Abstract
Introduction
In clinical practice, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are commonly discontinued after response to biologic therapy is achieved in patients with axial spondyloarthritis (axSpA), but the impact of NSAID discontinuation has not been assessed in prospective controlled trials. The aim of the SPARSE study was to evaluate the effects of the anti-tumor necrosis factor agent etanercept on NSAID intake and conventional clinical outcomes in axSpA patients.
Methods
In the double-blind, placebo-controlled period, patients with active (mini Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Index (BASDAI) ≥4) axSpA despite optimal NSAID intake were randomized to receive etanercept 50 mg or placebo once weekly for 8 weeks. All patients were advised to taper/discontinue their NSAID intake during the treatment period. NSAID intake was self-reported by diary and Assessment of SpondyloArthritis International Society (ASAS)-NSAID scores calculated based on ASAS recommendations. The primary endpoint was change from baseline to week 8 in ASAS-NSAID score (analysis of covariance).
Results
In 90 randomized patients at baseline, mean age (standard deviation) was 38.9 (11.8) years; disease duration, 5.7 (8.1) years; 59/90 (66%) were human leukocyte antigen-B27 positive; 51/90 (57%) had radiographic sacroiliitis; and 45/90 (50%) were magnetic resonance imaging sacroiliitis-positive. Mean ASAS-NSAID scores were similar between etanercept and placebo groups at baseline (98.2 (39.0) versus 93.0 (23.4)), as were BASDAI (6.0 (1.7) versus 5.9 (1.5)), and Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Functional Index (5.2 (2.1) versus 5.1 (2.2)). Mean changes (SE) in ASAS-NSAID score from baseline to week 8 were –63.9 (6.1) and –36.6 (5.9) in the etanercept and placebo groups (between-group difference, –27.3; P = 0.002). Significantly higher proportions of patients receiving etanercept versus placebo had an ASAS-NSAID score <10 (46% versus 17%; P = 0.008) and ASAS-NSAID score of 0 (41% versus 14%; P = 0.013) at this time point. Significantly more patients in the etanercept versus placebo group achieved BASDAI50 (39% versus 18%; P = 0.032) and ASAS40 (44% versus 21%; P = 0.028) at week 8.
Conclusions
In patients with axSpA, etanercept was associated with clinically relevant NSAID-sparing effects in addition to significant improvements in conventional clinical outcomes.
Trial registration
ClinicalTrials.gov NCT01298531. Registered 16 February 2011.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Spondyloarthritis (SpA) encompasses a cluster of rheumatic conditions, characterized by inflammation of the spine, entheses, and peripheral joints, that share an association with the major histocompatibility complex class 1 antigen (human leukocyte antigen-B27) and with clinical extra-articular manifestations, such as inflammatory bowel disease, psoriasis, and uveitis [1]. Classification criteria of the Assessment of SpondyloArthritis International Society (ASAS) distinguish between predominantly axial and peripheral disease manifestations. Patients with back pain persisting for longer than 3 months and symptom onset before 45 years of age are classified as having axial SpA (axSpA) if they have evidence of sacroiliitis on imaging (that is, structural damage observed on plain X-ray images or inflammatory lesions observed on magnetic resonance imaging) in addition to at least one SpA feature (satisfying criteria for the imaging arm) or, in the absence of imaging evidence of sacroiliitis, if they have human leukocyte antigen-B27 positivity and at least two SpA features (satisfying criteria for the clinical arm) [2]. Patients with axSpA on imaging and nonradiographic axSpA have shown similar burden of illness, with comparable levels of disease activity and pain, as well as functional and quality-of-life impairment [3]-[5].
Since the beginning of the new millennium, the introduction of biologic agents for use in persistent disease has transformed the SpA treatment paradigm. Despite these important developments, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) continue to serve as first-line pharmacotherapy, particularly for axSpA [6],[7]. In fact, a good response to NSAID therapy is one of the SpA features included in candidate criteria for both the imaging and clinical arms of the ASAS axSpA classification [2]. NSAIDs effectively reduce pain and stiffness in patients with SpA after 2 to 3 days [8]-[10] and also may reduce levels of biological inflammatory markers [11]. In addition, some data suggest that NSAIDs reduce progression of structural damage [12]-[14]. However, the symptomatic, anti-inflammatory, and potential structural benefits of NSAIDs are dependent on their continuous daily use, which may be problematic because of gastrointestinal, cardiovascular, and renal toxicity associated with protracted therapy [15]-[19]. In light of safety concerns, national health agencies have recommended use of NSAIDs at the minimum effective dose for the shortest possible period [20],[21].
Anti–tumor necrosis factor (TNF) agents have been shown to improve signs and symptoms in patients with still-active axSpA despite stable background NSAID therapy in controlled clinical trials [22]-[28]. In patients who respond to anti-TNF therapy, clinicians may advise continuation of systematic daily NSAID intake in combination with the biologic therapy because of the potential structural effects of NSAIDs and potential lack of structural effects of anti-TNF agents, with the aim of reducing long-term disability. A preliminary study suggests potential structural benefits of anti-TNF agents [29], but these observations need to be confirmed in additional clinical trials. Alternatively, patients may be advised to discontinue NSAIDs once symptoms improve or disappear with anti-TNF therapy to avoid the possible complications of long-term NSAID intake. For many clinicians, the putative structural benefits of NSAIDs do not outweigh the risk of adverse effects.
Although NSAID discontinuation after biologic response in axSpA patients may be common in the clinical practice setting [30], the impact of NSAID reduction or withdrawal has never been evaluated in a prospective randomized placebo-controlled trial in this population. The amount of NSAID intake has been proposed by the ASAS to be a clinically relevant outcome measure for clinical studies in axSpA to evaluate NSAID toxicity as well as the potential NSAID-sparing effects of other treatments [31]. The ASAS-NSAID scoring system has recently been developed as a standardized method of evaluating NSAID intake in clinical trials [31]. The aim of the present randomized, controlled SPARSE study [ClinicalTrials.gov:NCT01298531] was twofold: first, to quantify the effects of treatment with the anti-TNF agent etanercept on NSAID intake in patients with axSpA using the ASAS-NSAID scoring method; and second, to evaluate the safety and efficacy of etanercept in improving the signs and symptoms of the disease.
