Abstract
Lytic polysaccharide monooxygenases (LPMOs) can oxidize recalcitrant polysaccharides and boost the conversion of the second most abundant polysaccharide chitin by chitinase. In this study, we aimed to achieve the efficient extracellular production of Serratia marcescens LPMO CBP21 and Aeromonas veronii B565 chitinase Chi92 by Escherichia coli. Twelve signal peptides reported with high secretion efficiency were screened to assess the extracellular production efficiency of CBP21 and Chi92, with glycine used as a medium supplement. The results showed that PelB was the most productive signal peptide for the extracellular production of CBP21 and Chi92 in E. coli. Furthermore, CBP21 facilitated the degradation of the three chitin substrates (colloidal chitin, β-chitin, and α-chitin) by Chi92. This study will be valuable for the industrial production and application of the two enzymes for chitin degradation.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Chitin, a water insoluble poly-β-1,4-N-acetylglucosamine, is the second most abundant natural polysaccharide and is widely distributed in organisms such as fungi, arthropods and nematodes. Chitooligosaccharides (COS), the degraded products of chitin, have attracted increasing interest because of their physicochemical properties and potential food and pharmaceutical applications (Zou et al. 2016).
Efficient enzymatic conversion of recalcitrant chitin polymers is crucial for an economically and environmentally sustainable bioeconomy. However, the efficiency has been not desirable. The recently discovered lytic polysaccharide monooxygenases (LPMOs) are capable of oxidizing recalcitrant polysaccharides at different carbon positions [e.g., C1 (Vaaje-Kolstad et al. 2010), C4 (Isaksen et al. 2014)] and thus render the substrate more susceptible to hydrolysis by conventional glycoside hydrolases, providing new avenues toward more efficient enzymatic conversion of biomass. CBP21 is a chitin-active LPMO [Auxiliary activity family 10 (AA10)] from Serratia marcescens that can boost chitin depolymerization by S. marcescens chitinases (Suzuki et al. 1998; Vaaje-Kolstad et al. b, 2010). Also, CBP21 can promote the activity ChiA and ChiB from Listeria monocytogenes more efficiently than LmLPMO10 (Paspaliari et al. 2015). Moreover, CBP21 can enhance the activity of ChiC from Aeromonas veronii B565 by 2 (shrimp shell chitin as substrate) and 9 (colloidal chitin as substrate) folds (Huo et al. 2014). CBP21 is of economical importance for the environment-friendly chitin degradation.
Chitinase is a key enzyme in chitin degradation and production of soluble COS. A. veronii B565 isolated from aquaculture pond sediment was reported to be capable of producing chitinases that can be used to control Myxozoa-related or fungal diseases in fish (Li et al. 2011; Liu et al. 2011). Strain B565 encodes three chitinases from GH18, namely Chi92 (GenBank number AEB48885.1), ChiA (AEB48887.1), ChiB565 (AEB48892.1), two chitinases from GH19, namely ChiC (AEB50059.1) and ChiP (AEB48889.1). Among the five chitinases from A. veronii B565, Chi92 had high exochitinase specific activity on colloidal chitin and showed good potential as aquafeed additive enzyme (Huo et al. 2016; Zhang et al. 2014).
For industrial use, it is important that the costs associated with production of chitinolytic enzymes are low. Because of the advantages of rapid growth, high-yield and easy-to-scale production (Rosano and Ceccarelli 2014), Escherichia coli is the pre-eminent host for protein production both for commercial application [30% of recombinant therapeutic proteins, (Ferrer-Miralles et al. 2009)] and for research purposes [>70% of proteins, (Bill 2014)]. Extracellular protein production in E. coli is highly desirable as it simplifies downstream purification processes and increases product yield (Choi and Lee 2004). For E. coli, secreting recombinant protein extracellularly requires efficient crossing of two membrane barriers to overcome its low secretion capacity. Four strategies have been used for enhancing the secretory production of target proteins, i.e., selection of the signal peptide, coexpression of proteins to assist translocation and folding, improvement of periplasmic release, and protection of target proteins from degradation and contamination (Yoon et al. 2010). The combination of selection of the signal peptide and improvement of periplasmic release is the preferred strategy for efficient protein secretion. Signal peptides generally mediate transport of a protein from intracellular to the periplasmic space by either Sec or Tat pathway in E. coli. Owing to discrepancies between proteins, it is difficult to predict protein secretion efficiency. Selecting a suitable signal peptide is important for improving protein secretion. Moreover, the permeability enhancer glycine can replace the alanine residues in the peptide component of the cell wall peptidoglycan, thus enhancing the outer membrane permeability, and is frequently used to improve protein secretion (Hammes et al. 1973; Ding et al. 2010; Zou et al. 2014).
