Abstract
Background
Increased Anti-Retroviral Therapy (ART) coverage improves health status and the survival of people living with Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) as a result, reproductive health needs of the clients are increased. As part of continuum HIV care, understanding fertility desire and reproductive health care needs of HIV positive peoples will play paramount role in planning and delivering appropriate health services. The finding of studies conducted on the fertility desire and associated factors among People Living with HIV in Ethiopia presented inconclusive. Therefore, this study aimed to assess the pooled prevalence of fertility desire and associated factors among people living with HIV in Ethiopia.
Methods
A total of 26 studies conducted in Ethiopia were included in this Meta-analysis. Pub Med, HINARI, Google scholar and Google data bases were searched. Data from the included articles were extracted using a standardized data extraction tool. The included studies were analyzed using a random effects meta-analysis model. Analysis was done Using STATA version 14 statistical software. Heterogeneity was assessed statistically using the standard Chi-square, I2. The association between fertility desire and factors were examined using a random effects model.
Result
In this meta-analysis, the pooled prevalence of fertility desire in Ethiopia is 42.21% (95%CI 39.18, 45.25). Fertility desire is significantly associated with sex: being female (OR = 0.71,95%CI 0.57,0.86), partners desire (OR = 16.8, 95% CI: 9.45, 29.88), not having child (OR = 5.46 95%CI 4.24, 7.040), age < 30(OR = 2.34, 95%CI 2.10, 2.60), formal education (OR = 1.31 95%CI 1.09, 1.59)). However, use of family planning, residence, and Knowledge on Prevention of Mother to Child Transmission and disclosure status didn’t show association with fertility desire.
Conclusion
In this finding, significant people of living with HIV have a desire to have a child. The finding showed the need to strengthen fertility desire and reproductive health care needs of HIV positive peoples. Therefore, strengthening the integration of fertility related issues with HIV continuum care will play a paramount role in averting risky sexual behaviors and Prevention of Mother to Child Transmission among peoples on ART.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) remains the major public problem in the world. Globally, at the end of 2018, about 37.9 million people were living with HIV. About 1.7 million people became newly infected with HIV, 770000 people died from Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndromes (AIDS)-related illnesses. At the end of June 2019, 24.5 million people were accessing antiretroviral therapy. Every week around 6000 young women aged 15–24 years become infected with HIV. In sub-Saharan Africa, four in five new infections among adolescents aged 15–19 years are in girls. In 2013, in Ethiopia there were an estimated 793,700 people living with HIV [1, 2].
Globally, people living with HIV particularly, women of reproductive age group remained the highest share holder of HIV/AIDS related morbidity and mortality [3]. According to 2017 WHO report, in Ethiopia, the estimated number of women age greater than 15 years living with HIV was around 400,000 and the rate of mother to child transmission (MTCT) of HIV was 16 in 2016 [4].
Since the beginning of PMTCT, Ethiopia has implemented various policies and programs of PMTCT. For instance, In Ethiopia, the first national PMTCT guideline was developed in 2001. Following this further adjustments were made in the year 2007, 2011 and 2013 to include international recommendations [5]. The current PMTCT guideline (2013) is based on the World Health Organizations option B+ PMTCT protocol [6], in which all HIV-positive pregnant women are immediately offered antiretroviral therapy (ART) for life irrespective of their CD4 count. This in turn changed the life expectancy and quality of life for mothers, children, and their sexual partners more than ever before. Despite this, retention on PMTCT and fertility issues are becoming challenging among peoples on ART in Ethiopia [7]. Moreover, the integration of family planning along the HIV/AIDS care continuum is very poor in deed even though there is high unmet need for family planning [8].
Even though it is possible to have a healthy pregnancy and HIV-negative child, in low income country where there is low coverage of prevention of mother to child transmission and antiretroviral therapy (ART) is existed, the desire to have a child among people living with HIV remains a major public health problem [9].
Increased ART coverage improves health status and increase the survival of people living with HIV; as a result, reproductive health needs of the clients are increased. Today, peoples living with HIV/AIDS are living their sexual and reproductive life better than ever before; however, initiating ART and improved health status didn’t increase the fertility desire of PLHIV. The reproductive health needs, particularly fertility desire, family planning and pregnancy needs are complicated and decreased because of their HIV status. Their HIV status hinders the desire of the women to have more children. Therefore, focusing on the essential needs of PLHIV specifically, sexual health needs of HIV-positive people are essential to global HIV prevention [10,11,12,13].