Methods
Study design and study drug
The 8-week, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled period of this two-period, multicenter, phase 4, prospective study commenced in May 2011; the study was completed in April 2013. All patients were enrolled at and the study conducted in 19 centers in France. At the screening visit, investigators requested that patients discontinue their NSAID and restart the NSAID only if they experienced symptom flare, adjusting treatment as needed to provide optimal symptomatic control. Patients who remained asymptomatic without NSAID treatment during the 2-week to 6-week screening period were considered ineligible and were withdrawn from the study. Patients who experienced a flare of symptoms after discontinuing their NSAID and had restarted NSAID treatment were randomized using an interactive voice response system (Impala NY, NY, US) in a 1:1 ratio to receive either etanercept 50 mg or placebo subcutaneously once weekly for 8 weeks, in addition to their background NSAID. All patients were advised to taper/discontinue their NSAID intake during the study treatment period.
Patients and physicians remained blinded to treatment assignment throughout the 8-week study period. Patients randomized to either treatment group were permitted an early escape to open-label etanercept 50 mg once weekly at week 4 if they experienced >50% increase from baseline in total back pain or the Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Index (BASDAI) [32] despite receiving NSAIDs at the maximum tolerated dosage. All patients who completed the double-blind period were eligible to receive etanercept 50 mg once weekly plus background NSAID during a subsequent 8-week open-label treatment period.
The study was conducted in accordance with the International Conference on Harmonization guidelines for good clinical practice and the Declaration of Helsinki. Study activities were not initiated until patients provided informed consent. The study was approved by the central independent review board of the Comité de Protection des Personnes Ile de France VIII, Hôpital Ambroise Paré 9, Avenue Charles de Gaulle, Boulogne Billancourt 92100, France (Chairperson: Dr Frédérique Barthod).
Inclusion/exclusion criteria
Adult patients were eligible for the study if they had axSpA, as defined by ASAS classification criteria [2]. Active axial involvement was required, defined by mini-BASDAI [33] ((Question 1 + Question 2 + (Question 5 + Question 6) / 2) / 3 ≥ 4 at screening and study baseline), with an inadequate response to at least two NSAIDs taken at the maximum tolerated doses (determined from medical history) for a total combined duration of more than 1 month. Enrolled patients were required to have received an NSAID for at least 5 days per week at two-thirds the maximum licensed dosage for 4 weeks before screening and 1 week before baseline. Patients were ineligible if they received previous biologic treatment; >10 mg/day prednisone or equivalent (or changed dose) within 4 weeks of baseline; or an intra-articular, intravenous, intramuscular, or subcutaneous corticosteroid within 6 weeks of screening. They were also excluded if they had uncontrolled inflammatory bowel disease or uveitis.
Outcome measures
Study data were collected in compliance with ASAS recommendations for clinical trials of SpA [34]. Imaging was read locally by the radiologist or rheumatologist providing care for the patient. The primary endpoint was the change from baseline to week 8 in the ASAS-NSAID score [31], calculated based on NSAID intake recorded in patient diaries. The ASAS-NSAID score takes into account the type of NSAID, the total daily dose, and number of days with intake during the period of interest (that is, 7 days before the respective visit).
A secondary measure of NSAID-sparing effects was the change in ASAS-NSAID score over time. Secondary clinical endpoints included the proportions of patients who achieved ASAS partial remission [35], the BASDAI50 response [32], ASAS20 and ASAS40 responses [36], and patient acceptable symptom state (PASS) during the double-blind and open-label periods [37],[38]. Mean scores over time for the BASDAI (0 to 10) [32], Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Score on the basis of C-reactive protein (ASDAS-CRP) [39], Physician Global Assessment of disease activity (0 to 10), total back pain, Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Functional Index (0 to 10) [40], and Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Metrology Index (0 to 10) were also measured. Post hoc analyses were also conducted for the proportions of patients achieving other NSAID-sparing endpoints at week 8 (that is, 50% decrease in ASAS-NSAID score compared with baseline, ASAS-NSAID score <10, and ASAS-NSAID score = 0); ASDAS-CRP inactive disease or moderate, high, or very high disease activity levels; and normal levels of C-reactive protein (that is, ≤1.25 × upper limit of normal (4.9 mg/l)) at week 8. Statistical analysis was not performed for the latter two post hoc analyses.
Sample size
The sample size was determined based on the following assumptions for the primary endpoint: a mean ASAS-NSAID score of 100 in both groups at baseline, and mean scores of 50 and 80 in the etanercept/etanercept and placebo/etanercept groups, respectively, at week 8. A target sample size of 39 patients per treatment group was estimated to provide a between-group difference of 30 for change from baseline to week 8 in the ASAS-NSAID score, assuming a standard deviation of 40 and based on at least 90% statistical power and two-sided testing at α = 0.05.
Collected NSAID diary data
The ASAS-NSAID score was calculated based on NSAID usage completed on diary cards. Patients were requested to record details of NSAID intake for every day of NSAID usage, including the NSAID name, the dose, and number of tablets taken each day.
Statistical analyses
Continuous baseline demographic and disease characteristic variables were summarized using descriptive statistics in the intent-to-treat (ITT) population, which comprised all randomized patients who received at least one dose of study drug. NSAID-sparing and clinical efficacy and safety analyses were also conducted in the ITT population unless otherwise noted.
The primary endpoint was the change from baseline to week 8 in the ASAS-NSAID score in the ITT population. The ASAS-NSAID score was calculated from NSAID usage completed on the patient diary cards for the previous 7 days for a particular visit. Scores were calculated only if at least 5 of the 7 days were completed. Missing data were imputed based on adjacent data and using the last observation carried forward approach. Analysis of covariance was used for the primary analysis of the primary endpoint, with baseline ASAS-NSAID score and treatment as explanatory variables. No adjustments were made for multiple testing.
