Abstract
Background
Parasite diversity and population structure influence malaria control measures. Malaria transmission at international borders affects indigenous residents and migrants, defying management efforts and resulting in malaria re-introduction. Here we aimed to determine the extent and distribution of genetic variations in Plasmodium vivax populations and the complexity of infections along the China–Myanmar border.
Methods
We collected clinical P. vivax samples from local and migrant malaria patients from Laiza and Myitsone, Kachin State, Myanmar, respectively. We characterized the polymorphisms in two P. vivax merozoite surface protein markers, Pvmsp-3α and Pvmsp-3β, by PCR-restriction fragment length polymorphism (PCR–RFLP) analysis. We sought to determine whether these genetic markers could differentiate these two neighboring parasite populations.
Results
PCR revealed three major size variants for Pvmsp-3α and four for Pvmsp-3β among the 370 and 378 samples, respectively. PCR–RFLP resolved 26 fragment-size alleles by digesting Pvmsp-3α with Alu I and Hha I and 28 alleles by digesting Pvmsp-3β with Pst I. PCR–RFLP analysis of Pvmsp-3α found that infections in migrant laborers from Myitsone bore more alleles than did infections in residents of Laiza, while such difference was not evident from genotyping Pvmsp-3β. Infections originating from these two places contained distinct but overlapping subpopulations of P. vivax. Infections from Myitsone had a higher multiplicity of infection as judged by the size of the Pvmsp-3α amplicons and alleles after Alu I/Hha I digestion.
Conclusions
Migrant laborers from Myitsone and indigenous residents from Laiza harbored overlapping but genetically distinct P. vivax parasite populations. The results suggested a more diverse P. vivax population in Myitsone than in the border town of Laiza. PCR–RFLP of Pvmsp-3α offers a convenient method to determine the complexity of P. vivax infections and differentiate parasite populations.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Malaria has been a major threat to public health and economic development [1]. With an estimated 13.8 million victims each year, Plasmodium vivax is widespread, occurring in endemic areas of Asia, Oceania, Central and South America, the Middle East, and West Africa [2]. Increasing imported malaria cases in mainland China often originate in Myanmar, which has the highest malaria burden in the Greater Mekong Subregion (GMS) [3]. In southwestern China, especially in Yunnan Province, malaria is particularly prevalent among border crossers, and ethnic minority groups in the border areas of Myanmar–Yunnan are at elevated risk. As the GMS aims to eliminate malaria by 2030, it is critical to understand the parasite populations and transmission dynamics in the border areas.
Genetic markers have been used to determine the diversity of parasite populations, spatial and temporal transmission dynamics, and complexity of infections. Molecular markers are also used to quantify the intensity of infections and determine the number of parasites harbored by an individual (the multiplicity of infection, or MOI). Many merozoite surface proteins, such as msp1, msp2, and glurp in Plasmodium falciparum [4], and msp1 and msp3α/β in P. vivax [6], have been used extensively for parasite genotyping since they display significant variations. While sequencing of regions of these genes can reveal much higher genetic diversity, another method that is often used for genotyping these markers is polymerase chain reaction-restriction fragment length polymorphism (PCR–RFLP), which offers the advantages of high sensitivity, convenience, and low cost [6].
The Pvmsp-3α and Pvmsp-3β genes encode merozoite surface proteins with an alanine-rich central domain, which strongly predicts coil-like tertiary structure [8]. The central domain is prone to large insertion/deletion mutations, thus displaying substantial length variations [10]. The Pvmsp-3α length polymorphism was first identified in parasites from Asia, South America, and the South Pacific region, with four major amplified fragment types reported [6]. Similarly, length variations in Pvmsp-3β allow the differentiation of P. vivax from different geographical areas [12]. When combined, two markers provide increasing power to differentiate parasite isolates [13]. For example, Pvmsp-3α and Pvmsp-3β have been used to study the genetic diversity of P. vivax from Pakistan [7] and Kachin State, Myanmar [14].
