown in Table 2, osteoporosis was common among patients undergoing hemodialysis. 23% of patients have osteoporosis and 45% have osteopenia. Osteoporosis affected the hip more than the spine.
Correlation between biological parameters
There was a positive correlation between bAP and CTX. Moreover, both bone markers showed positive correlations with serum PTH levels. Table 3 demonstrated correlations between biological parameters.
Associated factors of BMD
As illustrated in Table 4, patients with osteoporosis were older than patients without osteoporosis. Men had higher DXA BMD than women at only the total body (1.160 ± 0.141 vs 1.053 ± 0.105 g/cm2, p< 10-3).
The mean BMD was significantly lower among patients with a history of diabetes at the total hip femoral (0.894 ± 0.162 in patients with diabetes vs. 0.894 ± 0.162 in patients without diabetes, p: 0.003). Diabetic nephropathy was the most common etiology associated with decreased BMD at the femoral site whereas patients with polycystic kidney disease tended to have higher BMD than the other patients (0.789 ± 0.118 g/cm2 in patient with diabetic nephropathy vs. 0.980 ± 0.249 in patient with polycystic kidney disease, p: 0.031).
Parathyroid hormone levels were significantly increased in patients with osteoporosis affecting the total hip. Fibroblast growth factor 23 levels were significantly increased in patients with osteoporosis affecting the lumbar. However, vitamin D levels did not differ significantly between patients with and without osteoporosis.
The Pearson’s correlations between clinical, anthropometric, biological and BMD were presented in Table 5.
As shown in Table 6, age and PTH levels significantly predicted the total hip BMD.
Associated factors of fractures
As demonstrated in Table 7, PTH levels were significantly lower in patients with fractures. Besides, patients with osteoporosis had more osteoporotic fractures than patients without osteoporosis.
Discussion
Patients with chronic kidney disease on dialysis (CKD-5D) are at increased risk of osteoporosis and fractures than the general population [6]. In this bone DXA densitometry-based study, we detected that osteoporosis was common in dialysis patients, observed in 23% of cases. Indeed, literature data showed that the prevalence of osteoporosis varied from 4 to 47% at the lumbar spine and from 10 to 64% at the femoral site [7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15]. Moreover, Avramovski et al. [16] demonstrated that the progression of bone mass loss was significantly greater in chronic hemodialysis patients than in general population patients. Using DXA assessment, Sit D et al. [13] showed that the lumbar spine was the region with the highest prevalence of osteoporosis. However, other studies are consistent with our study showing that osteoporosis affected the total hip (20%) more than the lumbar spine (9%). DXA technology can overestimate the BMD measured in the lumbar because of the existence of osteophytes and aortic calcification, frequently observed in hemodialysis patients [17].
Bone mass loss is considered as the consequence of several factors in hemodialysis patients. Several studies are consistent with our study showing that BMD decreased as age increased [14, 17, 18]. The effect of gender on bone mass in hemodialysis is controversial [19, 20]. We found that BMD was significantly lower in women at the total body. The impact of diabetes on BMD is not yet clear. According to the study of Elder et al., we found that BMD at total hip was lower among dialysis patients with diabetes [21].
Chronic kidney disease is associated with hyperphosphatemia and hypocalcemia, observed in 62.22% in our patients, and induce secondary hyperparathyroidism. Fifty-six percent of patients have PTH values between 2 and 9 times the upper normal limit of the assay as recommended by KDIGO [1]. Observational studies demonstrated that PTH values at the extremes (lower than 2 times and more than 9 times) are associated with an increased relative risk of death in dialysis patients. Nevertheless, until now, there is no reference range of PTH values corresponding with normal bone turnover [22]. As in our study, Taal et al. [7] showed that the total hip BMD had a negative correlation with PTH. Besides, TAP correlated negatively with BMD in the total body. We didn’t find an association between the serum albumin level and BMD. Even if Huang et al. [23] found a positive correlation between serum albumin levels and femoral neck BMD in dialysis patients. Lai et al. [24] showed that there was no relationship between these parameters.
Even if CTX is cleared by the kidney, our study showed that circulating bAP and CTX levels are correlated with serum PTH levels. Serum CTX levels have been found to predict bone loss in patients under dialysis [25, 26]. Several studies have also demonstrated that CTX concentrations are raised in patients with CKD-5D and correlate well with BMD measurements [27]. Moreover, Maeno et al. [26] reported that CTX levels significantly correlate with annual bone loss with sensitivity and specificity at respectively 41 and 83%.