Similar to HIV negative peoples, People living with HIV have strong fertility desire. But the fertility desire of PLHIV is lower than the general populations as a result of hindering factors [14, 15]. Studies have shown that factors such as age, gender, marital status, number of children, partner’s fertility desire, and HIV status of partner had an association with fertility desire of People living with HIV [16,17,18].
The finding of studies conducted on the fertility desire and associated factors among PLWH in Ethiopia presented wide ranging variations. For instance, the prevalence of fertility desire among PLWH in Ethiopia ranges from 23.58 to 66.12%. Beside to this there is no nationally pooled data regarding the fertility desire of PLWH in Ethiopia. Hence, this systematic review and meta-analysis was aimed to do the pooled prevalence of fertility desire and effect size of associated factors among people living with HIV in Ethiopia.
Methods
Search strategies
The search strategy aimed to find both published and unpublished studies. A three-step search strategy was utilized in this review. An initial limited search of Pub Med, Google Scholar, was undertaken followed by an analysis of the text words contained in the title and abstract, and of the index terms used to describe the article. A second search using all identified keywords and index terms was undertaken across all included databases. Thirdly, the reference list of all identified reports and articles was searched for additional studies. We searched databases include: Pub Med, HINARI, Google scholar and Google The search for unpublished studies such as thesis, and dissertations were checked in Addis Ababa University Digital Library. The literature search was done from November 10 to December 25, 2019. The search was carried out using the following keywords by Boolean operator: “fertility desire” OR “fertility intention” “OR” “fertility need” OR “desire to have child” AND “HIV patients” OR “PLHIV” OR “PLWHA” AND “Ethiopia”. The review protocol was registered in the International Prospective Register of Systematic Reviews (PROSPERO) (Registration number CRD42019130966) Availablefrom: https://www.crd.york.ac.uk/prospero/display_record.php?ID=CRD42019130966
Selection and eligibility criteria
Inclusion criteria
This systematic review and meta-analysis included studies that were conducted on the prevalence and determinants of fertility desire among Peoples living with HIV/AIDS (PLWH) in Ethiopia. Two investigators (GM & DM) independently reviewed the contents of each articles and finally articles fulfilled the following criteria were included in the study. The Study populations were all people living with HIV/AIDS in Ethiopia. Studies, which were conducted in Ethiopia, were included in the review. For this review, we included all observational study designs reporting prevalence of fertility desire among PLHIV in Ethiopia. Articles reported in the English language were included.
Exclusion criteria
For this review, we excluded papers that were not fully accessible, after at least two email contact attempts with the primary authors.
Outcome measurement
The review considered two main outcomes. Prevalence of Fertility desire (defined here as the desire to have child/children in the future) among people living with HIV was the primary outcome of this study. The second outcome of this study was to identify factors associated with fertility desire among PLHIV. For the second outcome, we determined the association between Fertility desire and associated factors in the form of the log odds ratio. Factors included in this review were sex, age, educational status, residence, use of family planning, Knowledge on PMTC, number of alive child, partner fertility desire and disclosure status.
Data extraction
Two authors (GM and DM) extracted the data using data extraction checklists on Microsoft excel. For the outcome variable (fertility desire) and its determinants, data were extracted in a format of two by two tables, and then the log OR was calculated based on the findings of the original studies. The checklist for data extraction contains the title, author name, year of publication, region (the area where the study was conducted), study design, sample size, response rate, and the number of participants with the outcome. When articles did not have adequate data, the corresponding authors of the research articles were contacted through their email.
Quality assessment
The quality of each original study was assessed using standardized critical appraisal instruments from the Joanna Briggs Institute Meta-Analysis of Statistics Assessment and Review Instrument [19]. In this review risk of bias was assessed using PRISMA guidelines with the two reviewers independently. Any disagreements between the two reviewers were addressed by taking the mean score of the two reviewers.