The continued transmission of P. vivax in the border region of Myanmar and its contribution to imported malaria to China prompted us to investigate the changes in the parasite population and the spatio-temporal transmission dynamics in the border region [15]. Specifically, we sought to characterize the polymorphisms of Pvmsp-3α and Pvmsp-3β from two P. vivax populations along the China–Myanmar border to see if they can be used to differentiate these parasite populations and trace the parasite origins. Our study identified that migrant workers, who had acquired P. vivax infection from Myitsone while constructing the Myitsone Dam [17], harbored more genetically diverse P. vivax than the local malaria patients from Laiza.
Materials and methods
Sample collection, malaria diagnosis and DNA extraction
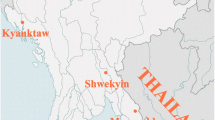
In this study, 442 samples of P. vivax were analyzed from symptomatic patients in hospitals or malaria clinics in two regions of the China–Myanmar border in 2012–2015. Among them, 230 samples were collected from 13 clinics around Laiza township, Kachin State, Myanmar (Fig. 1), during the high malaria season (June–September) in 2012–2013 (43 samples) and 2015 (187 samples). In 2013, 192 samples were collected from Chinese migrant laborers-patients returning from Myitsone, Kachin, through the immigration control checkpoints of Tengchong (Yunnan Province, China) (Fig. 1). These two areas, Laiza and Myitsone, represent regional hotspots for the transmission of P. vivax [18]. All patients had uncomplicated malaria, with a parasite density of 752–3579/μl. Each patient voluntarily signed an informed consent form. This study was reviewed and approved by the Institutional Review Board of Kunming Medical University.
Malaria infection was confirmed by microscopy of Giemsa-stained thick and thin blood films. Two five-milliliters of venous blood were drawn from each patient and stored at − 20 °C until use. Genomic DNA was extracted from 100 μl of whole blood using the High Pure PCR Template Preparation Kit (Roche, Germany).
Amplification of Pvmsp-3α and Pvmsp-3β genes
Nested PCR and genotyping of Pvmsp-3α and Pvmsp-3β used previously described methods [12] with modifications. Oligonucleotide primers and cycling conditions are listed in Additional file 1: Table S1 and Additional file 2: Fig. S1. For the first round of amplification, 1.0 μl DNA was added to a reaction of 25 μl, including 1.25 U TaKaRa Taq polymerase, 3 mM MgCl2, 0.4 mM dNTPs, distilled H2O, and 0.2 μl of each primer (10 pM). For nested PCR, 2.0 μl of the first amplification product was used as the template and added to a total volume of 50 μl of the reaction system, including distilled H2O, primers and Premix Taq™ (TaKaRa Taco™ version 2.0 plus dye). The PCR products were resolved on 0.8% agarose gel, and their sizes were determined using a 200 bp DNA ladder (Dye Plus; TaKaRa, Japan).
PCR–RFLP genotyping of Pvmsp-3α and Pvmsp-3β
Allelic polymorphism of the Pvmsp-3a and Pvmsp-3β genes was assessed using established PCR–RFLP techniques. Briefly, 3 μl of each PCR product were digested with restriction enzymes for more than 5 h. Pvmsp-3a amplicons were digested in 10 μl of reactions with 1 μl of Alu I (enzyme cutting site: 5′-AGC|T-3′) or Hha I (enzyme cutting site: 5′-GCG|C-3′). Pvmsp-3β was digested with 1.5 μl of Pst I (enzyme cutting site: 5′-TTA|TAA-3′) in 11 μl reactions (TaKaRa, Japan). Restriction fragments were separated and visualized in 1.8% agarose gels.