The extracellular production of CBP21 and Chi92 in E. coli has not been reported. In this study, we screened 12 signal peptides for efficient secretion of CBP21 and Chi92, all of which have been found effective for high protein secretion in E. coli, Bacillus subtilis, Streptomyces lividans or Trichoderma reesei. Moreover, glycine was chosen as a medium supplement to improve the production of extracellular CBP21 or Chi92. For improvement of the catalytic efficiency of Chi92, the synergistic effect of CBP21 on the chitin degradation rate of Chi92 was investigated.
Materials and methods
Strains, plasmids and growth conditions
All strains and plasmids were shown in Additional file 1: Table S1. E. coli DH5α (Transgen, Beijing, China) was used for gene cloning procedures. E. coli BL21 (DE3) (Novagen, Beijing, China) was used for recombinant protein production. S. marcescens GIM1.217 was purchased from Guangdong Microbiology Culture Center (GDMCC) and A. veronii B565 (CGMCC 3169) was a strain stored in our laboratory. Vector pET-28a(+) was used for cloning and expression of Chi92 and CBP21 genes. Cells were incubated at 37 °C in Luria broth with kanamycin (50 µg/mL).
Plasmid construction
DNA polymerase LA Taq and T4 DNA ligase were obtained from Takara (Beijing, China), and restriction enzymes were obtained from New England Biolabs or Fermentas (Beijing, China). TIANpure Mini Plasmid and Gel purification kits were from Tiangen (Beijing, China). The used primers were summarized in Additional file 1: Table S2.
All genes encoding the signal peptides listed in Table 1 were synthesized by overlap PCR, which contain restriction sites for XbaI and EcoRI respectively. The synthesized DNA fragments were inserted into the XbaI and EcoRI sites of pET-28(a) to generate vectors containing different signal peptide: pET28a-SacB, pET28a-PelB, pET28a-TorA, pET28a-WompA, pET28a-OmpASIL2, pET28a-LMSEA, pET28a-LSEAmut, pET28a-Exyl, pET28a-gIII, pET28a-STII, pET28a-XCs or pET28a-CBHI, respectively.
Chi92 gene encoding chitinase Chi92 and CBP21 gene encoding Lytic polysaccharide monooxygenase CBP21 (GenBank number MF150504) were amplified from the genomic DNAs of S. marcescens GIM1.217 and A. veronii strain B565, respectively. The amplified fragments without their respective signal peptide were cleaved by NcoI and XhoI and ligated into the above vectors containing different signal peptide to construct the plasmids as listed in Additional file 1: Table S1. The amplified fragments with or without their native signal peptide were cleaved by XbaI and XhoI and ligated into pET-28a(+) to construct the control plasmids as listed in Additional file 1: Table S1.
All plasmids were verified by DNA sequencing, and then the confirmed plasmids were separately transformed into competent E. coli DH5α or BL21 (DE3) cells.
Protein production and purification
For production of each recombinant protein, first, E. coli BL21 (DE3) samples transformed with expression plasmids were cultured in Luria–Bertani broth with shaking at 200 rpm over night at 37 °C for use as a seed culture. Each culture was then diluted 1:100 with Terrific Broth medium with 50 μg/ml kanamycin (pH 6.4) and cultured at 37 °C, 200 rpm until the OD600 of bacteria culture was 0.8. Then lactose was added to a final concentration of 2% (w/v) to induce target protein production. To study whether the addition of glycine affects the excretion of Chi92 and CBP21, 1% (w/v) glycine was further supplemented after 12 h lactose-induction for another 12 h incubation. The culture supernatant and cell pellet were separated by centrifugation (4 °C, 10,000g, 10 min). The pellet was resuspended in PBS buffer to an OD600 of 10. Proteins in the supernatants were precipitated by adding 2 volumes of ice-cold acetone for 1 h at −20 °C and then centrifuged at 12,000g for 10 min at 4 °C. To ensure comparability between culture supernatant fraction and cell pellet fraction, the pellet from cell supernatant fraction (medium fraction, M) were resuspended in the same volume of PBS buffer as that used for cell pellet (cellular fraction, C). Fractions added with SDS-PAGE loading buffer were boiled at 100 °C for 10 min, then centrifuged (4 °C, 12,000g, 10 min) before loading on gels (TGX Stain-Free™ FastCast™ Acrylamide Kit, 12%, Bio-Rad, Cat. No. 161-0185) for SDS-PAGE. The same volume of each supernatant was loaded per lane.
