Abstract
Background
In setting goals for orthodontic treatment, determining the morphologies of the alveolar bone and maxillary incisor root is important for avoiding root resorption, dehiscence, and fenestration. This study aimed to analyze the configurational relationships among maxillary incisors, the alveolar border, and the incisive canal by cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT).
Methods
Cone-beam CT images of 93 orthodontic patients were evaluated for length of the incisive canal (L); angles between the palatal plane and the maxillary alveolar border (θ1), the incisive canal (θ2), and maxillary incisor (θ3); distance from the left maxillary incisor to the incisive canal (D); and cross-sectional areas of the incisive canal (CSAs) at three vertical levels. Comparison of variables between male and female patients was performed with the two-sample t test. Correlations between parameters were examined by Pearson’s correlation analysis and Bonferroni correction for multiple comparisons.
Results
Male patients exhibited significantly greater values of L than female patients. There were significant positive correlations between θ1 and θ2, θ2 and θ3, and θ3 and θ1. While the value of D was the lowest at the oral opening, that of the cross-sectional area of the incisive canal (CSA) was the greatest at the incisal root apex.
Conclusions
This study demonstrated that the incisive canal had large inter-individual variability, and the proximity between the incisive canal and the incisal root could not be precisely predicted by the conventional cephalograms. Therefore, pre-treatment CBCT examination should be recommended when a large amount of maxillary anterior retraction and/or intrusion is planned in orthodontic diagnosis.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Orthodontic patients commonly require improvement of facial esthetics. Spatial position of the maxillary incisor is a critical factor in both facial esthetics and maxillofacial function [1]. Therefore, three-dimensional (3D) position and inclination of the maxillary incisor is regarded as a dominant factor when setting goals for orthodontic treatment [1,2,3,4,5]. With regard to maxillary incisor movement, Ackerman et al. presented the concept of “envelope of discrepancy” [6], which describes the limitations of the range of orthodontic movement of the maxillary incisor [7]. Contact with hard tissue structures, such as the labial, palatal, or incisive canal cortical plates, is a risk factor for apical root resorption in the maxillary incisor [8,9,10], and it is one of the iatrogenic complications of orthodontic treatment. In addition, excessive tooth movement during orthodontic treatment can induce root deviation from the alveolar housing of dentition, leading to dehiscence and fenestration [11]. Limitation of maxillary incisor movement in conjunction with cephalometric analysis has been proposed in order to avoid these potential complications; however, this approach remains controversial [12, 13].
In orthodontics, diagnosis and treatment planning have generally been performed by two-dimensional (2D) analysis of lateral and anteroposterior cephalometric measurements. However, the incisive canal and cortical plate on the sagittal plane of maxillary incisors cannot be precisely evaluated in conventional cephalometric radiographs. Recent developments in 3D analysis of dental cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT) images could help obtain more detailed information. Several studies using dental CBCT have suggested that determining the morphologies of maxillary incisor roots, the incisive canal, and the maxillary alveolar bone is important when setting goals for orthodontic treatment [8,9,10, 14, 15].
While previous CT and CBCT studies have clarified the anatomical relationships between maxillary incisors and the incisive canal [16], they suffered from inadequate image resolution for precise evaluation of alveolar bone shape and thickness. The aim of this study was to analyze the configurational relationships between maxillary incisors and the incisive canal in the anterior region of the maxillary alveolar bone using CBCT images.
Methods
Subjects
From among patients between the ages of 18 and 39 years who sought orthodontic treatment at the Tokyo Medical and Dental University Dental Hospital between 2012 and 2015, only those who required CBCT for diagnosis and treatment planning were selected. Written consent was obtained from all subjects after explanation of the research aims and goals.
The exclusion criteria were (1) history of orthodontic treatment, (2) missing or supernumerary maxillary incisors, 3) midline deviation of maxillary incisors ≥2 mm from the facial midline, (4) prosthodontic treatment of maxillary incisors, 5) evident nasopalatine pathology (e.g., nasopalatine duct cysts), (6) history of trauma to maxillary incisors, and 7) congenital anomalies (e.g., cleft lip and palate). Based on the inclusion and exclusion criteria, 93 subjects (male, 31; female, 62; mean age, 24.3 ± 5.6 years) were finally selected. Their skeletal pattern was Class I, Class II, and Class III and their mean ANB was 3.1 ± 3.5 (range −4.6–9.0).