Mixed-strain infections and MOI
Mixed-strain infections were inferred when PCR products of more than one size appeared in the initial amplification [6] or when the summed size of the DNA fragments resulting from RFLP restriction exceeded the size of the uncut PCR product [21]. Alleles were identified based on unique restriction banding patterns. Alleles were considered the same if the restriction banding patterns were estimated to be within 20 bp [22]. MOI denotes the number of distinct parasite genotypes in the same patient [24]. When the total fragment length generated by a single sample exceeded the mean value of the uncut band, but was less than twice the mean value of the uncut band, we judged the sample to constitute mixed infections of two subtypes. We estimated MOI for each patient to compare residents of Laiza with migrant laborers using Pvmsp-3α and Pvmsp-3β genotypes.
Statistical analysis
The Chi-square (χ2) test was used to compare the frequencies of RFLP alleles among the populations using the Prism GraphPad 6. Fisher’s exact test was used to compare the differences between two populations in individual alleles. T-test was used to compare the infection multiplicity between two populations. P values of < 0.05 were considered significant.
Results
Genotyping Pvmsp-3α and Pvmsp-3β genes by PCR
For Pvmsp-3a, we successfully genotyped 227 of 230 (98.7%) samples from Laiza and 178 of 192 (92.7%) Myitsone samples from Chinese migrant patients. Three different target bands (types A, B, and C, measuring 1900–2000, 1400–1500, and 1100–1300 bp, respectively) were amplified (Fig. 2). Among the samples from Laiza, those with multiple PCR bands occurred in 7.9% (18/227). Single infections of types A, B, and C occurred at frequencies of 22.9, 31.1, and 37.9%, respectively. In comparison, 9.5% (17/178) of the Myitsone samples from the migrants yielded multiple bands. Single infections of type A, B, and C occurred at 65.2, 5.6, and 19.7%, respectively (Fig. 3a). Thus, the three allele types occurred with approximate parity in Laiza, but type A predominated in the Myitsone population from migrant workers. Mixed infections diagnosed by Pvmsp-3a occurred at a similar frequency (P < 0.05).
Pvmsp-3β was successfully amplified in 220 of 230 (95.7%) Laiza samples and 173 of 192 (90.1%) Myitsone samples. The Pvmsp-3β PCR products had four amplicon length types (A, B, C, and D), corresponding to 1700–2200, 1400–1500, 1100–1300, and 600–800 bp, respectively (Fig. 4). Among the samples from Laiza, multiple band samples accounted for 0.9% (2/220), while single-band samples with types A, B, and D occurred at 68.6, 30.0, 0.5%, respectively. Types A and B were predominant, accounting for over 98.6% of the samples. Only one D-type allele was identified in a single patient, while Type C appeared only in mixed infections. In comparison, the Myitsone samples yielding multiple Pvmsp-3β PCR bands occurred at 7.5% (13/173). Notably, single-band samples were only present in two types; Type A occurred in 57.8% and type B in 34.7%. Types C and D appeared only in mixed infections (Fig. 3b). Thus, Types A and B predominated at comparable frequencies in the two regions. Significantly more mixed infections were detected among migrant workers than residents of Laiza by genotyping Pvmsp-3β (P > 0.05).
RFLP results of Pvmsp-3α gene
Figure 5a depicts the band patterns resulting from Alu I digestion of the amplified Pvmsp-3α gene. A total of 16 isoforms of Type A, 7 isoforms of Type B, and 3 isoforms of Type C were apparent in the two regions. Each region had 19 alleles, but with different allele types or frequencies. In the Laiza samples, 10 A, 6 B, and 3 C isoforms occurred, while in Myitsone samples, 12 A, 4 B, and 3 C isoforms occurred (Table 1). No significant difference was observed in the frequency distribution of isoforms across the two sampling locales (χ2 = 0.582, P = 0.748). However, the two sample populations had significantly different distributions of Type A alleles of Pvmsp-3a. The same is true for the alleles of Type B and C (Table 1).
