Abstract
Diazinon is widely consumed for plague control in the agricultural farms and in domestic and aquaculture aspects. The present research purposed to evaluate the effect of half-lethal concentration (LC50) of diazinon on some biochemical and hematological parameters of silver carp, hypophthalmichthys molitrix, after 0, 24, 48 and 96 h. The results showed that the values of leukocytes (WBC), haematocrit (Ht), hemoglobin (Hb), MCHC, lymphocyte, cortisol and glucose were significantly increased (P < 0.05). The mount of MCV and MCH were significantly increased at 48 h and then decreased at 96 h (P < 0.05). Moreover, there was a significant increasing in neutrophils count at 48 h, and then a significant decreasing at 96 h (P < 0.05). There were no significant differences in RBC, monocyte and eosinophile counts among treatment groups at different sampling intervals. Thereupon, low-term (96 h) exposure to diazinon at half-lethal concentration (LC50) caused biochemical and hematological changes in silver carp, and offers a simply implement to appraise toxicity-derivatived changes.
Similar content being viewed by others
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Introduction
Diazinon is a vast spectrum OP, often utilized in residential areas, while its major utilization is with regard to agricultural activities. It has been categorized as very toxic and its use has been prohibited in many developed countries, however, it is commercialized in expansing ones [1]. Diazinon is partly water-soluble, and simply comes into contiguity with aquatic organisms. Afterwards, inward the cells of these organisms, diazinon is metabolized to diazoxon, which is the toxic composition of this insecticide. In addition, diazinon affects abroad range of non-target organisms, such as invertebrates, birds, mammals and fishes, chiefly, those are habiting aquatic environment [2]. Kalender et al. [3] showed that diazinon causes alters in liver enzymes and biochemical indicators. Diazinon is widely utilized in the rice paddy farms of Mazandaran, Gillan, Golestan and other areas in Iran [4]. Based on reports of Bulletin of Agriculture Ministry, the annual utilization of diazinon in iran is appraised to be 3775 t [5]. Several studies related that some of the surface waters and the surrounding environments in Iran were infected with organophosphate pesticides like diazinon and its derivates [6].
Hematological parameters like MCH, MCV and MCHC and Hematological indices such as Hct, Hb, RBC, WBC values and biochemical indicators like glucose are widely utilized to assess the toxic stress of environmental contaminants [7]. Silver carp may be most abundant freshwater fish due to its fast growth [8]. In spite of the manufacture of silver carp is spreading out annually, the processing of this fish is limited. Silver carp rearing developed in many ponds that placed near agricultural fields.
The aim of this study was to investigate the effect of different diazinon concentrations on blood biochemical, hematological and hormonal indicators in silver carp (hypophthalmichthys molitrix).
Materials and methods
Preparation of fish in experimental condition
Fish with average weight 200 g of silver carp after 1-week adaptation to the new condition, were divided into 4 treatments (3 replicates for each treatment) and a control with 21 fish in each 400 L tank. All fish were hand-fed with trading pellet twice a day. Fish were exposed to a concentrations of 50 % LC50 (3.93 ± 0.34) of diazinon for a period of 24, 48 and 96 h. Temperature, dissolved oxygen, conductivity and pH were measured during the experiment.
Blood sampling and hematological assay
At the beginning, fish were unconscious with 200 ppm clove powder. Blood samples quickly collected from tail blood vessel by heparinized syringes and immediately stored on ice. Then, computation of the blood parameters were carried out on fresh blood. Numbers of Blood erythrocytes and leukocytes were performed by diluting heparinized blood with Giemsa stain at 1:30 dilution and cells were counted using a hemacytometer Neubauer under the light microscope. The leukocyte differential calculation was performed in peripheral blood spots stained by Merck Giemsa, giving the Neutrophils quantity of differential neutrophils and the mononuclear quantity of differential lymphocytes, eosinophile and monocyte. Hematocrite percent (Ht%) was shortly computed after act of collecting representative samples by placing fresh blood in glass capillary tubes and centrifuged in a microhematocrit centrifuge for 5 min at 10,000 rpm (Hettich, Germany), afterward, taking of dimensions the packed cell capacity. Hematocrite explanation was carried out with the usage of a microhematocrit reader. Hemoglobin levels (Hb mg/l) were resulted colorimetrically of cyanomethemoglobin by measuring the formation [9]. Erythrocytes Indices (M.C.H. or Mean Corpuscular Hemoglobin, M.C.H.C. or Mean Cell Hemoglobin Concentration and M.C.V. or Mean Corpuscular Volume) were accounted from RBC, Ht, and Hb [9, 10].