CBCT
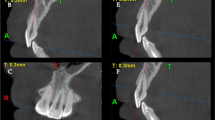
As a part of pre-treatment examination of each patient, CBCT (Finecube; Yoshida Dental MFG. Co., Tokyo, Japan) images of the maxillary and mandibular dentoalveolar regions were acquired for diagnosis and treatment planning, using the following settings: normal mode (16.8 s, 4.10 mGy, 90 kV, and 4 mA); slice thickness, 0.147 mm; field of view (FOV), 81 × 74 mm; and voxel size, 0.146 mm. All images were acquired with the head positioned along the Frankfort horizontal plane, running parallel to the floor. Images were saved as digital imaging and communication in medicine (DICOM) files, and sagittal and horizontal views of those were extracted and evaluated using an image analysis software (ImageJ version 1.48; National Institute of Mental Health, MD, USA). Prior to measurement, the three dimensions were calibrated and the three planes (i.e., sagittal, horizontal, and coronal) defined in each image (Fig. 1).
Landmarks, reference lines, and planes drawn on cone-beam computed tomography images. a Sagittal plane – passing through the midpalatal suture, perpendicular to the horizontal and coronal planes. b Horizontal plane – the palatal plane. c Coronal plane – passing through the right and left greater palatine foramina. Abbreviations: R right, L left, P posterior, A anterior
In the midsagittal plane, linear and angular measurements were defined as follows (Fig. 2):
Definitions of linear and angular measurements in the midsagittal plane. a PP palatal plane; L length of the incisive canal; θ1 and θ2 angles between the palatal plane and axes of the maxillary alveolar border and incisive canal, respectively. b θ3 angle between the palatal plane and axis of the maxillary left central incisor
-
P: palatal plane
-
L: length of the incisive canal
-
θ1, θ2, and θ3: angles between the palatal plane and axes of the maxillary alveolar border, the incisive canal, and maxillary left central incisor, respectively.
Linear and area measurements were acquired in the horizontal plane at three vertical levels: n, r, and o (levels of the nasal opening of the incisive canal, root apex of the maxillary incisor, and oral opening of the incisive canal, respectively; Fig. 3), and the distance from maxillary incisors to the incisive canal (D) and the cross-sectional area of the incisive canal (CSA) were measured at each level (Dn, Dr, and Do, respectively; CSAn, CSAr, and CSAo, respectively; Fig. 4). All measurements were performed by a single examiner, who repeated each measurement after a 2-month interval. The Dahlberg formula was used to calculate method error, as follows:
where d = difference between two measurements and n = number of measurement pairs [17].
Statistical analysis
All statistical analyses were performed using the computer software package SPSS 22.0 (IBM, Armonk, NY, USA). Mean values and standard deviations (SDs) were calculated for all measurements. Comparison of variables between male and female patients was performed with the two-sample t test. Correlations between parameters were examined by Pearson’s correlation analysis and Bonferroni correction for multiple comparisons. The significance level for all analyses was set at p < 0.05.
Results
Method errors for linear measurements L, Dr, and Do ranged between −0.2 and 0.2 mm, −0.4 and 0.5 mm, and −0.3 and 0.5 mm, respectively, while those for angular measurements θ1, θ2, and θ3 ranged between −1.5° and 2.5°, −1.4° and 1.3°, and −1.3° and 1.1°, respectively. Method errors for area measurements CSAn, CSAr, and CSAo ranged between −5.9 and 6.0 mm2, −5.5 and 6.2 mm2, and −4.9 and 5.5 mm2, respectively. There were no significant differences between the original and repeat measurements of any of the parameters.
The descriptive statistics of all measurements in the sagittal plane are presented in Table 1. Only L and θ2 exhibited significant sex-specific differences. The value of L in male patients (13.8 ± 2.2 mm) was significantly greater compared to that in female patients (12.2 ± 2.3 mm; p < 0.05), while θ2 in male patients (105.5° ± 8.6°) was significantly smaller compared to that in female patients (109.6° ± 7.9°; p < 0.05). There were significant positive correlations between θ1 and θ2 (p < 0.01; r = 0.719), θ2 and θ3 (p < 0.01; r = 0.488), and θ3 and θ1 (p < 0.01; r = 0.628; Table 2). While Dr (4.1 ± 1.8 mm) was significantly greater than Do (3.2 ± 1.3 mm; p < 0.05), CSAr (81.0 ± 17.3 mm2) was significantly greater than CSAn (74.0 ± 13.5 mm2) and CSAo (74.5 ± 13.3 mm2; both p < 0.05; Fig. 5).