Nevertheless, in another study, serum CTX levels were not different between patients with and without loss of BMD at the distal radius [28].
FGF23 plays an important role in regulating bone mineralization. In our study, FGF23 levels were significantly increased in patients with osteoporosis affecting the lumbar. High FGF23 levels were associated with reduced osteoid thickness in children undergoing dialysis [29]. However, in other studies, BMD was not correlated with serum FGF23 levels [30].
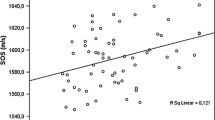
Insufficiency on vitamin D, observed in 41.11% in our study, is common among dialysis patients [31,32,33,34,35]. There has been much debate about the relationship between vitamin D and BMD. Several studies have demonstrated that low vitamin D level induced a decrease of cortical BMD in the presumed healthy adult [36]. Our study revealed a positive correlation between vitamin D levels and femoral BMD.
Fracture rates, observed in 12.1% in our study, are greatly increased in dialysis patients compared to the general population [37]. From our study, it is evident that lower PTH value was associated with an increased risk of osteoporotic fracture. It has been demonstrated that both high and low PTH levels can be associated with a high fracture rate [38, 39].
Another finding of interest in our study is that osteoporotic fractures were associated with the existence of osteoporosis. In a meta-analysis, Jamal et al. suggested that BMD is lower in patients with stage 5 CKD who have fractures [40]. The relationship between BMD measured by DXA and fracture in dialysis patients remains unclear.
There are numerous limitations to our study. First, it is a cross-sectional study. Besides, some other factors which might be associated with osteoporosis such as dosage of heparin and hypogonadism were not studied.
Conclusion
Our study showed that osteoporosis and fracture are common in patients under dialysis. We highlighted that bone mass loss is the consequence of several factors including age, diabetes and elevated levels of PTH. Osteoporotic fracture risk was associated with the existence of osteoporosis suggesting that DXA measurement is mandatory for the monitoring of bone loss. Our study showed also that both circulating bAP and CTX levels correlated positively with PTH levels. We suggest that bone metabolic markers including BAP and CTX may accurately reflect bone turnover. FGF23 levels were significantly increased in patients with lumbar osteoporosis. Certainly, FGF23 plays a role in the pathogenesis of bone disease in patients with CKD-5D. Other larger longitudinal studies are necessary to codify the assessment of bone disease.
Availability of data and materials
The datasets used and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Abbreviations
- 25(OH)D:
-
25(OH) vitamin D
- bAP:
-
bone-specific alkaline phosphatase
- BMD:
-
Bone mineral density
- CKD-5D:
-
Chronic kidney disease on dialysis
- CTX:
-
Carboxy-terminal telopeptides of type 1 collagen
- DXA:
-
Dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry
- FGF23:
-
Fibroblast growth factor 23
- PTH:
-
Intact parathyroid hormone
- TAP:
-
Total alkaline phosphatase
References
Ketteler M, Block GA, Evenepoel P, Fukagawa M, Herzog CA, McCann L, Moe SM, Shroff R, Tonelli MA, Toussaint ND, Vervloet MG, Leonard MB. Diagnosis, evaluation, prevention, and treatment of chronic kidney disease-mineral and bone disorder: synopsis of the kidney disease: improving global outcomes 2017 clinical practice guideline update. Ann Intern Med. 2018;168(6):422–30.
Zheng S, Chen Y, Zheng Y, Zhou Z, Li Z. Correlation of serum levels of fibroblast growth factor 23 and Klotho protein levels with bone mineral density in maintenance hemodialysis patients. Eur J Med Res. 2018;23(1):18.
Gordon PL, Frassetto LA. Management of Osteoporosis in CKD stages 3 to 5. Am J Kidney Dis. 2010;55:941–56.
Dawson-Hugues B, Mithal A, Bonjour JP, Boonen S, Burckhardt P, Fuleihan GEH, Josse RG, Lips P, Morales-Torres J, Yoshimura N. IOF position statement: vitamin D recommendations for older adults. Osteoporos Int. 2010;21:1151–4.
Kanis JA, Glüer CC. An update on the diagnosis and assessment of osteoporosis with densitometry. Committee of Scientific Advisors, international Osteoporosis Foundation. Osteoporos Int. 2000;11:192–202.