Statistical analysis
The included studies were analyzed using a random effects meta-analysis model. Analysis was done Using STATA version 14 statistical software. Heterogeneity was assessed statistically using the standard Chi-square, I2and also explored using subgroup analyses based on the different quantitative study designs included in this review. Tables and figures were used as appropriate to aid in data presentation. Statistical significance was considered at P –value < 0.05. In this Meta regression for assess presence of publication bias, funnel plot and Egger test at 5% significant level were computed.
Results
Study selection
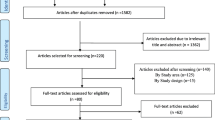
A systematic search of electronic databases and library catalogs identified a total of 62 articles. From these, 27 duplicates papers were removed. The abstracts and full text of the remaining 35 studies were assessed and screened for eligibility criteria based on the outcome variable. Then 9 articles were excluded for not meeting the inclusion criteria.
Finally, 26 articles that scored seven and above on the JBI quality appraisal eligibility criteria were included in the systematic review and meta-analysis. Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) flow diagram were used to present the systematic review process.
Twenty-six articles have been included in this Meta regression (Fig. 1) to show the pooled magnitude of fertility desire among peoples living with HIV in Ethiopia [20,21,22,23,24,25,26,27,28,29,30,31,32,33,34,35,36,37,38,39,40,41,42,43,44,45]. In those previous articles as individual record the smallest magnitude is finding in study conducted in Oromia regional state 23.58%(95%CI 20.27,26.89) [33] while the largest study is study conducted in Tigray regional state of Ethiopia 66.12% (95%CI 60.83, 71.42) [32] (Table 1).
There is high heterogeneity in the study (I2 = 92.5%, P = 0.00) and due to this random effect model was used to find the pooled prevalence of fertility desire among peoples living with HIV aids in Ethiopia. Accordingly, the pooled Meta regression indicated the prevalence of fertility desire in Ethiopia is 42.21% (95%CI 39.18, 45.25) (Fig. 2).
Subgroup analysis and publication bias
In this meta-analysis the prevalence of fertility desire among HIV positive peoples in Ethiopia have been computed subgroup analysis by region. Accordingly, the smallest magnitude of prevalence is observed in study conducted in Amhara regional state of Ethiopia 38.33% (95% CI 5.63, 41.03) [20, 29, 36, 41, 44]. The largest prevalence is observed in Harari regional state of Ethiopia that is 56.18(95% CI 51.90, 60.45) [21]. To assess publication bias, a graphical funnel plot and Egger’s test at 5% significance level were computed. The funnel plot shown a shape of symmetry, and Egger’s test was insignificance for the presence of publication (P = 0.362) (Figs. 3, 4).
Statistical analysis and synthesis
Sensitivity analysis was done using a random effect models to classify a single study influence on the general meta-analysis, and the result disclosed that there was no strong indication for the effect of the single study on the overall meta-analysis result (Fig. 5).
Factors associated with fertility desire among HIV positive patients in Ethiopia
Association between fertility desire and sex
To see association between fertility desire and sex fifteen articles have been involved in this study [20, 22,23,24, 26, 27, 30, 32, 33, 35, 38, 41, 43,44,45]. From those fifteen articles nine of them showed significant association [20, 22,23,24, 26, 33, 38, 43, 44]. Six of the articles don’t show significant association [27, 30, 32, 35, 41, 45]. However, the pooled meta regression indicated that sex of the participant is associated with fertility desire that is female has 0.71 less likely have fertility desire as compared with men (female have 29% of wish to have fertility desire (OR = 0.71, 95%CI 0.57,0.86)). In this meta regression since there is moderate hetrogenicity random effect model was used(I2 = 68.6% P = 0.00) (Fig. 6).
Association between fertility desire and partner fertility desire
In this Meta regression, to find association between fertility desire and partner fertility desire, eight articles have been included [20, 23, 26, 28, 39, 42,43,44]. All variables showed significance association. The pooled Meta regression indicated that, there is association between partner fertility desire and fertility desire (OR = 16.8, 95% CI: 9.45, 29.88) and random effect model was used for this analysis (I2 = 85.0%, P = < 0.001) (Fig. 7).