Discussion
To our knowledge, this is the first study involving a large population to investigate the anatomical characteristics of maxillary incisors, the incisive canal, and the maxillary alveolar border using CBCT images. First, in the present study, the length of the incisive canal in male patients was significantly greater compared to that in female patients, which is concordant with the findings of a previous study [18]. Second, inclination of maxillary incisors was significantly correlated with those of the maxillary alveolar border and axis of the incisive canal. Moreover, maxillary incisors were located closer to the incisive canal at the level of the root apex than at the level of oral opening of the incisive canal, and the CSA of the incisive canal at the level of the maxillary incisor root apex was significantly greater compared to those at the levels of oral and nasal openings.
Since DICOM data are divided into 512 × 512 matrices, a large FOV corresponds to large voxel size and reduction in image resolution. In contrast, a limited FOV provides high visibility, but leads to an increase in radiation dose per unit of tissue. Thus, FOV should be set with consideration of object size for evaluation [19, 20]. In orthodontics, accurate diagnosis requires careful observation of not only of the alveolar bone but also dental roots. The FOV of CBCT images in the present study (i.e., 81 × 74 mm) was smaller in comparison with those reported in previous studies [19, 20]. This limited FOV, set in order to achieve an adequate voxel size (0.146 mm) for accurate diagnosis, provided more accurate information.
The incisive canal, an anatomical structure located on the midsagittal plane of the maxillary bone running parallel and posterior to maxillary incisors, involves the nasopalatine vessels and nerves, branches of the trigeminal nerve, and the maxillary artery and is surrounded by a thick layer of cortical bone [21,22,23]. Because of its proximity to maxillary incisors, the possibility of sensory dysfunction in the anterior region and failure of osseointegration has been reported in cases of contact of the incisive canal through surgical interventions such as dental implant placement [24,25,26]. Recently, Chung et al. reported that proximity of maxillary incisal roots to the incisive canal might influence the degree of root resorption after large incisal retraction [27]. Therefore, when planning orthodontic treatment, it is critical to confirm the exact location of maxillary incisors and the incisive canal and determine the morphology of the alveolar bone. Imaging of anatomical structures at the maxillary anterior region by CBCT with a limited FOV has not been documented in literature. In the present study, the morphologies of and positional relationships between the incisive canal and maxillary incisors were evaluated by CBCT images acquired with a limited FOV.
For calculating the degree of maxillary incisor movement, 2D analysis can provide only limited information regarding the 3D maxillofacial structures. Apical root resorption has been frequently reported in the maxillary incisor region [28]. In some cases, unexpected apical root resorption in maxillary incisors after anterior retraction has been reported to have occurred because of proximity or contact of the roots with the labial, palatal, or incisive canal cortical plates [29, 30]. In clinical settings, several orthodontic treatments till date have been successfully performed solely with conventional cephalometric analysis. However, recent temporary anchorage devices (i.e., miniscrew implants) have expanded the range of orthodontic treatment and made it possible to achieve a large degree of maxillary incisor movement [6, 27, 31]. To manage post-orthodontic treatment complications such as root resorption, gingival recession, dehiscence, and fenestration following root deviation from the alveolar bone housing, anatomical features of the maxillofacial area should be carefully examined in each patient, and diagnosis should be formulated based on 3D information. The present findings suggest that FOV-limited CBCT is a useful modality for orthodontic diagnosis of maxillary protrusion.
Loss of a maxillary incisor affects the morphology of the maxillary alveolar border and, consequently, alters the morphology of the anterior wall of the incisive canal [32]. Moreover, changes in location and inclination of the maxillary incisors lead to morphological changes in the maxillary alveolar border [12, 33,34,35,36]. Therefore, pre and post-orthodontic treatment FOV-limited CBCT analyses for assessment of morphological changes in the maxillary anterior region and the incisive canal are required to ensure precise evaluation of tooth movement-induced anatomical changes in the surrounding tissues [27, 36].
Conclusions
Anatomic variations that are present in the anterior region of the maxillary alveolar bone yielded morphometric data that might be useful for orthodontic treatment planning in patients requiring significant correction of maxillary incisal inclination or root position or in patients requiring implant placement in the anterior region.