Major RFLP alleles of the Pvmsp-3α amplicons digested with Alu I (a) and Hha I (b). Lane M, DNA marker in bp. a Lane 1—B3; lanes 2, 6, 11, 14, 20—C1; lane 3—A7; lanes 4, 8, 9, 17, 18—A5; lanes 5, 13, 15—B4; lanes 7, 10, 19—A1; lanes 12, 16, 20—A4. b Lanes 1, 5, 7, 20—C1; lanes 2, 4, 11, 12, 15—A1; lanes 3, 23—A2; lanes 6, 8, 10, 19, 24—A3; lanes 9, 16—A4; lanes 14, 21—A13; lanes 17, 22—A8; lane 18—A14
Figure 5b depicts the results of Hha I digestion of Pvmsp-3α, revealing 16 Type A, 4 B, and 6 C isoforms. Laiza parasites had 17 isoforms (9 A, 3 B, and 5 C isoforms), compared to 23 isoforms in Myitsone (15 A, 2 B, and 6 C isoforms) (Table 3). The distribution of the Pvmsp-3α Hha I isoforms did not differ significantly between the two populations (χ2 = 0.911, P = 0.634). However, as described for Alu I digestion, the frequency distribution of these alleles was significantly different between the two populations (Table 2).
RFLP results of Pvmsp-3β gene
Pst I digestion of the Pvmsp-3β amplicon identified 14 Type A and 13 Type B isoforms (Fig. 6). The two populations harbored distinct distributions of these alleles (Table 3). The Laiza samples had 26 isoforms (14 A, 11 B, and 1 D); alleles A4, A5, A7, A9, A11, and B9 were most abundant, accounting for 52.3% of all samples. In the Myitsone population, fewer isoforms were observed (10 A and 9 B). Isoforms A11, A12, and B13 comprised 59% of the samples. The allele frequency distribution, however, did not differ significantly between the two populations (χ2 = 0.0065, P = 0.9357). Similarly, examining the distribution of A and B alleles separately failed to identify a significant difference between the two parasite populations (Table 3).
Multiplicity of infection (MOI)
PCR–RFLP analyses revealed occasional occurrences of mixed genotype infections in both parasite populations. The MOI of the Laiza samples ranged from 1 to 3 and 1 to 4, as judged by Pvmsp-3a and Pvmsp-3β, respectively. The MOI in the Myitsone samples ranged from 1 to 3 and 1 to 5 using these genes. Specifically, based on Alu I digestion of Pvmsp-3a, the MOI was estimated at 1.125 ± 0.412 and 1.173 ± 0.545 for the Laiza and Myitsone parasites (Table 4), respectively (P > 0.05). Hha I digestion yielded estimates of MOI at 1.23 ± 0.517 and 1.397 ± 0.637 (Table 4), respectively, which differed significantly (P < 0.01). When restricting the analysis of MOI to adults 18 and older, we found that the MOI, estimated by Hha I digestion of Pvmsp-3a, was significantly lower among the Laiza residents (1.221 ± 0.5099) than migrant workers (1.368 ± 0.6116) (P < 0.05).
Pst I digestion of Pvmsp-3β yielded statistically equivalent estimates of MOI in the two patient populations (2.04 ± 0.754 vs. 1.936 ± 0.882; P > 0.05) (Table 4). Although this amplification/digestion assay yielded larger estimates of MOI, it proved poorer in differentiating MOI among the two population samples. Restricting the analysis to adults yielded a similarly non-significant result (2.072 ± 0.793 vs. 1.897 ± 0.864, P > 0.05).