The primary analysis of the primary endpoint was repeated in the modified ITT population as a sensitivity analysis; the modified ITT population encompassed all patients in the ITT population, but for ITT patients who entered the escape arm, only data collected for time points up until initiation of open-label treatment were used. An additional sensitivity analysis was conducted with Wilcoxon rank-sum tests stratified by baseline ASAS-NSAID score. Hodges–Lehmann confidence intervals (CIs) were calculated for the treatment difference corresponding to unstratified Wilcoxon rank-sum tests. In addition, a post hoc sensitivity analysis was performed using a different approach to missing data imputation. Specifically, when data were missing for a particular day in the diary, the missing data were counted as no intake; both a last observation carried forward approach and a baseline observation carried forward approach (when no postbaseline diary data were available) were used. Analysis of covariance was used in the same manner as in the primary analysis described above.
The conventional clinical response outcomes at week 8 (that is, partial remission, BASDAI50, ASAS20 and ASAS40 responses, and PASS) were analyzed using a logistic regression model, including treatment and the corresponding baseline scores as covariates. The last observation carried forward approach was used for all clinical response outcomes except PASS, for which observed cases were analyzed. These clinical responses were also summarized at weeks 4, 8, 12, and 16 of the double-blind and open-label periods using observed cases. Changes from baseline in continuous NSAID-sparing and clinical endpoints were analyzed using analysis of covariance with treatment and the corresponding baseline score as covariates. The NSAID intake endpoints (that is, 50% decrease in ASAS-NSAID score compared with baseline, ASAS-NSAID score <10, and ASAS-NSAID score = 0) were analyzed using a logistic regression model including treatment and the baseline ASAS-NSAID score as covariates. Missing data were imputed as outlined for the primary endpoint. All statistical testing was two-sided and conducted at the 5% level; CIs were two-sided 95% CIs.
Results
Patients
Of 128 screened patients, 90 patients (etanercept group, n = 42; placebo group, n = 48) were randomized into the 8-week double-blind treatment period and included in the ITT, modified ITT, and safety populations (Figure 1). Eight patients (19%) in the etanercept group and 10 patients (21%) in the placebo group violated the NSAID inclusion criteria (that is, NSAID intake for at least 5 days/week at two-thirds the maximum licensed dosage during the week before the baseline visit). Fewer patients in the etanercept group escaped early during the double-blind period than in the placebo group (etanercept group, n = 6 (14%); placebo group, n = 11 (23%)). Eighty-one patients (etanercept group, n = 39; placebo group, n = 42) were included in the primary analysis of the primary endpoint. At baseline, one patient (2%) in the placebo group reported a missing NSAID diary; four patients (10%) in the etanercept group and 11 patients (23%) in the placebo group had some missing diary information. (A summary of missing NSAID diary data at baseline and during the double-blind period is provided in Additional file 1). A total of 66 patients (etanercept group, n = 33; placebo group, n = 33) completed the double-blind period and entered the open-label treatment period.
Demographic and disease characteristics at baseline were similar between the treatment groups (Table 1). Fifty-nine of 90 patients (66%) were human leukocyte antigen-B27–positive, 51/90 patients (57%) had radiographic sacroiliitis based on the modified New York criteria [41], and 45/90 patients (50%) had sacroiliac joint inflammation on magnetic resonance imaging based on the Outcome Measures in Rheumatology definition [42]. At baseline, patients had a moderate to high level of disease activity and functional impairment as measured by the BASDAI, ASDAS, and Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Functional Index. A relatively low level of spinal mobility impairment was suggested by the low baseline Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Metrology Index.
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug-sparing effects
For patients in the ITT population, the mean (standard deviation) ASAS-NSAID score at baseline was similar between the two groups: 98.2 (39.0) and 93.0 (23.4) in the etanercept (n = 42) and placebo (n = 45) groups, respectively. The primary analysis of the primary endpoint showed a significant difference of –27.3 (95% CI: –44.2 to –10.4; P = 0.002) between the etanercept (n = 39) and placebo (n = 42) groups in the change from baseline in ASAS-NSAID score at week 8 (Figure 2A).
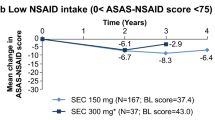
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug–sparing effects. (A) Change in ASAS-NSAID score from baseline to week 8 in patients in the etanercept and placebo groups (primary analysis of primary endpoint). Analysis of covariance, LOCF, with imputation of missing diary data, in the ITT population. (B) Proportion of patients in the etanercept and placebo groups achieving other NSAID-sparing endpoints at week 8 of the double-blind period. LOCF, with imputation, ITT population (n = number of patients achieving endpoint; N = number of patients with analyzable data). (C) Mean ASAS-NSAID scores (± SD) in the etanercept/etanercept and placebo/etanercept groups in the double-blind and open-label phases. ASAS-NSAID scores were calculated for observed cases, with no imputation of missing diary data. ASAS-NSAID, Assessment of SpondyloArthritis International Society nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug use; ETN, etanercept; ITT, intent-to-treat; LOCF, last observation carried forward; NSAID, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug; PBO, placebo; SD, standard deviation; SE, standard error.
Findings from the sensitivity analyses performed in the modified ITT population (etanercept, n = 39; placebo, n = 42) and with the Wilcoxon rank-sum test (etanercept, n = 39; placebo, n = 42) were consistent with those of the primary analysis, with differences of –27.8 (95% CI: –44.8 to –10.8; P = 0.002) and –33.3 (Hodges–Lehmann 95% CI: –50.0 to –11.4; P = 0.004), respectively. In the post hoc analysis of covariance sensitivity analysis of the primary endpoint (etanercept, n = 42; placebo, n = 47), a similar statistically significant difference of –30.4 (95% CI: –46.2 to –14.7; P = 0.0002) was found between the treatment groups.
At week 8, significantly higher proportions of etanercept-treated patients achieved the NSAID-sparing endpoints of ASAS-NSAID score <10 (P = 0.008) and ASAS-NSAID score of 0 (P = 0.013; Figure 2B). Significant reductions in the ASAS-NSAID score were observed from baseline to week 16 in the etanercept/etanercept group (n = 25) and from week 8 to week 16 in the placebo/etanercept group (n = 17): –65.93 (95% CI: –87.0 to –44.9; P <0.0001) and –39.2 (95% CI: –52.9 to –25.5; P <0.0001), respectively (Figure 2C).