Recombinant cells were resuspended in BugBuster protein extraction reagent at room temperature for 1 h and centrifugated to remove cell debris. The supernatant was incubated with pre-equilibrated Ni2+–NTA His·Bind resin at 4 °C for 1 h, and washed sequentially with 5 column volumes of elution buffer containing 20, 50 and 500 mM imidazole. Purified protein were analyzed using 12% SDS-PAGE.
Preparation of chitin substrates
α-Chitin from shrimp shells was purchased from Sigma-Aldrich (V900332). Preparation of colloidal chitin from shrimp shell chitin (Sigma V900332) was according to the method described by Zhang et al. (2014). To prepare β-chitin, squid pens from the common squid fishes were dried and ground into powder, then treated with 8% HCl solution at a 1:14 (w/v) solid-liquid ratio for 30 min at 25 °C for decalcification. After filtration, the sample was washed to neutral, and then treated by 10% NaOH solution at a 1:10 (w/v) for 2 h at 100 °C for deproteinization, filtered, washed to neutral and dried, and got β-chitin.
Synergistic effects on enzymatic hydrolysis of chitin
To determine the influence of CBP21 on Chi92 efficiency, 250 µl of different contents (0, 0.005, 0.05, 0.5, 5, 50, 500 nmol) of CBP21 and 250 µl of 1% substrate (α-chitin, β-chitin or colloidal chitin) in sodium phosphate buffer (50 mM, pH 7.0) were incubated for 2 h at 37 °C, then 250 μl of Chi92 (21 nmol) was added and these mixtures were incubated for another 1 h at 37 °C. At the end of reaction, the released reducing sugars were measured by the 3,5-dinitrosalicylic acid assay (Liu et al. 2011). All reactions were performed in triplicate.
Results
Signal peptide for the efficient extracellular production of CBP21 and Chi92 in E. coli
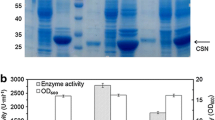
Since signal peptides can differ greatly in their ability for the secretion of a given protein, a signal peptide screening procedure is crucial for efficient secretion. To select the suitable signal peptide for the efficient extracellular production of CBP21 or Chi92, 12 signal peptides were fused respectively to the N-terminus of CBP21 or Chi92, and the intracellular and extracellular production of CBP21 or Chi92 was analyzed by SDS-PAGE. Two signal peptides, CBHI and PelB, significantly increased the production level of CBP21 (Fig. 1a). In addition, PelB can efficiently increase the release of intracellular CBP21 to extracellular milieu of recombinant E. coli.
Comparison of the extracellular production of CBP21 or Chi92 fused with different signal peptides. Recombinant E. coli cells were constantly cultured for 24 h in TB medium with lactose-induction or in TB medium with 1% glycine addition after 12 h lactose-induction followed by another 12 h incubation. The intracellular (C) and extracellular (M) production of CBP21 (a) or Chi92 (b) fused with different signal peptides (as indicated in the top of each lane) were analysed by SDS-PAGE. CBP21S and Chi92S represent CBP21 and Chi92 with their native signal peptide, respectively. CBP21 and Chi92 represent CBP21 and Chi92 without any signal peptide, respectively. The red arrows indicate the CBP21s and Chi92s with molecular weight estimation of 20–25 or 91–96 kDa, respectively
To enhance the extracellular production of CBP21, recombinant cells after 12 h lactose induction were further cultured with 1% glycine for 12 h. Compared with the absence of glycine, glycine supplementation increased the amount of extracellular total protein from recombinant E. coli with pPelB-CBP21 (from 0.83 to 0.94 mg/ml). Furthermore, the intensity [Area of 5188 using Iimage J analysis (NIH, USA, Version: ij150-win-jre6-32-bit)] of extracellular CBP21 band in glycine-supplementation group is higher than that (Area of 5675) in the non-glycine control group (Fig. 1a), indicating that glycine supplementation increased the extracellular production of PelB-fused CBP21 from recombinant E. coli.