Association between fertility desire and number of alive child
In this Meta regression to find association between fertility desire and number of alive children that the parents have, sixteen articles have been included [22,23,24,25,26,27,28,29, 32, 33, 36, 39,40,41,42,43,44]. Except one article [32] all of them showed significant association. The pooled meta-regression indicated that there is significant association between fertility desire and number of alive child that the parents have. Accordingly, those who have no children have fertility desire 5.46 times than those who has one and more (OR = 5.46 95%CI 4.24, 7.040). Again in this since there is high heterogeneity random effect model was used (I2 = 5.46 P = 0.00) (Fig. 8).
Association between fertility desire and use of family planning
To find association between fertility desire and use of family planning four articles have been included in this study [20, 30, 36, 42]. All articles didn’t show significant association. The pooled finding of meta-analysis showed that there is no significant association between use of family planning and fertility desire (OR = 1.23 95% CI 0.85, 1.78) and random effect model was used for this regression (Fig. 9).
Association between fertility desire and disclosure status
In this Meta regression, to find association between fertility desire and disclosure status, five articles have been included [20, 28, 35, 39, 40]. From these variables, only one showed significance association [39]. The pooled Meta regression indicated that, there is no association between disclosure status and fertility desire (OR = 1.10, 95% CI: 0.69, 1.75) and random effect model was used for this analysis (I2 = 69.3.0%, P = < 0.011) (Fig. 10).
Association between fertility desire and residence
To find the association between fertility desire and residences of the participants, three articles have been included in this study [30, 36, 40]. Nothings of those article has been showed significant association and the pooled Meta regression also showed that there is no significant association between fertility desire and residence of the participants (OR = 1.20 95% CI 0.96, 1.50). Since there is no heterogeneity fixed effect model was used in this Meta regression (I2 = 0.00 P = 0.892) (Fig. 11).
Association between fertility desire and knowledge of participant about PMTCT
To find association between knowledge of peoples with HIV positive about PMTCT, four articles have been included in this study [20, 30, 35, 45]. From all involved article nothing of them showed significant association. The pooled Meta regression again showed consistence indication that there is no significant association between fertility desire and knowledge about fertility in people with HIV positive (OR = 0.96955 CI 0.58, 1.59) and random effect model was used in this analysis (I2 = 62.1 P = 0.048) (Fig. 12).
Association between fertility desire and age
To find the fertility desire and age of the peoples with HIV positives thirteen article have been included in this study [22,23,24,25,26,27, 30, 38, 39, 41,42,43,44]. From all articles only one doesn’t show significant association [30]. The pooled Meta regression indicated that there is significant association between fertility desire and age of people with HIV. Accordingly, the pooled Meta regression indicated that those with age less than thirty have fertility desire 2.34 times more than with those aged greater than thirteen (OR = 2.34,95%CI 2.10,2.60). Since there is no more heterogeneity fixed effect model was used in this Meta regression (I2 = 46.7 P = 0.032) (Fig. 13).
Association between fertility desire and educational status
In this meta regression to find the association between educational status and fertility desire among HIV positive peoples twelve article have been included [20, 23, 25, 27, 29, 32, 35, 36, 40, 43,44,45]. From those seven of them don’t show significant association [20, 27, 32, 35, 43,44,45] The pooled finding indicated that there is significant association, that is these who have education have fertility desire 1.31 times than those who has no education (OR = 1.31 95%CI 1.09,1.59) and for this random effect model was used (I2 = 66.7%, P = 0.00) (Fig. 14).
Discussion
Globally, people living with HIV specifically, women of reproductive age group remained the highest share holder of HIV/AIDS related morbidity and mortality. Nowadays peoples living with HIV/AIDS are living their sexual and reproductive life better than ever before. Similar to HIV negative peoples, PLWHA also desires to have a biological child and preserve the endurance of their descendants to the forthcoming generation. Therefore, as part of continuum HIV care, understanding fertility desire and reproductive health care needs of HIV positive women is a right thing for a right and important in planning and organizing appropriate health services.
In this systematic review and meta-analysis, we computed the pooled estimates of prevalence of fertility desire and associated factors. We found that fertility desire was high among PLHIV on ART in Ethiopia. Even though the prevalence of fertility desire differs from region to region, this study illustrated that the pooled prevalence of fertility desire among women on ART in Ethiopia is 42.21%. The difference from region to region might be attributed to the year and study population. Indeed, the relative increment from previous studies to recent one might also be attributed to improvement in health related quality of life of PLWHA than ever before.