Discussion
Parasite genetic diversity illuminates the dynamics of malaria transmission and the fate of control efforts. Malaria eradication remains a public health goal, so a better understanding of malaria transmission dynamics and population genetics is essential. Laiza and Myitsone are hot spots of P. vivax transmission along the China–Myanmar border [16]. Despite their proximity, we lack knowledge about the impact of control measures on parasite populations from these two areas. Thus, regional assessments will provide needed information on local epidemiological conditions to guide targeted malaria elimination efforts [26]. Here, we simultaneously characterized variations in Pvmsp-3α and Pvmsp-3β among P. vivax populations from two adjacent areas (Laiza and Myitsone) of Kachin State, Myanmar. The results showed different patterns and degrees of genetic diversity in the two populations. The higher genetic diversity of parasites from Myitsone suggested a higher level of malaria transmission there.
PCR–RFLP genotyping of Pvmsp-3α and Pvmsp-3β indicated high genetic diversity of the P. vivax population from this region, revealing large numbers of fragment-size alleles of the two polymorphic markers. Genotyping Pvmsp-3α also identified significantly different allele distributions and frequencies in the two neighboring areas, suggesting population differentiation. These two areas differed considerably in the prevalence of the Pvmsp-3α PCR size polymorphism, with the Laiza samples having more evenly distributed frequencies of the A, B, and C types as compared to the predominant A type found in the Myitsone samples (Fig. 3). Similarly, restriction digestions of the Pvmsp-3α amplicons corroborated this finding (Tables 2, 3). However, genotyping Pvmsp-3β was less informative and failed to differentiate these regional parasite populations, although Pvmsp-3β also had a large number of alleles (26 PCR–RFLP alleles).
A comparison of the parasite samples studied here with earlier publications suggested population changes in the China–Myanmar border, probably reflecting the impact of scaled-up control in the region. Pvmsp-3α Type A was the dominant infection type in central China, Thailand, Myanmar and other regions, while Type C was reportedly rare or absent [11]. The Myitsone samples more conformed to this allele type distribution. In Laiza, however, compared to the 2006–2008 parasite population, which showed that the Type A allele was most frequent, followed by Type B [14], this study identified a more evenly distributed Pvmsp-3α types, with Type C being the most abundant (37%). This difference may reflect recent parasite population expansion events revealed by whole-genome sequencing analysis [27], since the Laiza parasite population has experienced several outbreak events [16].
Multiple infections of genetically distinct clones of the same Plasmodium species are common in many places where malaria is endemic [29]. Some studies reported a reduced risk of clinical malaria in polyclonal infections [31], whereas other studies reported that mono-infections and prevalent genotypes were more likely to cause severe malaria than polyclonal infections [34]. Regardless, MOI may represent a measure to gauge the transmission intensity, with higher MOI occurring more often in high transmission areas. From our present study, mixed infections in Myitsone laborers appeared more frequent than in residents of Laiza, as estimated from Pvmsp-3α (P < 0.05). Consistently, a higher MOI was estimated from Myitsone laborers than residents of Laiza using Pvmsp-3α digested by Hha I (P < 0.05). Again, Pvmsp-3α provided more power to differentiate multiple infections than Pvmsp-3β. These results indicate greater malaria transmission intensity among these laborers during their stay in Myitsone.
We showed that PCR–RFLP analysis of Pvmsp-3α and Pvmsp-3β genes is a convenient method to identify the genetic diversity of the parasites from the China–Myanmar border [26]. Especially with Pvmsp-3α, it allowed us to differentiate parasite populations and identify mixed infections. However, PCR–RFLP analysis using these markers also has lower sensitivity in distinguishing closely related alleles, and may not be suitable for tracking cross-border parasite migration [36]. Deep sequencing of these amplicons would be more suitable for identifying the entire repertoire of these genetic variants [37].
Conclusions
By PCR–RFLP genotyping Pvmsp-3α and Pvmsp-3β genes, we found evidence of genetic differences in P. vivax populations from two adjacent regions along the China–Myanmar border. Patients from Myitsone harbored more mixed infections and had higher MOI than those from Laiza.
References
WHO: World malaria report 2021. In.; 2021.