As shown in Fig. 1b, most signal peptides, such as CBHI, WompA, LMSEA, LSEA-mut, gIII, PelB, OmpASIL2 and StII, significantly increased the production level of Chi92. Furthermore, signal peptides StII, LMSEA, LSEA-mut and XCs can secrete Chi92 to the extracellular medium of recombinant E. coli. Compared with the respective controls, several signal peptides, such as PelB, OmpASIL2, WompA, LMSEA and gIII, markedly improved the extracellular production level of Chi92 from recombinant E. coli cultured in glycine supplemented medium. Collectively, PelB was the most productive signal peptide for the extracellular production of CBP21 and Chi92 in E. coli cultured in glycine supplemented medium.
Enhancement of the hydrolytic activity of Chi92 on various chitin substrates by CBP21
Different concentrations of CBP21 were first pre-incubated with the three substrates for 2 h, then purified Chi92 was added to hydrolyze substrates for 1 h. The results showed a dose-dependent synergistic effect of CBP21 on the hydrolytic efficiency of Chi92. Chi92 displays maximum degradation rates at the CBP21 concentration of 666.67 µM. In the presence of 66.67 or 666.67 µM CBP21, Chi92 incubated with colloidal chitin, α-chitin and β-chitin produced 2.49 or 3.03-times, 1.59 or 1.84-times and 2.61 or 3.22-times of the product of the control group, respectively (Fig. 2). These results demonstrated that CBP21 facilitated the degradation of three chitin substrates by Chi92.
Dose-response effects of CBP21 on the activity of Chi92 to colloidal chitin, α-chitin or β-chitin. 250 µl of different contents (0, 0.005, 0.05, 0.5, 5, 50, 500 nmol) of CBP21 and 250 µl of 1% substrate (colloidal chitin, α-chitin or β-chitin) in sodium phosphate buffer (50 mM, pH 7.0) were incubated in 37 °C for 2 h, then 250 μl of Chi92 (21 nmol) was added and these reaction mixtures were incubated in 37 °C for another 1 h. Sample were measured by the 3,5-dinitrosalicylic acid (DNS) assay. Each data value represents the average of three measurements
Discussion
Signal peptides showed large variations in secretion efficiencies, depending on the nature of the secreted protein. A suitable signal peptide for one protein may not be efficient for another protein (Low et al. 2013). A similar outcome was obtained in the present study, all 12 selected signal peptides increased the production level of Chi92 in varying degrees, whereas only four signal peptides, including PelB, CBHI, SacB and XCs, increased the production level of CBP21. Without glycine addition, StII, LMSEA, LSEA-mut and XCs can efficiently improve the release of intracellular Chi92 to culture media, while only PelB can promote the release of CBP21 to culture media with high efficiency. The cleavage efficiency of the signal peptide affects protein secretion levels (Low et al. 2013). Interleukin-2 production in E. coli periplasm was increased drastically by a single amino acid substitution in OmpA cleavage site (Robbens et al. 2006). Substitution of the Staphylococcus staphilococcic enterotoxin A leader sequence of Val–Asn–Gly with a conserved E. coli signal peptidase recognition sequence of Ala–Ser–Ala significantly increased enterotoxin A secretion to the periplasm (Manuvera et al. 2010). The modified signal peptide (OmpASIL2 and LSEA-mut) and their respective controls (WompA and LMSEA) reported previously (Manuvera et al. 2010; Robbens et al. 2006) were also used for the secretion of CBP21 or Chi92, but the reported improvements in efficiency were not observed in CBP21 or Chi92, which is consistent with the variation in secretion efficiency of signal peptides for different proteins. The effects of glycine on the extracellular production of various signal peptides are also different. Glycine addition can significantly improve the extracellular production of Chi92 fused with PelB, WOmpA, OmpASIL2, gIII or LMSEA, but can’t improve the extracellular production of StII- and CBHI-fused Chi92. This may be due to the differences in the ability of the different signal peptides to transport protein to periplasm.
CBP21 binds stronger to β-chitin than to α-chitin (Suzuki et al. 1998; Vaaje-Kolstad et al. b). As shown in Table 2, most of the reported chitin-active LPMOs tend to bind β-chitin, and some chitin-active LPMOs bind equally well to α-chitin and β-chitin, and a few chitin-active LPMOs strictly bind to α-chitin. Substrate accessibility should be a key determinant for binding preference of LPMOs. The interaction of the chitin chains in β-chitin is more loosely than in α-chitin, and β-chitin has a higher water content and easier accessibility (Rinaudo 2006; Vaaje-Kolstad et al. 2005a), which could explain why most LPMOs showed higher affinity for β-chitin than for α-chitin. The conserved exposed aromatic residue in the substrate-binding surface of LPMOs seems to have impact on binding affinity. CBP21, with higher binding preference to β-chitin, has a Tyr in this position (Tyr54) (Suzuki et al. 1998; Vaaje-Kolstad et al. b), whereas CHB1 and CHB2 from Streptomyces avermitilis and Streptomyces reticuli, which specifically binding α-chitin, have a Trp in this position (W57 and W56, respectively) (Kolbe et al. 1998; Zeltins and Schrempf 1997). Mutation of the corresponding residue in LPMOs impacted either substrate-binding preferences or synergism (Nakagawa et al. 2015; Vaaje-Kolstad et al. b; Zeltins and Schrempf 1997).