Moreover the fertility desire among PLHIV in our study is slightly lower than the general fertility desire of the general population of Ethiopia for the 3 years preceding the survey in which 56 % of the general population wants to have another child [46]. This difference with the general population perhaps be attributed to the concern of PLWH about the vertical transmission (in which women might worry for their newborn child become infected) as evidenced by study conducted in Addis Ababa in which 4% of HIV-exposed children were positive by their 18 months [5].
The finding is comparable with findings from different countries like Brazil (39.9%) [47], Tanzania (37.1%) [14]. However, the finding is lower than findings from Canada in which 69% of the respondents want to give birth [48]. This discrepancy might be attributed to the socio-demographic characteristics and the life styles of the study populations.
This systematic review and meta-analysis also identified factors associated fertility desire among PLWHA in Ethiopia. Sex of the participants is one of the factors that had association with a fertility desire. Being female had negative association with fertility desire as compared with men. This finding is supported by a study conducted in different developing countries [12, 49,50,51,52,53] Men’s greater desire may be due to the fact that Men are more likely to reproduce their offspring and leave something of themselves and ancestry behind when they die. Thus it is vital that it helps policy makers and health care providers to improve partners’ involvement in decision making regarding the reproductive health service utilization in order to prevent unwanted pregnancy and mother to child transmission. And also, it might be attributed to the fact that women had less decision making power than their husbands.
Partner’s fertility desire is also another important factor that is associated with fertility desire of PLWHA. This finding is supported by evidence from Dominican Republic, in which participants who had negative perception about their partners towards pregnancy are less likely to desire pregnancy [54] Similarly, this finding is also supported by findings from South Africa [53] This finding has great policy implication in which policy makers and health care providers can capitalize on family planning and fertility related issues information should focus on couple centered.
This analysis also found that participants who had no alive child were more likely to be fertile than their counter parts. This finding is supported by review done by Berhan, Y et.al [55] and findings from Uganda [56]. Hence, according to this finding there is high probability of participants who desire child to be engaged in pregnancy risk behavior. Therefore, HIV care and treatment could be an important get way to provide information and counseling to the partners that would assure their involvement more in reproductive health services and PMTCT.
The other finding from this study is that those participants aged less than thirty were more likely to desire fertility in the future than participants aged greater than thirty. This indicates as being young is associated with likelihood of being fertile [53]. Beside this, it might be attributed the fact that majority of human being in the fertile age regardless of HIV status are more likely to have a child. Also, since young individuals are sexually active than their counterparts targeting those cohorts will play paramount role in reducing risky sexual behaviors and PMTCT. Beside this many efforts are needed to make family planning services accessible for the young females in the developing regions of the country according to their context.
This systematic review and meta-analysis also identified educational status of the participants is another important factors that determines the fertility desire of PLWHA. Those who have education are more likely to desire future fertility than their counterparts. This might be attributed to the fact that educated peoples have better decision making than individuals with no formal education. Beside this, educated peoples have better adherence status which in turn results in suppression of viral load and this makes them to regain their previous healthy life However, our finding is contrary to previous review done by Berhanet. al. which found as educational level is found to have no influence on their fertility desire [55].
Limitation of the study
In this review all of the studies included in the current review were cross-sectional study design in nature; as a result, the outcome variable might be affected by other confounding variables.
Conclusion
In this finding, significant people of living with HIV have a desire to have a child. Males, young age, educated and childless have strong desire for a child. The finding showed the need to strengthen fertility desire and reproductive health care needs of HIV positive peoples. People living with HIV need a great support to have safe conception and meet their fertility desire. This shows health policy should strengthen the reproductive health services of women’s living with HIV to meet their fertility needs. Therefore, strengthening the integration of fertility related issues with HIV continuum care will play a paramount role in averting risky sexual behaviors and PMTC among peoples on ART.
Availability of data and materials
All relevant data are within the paper and its Supporting Information files.
Abbreviations
- PLHIV:
-
People Living with HIV
- ART:
-
Anti-retroviral Therapy
- PMTCT:
-
Prevention of Mother to Child Transmission
- HIV:
-
Human Immunodeficiency Virus
References
UNAIDS GH. AIDS statistics—2019 fact sheet; 2019.
