Abstract
In this paper, we propose a simple network consisting of only two nodes and two paths. The first node, which is called the source, has three competing firms that send their quantities of load via the two paths to the second node, called the destination node. The static game that describes the reaction among the three firms is constructed. The Nash equilibrium point of the static game is discussed. Assuming a gradient firm based rule we investigate the dynamic game which has the same Nash equilibrium as in the static game. The local stability conditions of the Nash equilibrium are obtained in terms of the reactivity parameters among the firms and the nonlinear costs functions adopted by those firms. The obtained results are supported by a numerical simulation that in turn gives routes where Nash equilibrium may lose its stability. The simulation shows that Nash equilibrium loses its stability via flip and fold bifurcations and then chaos exists.
Similar content being viewed by others
1 Introduction
Modeling competition among players over a finite set of resources whose cost change with demand is a type of congestion games. Traditionally, such games may be known as cost minimization games. The congestion game can be simply defined as a game of resources where players can allocate some of these resources. Each resource should be accompanied by certain costs. These costs depend on the load each player wants to induce. Such games are considered quite simple; however, they have enough structure for interesting situations spanning from oligopoly, migration and the internet to possibly be modeled [1]. Such types of games always have a Nash equilibrium in pure strategies as cited by Rosenthal in [2]. In the literature, there is a variety of work that has studied such games. The applicability of those games makes researchers investigate them more and hence new directions are being explored and discussed. For instance, in [3], the worst-case price of anarchy that is defined as the ratio between summation of players’ costs in a Nash equilibrium and in a minimum cost outcome of congestion games has been studied. This summation is used to measure social cost. That polynomial latency functions could be used as the transportation costs along the network has been proved for two different congestion games in [4]. A generalization of oligopolistic games via networks has been studied in [5]. This game was known as a type of atomic game. In [6], it has been proved that the price of anarchy of a dynamic Cournot game under coalition information was bounded by the number of players.
In the current paper, we focus on the dynamic case and the properties of a Nash equilibrium point. Our investigation starts with modeling the suggested congestion game and then it is studied as statically. Moving from the static to the dynamic versions we assume that the three firms adopt a gradient rule by which they can react with each other. This gradient approach has been intensively studied in the literature. It has been studied in the context of monopoly, duopoly and triopoly [7–12]. In addition, it has been investigated by Perc and many coauthors in other contexts such as in the prisoner’s dilemma and public good games (see [13–16]). Indeed, in our paper we have got a unique Nash equilibrium for the dynamical system describing the suggested congestion game. According to the gradient mechanism we generate our system and study its complex dynamics. The first finding we get is that the stability of the Nash equilibrium is influenced by the volume of resources and the nonlinearity of the cost functions. We stress in our investigation the role of destabilization that the Nash equilibrium may face. The destabilization is obtained via two types of bifurcation, which are period-doubling and fold bifurcations. Interestingly, our numerical simulation experiments show the presence of irregular fluctuations near the Nash equilibrium. Those kinds of fluctuations around Nash equilibrium are not normally distributed as supported by the simulation and empirical literature [1].
Now, we summarize the current paper as follows. In Sect. 2, we introduce a congested triopoly model. We give some definitions related to congestion games. This also includes the type of nonlinear costs functions adopted by each firm with the amount of quantities that must be transferred via paths of the network. Hence, in Sect. 3 we present some theoretical investigations on setting the dynamical system that describes the congestion game handled in this paper. Furthermore, in Sect. 3, we follow the standard direction to discuss the conditions of stability of the Nash equilibrium. In Sect. 4, we perform an intensive numerical simulation to validate the obtained results that include bifurcation, time series, and 2D-bifurcation analysis.
2 The model
Suppose we have three firms (players) that send their productions from a source node (S) to a destination node (T). Those two nodes are connected by only two paths, path 1 and path 2. Each firm, indexed by \(i=1,2,3\), must send a \(d_{i}\) unit via these paths from their source node to the destination node as follows:
or it can be rewritten in the simple form,
where \(d_{i}\), \(i=1,2,3\), refers to the total unit sent from firm i to the destination node (T) through the two paths \(\{1,2\}\). Since we have a simple network with two nodes and two paths, the three players will provide a total load on each path as follows:
or
Indeed, each firm will get a cost of total load on each path. We denote by \(\ell _{1}(x_{1})\) and \(\ell _{2}(x_{2})\) the cost on path 1 and path 2, respectively. We follow [1] and restrict these two costs to the following form:
or
where the convexity of the above costs is guaranteed under the condition \(p_{j}\geq 1\); \(j=1,2\) and \(p_{j}\in \mathbb{N} \). Now, the cost of each player for a given strategy profile \(X= ( x_{i} ) _{i\in \mathbb{N} }\) can be written in the following form:
which each player wants to minimize. The aim of this paper is to study the dynamics belonging to this game. This requires one to model the behaviors of the competing players within the game by repeating their behaviors in a discrete time dynamic game. These competing players (or firms) have some preferences to be maximized. The following utility functions are used to describe those preferences:
These utilities can be simplified using (1) and the variables, x, y and z for \(x_{11}\), \(x_{21}\) and \(x_{31}\), respectively, as follows:
where we assume also \(d_{i}=d\), \(i=1,2,3\), to reduce the number of game parameters. Now, we assume that the three players adjust their works over time proportionally to their marginals. This means that the change in their choices at any time t and the next one will be governed by the following relation:
where \(X_{t}\) refers to the firm’s choice at any period t.