Different LPMOs had different synergy effects on a given chitinase. CBP21 was able to boost the activity of both ChiA and ChiB from Listeria monocytogenes more than LmLPMO10 (Paspaliari et al. 2015). A. veronii B565 also encodes a chitin binding protein (CBP) (AEB51592.1) [Auxiliary activity family 10 (AA10)]. Our unpublished research found that CBP had no effect on the activity of Chi92 to colloidal chitin or α-chitin compared with CBP21 (data not shown). CBP contains 9 of the 11 key amino acid residues present on the substrate binding surface of CBP21 (Fig. 3). The other two key residues Y54 and L110 in CBP21, which were associated with chitin binding on the CBP21 surface, were replaced by W51 and F107 in the corresponding positions of CBP (Fig. 3). Whether the two residues affect the auxiliary activity of CBP to Chi92 requires further investigation. CBP21 had differential effect on the activity of different chitinases. CBP21 greatly boosted the activities of exo-acting GH18s ChiA and ChiB (Hamre et al. 2015). Oxidative cleavage of recalcitrant polysaccharide glycosidic bonds by a LPMO has been presumed to generate new chain ends as new attacking points for chitinases or cellulases (Vaaje-Kolstad et al. 2010). Like ChiA and ChiB, Chi92 is an exo-acting GH18 (Fig. 4) (Huo et al. 2016), and the synergistic effect of Chi92 with CBP21 also suggested that new ends generated by CBP21 are key for the enhancement of Chi92 activity. However, CBP21 had no effect on the initial rate of the endo-acting GH18 ChiC (Hamre et al. 2015). The mechanism underlying the specificity of synergy between LMPO and chitinase deserves further study.
Alignment of CBP21 from S. marcescens (PDB ID: 2BEM), GbpA from Vibrio cholerae (PDB ID: 2XWX) (Wong et al. 2012), Efcbm33a from Enterococcus faecalis (PDB ID: 4A02) (Vaaje-Kolstad et al. 2012), Chitin Binding Domain from Burkholderia pseudomallei (PDB ID: 3UAM) and CBP from A. veronii B565 using PROMALS3D (http://prodata.swmed.edu/promals3d/promals3d.php). Predicted secondary structures: red h: alpha-helix; blue e: beta-strand. Residues involved in chitin binding based on a 2H/1H exchange experiment (Q53, Q57, S58, L110, T111, A112, H114 and T116 of CBP21) (Aachmann et al. 2012) or determined by site-directed mutagenesis (Y54, E55, E60, H114, D182 and N185 of CBP21) (Vaaje-Kolstad et al. b) or highly conserved residues on the CBP21 substrate binding surface determined by ConSurf analysis (H28, E55, S58, E60, T111, A112, H114, D182, T183, N185 and F186 of CBP21) (Ashkenazy et al. 2010) showed by yellow surface coloring
Abbreviations
- LPMOs:
-
lytic polysaccharide monooxygenases
- CBP:
-
chitin binding protein
- AA10:
-
auxiliary activity family 10
- COS:
-
chitooligosaccharides
- GH18:
-
glycoside hydrolase family 18
- GH19:
-
glycoside hydrolase family 19
References
Aachmann FL, Sorlie M, Skjak-Braek G, Eijsink VG, Vaaje-Kolstad G (2012) NMR structure of a lytic polysaccharide monooxygenase provides insight into copper binding, protein dynamics, and substrate interactions. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 109(46):18779–18784. doi:10.1073/pnas.1208822109
Ashkenazy H, Erez E, Martz E, Pupko T, Ben-Tal N (2010) ConSurf 2010: calculating evolutionary conservation in sequence and structure of proteins and nucleic acids. Nucleic Acids Res 38(Web Server issue):W529–W533. doi:10.1093/nar/gkq399
Bill RM (2014) Playing catch-up with Escherichia coli: using yeast to increase success rates in recombinant protein production experiments. Front Microbiol 5:85. doi:10.3389/fmicb.2014.00085
Chang CN, Rey M, Bochner B, Heyneker H, Gray G (1987) High-level secretion of human growth hormone by Escherichia coli. Gene 55(2–3):189–196
Choi JH, Lee SY (2004) Secretory and extracellular production of recombinant proteins using Escherichia coli. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 64(5):625–635. doi:10.1007/s00253-004-1559-9