Clinical efficacy
In the double-blind period, a significantly greater proportion of patients in the etanercept group than in the placebo group achieved BASDAI50 and ASAS40 responses and PASS at week 8 (P <0.05; Figure 3A). Numerically greater proportions of patients receiving etanercept achieved all clinical efficacy endpoints compared with patients receiving placebo at weeks 4 and 8 of the double-blind period. At weeks 4 and 8 of the double-blind period, etanercept was associated with significantly greater improvement in most axSpA signs and symptoms compared with placebo, including ASDAS-CRP, Physician Global Assessment of disease activity, total back pain, and Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Functional Index (Table 2). Although the difference between treatment groups in change from baseline to week 8 in the BASDAI was not statistically significant at week 8 (P = 0.051), the difference was significant at week 4 (P = 0.015). No significant difference in the Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Metrology Index was observed between the etanercept and placebo groups at weeks 4 or 8.
Clinical efficacy. (A) Proportion of patients in the etanercept and placebo groups achieving clinical endpoints at week 8 of the double-blind period. Logistic regression, LOCF (except PASS, which was calculated in observed cases). (B) Proportion of patients in the etanercept and placebo groups achieving ASDAS-CRP disease activity states at week 8 of the double-blind period. Post hoc analysis of ITT population; n = number of patients with nonmissing ASDAS-CRP results at each visit. Inactive disease = ASDAS-CRP <1.3; moderate disease activity = 1.3 ≤ ASDAS-CRP <2.1; high disease activity = 2.1 ≤ ASDAS-CRP <3.5; very high disease activity = ASDAS-CRP ≥3.5. ASAS, Assessment of SpondyloArthritis International Society; ASDAS-CRP, Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Score based on C-reactive protein; BASDAI, Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Index; ITT, intent-to-treat; LOCF, last observation carried forward; PASS, patient acceptable symptom state.
At week 8, 20% and 13% of patients in the etanercept and placebo groups, respectively, achieved ASDAS-CRP inactive disease, whereas 37% and 13% of patients in these groups had ASDAS-CRP moderate disease activity at week 8 (Figure 3B). Normal C-reactive protein levels were observed in 50% and 65% of patients receiving etanercept and placebo at baseline and in 95% and 57% at week 8. Throughout the open-label period, response rates increased for most clinical efficacy endpoints, with steeper increases observed in the placebo/etanercept group than in the etanercept/etanercept group (Additional file 2). At week 16, 54% and 57% of patients treated with etanercept in both the double-blind and open-label periods achieved BASDAI50 and ASAS40 responses, respectively; 49% and 56% of patients who received placebo for 8 weeks followed by etanercept for 8 weeks achieved these responses. As seen with the clinical efficacy endpoints, mean improvements in axSpA signs and symptoms increased further from weeks 8 to 16, with the most pronounced improvements in the placebo/etanercept group.
Safety
In the double-blind period, treatment-emergent adverse events (AEs) were reported in 81% and 54% of patients in the etanercept and placebo groups, respectively (Table 3). The most common AEs during this period in the etanercept group were rhinitis (12%); asthenia, hypercholesterolemia, injection site hypersensitivity, and injection site reactions (7% each); and headache, injection site erythema, and rash (5%). The most common AEs in the placebo group were asthenia and abdominal pain (6% each); and rhinitis, hypertension, injection site pruritus, alopecia, diarrhea, and pruritus (4% each). A serious AE was reported in one patient in the etanercept group (that is, duodenitis) and in two patients in the placebo group (that is, traffic accident and chest pain).
In the open-label period, AEs were reported in 39% and 52% of patients in the etanercept/etanercept and placebo/etanercept groups, respectively. The most common AEs in the etanercept/etanercept group were headache, injection site pruritus, migraine, and oral herpes (6% each), and in the placebo/etanercept group were injection site erythema (12%), injection site reaction (9%), and headache, nasopharyngitis, and pharyngitis (6% each). One patient in the etanercept/etanercept group had a serious AE (that is, cholecystitis).
AEs of special interest, including infections, were reported in similar proportions of patients in the etanercept and placebo groups. No cases of tuberculosis, demyelinating disorders, malignancies, or deaths were reported. No significant changes from baseline to week 4 or week 8 in diastolic or systolic blood pressure were observed in either the etanercept or placebo group; differences between treatment groups in blood pressure changes were also not significant in the double-blind period. Finally, minimal changes in weight were seen in patients receiving etanercept/etanercept and placebo/etanercept during the double-blind and open-label periods.
Discussion
Etanercept was associated with NSAID-sparing effects in this prospective, randomized, placebo-controlled study, which was specifically conducted to test this efficacy outcome. The primary outcome measure was recommended by ASAS (for example, ASAS-NSAID score based on NSAID category and daily dose intake) [31]. Importantly, despite the fact that more patients were able to reduce their NSAID intake in the etanercept group, this study also showed the clinically relevant symptomatic effects of etanercept versus placebo.
To our knowledge, this double-blind, placebo-controlled study is the first to evaluate the NSAID-sparing effect of an anti-TNF agent using the ASAS-NSAID score as the primary endpoint. Because of the innovative design of this study, and despite the observed statistically significant difference, estimation of the clinical relevance of the observed results is challenging. In a previous clinical trial in which the ASAS-NSAID score was evaluated as an outcome measure, a change from baseline in ASAS-NSAID score of –24 after open-label anti-TNF therapy was considered to be clinically relevant [43]. The design, in particular the sample size, of the present study was elaborated by defining a between-group difference in ASAS-NSAID score of 30 as clinically relevant. The between-group differences in this score observed in primary and secondary and post hoc sensitivity analyses (that is, –27.3, –27.8, –33.3, and –30.4) closely approximate the anticipated difference, suggesting that the study’s statistically significant results are also clinically relevant. Moreover, to further evaluate clinical relevance, post hoc analyses of binary endpoints were performed at week 8, including the proportions of patients achieving a 50% reduction in ASAS-NSAID score and very low ASAS-NSAID scores (that is, <10 and 0). Findings of these analyses also support the clinically significant NSAID-sparing effect of etanercept over placebo.