Proposition 1
The suggested game above admits a unique Nash equilibrium point whose variables satisfy the condition
Proof
It is similar to [1]. □
Proposition 2
The static equilibrium point of the above congested game is an increasing function of the variables\(x^{\ast } ( p_{1},p_{2} ) \)if the following conditions are satisfied:
Proof
A Nash equilibrium should satisfy the condition
By differentiating this condition with respect to \(p_{1}\) and \(p_{2}\), respectively, we get
where
With simple calculations (11) can be rewritten in the following form:
which are positive if
and then the proof is completed. □
Proposition 3
In the case of a small asymmetry (\(p_{2}=p_{1}+\epsilon \)) whereϵis very small then
Proof
Since we know that \(x(p_{1},p_{2})\) is the only solution of
by setting \(p_{2}=p_{1}+\epsilon \) we get
which can be simplified to
where \(\lim_{\epsilon \rightarrow 0} \frac{c_{p_{1}}}{c_{p_{1}+\epsilon }}=1\). Now, (13) can be rewritten as
with simple calculations, (14) takes the following form:
as ϵ is very small we obtain
which can be simplified to
This completes the proof. □
3 Stability of the dynamic model
This section is organized to study the dynamic characteristics of the congested game described in the previous section. We assume that the firms’ allocations choices can be modeled according to the following bounded rationality rule:
which can be written in the form
where we assume that \(\gamma (X_{t})=\gamma \) as a constant parameter in order to make the above system admits a unique Nash equilibrium obtained above. Now, to study the stability of the Nash equilibrium we need to calculate the Jacobian of the dynamical system (16),
So to calculate the Jacobian, the following proposition is given.
Proposition 4
For the above discussed Nash equilibrium, the Jacobian can be written in the following simple form:
where
Proof
See the Appendix. □
In order to study the stability of the Nash equilibrium of our model we need to investigate which types of bifurcations would have influence on the stability. So we need to recall the stability conditions which are known as Routh–Hurwitz conditions. The characteristic equation of the above Jacobian takes the form
where
Hence, the eigenvalues are
which are real and lie within the unit circle if
Proposition 5
The Nash equilibrium is stable if and only if the following conditions are satisfied:
Proof
The first condition can be simplified to
which is always positive due to (17). The second condition can be simplified to
It is also positive due to (17). The third condition can be simplified to
Also, this condition is satisfied (becomes less than 1) if (17) holds. The last condition is satisfied if
□
4 Numerical simulations
The above discussion tells us that the main parameters γ, \(p_{1}\), \(p_{2}\) and d have a serious impact on the stability of the Nash equilibrium point. So we carry out some numerical experiments in order to investigate more the influences of those parameter values on the behavior of system (16). Our analysis includes some tools such as bifurcations, time series and the basin of attractions.