Nickolas TL, Leonard MB, Shane E. Chronic kidney disease and bone fracture: a growing concern. Kidney Int. 2008;74(6):721–31.
Taal MW, Masud T, Green D, Cassidy MJ. Risk factors for reduced bone density in haemodialysis patients. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 1999;14:1922–8.
Fontaine MA, Albert A, Dubois B, Saint-Remy A, Rorive G. Fracture and bone mineral density in hemodialysis patients. Clin Nephrol. 2000;54:218–26.
Ureña P, Bernard-Poenaru O, Ostertag A, Baudoin C, Cohen-Solal M, Cantor T, de Vernejoul MC. Bone mineral density, biochemical markers and skeletal fractures in haemodialysis patients. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2003;18:2325–31.
Yücel AE, Kart-Köseoglu H, Isiklar I, Kuruinci E, Ozdemir FN, Arslan H. Bone mineral density in patients on maintenance hemodialysis and effect of chronic hepatitis C virus infection. Ren Fail. 2004;26:159–64.
Mucsi I, Almasi C, Deak G, Marton A, Ambrus C, Berta K, et al. Serum 25(OH)-vitamin D levels and bone metabolism in patients on maintenance hemodialysis. Clin Nephrol. 2005;64:288–94.
Petrauskiene V, Petrauskienė V, Bumblytė IA, Šileikienė E, Gineikaitė R, Burbulytė R. Evaluation of bone mineral density and its importance for hemodialysis patients. Medicina. 2007;43:90–5.
Sit D, Kadiroglu AK, Kayabasi H, Atay AE, Yilmaz Z, Yilmaz ME. Relationship between bone mineral density and biochemical markers of bone turnover in hemodialysis patients. Adv Ther. 2007;24:987–95.
Avila M, Prado C, Ventura MJ, Mora C, Briones D, Valdez H, et al. Vitamin D receptor gene, biochemical bone markers and bone mineral density in Mexican women on dialysis. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2010;25:2259–65.
Khan MI, Syed GM, Khan AI, Sirwal IA, Anwar SK, Al-Oufi AR, Balbaid KA. Mean bone mineral density and frequency of occurrence of osteopenia and osteoporosis in patients on hemodialysis: a single-center study. Saudi J Kidney Dis Transpl. 2013;25:38–43.
Avramovski P, Sikole A. The progression of bone mineral density loss in Dialysis patients compared with the general population. Korean J Intern Med. 2012;27:436–42.
Toussaint ND, Lau KK, Strauss BJ, Polkinghorne KR, Kerr PG. Associations between vascular calcification, arterial stiffness and bone mineral density in chronic kidney disease. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2008;23:586–93.
Malluche HH, Davenport DL, Cantor T, Monier-Faugere MC. Bone mineral density and serum biochemical predictors of bone loss in patients with CKD on dialysis. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2014;9(7):1254–62.
Nybo M, Jespersen B, Aarup M, Ejersted C, Hermann AP, Brixen K. Determinants of bone mineral density in patients on haemodialysis or peritoneal dialysis--across-sectional, longitudinal study. Biochem Med. 2013;23(3):342–50.
Valkovsky I, Olsanska R, Tvrdik J, Martinek A, Svagera Z, Pernicova M, Dedochova J, Cermakova Z. Evaluation of biochemical markers and bone mineral density in patients with chronic kidney disease stage 5D at the start of hemodialysis treatment. Biomed Pap Med Fac Univ Palacky Olomouc Czech Repub. 2015;159(1):93–9.
Elder GJ, Mackun K. 25-Hydroxyvitamin D Deficiency and Diabetes Predict Reduced BMD in Patients With Chronic Kidney Disease. J Bone Miner Res. 2006;21:1778–84.
Souberbielle JP, Roth H, Fouque DP. Parathyroid hormone measurement in CKD. Kidney Int. 2010;77:93–100.
Huang GS, Chu TS, Lou MF, Hwang SL, Yang RS. Factors associated with low bone mass in the hemodialysis patients—a cross-sectional correlation study. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2009;10:60.
Lai MN, Hsu IS, Chen YY, Gee MJ, Kao MT. Osteoporosis and associated risk factors for chronic hemodialysis patients. Acta Nephrol. 2002;16:25–30.