Price RN, Tjitra E, Guerra CA, Yeung S, White NJ, Anstey NM. Vivax malaria: neglected and not benign. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2007;77(6 Suppl):79–87.
Yin JH, Yang MN, Zhou SS, Wang Y, Feng J, Xia ZG. Changing malaria transmission and implications in China towards National Malaria Elimination Programme between 2010 and 2012. PLoS ONE. 2013;8(9): e74228.
Deshmukh A, Chourasia BK, Mehrotra S, Kana IH, Malhotra P. Plasmodium falciparum MSP3 exists in a complex on the merozoite surface and generates antibody response during natural infection. Infect Immunity. 2018;86(8):IAI.00067-00018.
Zakeri S, Bereczky S, Naimi P, Gil JP, Bjrkman A. Multiple genotypes of the merozoite surface proteins 1 and 2 in Plasmodium falciparum infections in a hypoendemic area in Iran. Tropical Med Int Health. 2010;10(10):1060–4.
Bruce MC, Galinski MR, Barnwell JW, Snounou G, Day KP. Polymorphism at the merozoite surface protein-3alpha locus of Plasmodium vivax: global and local diversity. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1999;61(4):518–25.
Khan SN, Khan A, Khan S, Ayaz S, Attaullah S, Khan J, Khan MA, Ali I, Shah AH. PCR/RFLP-based analysis of genetically distinct Plasmodium vivax population of Pvmsp-3α and Pvmsp-3β genes in Pakistan. Malar J. 2014;13:355.
Galinski MR, Corredor-Medina C, Povoa M, Crosby J, Ingravallo P, Barnwell JW. Plasmodium vivax merozoite surface protein-3 contains coiled-coil motifs in an alanine-rich central domain. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1999;101(1–2):131–47.
Rice BL, Acosta MM, Pacheco MA, Carlton JM, Barnwell JW, Escalante AA. The origin and diversification of the merozoite surface protein 3 (msp3) multi-gene family in Plasmodium vivax and related parasites. Mol Phylogenet Evol. 2014;78:172–84.
Rayner JC, Huber CS, Feldman D, Ingravallo P, Galinski MR, Barnwell JW. Plasmodium vivax merozoite surface protein PvMSP-3 beta is radically polymorphic through mutation and large insertions and deletions. Infect Genet Evol. 2004;4(4):309–19.
Cui L, Mascorro CN, Fan Q, Rzomp KA, Khuntirat B, Zhou G, Chen H, Yan G, Sattabongkot J. Genetic diversity and multiple infections of Plasmodium vivax malaria in Western Thailand. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2003;68(5):613–9.
Yang Z, Miao J, Huang Y, Li X, Putaporntip C, Jongwutiwes S, Gao Q, Udomsangpetch R, Sattabongkot J, Cui L. Genetic structures of geographically distinct Plasmodium vivax populations assessed by PCR/RFLP analysis of the merozoite surface protein 3beta gene. Acta Trop. 2006;100(3):205–12.
Schoepflin S, Valsangiacomo F, Lin E, Kiniboro B, Mueller I, Felger I. Comparison of Plasmodium falciparum allelic frequency distribution in different endemic settings by high-resolution genotyping. Malar J. 2009;8:250.
Zhong D, Bonizzoni M, Zhou G, Wang G, Chen B, Vardo-Zalik A, Cui L, Yan G, Zheng B. Genetic diversity of Plasmodium vivax malaria in China and Myanmar. Infect Genet Evol. 2011;11(6):1419–25.
Cui L, Yan G, Sattabongkot J, Cao Y, Chen B, Chen X, Fan Q, Fang Q, Jongwutiwes S, Parker D, et al. Malaria in the Greater Mekong Subregion: heterogeneity and complexity. Acta Trop. 2012;121(3):227–39.