Because patients were advised to decrease their NSAID intake during the treatment period and more patients in the etanercept group were found to have substantially reduced their NSAID intake, a lesser treatment effect of etanercept compared with placebo could reasonably have been expected for conventional outcome measures such as ASAS responses. In fact, in addition to the NSAID-sparing effect of etanercept, this study also demonstrated a symptomatic treatment effect of etanercept over placebo similar to that observed in conventional clinical trials in which NSAID intake was mandatory at baseline and stable NSAID levels were required during the double-blind period. For example, such conventional methodology was followed in the SPINE trial, which assessed the efficacy of etanercept versus placebo in patients with radiographic axSpA who were recruited in similar centers to those participating in the present study [44]. In the SPINE trial, 44% versus 23% of patients receiving etanercept versus placebo, respectively, achieved an ASAS40 response after 12 weeks; whereas in the SPARSE study, 44% versus 21% of patients receiving etanercept versus placebo achieved this endpoint after 8 weeks. Also noteworthy, and consistent with other clinical trials [44],[45], the ASDAS demonstrated greater discriminant capacity than the BASDAI in detecting the treatment effect of etanercept in the SPARSE study, as a significant difference was observed between etanercept and placebo at week 8 with the former, but not the latter, measure.
The present study has several noteworthy strengths and weaknesses. The main strength is its design (for example, prospective, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study) with the NSAID-sparing effect specified as the primary objective. The short duration of the study’s double-blind, placebo-controlled period may be considered a weakness. The 8-week duration was selected as it was considered sufficient to demonstrate the NSAID-sparing effect of the biologic agent while limiting the duration of exposure to placebo in patients with this painful, disabling condition. However, the magnitude of such a treatment effect would probably have been greater in a longer trial; as noted in international ASAS recommendations, response rates in patients with axSpA treated with anti-TNF agents have been shown to plateau at and after 12 weeks in phase III clinical trials [46]. Another weakness of the study involved protocol violations related to NSAID intake, which were mainly attributed to investigators’ difficulty in ensuring that enrolled patients had taken NSAIDs for at least 5 days at two-thirds the maximum licensed dosage in the week before the baseline visit. In future studies, investigators may be provided with a calculator or access to an electronic system during screening to improve their ability to check such eligibility criteria. The amount of missing data in patients’ diaries may also be perceived as a weakness. When the study protocol was designed, the optimal means of data collection, either by patient diary or physician interview, was the subject of debate. Given the shortcomings of patient collection using paper diaries encountered in this study (that is, missing data), and the avoidance of such shortcomings in the German Spondyloarthropathy Inception Cohort (GESPIC) [47] and Outcome of Recent Undifferentiated Spondyloarthritis (DESIR) [48] cohort studies, which relied on physician interviews, electronic patient diaries or investigator collection may be considered stronger options in future studies.
Evaluation of the safety profile of etanercept was not the main objective of this study, but no new information was revealed in this area. The study duration was too short to allow evaluation of potential benefits associated with the reduction in NSAID intake in etanercept-treated patients. The observed reductions in NSAID dosage are likely to be more clinically relevant if extended long term; whether such reductions achieved over 8 weeks are clinically relevant has not yet been shown. In particular, no difference was observed in weight or blood pressure changes between the etanercept and placebo groups.
Conclusions
In this population of patients with axSpA who participated in the SPARSE trial, treatment with etanercept was associated with clinically relevant NSAID-sparing effects, which coincided with significant improvements in conventional clinical outcomes. Additional studies are required to further evaluate the ASAS-NSAID score as a meaningful outcome measure. Long-term observational cohorts are specifically needed to estimate the relationship between NSAID intake and AEs such as renal failure, but other studies are also necessary to determine the optimal means of presenting the obtained results, such as using the ASAS-NSAID score as a continuous or a binary variable.
Additional files
Abbreviations
- AE:
-
adverse event
- ASAS:
-
Assessment of SpondyloArthritis International Society
- ASDAS-CRP:
-
Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Score on the basis of C-reactive protein
- axSpA:
-
axial spondyloarthritis
- BASDAI:
-
Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Index
- CI:
-
confidence interval
- ITT:
-
intent-to-treat
- NSAID:
-
nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug
- PASS:
-
patient acceptable symptom state
- SpA:
-
spondyloarthritis
- TNF:
-
tumor necrosis factor
References
Dougados M, Baeten D: Spondyloarthritis. Lancet. 2011, 377: 2127-2137. 10.1016/S0140-6736(11)60071-8.
Rudwaleit M, van der Heijde D, Landewe R, Listing J, Akkoc N, Brandt J, Braun J, Chou CT, Collantes-Estevez E, Dougados M, Huang F, Gu J, Khan MA, Kirazli Y, Maksymowych WP, Mielants H, Sørensen IJ, Ozgocmen S, Roussou E, Valle-Oñate R, Weber U, Wei J, Sieper J: The development of Assessment of SpondyloArthritis International Society classification criteria for axial spondyloarthritis (part II): validation and final selection. Ann Rheum Dis. 2009, 68: 777-783. 10.1136/ard.2009.108233.
Rudwaleit M, Haibel H, Baraliakos X, Listing J, Marker-Hermann E, Zeidler H, Braun J, Sieper J: The early disease stage in axial spondylarthritis: results from the German Spondyloarthritis Inception Cohort. Arthritis Rheum. 2009, 60: 717-727. 10.1002/art.24483.
Kiltz U, Baraliakos X, Karakostas P, Igelmann M, Kalthoff L, Klink C, Krause D, Schmitz-Bortz E, Florecke M, Bollow M, Braun J: Do patients with non-radiographic axial spondylarthritis differ from patients with ankylosing spondylitis?. Arthritis Care Res. 2012, 64: 1415-1422. 10.1002/acr.21688.