Statistical analyses
To observation of significant differences to appraise, the effect of diazinon on blood parameters of silver carp was used an analysis of variance (ANOVA) with Duncan Post Hoc. Pearson coefficients of correlation (r) were calculated between half-lethal concentration of diazinon and blood parameters to examine coalition between bioaccumulation and its impacts. To determine the unity between diazinon concentration and blood parameters were utilized multiple regressions. Data were analyzed statistically at p < 0.05 by SPSS software version 16.
Ethical approval
This work was approved by ethical committee of GAU University numbered 6177515-5. To minimize suffering of the fish, all animals were exposed with clove essence, low dose for anesthesia; hypothermia prior to euthanasia and eventually spinal cord dislocation for euthanasia.
Results and discussion
Hematological parameters
In this study, we surveyed effects of 50 % LC50 diazinon pesticide on a series of hematological, biochemical and Immunological parameters of silver carp for 96 h.
Hematocrit content significantly elevated after subchronic exposure, exhibiting the importance of the route of pollution (Fig. 1). Also, Ht and Hb levels significantly increased that was similar with results of Ahmad [11] on Cyprinus carpio in exposed to diazinon but was conversed with the findings Shaluie et al. [12] on silver carp exposed to Nanocid. Also Banaee et al. [13] and Anees [14], respectively, to study on Cyprinus carpio and Bloch (Channa punctatus) concluded that Ht and Hb levels significantly increased in exposed to diazinon. In another studies, Oimoek Köprücü et al. [15] found out that Ht and Hb levels increased in fingerling European catfish (Silurus glanis L.) exposed to diazinon. Observed results were agreement with results of Chowdhury et al. [16], who stated an elevation of blood hemoglobin and hematocrit happen in exposed to environmental hypoxia and chronic doses of waterborne metals that elevate blood oxygen carrying capacity caused to disorder of gas exchange.
Our findings showed that MCV and MCH levels increased in fish exposed to 50 % LC50 diazinon at 48 h but MCHC level increased at 96 h (Fig. 2). Results of the study were similar with the findings of Banaee et al. [13] about MCV and MCH. Shaluie et al. [12] to survey on silver carp exposed to Nanocid expressed that MCH and MCHC levels raised. Also, Mohammad Nejad et al. [17] and Anees [14] to studying on Rutilus frisii kutum and Bloch (Channa punctatus) in exposed to diazinon found out that MCH, MCV and MCHC levels increased that were agreement with our study.
In the present study, WBC level of silver carp blood significantly increased in exposed to diazinon. Whereas, Banaee et al. [13] and Mohammad Nejad et al. [17] obtained opposite results to this finding. The number of red blood cells (RBC) was less sensitive toward diazinon exposure so that the RBC count did not significantly changed in fish. This finding was not similar with Mohammad Nejad et al. [17], Banaee et al. [13], Khoshbavar Rostami and Soltani [18] and Anees’s studies [14] on Rutilus frisii kutum, Cyprinus carpio, Acipenser nudiventris and Bloch (Channa punctatus) in exposed to diazinon. Plenty of WBC provides an exhibition of fish health and a high WBC number may exhibit a subclinical infection.
The correlation between diazinon with all parameters statistically examined by analyzing the data obtained during the diazinon exposed for 96 h. In this concentration (LC50–96h) Ht, MCV, MCH and MCHC levels indicated significant positive correlation (p < 0.01) and WBC, RBC and Hb levels did not showed significant correlation with diazinon exposure.
Biochemical analysis
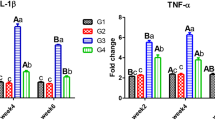
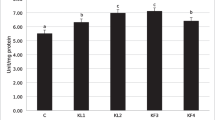
Glucose level significantly (p < 0.05) increased in 50 % LC50 concentration of diazinon in comparison of control group (Fig. 3) and showed significant positive correlation (p < 0.01) in exposure to diazinon.
It has been stated that the raised blood glucose is usually perceived in fish under unfavorable situations and it helps the animal by readying energy substrates to vital organs to afford with the increased energy demand [13]. Also, increased of blood glucose level was vastly used as a secondary marker of a stress response [19]. Increased in blood glucose levels have been reported in Silver carp [12] and Cyprinus carpio [13], after exposure to copper sulfate and diazinon, respectively, that was comparable to our findings of glucose on silver carp.