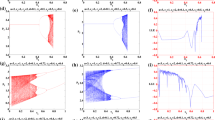
Let us first set our parameter values as follows: \(x_{o}=1.5\), \(y_{o}=1.5\), \(z_{o}=1.5\), \(d=2\), \(p_{1}=1.66\) and \(p_{2}=2\). It is worth mentioning here that the reader should observe that we begin with values for the parameter \(p_{1}\) less than \(p_{2}\). Later on we investigate the dynamic characteristics of (16) when \(p_{1}\geq p_{2}\). This setting shows the influence of the parameter γ on the equilibrium point. Figure 1(a) shows the bifurcation diagram of system (16) when varying the parameter γ in the interval \([ 0,0.0616 ] \). It is clear that this parameter has no effect on the Nash equilibrium point up to the point 0.04586 where the first period-doubling occurs. This is also seen in the Lyapunov exponent that corresponds to the bifurcation diagram. After that value, the periods of the cycles increase when varying the value of γ. For instance, at \(\gamma =0.056\) a stable period-2 cycle appears. Its phase portrait is given in Fig. 1(b) with the time series. It is obvious that the period-2 cycle lies on the diagonal due to the symmetry in system (16). Now, we go forward to the next period-doubling by fixing the previous parameter values and changing the value of γ to 0.057. This small change in the parameter gives rise to the stable period-4 cycle as shown in Fig. 1(c). This figure shows the four period points in the phase portrait and they lie in the diagonal because of the symmetry of the system. Increasing the parameter γ further to the point 0.059 gives birth to the stable period-8 cycle as shown in Fig. 1(d). More experiments are carried out to discover the period-6 cycle but the simulation gives nothing. For any values of the parameter γ in the interval \([ 0.057,0.059 ) \) we get only a stable period-4 cycle. There is no indication of a period-6 cycle. Changing this parameter slightly to 0.0591 the system’s behavior jumps to stable period-16 cycles and no indication of a period-10 cycle exists. The phase portrait of this periodic cycle is given in Fig. 1(e). Interestingly, when increasing the value of the parameter γ with 0.0001 simulation gives birth to 8 pieces of chaotic attractors as shown in Fig. 1(f). Pieces of chaotic attractors still exist for any increase of γ; then they turn to a stable period-10 cycle at the value \(\gamma =0.05998\) as presented in Fig. 1(g). Increasing this parameter value gives different types of periodic cycles and pieces of chaotic attractor till the value 0.0617, where we only witness the birth of a one-piece chaotic attractor. We end this part of simulation analysis by giving the influences of the other parameters \(p_{1}\), \(p_{2}\) and d via plotting their bifurcation diagrams. Those bifurcations are presented in Fig. 1(h), Fig. 1(i) and Fig. 1(j). It is obvious that those parameters have a destabilization impact on the system’s Nash equilibrium when varying them. In addition, we give a 2D-bifurcation diagram for the parameters γ versus d. We also plot the basin of attraction for x versus y for the stable period-32 cycle at the parameter values \(z_{o}=1.5\), \(\gamma =0.05913\), \(d=2\), \(p_{1}=1.66\) and \(p_{2}=2\) in Fig. 1(k) and Fig. 1(l), respectively.
The complex analysis of the system (16) via bifurcations, phase portrait of the period cycles and chaotic attractor, time series and Lyapunov exponent when varying the parameter values of γ, \(p_{1}\), \(p_{2}\) and d separately
The gray color in Fig. 1(k) refers to the stable period-1 cycle and the other colors are for different periodic cycles. Furthermore, the 2D-bifurcation diagram between γ and d includes some regions where periodic cycles with odd order can be found. For instance, at the parameter values \(\gamma =0.05626133\) and \(d=2.294044\), another stable period-5 cycle arises. At \(\gamma =0.0561244\) and \(d=2.262711\), a stable period-5 cycle arises. Now, we study the case when the two parameters \(p_{1}\) and \(p_{2}\) are equal. We set the parameter values to \(x_{o}=1.5\), \(y_{o}=1.5\), \(z_{o}=1.5\), \(d=2\), \(p_{1}=2\) and \(p_{2}=2\). The bifurcation diagram when varying the parameter γ is given in Fig. 2(a). The Jacobian of the system (16) at those values of the parameters and for \(\gamma =0.033333\) takes the form
whose eigenvalues are
where \(\vert \mu _{1,3} \vert <1\) and \(\vert \mu _{2} \vert \approx 1\), which means that the Nash equilibrium may lose its stability via a fold bifurcation type. Keeping the other parameter values fixed and reducing γ to 0.033 we get a situation where the Nash equilibrium of system (16) becomes stable. This is depicted in Fig. 2(b) and as one can see from the time series the Nash equilibrium point becomes stable. The influence of the other parameters, d, \(p_{1}\) and \(p_{2}\), are also important and we give only here their bifurcations just to reduce our analysis. The interesting reader is advised to investigate further this case, as the previous case. Furthermore, we can see from Fig. 2(d) that the 2D-bifurcation diagram of γ versus d indicates that there is only period-2 cycle. Now, we study the case when we have \(p_{1}>p_{2}\). We set the parameter values to \(x_{o}=1.5\), \(y_{o}=1.5\), \(z_{o}=1.5\), \(d=2\), \(p_{1}=2\), \(p_{2}=1.3\) and \(\gamma =0.085\). The Jacobian matrix of system (16) at these values takes the form
whose eigenvalues are
which are real and \(\vert \eta _{2} \vert >1\) means that the Nash equilibrium loses its stability via a period-doubling bifurcation only. At those parameter values and when varying the parameter γ, the Nash equilibrium becomes stable until the parameter approaches the value 0.066 where we see the birth of a period-2 cycle. After that it becomes unstable due to chaos as shown in Fig. 2(e). Other numerical simulations for this case give interesting results but we end our numerical analysis here and give the bifurcation diagrams for the parameters d and \(p_{2}\) in Fig. 2(f).