Ciurea A, Scherer A, Exer P, Bernhard J, Dudler J, Beyeler B, Kissling R, Stekhoven D, Rufibach K, Tamborrini G, Weiss B, Müller R, Nissen MJ, Michel BA, van der Heijde D, Dougados M, Boonen A, Weber U: Tumor necrosis factor alpha inhibition in radiographic and nonradiographic axial spondyloarthritis: results from a large observational cohort. Arthritis Rheum. 2013, 65: 3096-3106. 10.1002/art.38140.
Dougados M, Dijkmans B, Khan M, Maksymowych W, van der Linden S, Brandt J: Conventional treatments for ankylosing spondylitis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2002, 61: iii40-iii50. 10.1136/ard.61.suppl_3.iii40.
Braun J, van den Berg R, Baraliakos X, Boehm H, Burgos-Vargas R, Collantes-Estevez E, Dagfinrud H, Dijkmans B, Dougados M, Emery P, Geher P, Hammoudeh M, Inman RD, Jongkees M, Khan MA, Kiltz U, Kvien T, Leirisalo-Repo M, Maksymowych WP, Olivieri I, Pavelka K, Sieper J, Stanislawska-Biernat E, Wendling D, Ozgocmen S, van Drogen C, van Royen B, van der Heijde D: 2010 update of the ASAS/EULAR recommendations for the management of ankylosing spondylitis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2011, 70: 896-904. 10.1136/ard.2011.151027.
Dougados M, Gueguen A, Nakache JP, Velicitat P, Veys EM, Zeidler H, Calin A: Ankylosing spondylitis: what is the optimum duration of a clinical study? A one year versus a 6 weeks non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug trial. Rheumatology (Oxford). 1999, 38: 235-244. 10.1093/rheumatology/38.3.235.
Dougados M, Behier JM, Jolchine I, Calin A, van der Heijde D, Olivieri I, Zeidler H, Herman H: Efficacy of celecoxib, a cyclooxygenase 2-specific inhibitor, in the treatment of ankylosing spondylitis: a six-week controlled study with comparison against placebo and against a conventional nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drug. Arthritis Rheum. 2001, 44: 180-185. 10.1002/1529-0131(200101)44:1<180::AID-ANR24>3.0.CO;2-K.
Miceli-Richard C, Dougados M: NSAIDs in ankylosing spondylitis. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2002, 20: S65-S66.
Benhamou M, Gossec L, Dougados M: Clinical relevance of C-reactive protein in ankylosing spondylitis and evaluation of the NSAIDs/coxibs’ treatment effect on C-reactive protein. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2010, 49: 536-541. 10.1093/rheumatology/kep393.
Wanders A, Heijde D, Landewe R, Behier JM, Calin A, Olivieri I, Zeidler H, Dougados M: Nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs reduce radiographic progression in patients with ankylosing spondylitis: a randomized clinical trial. Arthritis Rheum. 2005, 52: 1756-1765. 10.1002/art.21054.
Kroon F, Landewe R, Dougados M, van der Heijde D: Continuous NSAID use reverts the effects of inflammation on radiographic progression in patients with ankylosing spondylitis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2012, 71: 1623-1629. 10.1136/annrheumdis-2012-201370.
Poddubnyy D, Rudwaleit M, Haibel H, Listing J, Marker-Hermann E, Zeidler H, Braun J, Sieper J: Effect of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs on radiographic spinal progression in patients with axial spondyloarthritis: results from the German Spondyloarthritis Inception Cohort. Ann Rheum Dis. 2012, 71: 1616-1622. 10.1136/annrheumdis-2011-201252.
Straube S, Tramer MR, Moore RA, Derry S, McQuay HJ: Mortality with upper gastrointestinal bleeding and perforation: effects of time and NSAID use. BMC Gastroenterol. 2009, 9: 41-10.1186/1471-230X-9-41.
Boers M, Tangelder MJ, van Ingen H, Fort JG, Goldstein JL: The rate of NSAID-induced endoscopic ulcers increases linearly but not exponentially with age: a pooled analysis of 12 randomised trials. Ann Rheum Dis. 2007, 66: 417-418. 10.1136/ard.2006.055012.
Scott PA, Kingsley GH, Smith CM, Choy EH, Scott DL: Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and myocardial infarctions: comparative systematic review of evidence from observational studies and randomised controlled trials. Ann Rheum Dis. 2007, 66: 1296-1304. 10.1136/ard.2006.068650.
Farkouh ME, Greenberg BP: An evidence-based review of the cardiovascular risks of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Am J Cardiol. 2009, 103: 1227-1237. 10.1016/j.amjcard.2009.01.014.
Schneider V, Levesque LE, Zhang B, Hutchinson T, Brophy JM: Association of selective and conventional nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs with acute renal failure: a population-based, nested case-control analysis. Am J Epidemiol. 2006, 164: 881-889. 10.1093/aje/kwj331.
Fick DM, Cooper JW, Wade WE, Waller JL, Maclean JR, Beers MH: Updating the Beers criteria for potentially inappropriate medication use in older adults: results of a US consensus panel of experts. Arch Intern Med. 2003, 163: 2716-2724. 10.1001/archinte.163.22.2716.
Rappel des règles de bon usage des AINS. [http://ansm.sante.fr/var/ansm_site/storage/original/application/257d8be960ac8372dbdc513708956d50.pdf]
Braun J, van der Horst-Bruinsma IE, Huang F, Burgos-Vargas R, Vlahos B, Koenig AS, Freundlich B: Clinical efficacy and safety of etanercept versus sulfasalazine in ankylosing spondylitis patients: a randomized, double-blind study (ASCEND Trial). Arthritis Rheum. 2010, 63: 1543-1551. 10.1002/art.30223.
Davis JC, Van Der Heijde D, Braun J, Dougados M, Cush J, Clegg DO, Kivitz A, Fleischmann R, Inman R, Tsuji W: Recombinant human tumor necrosis factor receptor (etanercept) for treating ankylosing spondylitis: a randomized, controlled trial. Arthritis Rheum. 2003, 48: 3230-3236. 10.1002/art.11325.
van der Heijde D, Kivitz A, Schiff MH, Sieper J, Dijkmans BA, Braun J, Dougados M, Reveille JD, Wong RL, Kupper H, Davis JC: Efficacy and safety of adalimumab in patients with ankylosing spondylitis: results of a multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Arthritis Rheum. 2006, 54: 2136-2146. 10.1002/art.21913.