Choi JH, Jeong KJ, Kim SC, Lee SY (2000) Efficient secretory production of alkaline phosphatase by high cell density culture of recombinant Escherichia coli using the Bacillus sp. endoxylanase signal sequence. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 53(6):640–645
Chu HH, Hoang V, Hofemeister J, Schrempf H (2001) A Bacillus amyloliquefaciens ChbB protein binds beta- and alpha-chitin and has homologues in related strains. Microbiology 147(Pt 7):1793–1803. doi:10.1099/00221287-147-7-1793
Ding R, Li Z, Chen S, Wu D, Wu J, Chen J (2010) Enhanced secretion of recombinant alpha-cyclodextrin glucosyltransferase from E. coli by medium additives. Process Biochem 45(6):880–886. doi:10.1016/j.procbio.2010.02.009
Ferrer-Miralles N, Domingo-Espin J, Corchero JL, Vazquez E, Villaverde A (2009) Microbial factories for recombinant pharmaceuticals. Microb Cell Fact 8:17. doi:10.1186/1475-2859-8-17
Forsberg Z, Nelson CE, Dalhus B, Mekasha S, Loose JSM, Crouch LI, Rohr AK, Gardner JG, Eijsink VGH, Vaaje-Kolstad G (2016) Structural and functional analysis of a lytic polysaccharide monooxygenase important for efficient utilization of chitin in Cellvibrio japonicus. J Biol Chem 291(14):7300–7312. doi:10.1074/jbc.M115.700161
Hammes W, Schleifer KH, Kandler O (1973) Mode of action of glycine on the biosynthesis of peptidoglycan. J Bacteriol 116(2):1029–1053
Hamre AG, Eide KB, Wold HH, Sorlie M (2015) Activation of enzymatic chitin degradation by a lytic polysaccharide monooxygenase. Carbohydr Res 407:166–169. doi:10.1016/j.carres.2015.02.010
Huo FM, Yang YL, Xu L, Zhang MC, He SH, Zhou ZG (2014) Studies on character of a chitinase ChiC from Aeromonas veronii B565 and its synergism with chitin binding protein. J Agric Sci Tech 16(04):167–175 (Chinese)
Huo FM, Ran C, Yang YL, Hu J, Zhou ZG (2016) Gene cloning, expression and characterization of an exo-chitinase with high beta-glucanase activity from Aeromonas veronii B565. Acta Microbiologica Sinica 56(5):787–803
Isaksen T, Westereng B, Aachmann FL, Agger JW, Kracher D, Kittl R, Ludwig R, Haltrich D, Eijsink VG, Horn SJ (2014) A C4-oxidizing lytic polysaccharide monooxygenase cleaving both cellulose and cello-oligosaccharides. J Biol Chem 289(5):2632–2642. doi:10.1074/jbc.M113.530196
Khushoo A, Pal Y, Mukherjee KJ (2005) Optimization of extracellular production of recombinant asparaginase in Escherichia coli in shake-flask and bioreactor. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 68(2):189–197. doi:10.1007/s00253-004-1867-0
Kolbe S, Fischer S, Becirevic A, Hinz P, Schrempf H (1998) The Streptomyces reticuli alpha-chitin-binding protein CHB2 and its gene. Microbiology 144(Pt 5):1291–1297. doi:10.1099/00221287-144-5-1291
Lee CC, Wong DW, Robertson GH (2001) An E. coli expression system for the extracellular secretion of barley alpha-amylase. J Protein Chem 20(3):233–237
Li Y, Liu Y, Zhou Z, Huang H, Ren Y, Zhang Y, Li G, Zhou Z, Wang L (2011) Complete genome sequence of Aeromonas veronii strain B565. J Bacteriol 193(13):3389–3390. doi:10.1128/JB.00347-11
Liu Y, Zhou Z, Miao W, Zhang Y, Cao Y, He S, Bai D, Yao B (2011) A Chitinase from Aeromonas veronii CD3 with the potential to control myxozoan disease. PLoS ONE 6(12):e29091. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0029091
Low KO, Muhammad MN, Md IR (2013) Optimisation of signal peptide for recombinant protein secretion in bacterial hosts. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 97(9):3811–3826. doi:10.1007/s00253-013-4831-z
Manjeet K, Purushotham P, Neeraja C, Podile AR (2013) Bacterial chitin binding proteins show differential substrate binding and synergy with chitinases. Microbiol Res 168(7):461–468. doi:10.1016/j.micres.2013.01.006