Ethiopia F. Country Progress report on the HIV response; 2014.
Wilcher R, Petruney T, Reynolds H, Cates W. From effectiveness to impact: contraception as an HIV prevention intervention. Sexually Transmitted Infect. 2008;84(Suppl 2):ii54–60.
World Health Organization. HIV Country Profile: 2016, Ethiopia,2017. Available at: https://www.who.int/hiv/data/Country_profile_Ethiopia.pdf?ua=1.
Mirkuzie AH. Implementation and outcomes of guideline revisions for the prevention of mother-to-child HIV transmission in mother support Programme, Addis Ababa, Ethiopia. PloS one. 2018;13(6):e0198438.
Federal Ministry of Health. National comprehensive PMTCT/MNCH/RH training package guideline reference manual. Addis Ababa: FMOH; 2013.
Tolossa T, Mulisa D, Fetensa G, Fekadu G. Magnitude and factors associated with lost to follow-up among women under option B+ PMTCT program at East Wollega public health facilities, Western Ethiopia. Int J Africa Nursing Sciences. 2020;100212.
Feyissa TR, Melka AS. Demand for modern family planning among married women living with HIV in western Ethiopia. PLoS One. 2014;9(11):e113008.
Mantell JE, Smit JA, Stein ZA. The right to choose parenthood among HIV-infected women and men. J Public Health Policy. 2009;30(4):367–78.
Wekesa E, Coast E. Fertility desires among men and women living with HIV/AIDS in Nairobi slums: a mixed methods study. PLoS One. 2014;9(8):e106292.
Boonstra H. Meeting the sexual and reproductive health needs of people living with HIV. Issues in Brief (Alan Guttmacher Institute). 2006(6):1–4.
Ayieko J, Ti A, Hagey J, Akama E, Bukusi EA, Cohen CR, et al. HIV status and treatment influence on fertility desires among women newly becoming eligible for antiretroviral therapy in western Kenya: insights from a qualitative study. Reprod Health. 2017;14(1):93.
Mujumdar V, Berman D, Schafer KR. Reproduction and fertility beliefs, perceptions, and attitudes in people living with HIV. AIDS Res Treatment. 2018;2018.
Mmbaga EJ, Leyna GH, Ezekiel MJ, Kakoko DC. Fertility desire and intention of people living with HIV/AIDS in Tanzania: a call for restructuring care and treatment services. BMC Public Health. 2013;13(1):86.
Wanyenze RK, Wagner GJ, Tumwesigye NM, Nannyonga M, Wabwire-Mangen F, Kamya MR. Fertility and contraceptive decision-making and support for HIV infected individuals: client and provider experiences and perceptions at two HIV clinics in Uganda. BMC Public Health. 2013;13(1):98.
Jose H, Madi D, Chowta N, Ramapuram J, Bhaskaran U, Achappa B, et al. Fertility desires and intentions among people living with HIV/AIDS (PLWHA) in southern India. J Clin Diagnostic Res. 2016;10(6):OC19–22.
Pottinger AM, Carroll K. Reproductive needs of PLHIV in Jamaica: relationship between fertility desire, motives and depression. J Reprod Infant Psychology. 2020;38(1):38–48.
Kaoje A, Ibrahim M, Njoku C, Gusau G, Saad A, Raji M. Predictors of fertility desire among people living with HIV attending anti-retroviral clinic in a tertiary health facility in Sokoto, Northern Nigeria. Sahel Medical Journal. 2015;18(1):14.
Institute JB. Meta-analysis of statistics: assessment and review instrument (JBI MASTARI). Adelaide: Joanna Briggs Institute. 2006;20032007.
Ahmed M, Kahsay A, Miruts G, Berhe K. Magnitude and factors affecting the fertility desire of people living with HIV infection in ethiopia-a cross sectional study. J AIDS Clinical Res. 2014;5:9.
Haile F, Isahak N, Dessie A. Fertility desire and associated factors among people living with HIV on ART. Harari Regional State, Eastern Ethiopia. J Trop Dis. 2014;2:3.