Abbreviations
- 2D:
-
Two-dimensional
- 3D:
-
Three-dimensional
- CBCT:
-
Cone-beam computed tomography
- CSA:
-
Cross-sectional area of the incisive canal
- D:
-
The distance from the left maxillary incisor to the incisive canal
- DICOM:
-
Digital imaging and communication in medicine
- FOV:
-
Field of view
- L:
-
The length of the incisive canal
- n:
-
The level of the nasal opening of the incisive canal
- o:
-
The level of the oral opening of the incisive canal
- P:
-
Palatal plane
- r:
-
The level of the root apex of the maxillary incisor
- θ1:
-
The angles between the palatal plane and the maxillary alveolar border
- θ2:
-
The angles between the palatal plane and the incisive canal
- θ3:
-
The angles between the palatal plane and maxillary incisor
References
Sarver DM. The importance of incisor positioning in the esthetic smile: the smile arc. Am J Orthod Dentofac Orthop. 2001;120:98–111.
Turley PK. Evolution of esthetic considerations in orthodontics. Am J Orthod Dentofac Orthop. 2015;148:374–9.
Sarver DM. Interactions of hard tissues, soft tissues, and growth over time, and their impact on orthodontic diagnosis and treatment planning. Am J Orthod Dentofac Orthop. 2015;148:380–6.
Shuying Y, Yunfei G, Xianrui Y, Feng Z, Jian W, Jingyi Q, et al. Effect of mesiodistal angulation of the maxillary central incisors on esthetic perceptions of the smile in the frontal view. Am J Orthod Dentofac Orthop. 2015;148:396–404.
Spear FM, Kokich VG, Mathews DP. Interdisciplinary management of anterior dental esthetics. J Am Dent Assoc. 2006;137:160–9.
Ackerman JL, Proffit WR, Sarver DM. The emerging soft tissue paradigm in orthodontic diagnosis and treatment planning. Clin Orthod Res. 1999;2:49–52.
Graber LW, Vanarsdall Jr RL, Vig KW. Orthodontics: current principles and techniques. 5th ed. Philadelphia: Elsevier; 2011. p. 15–7.
Tian YL, Liu F, Sun HJ, Lv P, Cao YM, Yu M, et al. Alveolar bone thickness around maxillary central incisors of different inclination assessed with cone-beam computed tomography. Korean J Orthod. 2015;45:245–52.
Handelman CS. The anterior alveolus: its importance in limiting orthodontic treatment and its influence on the occurrence of iatrogenic sequelae. Angle Orthod. 1996;66:95–109.
Weltman B, Vig KW, Fields HW, Shanker S, Kaizar EE. Root resorption associated with orthodontic tooth movement: a systematic review. Am J Orthod Dentofac Orthop. 2010;137:462–76.
Enhos S, Uysal T, Yagci A, Veli İ, Ucar FI, Ozer T. Dehiscence and fenestration in patients with different vertical growth patterns assessed with cone-beam computed tomography. Angle Orthod. 2012;82:868–74.
Ackerman JL, Proffit WR. Soft tissue limitations in orthodontics: treatment planning guidelines. Angle Orthod. 1997;67:327–36.
Melsen B. Biological reaction of alveolar bone to orthodontic tooth movement. Angle Orthod. 1999;69:151–8.
Kapila SD, Nervina JM. CBCT in orthodontics: assessment of treatment outcomes and indications for its use. Dentomaxillofac Radiol. 2015;44:20140282.
Horiuchi A, Hotokezaka H, Kobayashi K. Correlation between cortical plate proximity and apical root resorption. Am J Orthod Dentofac Orthop. 1998;114:311–8.
Cho EA, Kim SJ, Choi YJ, Kim KH, Chung CJ. Morphologic evaluation of the incisive canal and its proximity to the maxillary central incisors using computed tomography images. Angle Orthod. 2016;86:571–6.
Springate SD. The effect of sample size and bias on the reliability of estimates of error: a comparative study of Dahlberg’s formula. Eur J Orthod. 2012;34:158–63.
Güncü GN, Yıldırım YD, Yılmaz HG, Galindo-Moreno P, Velasco-Torres M, Al-Hezaimi K, et al. Is there a gender difference in anatomic features of incisive canal and maxillary environmental bone? Clin Oral Implants Res. 2013;24:1023–6.
Da Silveira PF, Fontana MP, Oliveira HW, Vizzotto MB, Montagner F, Silveira HL, et al. CBCT-based volume of simulated root resorption—influence of FOV and voxel size. Int Endod J. 2015;48:959–65.