Braun J, Baraliakos X, Listing J, Fritz C, Alten R, Burmester G, Krause A, Schewe S, Schneider M, Sorensen H, Zeidler H, Sieper J: Persistent clinical efficacy and safety of anti-tumour necrosis factor alpha therapy with infliximab in patients with ankylosing spondylitis over 5 years: evidence for different types of response. Ann Rheum Dis. 2008, 67: 340-345. 10.1136/ard.2007.075879.
Sieper J, van der Heijde D, Dougados M, Mease PJ, Maksymowych WP, Brown MA, Arora V, Pangan AL: Efficacy and safety of adalimumab in patients with non-radiographic axial spondyloarthritis: results of a randomised placebo-controlled trial (ABILITY-1). Ann Rheum Dis. 2013, 72: 815-822. 10.1136/annrheumdis-2012-201766.
Song IH, Weiss A, Hermann KG, Haibel H, Althoff CE, Poddubnyy D, Listing J, Lange E, Freundlich B, Rudwaleit M, Sieper J: Similar response rates in patients with ankylosing spondylitis and non-radiographic axial spondyloarthritis after 1 year of treatment with etanercept: results from the ESTHER trial. Ann Rheum Dis. 2013, 72: 823-825. 10.1136/annrheumdis-2012-202389.
Landewe R, Braun J, Deodhar A, Dougados M, Maksymowych WP, Mease PJ, Reveille JD, Rudwaleit M, van der Heijde D, Stach C, Hoepken B, Fichtner A, Coteur G, de Longueville M, Sieper J: Efficacy of certolizumab pegol on signs and symptoms of axial spondyloarthritis including ankylosing spondylitis: 24-week results of a double-blind randomised placebo-controlled phase 3 study. Ann Rheum Dis. 2014, 73: 39-47. 10.1136/annrheumdis-2013-204231.
Haroon N, Inman RD, Learch TJ, Weisman MH, Lee M, Rahbar MH, Ward MM, Reveille JD, Gensler LS: The impact of tumor necrosis factor alpha inhibitors on radiographic progression in ankylosing spondylitis. Arthritis Rheum. 2013, 65: 2645-2654.
Molto A, Paternotte S, Claudepierre P, Breban M, Dougados M: Effectiveness of tumor necrosis factor alpha blockers in early axial spondyloarthritis: data from the DESIR cohort. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2014, 66: 1734-1744. 10.1002/art.38613.
Dougados M, Simon P, Braun J, Burgos-Vargas R, Maksymowych WP, Sieper J, van der Heijde D: ASAS recommendations for collecting, analysing and reporting NSAID intake in clinical trials/epidemiological studies in axial spondyloarthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2011, 70: 249-251. 10.1136/ard.2010.133488.
Garrett S, Jenkinson T, Kennedy LG, Whitelock H, Gaisford P, Calin A: A new approach to defining disease status in ankylosing spondylitis: the Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Index. J Rheumatol. 1994, 21: 2286-2291.
Song IH, Rudwaleit M, Listing J, Sieper J: Comparison of the Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Index and a modified version of the index in assessing disease activity in patients with ankylosing spondylitis without peripheral manifestations. Ann Rheum Dis. 2009, 68: 1701-1707. 10.1136/ard.2008.099226.
Dougados M, Braun J, Vargas RB, Gossec L, Maksymowych W, Sieper J, van der Heijde D: ASAS recommendations for variables to be collected in clinical trials/epidemiological studies of spondyloarthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2012, 71: 1103-1104. 10.1136/annrheumdis-2011-201038.
Anderson JJ, Baron G, van der Heijde D, Felson DT, Dougados M: Ankylosing spondylitis assessment group preliminary definition of short-term improvement in ankylosing spondylitis. Arthritis Rheum. 2001, 44: 1876-1886. 10.1002/1529-0131(200108)44:8<1876::AID-ART326>3.0.CO;2-F.
van der Heijde D, Dougados M, Davis J, Weisman MH, Maksymowych W, Braun J, Hallegua DS, Bruckel J: ASsessment in Ankylosing Spondylitis International Working Group/Spondylitis Association of America recommendations for conducting clinical trials in ankylosing spondylitis. Arthritis Rheum. 2005, 52: 386-394. 10.1002/art.20790.
Tubach F, Pham T, Skomsvoll JF, Mikkelsen K, Bjorneboe O, Ravaud P, Dougados M, Kvien TK: Stability of the patient acceptable symptomatic state over time in outcome criteria in ankylosing spondylitis. Arthritis Rheum. 2006, 55: 960-963. 10.1002/art.22342.
Dougados M, Luo MP, Maksymowych WP, Chmiel JJ, Chen N, Wong RL, Davis JC, van der Heijde D: Evaluation of the patient acceptable symptom state as an outcome measure in patients with ankylosing spondylitis: data from a randomized controlled trial. Arthritis Rheum. 2008, 59: 553-560. 10.1002/art.23527.
van der Heijde D, Lie E, Kvien TK, Sieper J, Van den Bosch F, Listing J, Braun J, Landewe R: ASDAS, a highly discriminatory ASAS-endorsed disease activity score in patients with ankylosing spondylitis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2009, 68: 1811-1818. 10.1136/ard.2008.100826.
Calin A, Garrett S, Whitelock H, Kennedy LG, O’Hea J, Mallorie P, Jenkinson T: A new approach to defining functional ability in ankylosing spondylitis: the development of the Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Functional Index. J Rheumatol. 1994, 21: 2281-2285.
van der Linden S, Valkenburg HA, Cats A: Evaluation of diagnostic criteria for ankylosing spondylitis. A proposal for modification of the New York criteria. Arthritis Rheum. 1984, 27: 361-368. 10.1002/art.1780270401.