Okuno S, Inaba M, Kitatani K, Ishimura E, Yamakawa T, Nishizawa Y. Serum levels of C-terminal telopeptide of type I collagen: a useful new marker of cortical bone loss in hemodialysis patients. Osteoporos Int. 2005;16:501–9.
Maeno Y, Inaba M, Okuno S, Yamakawa T, Ishimura E, Nishizawa Y. Serum concentrations of cross-linked N-telopeptides of type I collagen: new marker for bone resorption in hemodialysis patients. Clin Chem. 2005;51:2312–7.
Herrmann M, Seibel MJ. The amino- and carboxyterminal cross-linked telopeptides of collagen type I, NTX-I and CTX-I: a comparative review. Clin Chim Acta. 2008;393(2):57–75.
Ueda M, Inaba M, Okuno S, Maeno Y, Ishimura E, Yamakawa T, Nishizawa Y. Serum BAP as the clinically useful marker for predicting BMD reduction in diabetic hemodialysis patients with low PTH. Life Sci. 2005;77:1130–9.
Bacchetta J, Cochat P, Salusky IB, Wesseling-Perry K. Uric acid and IGF1 as possible determinants of FGF23 metabolism in children with normal renal function. Pediatr Nephrol. 2012;27:1131–8.
Urena Torres P, Friedlander G, de Vernejoul MC, Silve C, Prié D. Bone mass does not correlate with the serum fibroblast growth factor 23 in hemodialysis patients. Kidney Int. 2008;73:102–7.
Wolf M, Shah A, Gutierrez O, Ankers E, Monroy M, Tamez H, et al. Vitamin D levels and early mortality among incident hemodialysis patients. Kidney Int. 2007;72:1004–13.
Jean G, Charra B, Chazot C. Vitamin D deficiency and associated factors in hemodialysis patients. J Ren Nutr. 2008;18:395–9.
Seck SM, Cisse MM, Ka EF, Doupa D. Epidemiology of vitamin D deficiency in west African hemodialysis patients: a pilot study from Senegal. Indian J Nephrol. 2014;24:27–128.
Krassilnikova M, Ostrow K, Bader A, Heeger P, Mehrotra A. Low dietary intake of vitamin D and vitamin D deficiency in hemodialysis patients. J Nephrol Ther. 2014;4. https://doi.org/10.4172/2161-0959.1000166.
Drechsler C, Verduijn M, Pilz S, Dekker FW, Krediet RT, Ritz E, et al. Vitamin D status and clinical outcomes in incident dialysis patients: results from the NECOSAD study. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2011;26:1024–32.
Guinota C, Ezzedinec K, Maugera E, Ambroisinea L, Latreillea J, Bertraisd S, et al. Phototype, vitamin D status and bone mineral density among women at risk of osteoporosis. Rev Med Intern. 2006;27:369–74.
Pimentel A, Ureña-Torres P, Zillikens MC, Bover J, Cohen-Solal M. Fractures in patients with CKD-diagnosis, treatment, and prevention: a review by members of the European calcified tissue society and the European renal Association of Nephrology Dialysis and Transplantation. Kidney Int. 2017;92(6):1343–55.
Guh JY, Chen HC, Chuang HY, Huang SC, Chien LC, Lai YH. Risk factors and risk for mortality of mild hypoparathyroidism in hemodialysis patients. Am J Kidney Dis. 2002;39:1245–54.
Lertdumrongluk P, Lau WL, Park J, Rhee CM, Kovesdy CP, Kalantar-Zadeh K. Impact of age on survival predictability of bone turnover markers in hemodialysis patients. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2013;28:2535–45.
Jamal SA, Hayden JA, Beyene J. Low bone mineral density and fractures in long-term hemodialysis patients: a meta-analysis. Am J Kidney Dis. 2007;49(5):674–81.
Acknowledgements
Not applicable
Funding
The authors declare that they have no funding for the research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
MS has drafted the work. HS has substantively revised the work. AB has made substantial contributions to the analysis of data. LL has made substantial contributions to the interpretation of data. WS, SR, IG and MS have made substantial contributions to the acquisition of data. FBM has made substantial contributions to the design of the work. ME has approved the submitted version. EC has made substantial contributions to the conception of the work. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated.
About this article
Cite this article
Slouma, M., Sahli, H., Bahlous, A. et al. Mineral bone disorder and osteoporosis in hemodialysis patients. Adv Rheumatol 60, 15 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1186/s42358-020-0118-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s42358-020-0118-0