Gayesa RT, Mengistu D, Moorhead C. Desire for fertility and associated factors among people living with hiv/aids (plwha) in selected antiretroviral therapy (art) clinics of horro guduru wollega zone, north west oromia, Ethiopia-a cross sectional study. Int J Pharmaceutical Sci Res. 2013;4(6):2312.
Abebe M, Endazenaw GJASRJfE, Technology,, Sciences. Fertility Intention and Family Planning use Among People Living with HIV/AIDS (PLHIV) on Follow up Care Western Shoa Zone, Anti Retroviral Treatment (ART) Unit, Oromia, Ethiopia 2015;12(1):75–91.
Kebede Y, Tola G, Habtamu A. Understanding the socio-psychological, Demographic, obstetric and treatment-status aspects of fertility desire among anti-retroviral treatment clients, Dodota District, Oromia, Ethiopia. Epidemiology (Sunnyvale). 2019;9(373):2161–1165.1000373.
Asfaw HM, Gashe FE. Fertility intentions among HIV positive women aged 18-49 years in Addis Ababa Ethiopia: a cross sectional study. Reprod Health. 2014;11:36.
Regassa T, Fantahun MJS. Fertility desire and reproductive health care needs of men and women living with HIV/AIDS in Nekemte, East Wollega, Ethiopia. Technology and Arts Research J. 2012;1(3):31–8.
Abebe M, Addissie A, Regassa TJS. Fertility desire and contraceptive utilization among people living with HIV/AIDS on ART in Hosanna Town, Southern Ethiopia. Technology and Arts Research J. 2012;1(4):38–46.
Melka AS, Wordofa MA, Wossen BA. Determinants of fertility intention among women living with hiv in western Ethiopia: implications for service delivery. Afr J Reprod Health. 2014;18(4):54–60.
Mohammed A. Assessment of pregnancy and fertility desire among HIV positive women clients who were attending ART clinics in North Gondar administrative Zone; 2010.
Koyra HC, Biramo YB, Tufa EGJAJPHR. Fertility desire and associated factors among people living with HIV/AIDs at selected health facilities of Wolaita Zone. Southern Ethiopia: cross-sectional study. 2017;5(3):79–88.
Desta A. The desire to have children: is Pmtct an opportunity for Hiv positive people? A cross sectional study in Mekelle health institutions, Tigray/Ethiopia, 2009: Addis Ababa university; 2009.
Alemayehu B, Aregay AJJoA, research H. Desire to procreate among people living with HIV/AIDS: Determinants in Ethiopia: a cross-sectional study 2012;4(5):128–135.
Hassen K, Abdullahi MJGJoMR. Assessment of Sexual Behavior, Unmet Reproductive Health Needs and Fertility Intention of People Living with HIV/AIDS, Jimma, South West of Ethiopia. 2013.
Mokwena K, Bogale YRJSAFP. Fertility intention and use of contraception among women living with the human immunodeficiency virus in Oromia region. Ethiopia. 2017;59(1):46–51.
Adilo TM, Wordofa HM. Prevalence of fertility desire and its associated factors among 15- to 49-year-old people living with HIV/AIDS in Addis Ababa, Ethiopia: a cross-sectional study design. HIV AIDS (Auckl). 2017;9:167–76.
Mekonnen B, Minyihun A. Fertility Desire And Associated Factors Among HIV Positive Women Attending ART Clinics In Amhara Region Referral Hospitals In Northwest Ethiopia, 2017. Hiv/aids (Auckland, NZ). 2019;11:247.
Assefa W. Fertility desire and associated factors among adult on anti-retroviral therapy users in bale ZONE HOSPITALS. SOUTH EAST ETHIOPIA: OROMIA REGIONAL STATE; 2017.
Tadesse L. Assessment of fertility desire and family planning utilization among HIV positive people who are on antiretroviral treatment, Asella hospital, Arsi Zone, Oromia region, 2011: Addis Abeba university; 2011.
Demissie DB, Tebeje B, Tesfaye T. Fertility desire and associated factors among people living with HIV attending antiretroviral therapy clinic in Ethiopia. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2014;14:382.
Melaku YA, Zeleke EG, Kinsman J, Abraha AK. Fertility desire among HIV-positive women in Tigray region, Ethiopia: implications for the provision of reproductive health and prevention of mother-to-child HIV transmission services. BMC Womens Health. 2014;14:137.