Ballrick JW, Palomo JM, Ruch E, Amberman BD, Hans MG. Image distortion and spatial resolution of a commercially available cone-beam computed tomography machine. Am J Orthod Dentofac Orthop. 2008;134:573–82.
Mraiwa N, Jacobs R, Van Cleynenbreugel J, Sanderink G, Schutyser F, Suetens P, et al. The nasopalatine canal revisited using 2D and 3D CT imaging. Dentomaxillofac Radiol. 2004;33:396–402.
Liang X, Jacobs R, Martens W, Hu Y, Adriaensens P, Quirynen M, et al. Macro- and micro-anatomical, histological and computed tomography scan characterization of the nasopalatine canal. J Clin Periodontol. 2009;36:598–603.
Song WC, Jo DI, Lee JY, Kim JN, Hur MS, Hu KS, et al. Microanatomy of the incisive canal using three-dimensional reconstruction of microCT images: an ex vivo study. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2009;108:583–90.
Artzi Z, Nemcovsky CE, Bitlitum I, Segal P. Displacement of the incisive foramen in conjunction with implant placement in the anterior maxilla without jeopardizing vitality of nasopalatine nerve and vessels: a novel surgical approach. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2000;11:505–10.
Kan JY, Rungcharassaeng K, Roe P, Mesquida J, Chatriyamuyoke P, Caruso JM. Maxillary central incisor-incisive canal relationship: a cone beam computed tomography study. Am J Esthet Dent. 2012;2:180–7.
Kraut RA, Boyden DK. Location of incisive canal in relation to central incisor implants. Implant Dent. 1998;7:221–5.
Chung CJ, Choi YJ, Kim KH. Approximation and contact of the maxillary central incisor roots with the incisive canal after maximum retraction with temporary anchorage devices: Report of 2 patients. Am J Orthod Dentofac Orthop. 2015;148:493–502.
Makedonas D, Lund H, Gröndahl K, Hansen K. Root resorption diagnosed with cone beam computed tomography after 6 months of orthodontic treatment with fixed appliance and the relation to risk factors. Angle Orthod. 2012;82:196–201.
Segal GR, Schiffman PH, Tuncay OC. Meta analysis of the treatment-related factors of external apical root resorption. Orthod Craniofac Res. 2004;7:71–8.
Nakada T, Motoyoshi M, Horinuki E, Shimizu N. Cone-beam computed tomography evaluation of the association of cortical plate proximity and apical root resorption after orthodontic treatment. J Oral Sci. 2016;58:231–6.
Upadhyay M, Yadav S, Nagaraj K, Patil S. Treatment effects of mini-implants for en-masse retraction of anterior teeth in bialveolar dental protrusion patients: a randomized controlled trial. Am J Orthod Dentofac Orthop. 2008;134:18–29.
Asaumi R, Kawai T, Sato I, Yoshida S, Yosue T. Three-dimensional observations of the incisive canal and the surrounding bone using cone-beam computed tomography. Oral Radiol. 2010;26:20–8.
Henriksen B, Bavitz B, Kelly B, Harn SD. Evaluation of bone thickness in the anterior hard palate relative to midsagittal orthodontic implants. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2003;18:578–81.
Schlegel KA, Kinner F, Schlegel KD. The anatomic basis for palatal implants in orthodontics. Int J Adult Orthod Orthognath Surg. 2002;17:133–9.
Thongudomporn U, Charoemratrote C, Jearapongpakorn S. Changes of anterior maxillary alveolar bone thickness following incisor proclination and extrusion. Angle Orthod. 2015;85:549–54.
Ahn HW, Moon SC, Baek SH. Morphometric evaluation of changes in the alveolar bone and roots of the maxillary anterior teeth before and after en masse retraction using cone-beam computed tomography. Angle Orthod. 2013;83:212–21.
Funding
This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
YI participated in the study conception, data collection, and manuscript formatting. AK participated in the study conception, data collection, manuscript formatting, and statistical analysis. TO participated in the study conception, and manuscript formatting. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
This study was approved by the Institutional Ethical Committee of the Tokyo Medical and Dental University (approval numbers: 846 and 1254) and conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made.
About this article
Cite this article
Matsumura, T., Ishida, Y., Kawabe, A. et al. Quantitative analysis of the relationship between maxillary incisors and the incisive canal by cone-beam computed tomography in an adult Japanese population. Prog Orthod. 18, 24 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40510-017-0181-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s40510-017-0181-1