Blood cortisol is an important corticosteroid hormone in fish and may have a meaningful effect on its dynamics [20]. In the present study, cortisol level in concentration of 50 % LC50 for 48 h significantly increased toward control (Fig. 3) and did not show significant correlation in exposure to diazinon. The blood serum cortisol results were indicated in (Fig. 4), revealed a significant increasing at 48 h in the exposed fish. Bakhshwan et al. [21] and Shaluie et al. [12] obtained similar results to studying on Clarias gariepinus and silver carp in exposed to diazinon and Nanocid, respectively. The above data may be stated by the activation hypothalamo-pituitary- inter renal axis with their discharge of steroid cortisol in blood circuit due to stress [22]. In addition, it could be ascribed to the raise in osmotic water-influx, which may reason a cortisol promotion, to mend the hydromineral balance [21].
Immunological indices
Lymphocyte level was significantly increased in exposed to diazinon for 96 h and neutrophil level was significantly increased for 48 h (p < 0.05) (Fig. 4). Eosinophiles and monocyte did not show significant correlation in 50 % LC50 concentration.
Results of current study showed that there were significant increases in lymphocyte and neutrophil counts. Hedayati and Jahanbakhshi [23] reported increasing in neutrophil and decreasing in lymphocyte to study on the great sturgeon Huso huso in exposed to diesel oil. In addition, Soltani and Khoshbavar Rostami [24] stated elevation neutrophil count and decreasing of lymphocyte count in Acipenser guldenstadti. In other studies, Svoboda et al. [25] and Banaee et al. [13] observed neutrophil count increased but lymphocyte count decreased. It is believed that neutrophils have phagocytic activity, which might describe their elevated percentage during infectious status.
To determine the relationship between diazinon concentration with hematological, biochemical and immunological activity were utilized curve estimation regressions data. Ht, MCV, MCH, MCHC, Lymphocyte and Glucose levels in fish exposed to diazinon indicated significant linear regression (p < 0.01) Y = a ± bX.
Conclusion
The present results indicated that diazinon can cause serious hematological and biochemical alterations in silver carp at the physiological level. Finally, the results got in this study exactly indicated under experimental conditions, blood parameters were sensitive to different prospect of diazinon exposure. Hematological and biochemical properties of this fish exposed to diazinon are poorly understood and there is not adequate knowledge concerning the metabolism of reference toxicants. More knowledge of these activities in fish is necessary before they can be employed as biochemical indicators of stress due to pollutions.
References
Tinoco R, Halperin D. Poverty, production and health inhibition of erythrocytes choline esterase via occupational exposure to organophosphate insecticides in Chiapas, Mexico. Arch Environ Health. 1998;53:29–35.
Burkepile DE, Moore MT, Holland MM. The susceptibility of Wvenontarget organisms to aqueous diazinon exposure. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol. 2000;64:114–21.
Kalender S, Ogutcu A, Uzunhisarcikli M, Acikgoz F, Durak D, Ulusoy Y, et al. Diazinon-induced hepatotoxicity and protective effect of Vitamin E on some biochemical indices and ultrastructural changes. Toxicology. 2005;211:197–206.
Shayeghi M, Darabi H, Abtahi H, Sadeghi M, Pakbaz F, Golestaneh SR. Assessment of persistence and residue of diazinon and malathion in three Rivers (Mond, Shahpour and Dalaky) of Bushehr province in 2004–2005 years. Iran South Med J. 2007;10(1):54–60.
Annual report of performance of the Ministry of Agriculture of Iran (ARMAI) (2005–2006). Ministry of Agriculture of Iran; 215–17 p.
Arjmandi R, Tavakol M, Shayeghi M. Determination of organophosphorus insecticide residues in the rice paddies. Int J Environ Sci Tech. 2010;7(1):175–82.
Kavitha C, Malarvizhi A, Senthil Kumaran S, Ramesh M. Toxicological effects of arsenate exposure on hematological, Biochemical and liver transaminases activity in an Indian major carp, Catla catla. Food Chem Toxicol. 2010;48:2848–54.
Aryanta RW, Fleet GH, Buckle KA. The occurrence and growth of microorganisms during the fermentation of fish sausage. Int J Food Microbio. 1991;13(2):143–55.