The complex analysis of the system (16) via bifurcations and Lyapunov exponent when varying the parameter values of γ, \(p_{2}\) and d separately for the cases when \(p_{1}=p_{2}\) and \(p_{1}>p_{2}\)
5 Conclusion
The current paper has investigated the chaotic characteristics of a congested triopoly game, where three firms use a simple network to send their goods to the destination node. The static framework of the congestion game has been introduced and studied. Moving to the dynamic case it has been assumed that the three firms adopt the gradient rule in order to react with the decisions made by their agents. Due to the symmetry of the discrete dynamic model describing this game, we have discussed the influence of the model’s parameters using experimental simulation. The simulation has shown that the game’s Nash equilibrium may lose its stability using two types of bifurcations which are period-doubling and fold bifurcation. However, the simulation has provided interesting results that support and extend the results found in the literature [1], the complex phenomenon of strange chaotic attractor has not existed before. Furthermore, the simulation has provided some irregular fluctuations around the Nash equilibrium point.
References
Naimzada, A.K., Raimondo, R.: Chaotic congestion games. Appl. Math. Comput. 321, 333–348 (2018)
Rosenthal, R.W.: A class of games possessing pure-strategy Nash equilibria. Int. J. Game Theory 2(1), 65–67 (1973)
Roughgarden, T., Schoppmann, F.: Local smoothness and the price of anarchy in splittable congestion games. J. Econ. Theory 156, 317–342 (2015)
Aland, S., Dumrauf, D., Gairing, M., Monien, B., Schoppmann, F.: Exact price of anarchy for polynomial congestion games. In: Durand, B., Thomas, W. (eds.) STACS 2006. STACS 2006. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol. 3884. Springer, Berlin (2006)
Cominetti, R., Correa, J.R., Stier-Moses, N.E.: The impact of oligopolistic competition in networks. Oper. Res. 57(6), 1421–1437 (2009)
Feldman, M., Immorlica, N., Lucier, B., Roughgarden, T., Syrgkanis, V.: The price of anarchy in large games. In: Proceedings of the 48th ACM Symposium on Theory of Computing, pp. 963–976 (2016)
Askar, S.S.: The rise of complex phenomena in Cournot duopoly games due to demand functions without inflection points. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 19, 1918–1925 (2014)
Puu, T.: A new approach to modeling Bertrand duopoly. Rev. Behav. Econ. 4, 51–67 (2017)
Agliari, A., Naimzada, A.K., Pecora, N.: Nonlinear dynamics of a Cournot duopoly game with differentiated products. Appl. Math. Comput. 281, 1–15 (2016)
Ma, J., Sun, L., Hou, S., Zhan, X.: Complexity study on the Cournot–Bertrand mixed duopoly game model with market share preference. Chaos 28, 023101 (2018)
Askar, S.S.: Tripoly Stackelberg game model: one leader versus two followers. Appl. Math. Comput. 328, 301–311 (2018)
Elsadany, A.A.: Dynamics of a Cournot duopoly game with bounded rationality based on relative profit maximization. Appl. Math. Comput. 294, 253–263 (2017)
Perc, M., Szolnoki, A.: Social diversity and promotion of cooperation in the spatial prisoner’s dilemma game. Phys. Rev. E 77, 011904 (2008)
Perc, M., Wang, Z.: Heterogeneous aspirations promote cooperation in the prisoner’s dilemma game. PLoS ONE 5, e15117 (2010)
Liu, L., Chen, X., Perc, M.: Evolutionary dynamics of cooperation in the public goods game with pool exclusion strategies. Nonlinear Dyn. 97, 749–766 (2019)
Perc, M.: Success-driven distribution of public goods promotes cooperation but preserves defection. Phys. Rev. E 84, 037102 (2011)
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to extend their sincere appreciation to the Deanship of Scientific Research at king Saud University for its funding this Research group NO (RG-1435-054).
Availability of data and materials
The data sets generated during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Funding
This research was funded by the Deanship of Scientific Research at King Saud University No. RG-1435-054.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The authors contributed equally to this work. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare that this article content has no conflict of interest.
Appendix
Appendix
The proof of Proposition 4 is given below in detail.
Proof
The partial derivatives in the Jacobian can be written as follows:
and
and
At the Nash equilibrium the above can be simplified to
and
and
which can be simplified further to
which completes the proof. □
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Askar, S.S., Al-khedhairi, A. Chaotic triopoly game: a congestion case. Adv Differ Equ 2020, 216 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13662-020-02683-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s13662-020-02683-0