Manuvera VA, Mordkovich NN, Veiko VP, Debabov VG (2010) Effects of signal peptide primary structure on efficiency of recombinant Staphylococcus aureus pro-enterotoxin A transmembrane translocation in E. coli cells. Appl Biochem Microbiol 46(9):831–837. doi:10.1134/S0003683810090036
Mekasha S, Forsberg Z, Dalhus B, Bacik J, Choudhary S, Schmidt-Dannert C, Vaaje-Kolstad G, Eijsink VGH (2016) Structural and functional characterization of a small chitin-active lytic polysaccharide monooxygenase domain of a multi-modular chitinase from Jonesia denitrificans. FEBS Lett 590(1):34–42. doi:10.1002/1873-3468.12025
Miyazaki T, Noda S, Tanaka T, Kondo A (2013) Hyper secretion of Thermobifida fusca beta-glucosidase via a Tat-dependent signal peptide using Streptomyces lividans. Microb Cell Fact 12:88. doi:10.1186/1475-2859-12-88
Moser F, Irwin D, Chen S, Wilson DB (2008) Regulation and characterization of Thermobifida fusca carbohydrate-binding module proteins E7 and E8. Biotechnol Bioeng 100(6):1066–1077. doi:10.1002/bit.21856
Nakagawa YS, Kudo M, Loose JS, Ishikawa T, Totani K, Eijsink VG, Vaaje-Kolstad G (2015) A small lytic polysaccharide monooxygenase from Streptomyces griseus targeting alpha- and beta-chitin. FEBS J 282(6):1065–1079. doi:10.1111/febs.13203
Paspaliari DK, Loose JS, Larsen MH, Vaaje-Kolstad G (2015) Listeria monocytogenes has a functional chitinolytic system and an active lytic polysaccharide monooxygenase. FEBS J 282(5):921–936. doi:10.1111/febs.13191
Purushotham P, Arun PVPS, Prakash JSS, Podile AR (2012) Chitin binding proteins act synergistically with chitinases in Serratia proteamaculans 568. PLoS ONE 7:e367145. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0036714
Rinaudo M (2006) Chitin and chitosan: properties and applications. Prog Polym Sci 31(7):603–632. doi:10.1016/j.progpolymsci.2006.06.001
Robbens J, De Coen W, Fiers W, Remaut E (2006) Improved periplasmic production of biologically active murine interleukin-2 in Escherichia coli through a single amino acid change at the cleavage site. Process Biochem 41(6):1343–1346. doi:10.1016/j.procbio.2006.01.009
Rosano GL, Ceccarelli EA (2014) Recombinant protein expression in Escherichia coli: advances and challenges. Front Microbiol 5:172. doi:10.3389/fmicb.2014.00172
Saito A, Miyashita K, Biukovic G, Schrempf H (2001) Characteristics of a Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2) extracellular protein targeting chitin and chitosan. Appl Environ Microb 67(3):1268–1273. doi:10.1128/AEM.67.3.1268-1273.2001
Suzuki K, Suzuki M, Taiyoji M, Nikaidou N, Watanabe T (1998) Chitin binding protein (CBP21) in the culture supernatant of Serratia marcescens 2170. Biosci Biotech Bioch 62(1):128–135. doi:10.1271/bbb.62.128
Vaaje-Kolstad G, Horn SJ, van Aalten DM, Synstad B, Eijsink VG (2005a) The non-catalytic chitin-binding protein CBP21 from Serratia marcescens is essential for chitin degradation. J Biol Chem 280(31):28492–28497. doi:10.1074/jbc.M504468200
Vaaje-Kolstad G, Houston DR, Riemen A, Eijsink V, van Aalten D (2005b) Crystal structure and binding properties of the Serratia marcescens chitin-binding protein CBP21. J Biol Chem 280(12):11313–11319. doi:10.1074/jbc.M407175200
Vaaje-Kolstad G, Bunaes AC, Mathiesen G, Eijsink VG (2009) The chitinolytic system of Lactococcus lactis ssp. lactis comprises a nonprocessive chitinase and a chitin-binding protein that promotes the degradation of alpha- and beta-chitin. FEBS J 276(8):2402–2415
Vaaje-Kolstad G, Westereng B, Horn SJ, Liu Z, Zhai H, Sorlie M, Eijsink VG (2010) An oxidative enzyme boosting the enzymatic conversion of recalcitrant polysaccharides. Science 330(6001):219–222. doi:10.1126/science.1192231
Vaaje-Kolstad G, Bohle LA, Gaseidnes S, Dalhus B, Bjoras M, Mathiesen G, Eijsink VGH (2012) Characterization of the chitinolytic machinery of Enterococcus faecalis V583 and high-resolution structure of its oxidative CBM33 enzyme. J Mol Biol 416(2):239–254. doi:10.1016/j.jmb.2011.12.033