Cui L, Sattabongkot J, Aung PL, Brashear A, Cao Y, Kaewkungwal J, Khamsiriwatchara A, Kyaw MP, Lawpoolsri S, Menezes L, et al. Multidisciplinary investigations of sustained malaria transmission in the Greater Mekong Subregion. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2022;107(4_Suppl):138–51.
Wang X, Yang L, Jiang T, Zhang B, Wang S, Wu X, Wang T, Li Y, Liu M, Peng Q, et al. Effects of a malaria elimination program: a retrospective study of 623 cases from 2008 to 2013 in a Chinese county hospital near the China–Myanmar border. Emerging microbes & infections. 2016;5(1): e6.
Hu Y, Zhou G, Ruan Y, Lee MC, Xu X, Deng S, Bai Y, Zhang J, Morris J, Liu H, et al. Seasonal dynamics and microgeographical spatial heterogeneity of malaria along the China-Myanmar border. Acta Trop. 2016;157:12–9.
Singh B, Bobogare A, Cox-Singh J, Snounou G, Abdullah MS, Rahman HA. A genus- and species-specific nested polymerase chain reaction malaria detection assay for epidemiologic studies. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1999;60(4):687–92.
Snounou G, Viriyakosol S, Zhu XP, Jarra W, Pinheiro L, do Rosario VE, Thaithong S, Brown KN. High sensitivity of detection of human malaria parasites by the use of nested polymerase chain reaction. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1993;61(2):315–20.
Bruce MC, Galinski MR, Barnwell JW, Donnelly CA, Walmsley M, Alpers MP, Walliker D, Day KP. Genetic diversity and dynamics of Plasmodium falciparum and P. vivax populations in multiply infected children with asymptomatic malaria infections in Papua New Guinea. Parasitology. 2000;121(Pt 3):257–72.
Cattamanchi A, Kyabayinze D, Hubbard A, Rosenthal PJ, Dorsey G. Distinguishing recrudescence from reinfection in a longitudinal antimalarial drug efficacy study: comparison of results based on genotyping of msp-1, msp-2, and glurp. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2003;68(2):133–9.
Mayengue PI, Ndounga M, Malonga FV, Bitemo M, Ntoumi F. Genetic polymorphism of merozoite surface protein-1 and merozoite surface protein-2 in Plasmodium falciparum isolates from Brazzaville, Republic of Congo. Malar J. 2011;10:276.
Huang B, Tuo F, Liang Y, Wu W, Wu G, Huang S, Zhong Q, Su XZ, Zhang H, Li M, et al. Temporal changes in genetic diversity of msp-1, msp-2, and msp-3 in Plasmodium falciparum isolates from Grande Comore Island after introduction of ACT. Malar J. 2018;17(1):83.
Sattabongkot J, Cui L, Bantuchai S, Chotirat S, Kaewkungwal J, Khamsiriwatchara A, Kiattibutr K, Kyaw MP, Lawpoolsri S, Linn NYY, et al. Malaria research for tailored control and elimination strategies in the Greater Mekong Subregion. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2022;107(4_Suppl):152–9.
Cui L, Escalante AA, Imwong M, Snounou G. The genetic diversity of Plasmodium vivax populations. Trends Parasitol. 2003;19(5):220–6.
Brashear AM, Fan Q, Hu Y, Li Y, Zhao Y, Wang Z, Cao Y, Miao J, Barry A, Cui L. Population genomics identifies a distinct Plasmodium vivax population on the China-Myanmar border of Southeast Asia. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2020;14(8): e0008506.
Geng J, Malla P, Zhang J, Xu S, Li C, Zhao Y, Wang Q, Kyaw MP, Cao Y, Yang Z, et al. Increasing trends of malaria in a border area of the Greater Mekong Subregion. Malar J. 2019;18(1):309.
Lopez L, Koepfli C. Systematic review of Plasmodium falciparum and Plasmodium vivax polyclonal infections: impact of prevalence, study population characteristics, and laboratory procedures. PLoS ONE. 2021;16(6): e0249382.