Lee RG, Foerster J, Jukens J, Paraskevas F, Greer JP, Rodgers GM. Wintrobe’s clinical hematology. 10th ed. New York, USA: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 1988.
Plous S, Herzog H. Reliability of protocol reviews for animal research. Science. 2001;293:608–9.
Ahmad Z. Acute toxicity and hematological changes in common carp (Cyprinus carpio) caused by diazinon exposure. African J Biotech. 2011;10(63):13852–9.
Shaluie F, Hedayati A, Jahanbakhshi A, Miandareh HK, Fotovat M. Effect of subacute exposure to silver nanoparticle on hematological and plasma biochemical indices in silver carp (Hypophthalmichthys molitrix). Hum Exp Toxicol. 2013. doi:10.1177/0960327113485258.
Banaee M, Mirvagefei AR, Rafei GR, Majazi Amiri B. Effect of sub-lethal diazinon concentrations on blood plasma biochemistry. Int J Environ Res. 2008;2:189–98.
Anees MA. Haematological abnormalities in a freshwater teleost, Channa punctatus, (Bloch), exposed to sublethal and chronic levels of three organophosphorus insecticides. Int J Ecol Environ Sci. 1978;4:53–60.
Oimoek Köprücü S, Köprücü K, Sener Ural M, Ispir U, Pala M. Acute toxicity of organophosphorous pesticide diazinon and its effects on behavior and some hematological parameters of fingerling European catfish (Silurus glanis). Pest Biochem Physiol. 2006;86:99–105.
Chowdhury MJ, McDonald DG, Wood CC. Gastrointestinal uptake and fate of cadmium in rainbow trout acclimated to sublethal dietary cadmium. Aquat Toxicol. 2004;69:149–63.
Mohammad Nejad Shamoushaki M, Soltani M, Kamali A, Imanpoor MR, Sharifpour I, Khara H. Effects of organophosphate, diazinon on some haematological and biochemical changes in Rutilus frisii kutum male brood stocks. Iran J Fish Sci. 2012;11(1):105–17.
Khoshbavar Rostami HA, Soltani M. The effects of diazinon on haematological indices and LC50(96 h) of Acipenser nudiventris. Iran J Fish Sci. 2005;14(3):1–12.
Toal DG, Afonso LOB, Iwama GK. Stress response of juvenile rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) to chemical cues released from stressed conspecifics. Fish Physiol Biochem. 2004;30:103–8.
Mommsen TP, Vijayan MM, Moon TW. Cortisol in teleosts: dynamics, mechanisms of action and metabolic regulation. Rev Fish Biol Fish. 1999;9:211–68.
Bakhshwan SA, Marzouk MS, Hanna MI, Heba Hamed S. Some investigations on the clinical and biochemical alterations associated with dizinon toxicity in Clarias gariepinus. Egypt J Aquat Biol Fish. 2009;13(2):173–97.
Reddy PK, Leatherland JF. Stress physiology. In: Leatherland JF, Woo PTK, editors. Fish disease and disorders, vol.2 non–infections disorders. UK: Cabi Pub; 1998. p. 279–301.
Hedayati A, Jahanbakhshi A. The effect of water-soluble fraction of diesel oil on some hematological indices in the great sturgeon Hus huso. Fish Physiol Biochem. 2012. doi:10.1007/s10695-012-9672-7.
Soltani M, Khoshbavar Rostami HA. Effect of Diazinon on some hematological and biochemical indices in Russian sturgeon (Acipenser guldenstadti. Iranian). J Mar Sci Tech Iran. 2001;4:1–11.
Svoboda M, Luskova V, Drastichova J, Zlabek V. The effect of Diazinon on haematological indices of common carp (Cyprinus carpio). Acta Vet Brno. 2001;70:457–65.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the aquaculture research center and Fishery group for the supply of research material. This study was supported by the Gorgan University of Agricultural Sciences and Natural resources and was done at Veniro wet laboratory.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Authors’ contributions
The authors declare that they have no contributions in this paper. Both authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Rights and permissions
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.0), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly credited.
About this article
Cite this article
Hedayati, A., Hassan Nataj Niazie, E. Hematological changes of silver carp (hypophthalmichthys molitrix) in response to Diazinon pesticide. J Environ Health Sci Engineer 13, 52 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40201-015-0208-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s40201-015-0208-9