Wang Y, Liu Y, Wang Z, Lu F (2014) Influence of promoter and signal peptide on the expression of pullulanase in Bacillus subtilis. Biotechnol Lett 36(9):1783–1789. doi:10.1007/s10529-014-1538-x
Wong E, Vaaje-Kolstad G, Ghosh A, Hurtado-Guerrero R, Konarev PV, Ibrahim AF, Svergun DI, Eijsink VG, Chatterjee NS, van Aalten DM (2012) The Vibrio cholerae colonization factor GbpA possesses a modular structure that governs binding to different host surfaces. PLoS Pathog 8(1):e1002373. doi:10.1371/journal.ppat.1002373
Yang C, Freudl R, Qiao C (2009) Export of methyl parathion hydrolase to the periplasm by the twin-arginine translocation pathway in Escherichia coli. J Agric Food Chem 57(19):8901–8905. doi:10.1021/jf901739g
Yoon SH, Kim SK, Kim JF (2010) Secretory production of recombinant proteins in Escherichia coli. Recent Pat Biotechnol 4(1):23–29. doi:10.2174/187220810790069550
Zeltins A, Schrempf H (1997) Specific interaction of the Streptomyces chitin-binding protein CHB1 with alpha-chitin—the role of individual tryptophan residues. Eur J Biochem 246(2):557–564
Zhang Y, Zhou Z, Liu Y, Cao Y, He S, Huo F, Qin C, Yao B, Ringo E (2014) High-yield production of a chitinase from Aeromonas veronii B565 as a potential feed supplement for warm-water aquaculture. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 98(4):1651–1662. doi:10.1007/s00253-013-5023-6
Zhang H, Zhao Y, Cao H, Mou G, Yin H (2015) Expression and characterization of a lytic polysaccharide monooxygenase from Bacillus thuringiensis. Int J Biol Macromol 79:72–75. doi:10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2015.04.054
Zhong Y, Liu X, Xiao P, Wei S, Wang T (2011) Expression and secretion of the human erythropoietin using an optimized cbh1 promoter and the native CBH I signal sequence in the industrial fungus Trichoderma reesei. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 165(5–6):1169–1177. doi:10.1007/s12010-011-9334-8
Zou C, Duan X, Wu J (2014) Enhanced extracellular production of recombinant Bacillus deramificans pullulanase in Escherichia coli through induction mode optimization and a glycine feeding strategy. Bioresour Technol 172:174–179. doi:10.1016/j.biortech.2014.09.035
Zou P, Yang X, Wang J, Li Y, Yu H, Zhang Y, Liu G (2016) Advances in characterisation and biological activities of chitosan and chitosan oligosaccharides. Food Chem 190:1174–1181. doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2015.06.076
Authors’ contributions
Participated in research design: YY and ZZ; Conducted experiments and performed data analysis: YY, JL, XL and XP; Wrote the manuscript or contributed to the manuscript: YY, JL, JH, CR and ZZ. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Acknowledgements
This study was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 31672294), the National Key Basic Research Program of China (973 Program) (2015CB150605), and Public science and technology research funds projects of ocean (201305022-6).
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Availability of data and materials
All the data are presented in the main paper or Additional file 1.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
No animal or human subjects were used in this work.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional file
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made.
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, Y., Li, J., Liu, X. et al. Improving extracellular production of Serratia marcescens lytic polysaccharide monooxygenase CBP21 and Aeromonas veronii B565 chitinase Chi92 in Escherichia coli and their synergism. AMB Expr 7, 170 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13568-017-0470-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s13568-017-0470-6