Zhong D, Koepfli C, Cui L, Yan G. Molecular approaches to determine the multiplicity of Plasmodium infections. Malar J. 2018;17(1):172.
Nielsen MA, Staalsoe T, Kurtzhals JA, Goka BQ, Dodoo D, Alifrangis M, Theander TG, Akanmori BD, Hviid L. Plasmodium falciparum variant surface antigen expression varies between isolates causing severe and nonsevere malaria and is modified by acquired immunity. J Immunol. 2002;168(7):3444–50.
Al-Yaman F, Genton B, Reeder JC, Anders RF, Smith T, Alpers MP. Reduced risk of clinical malaria in children infected with multiple clones of Plasmodium falciparum in a highly endemic area: a prospective community study. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1997;91(5):602–5.
Bereczky S, Liljander A, Rooth I, Faraja L, Granath F, Montgomery SM, Farnert A. Multiclonal asymptomatic Plasmodium falciparum infections predict a reduced risk of malaria disease in a Tanzanian population. Microbes Infect. 2007;9(1):103–10.
Durand R, Ariey F, Cojean S, Fontanet A, Ranaivo L, Ranarivelo LA, Vonimpaisomihanta JA, Menard D, Pietra V, Le Bras J, et al. Analysis of circulating populations of Plasmodium falciparum in mild and severe malaria in two different epidemiological patterns in Madagascar. Trop Med Int Health. 2008;13(11):1392–9.
Amodu OK, Oyedeji SI, Ntoumi F, Orimadegun AE, Gbadegesin RA, Olumese PE, Omotade OO. Complexity of the msp2 locus and the severity of childhood malaria, in south-western Nigeria. Ann Trop Med Parasitol. 2008;102(2):95–102.
Rice BL, Acosta MM, Pacheco MA, Escalante AA. Merozoite surface protein-3 alpha as a genetic marker for epidemiologic studies in Plasmodium vivax: a cautionary note. Malar J. 2013;12:288.
Lin JT, Hathaway NJ, Saunders DL, Lon C, Balasubramanian S, Kharabora O, Gosi P, Sriwichai S, Kartchner L, Chuor CM, et al. Using amplicon deep sequencing to detect genetic signatures of Plasmodium vivax relapse. J Infect Dis. 2015;212(6):999–1008.
He X, Zhong D, Zou C, Pi L, Zhao L, Qin Y, Pan M, Wang S, Zeng W, Xiang Z, et al. Unraveling the complexity of imported malaria infections by amplicon deep sequencing. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2021;11: 725859.
Funding
This study was supported by the National Science Foundation of China (31860604 and U1802286), a grant (U19AI089672) from the National Institutes of Health, USA, Major science and technology projects of Yunnan Province (2018ZF0081), and International Science and Technology Cooperation-Yunnan International Science and Technology Cooperation Base (202003AE140004). XC, ZX, and YZ were under sponsoring by the Yunnan Applied Basic Research Projects-Union Foundation (2018FE001-190, 2019FE001-015 and 202101AY070001-108, respectively). YW was supported by the Hundred-Talent Program of Kunming Medical University (60117190439), Foundation of the Education Department of Yunnan Province (2018JS151), and the Innovation Experiment Project of Yunnan Province (202010678064) and Kunming Medical University (2020JXD014). YQ was supported by Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region Health Commission of Scientific Research Project (Z20190892). WZ was supported by the Education Department Fund of Yunnan Province (2019J1184). BR was supported by USDA project 8042-32000-113-00D.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Additional file 1.
Supplementary Tables.
Additional file 2.
Supplementary Figures.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, X., Bai, Y., Xiang, Z. et al. Genetic diversity of Plasmodium vivax populations from the China–Myanmar border identified by genotyping merozoite surface protein markers. Trop Med Health 51, 2 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1186/s41182-022-00492-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s41182-022-00492-7