Abbawa F, Awoke W, Alemu Y. Fertility desire and associated factors among clients on highly active antiretroviral treatment at finoteselam hospital Northwest Ethiopia: a cross sectional study. Reprod Health. 2015;12:69.
Shiferaw T, Kiros G, Birhanu Z, Gebreyesus H, Berhe T, Teweldemedhin M. Fertility desire and associated factors among women on the reproductive age group of antiretroviral treatment users in Jimma town, South West Ethiopia. BMC Res Notes. 2019;12(1):158.
Tamene W, Fantahun M. Fertility desire and family-planning demand among HIV-positive women and men undergoing antiretroviral treatment in Addis Ababa. Ethiopia Afr J AIDS Res. 2007;6(3):223–7.
Tesfaye L, Admassu M, Getachew A, Sharma HRJVC, Studies Y. Fertility desires and family planning demand among HIV-positive clients in follow-up care at antiretroviral treatment unit in Gondar university hospital. Ethiopia. 2012;7(1):20–35.
Gossa T. Fertility needs assessment among people living with HIV/AIDS in four regional Hospitals. Addis Ababa: Addis Ababa University; 2010.
Demographic E. Health survey: Addis Ababa, vol. 2011. Ethiopia and Calverton, Maryland: Central statistics agency and ORC macro; 2011.
Nóbrega AA, Oliveira FA, Galvão MT, Mota RS, Barbosa RM, Dourado I, et al. Desire for a child among women living with HIV/AIDS in Northeast Brazil. AIDS Patient Care STDs. 2007;21(4):261–7.
Loutfy MR, Hart TA, Mohammed SS, Su D, Ralph ED, Walmsley SL, et al. Fertility desires and intentions of HIV-positive women of reproductive age in Ontario, Canada: a cross-sectional study. PLoS One. 2009;4(12):e7925.
Kawale P, Mindry D, Stramotas S, Chilikoh P, Phoya A, Henry K, et al. Factors associated with desire for children among HIV-infected women and men: a quantitative and qualitative analysis from Malawi and implications for the delivery of safer conception counseling. AIDS Care. 2014;26(6):769–76.
Myer L, Morroni C, Rebe K. Prevalence and determinants of fertility intentions of HIV-infected women and men receiving antiretroviral therapy in South Africa. AIDS Patient Care STDs. 2007;21(4):278–85.
Nakayiwa S, Abang B, Packel L, Lifshay J, Purcell DW, King R, et al. Desire for children and pregnancy risk behavior among HIV-infected men and women in Uganda. AIDS Behav. 2006;10(1):95.
Yeatman S, Eaton JW, Beckles Z, Benton L, Gregson S, Zaba B. Impact of ART on the fertility of HIV-positive women in sub-Saharan Africa. Tropical Med Int Health. 2016;21(9):1071–85.
Cooper D, Mantell JE, Moodley J, Mall S. The HIV epidemic and sexual and reproductive health policy integration: views of South African policymakers. BMC Public Health. 2015;15(1):1–9.
Cernigliaro D, Barrington C, Perez M, Donastorg Y, Kerrigan D. Factors related to fertility desire among female sex workers living with HIV in the Dominican Republic. BMC Womens Health. 2018;18(1):117.
Berhan Y, Berhan A. Meta-analyses of fertility desires of people living with HIV. BMC Public Health. 2013;13:409.
Gutin SA, Namusoke F, Shade SB, Mirembe F. Fertility desires and intentions among HIV-positive women during the post-natal period in Uganda. Afr J Reprod Health. 2014;18(3):67–77.
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank all authors of the primary studies included in this systematic review and meta-analysis.
Funding
No funding was obtained for this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
GM was involved in conceptualization of the study, participated in its design, and performed result writing, analyzing the finding and writing the manuscript. GM & DM involved in data extraction and analysis: BW, DM, RT, GF, AO WE, MA&ET participated in its design, performed result writing, analyzing the finding and writing the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
About this article
Cite this article
Mosisa, G., Tsegaye, R., Wakuma, B. et al. Fertility desire and associated factors among people living with HIV in Ethiopia: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Arch Public Health 78, 123 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13690-020-00504-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s13690-020-00504-0