Rudwaleit M, Jurik AG, Hermann KG, Landewe R, van der Heijde D, Baraliakos X, Marzo-Ortega H, Ostergaard M, Braun J, Sieper J: Defining active sacroiliitis on magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) for classification of axial spondyloarthritis: a consensual approach by the ASAS/OMERACT MRI group. Ann Rheum Dis. 2009, 68: 1520-1527. 10.1136/ard.2009.110767.
Dougados M, Braun J, Szanto S, Combe B, Geher P, Leblanc V, Logeart I: Nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drug intake according to the Assessment of SpondyloArthritis International Society Score in clinical trials evaluating tumor necrosis factor blockers: example of etanercept in advanced ankylosing spondylitis. Arthritis Care Res. 2012, 64: 290-294. 10.1002/acr.20671.
Dougados M, Braun J, Szanto S, Combe B, Elbaz M, Geher P, Thabut G, Leblanc V, Logeart I: Efficacy of etanercept on rheumatic signs and pulmonary function tests in advanced ankylosing spondylitis: results of a randomised double-blind placebo-controlled study (SPINE). Ann Rheum Dis. 2011, 70: 799-804. 10.1136/ard.2010.139261.
van der Heijde D, Braun J, Dougados M, Sieper J, Pedersen R, Szumski A, Koenig AS: Sensitivity and discriminatory ability of the Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Score in patients treated with etanercept or sulphasalazine in the ASCEND trial. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2012, 51: 1894-1905. 10.1093/rheumatology/kes142.
van der Heijde D, Sieper J, Maksymowych WP, Dougados M, Burgos-Vargas R, Landewe R, Rudwaleit M, Braun J: Update of the international ASAS recommendations for the use of anti-TNF agents in patients with axial spondyloarthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2010, 2011: 905-908.
Poddubnyy D, Haibel H, Listing J, Marker-Hermann E, Zeidler H, Braun J, Sieper J, Rudwaleit M: Cigarette smoking has a dose-dependent impact on progression of structural damage in the spine in patients with axial spondyloarthritis: results from the GErman SPondyloarthritis Inception Cohort (GESPIC). Ann Rheum Dis. 2013, 72: 1430-1432. 10.1136/annrheumdis-2012-203148.
Molto A, Paternotte S, van der Heijde D, Claudepierre P, Rudwaleit M, Dougados M: Evaluation of the validity of the different arms of the ASAS set of criteria for axial spondyloarthritis and description of the different imaging abnormalities suggestive of spondyloarthritis: data from the DESIR cohort. In Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases. 2014/01/07th edition; 2014.
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to thank all patients who participated in this study, as well as all investigators and medical staff at all of the participating centers.
SPARSE study investigators: C Benhamou, F Berenbaum, P Bertin, A Cantagrel, B Combe, E Dernis, P Dieude, L Euller-Zieglar, B Fautrel, P Hilliquin, S Lassoued, L Marguerie, C Miceli, M Nguyen, B Pallot-Prades, G Razjbaum, T Schaeverbeke, M Soubrier, and O Vittecoq.
This study was sponsored by Pfizer Inc. Editorial/medical writing support was provided by Donna McGuire of Engage Scientific Solutions and was funded by Pfizer Inc.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Competing interests
MD has received consulting fees from Pfizer Inc and his department has received research grants from Pfizer Inc for this study; he has also received consulting fees and his department has received research grants from AbbVie, Celgene, Eli Lilly, Novartis, Roche, and Sanofi-Aventis. EW is a full-time employee of Quanticate, contracted and paid by Pfizer Inc to provide statistical input to the study and manuscript. BC has received grants/research support from Pfizer Inc and speakers bureau fees from Lilly, Merck, Novartis, Pfizer Inc, Roche-Chugai, and UCB. TS has received consulting fees from Pfizer Inc and his department has received research grants from Abbvie, BMS, Pfizer Inc, Roche, and UCB. CM-R has received consulting fees and/or research grants from AbbVie, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Janssen, and Pfizer Inc. FB has received grants/research support from Merck, Pfizer Inc, Roche, Bristol-Myers Squibb, and UCB, and consulting fees from AbbVie, Roche, and UCB. NK, AD, and IL are employees of Pfizer Inc. The authors confirm that they have no nonfinancial conflicts of interest to disclose.
Authors’ contributions
MD conceived of the study, participated in its design and coordination, drafted key segments of the manuscript, and oversaw overall content development of the manuscript. EW provided statistical support during the study, performed the post hoc statistical analyses, and helped to draft the manuscript. BC, TS, CM-R, and FB were study investigators and helped to draft the manuscript. NK and AD participated in the coordination of the study and helped draft the manuscript. IL conceived of the study, participated in its design and coordination, and helped draft the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Emily Wood, Bernard Combe, Thierry Schaeverbeke, Francis Berenbaum, Nandan Koppiker, Arnaud Dubanchet and Isabelle Logeart contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
13075_2014_481_MOESM1_ESM.doc
Additional file 1: Table S1.: presenting a summary of missing NSAID diary data at baseline and during the double-blind period. Intention-to-treat population. (DOC 53 KB)
13075_2014_481_MOESM2_ESM.pdf
Additional file 2: Figure S1.: showing the proportion of patients in the etanercept/etanercept and placebo/etanercept groups achieving clinical endpoints during the double-blind and open-label periods: (A) ASAS partial remission; (B) BASDAI50 response; (C) ASAS20 response; (D) ASAS40 response; and (E) PASS. Observed cases. (PDF 794 KB)
Authors’ original submitted files for images
Below are the links to the authors’ original submitted files for images.
Rights and permissions
This article is published under an open access license. Please check the 'Copyright Information' section either on this page or in the PDF for details of this license and what re-use is permitted. If your intended use exceeds what is permitted by the license or if you are unable to locate the licence and re-use information, please contact the Rights and Permissions team.
About this article
Cite this article
Dougados, M., Wood, E., Combe, B. et al. Evaluation of the nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug-sparing effect of etanercept in axial spondyloarthritis: results of the multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled SPARSE study. Arthritis Res Ther 16, 481 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13075-014-0481-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s13075-014-0481-5