Abstract
The molecular structure of the 2-(4-oxo-3-phenylthiazolidin-2-ylidene) malononitrile (3) is calculated using DFT B3LYP/6-311G(d, p) method. The calculated geometric parameters are in good agreement with the experimental data. The NBO calculations were performed to predict the natural atomic charges at the different atomic sites and study the different intramolecular charge transfer (ICT) interactions occurring in the studied system. The BD(2)C17–C19 → BD*(2)C14–C15, LP(2)O2 → BD*(1)N5–C9 and LP(1)N5 → BD*(2)C10–C11 ICT interactions causing stabilization of the system by 23.30, 30.63 and 52.48 kcal/mol, respectively. The two intense electronic transition bands observed experimentally at 249 nm and 296 nm are predicted using the TD-DFT calculations at 237.9 nm (f = 0.1618) and 276.4 nm (f = 0.3408), respectively. These electronic transitions are due to H-3 → L (94%) and H → L (95%) excitations, respectively.

Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Thiazoles are an important class of heterocyclic compounds that possess the sulphur and nitrogen beside carbon atoms in its five member ring [1]. They are part of a number of pharmaceutical drugs that have analgesic (meloxicam) [2], antihistamine (nizatidine) [3], antibacterial (penicillin) [4], antifungal (thiabendazole) [5], antiprotozoal [6], and a number of other biological properties [1]. They are also part of the essential vitamin B1 or thiamine [7]. In the past, several thiazolidine derivatives have been synthesized and their molecular structural properties have been studied both experimentally and theoretically [8]. In this article we have selected a thiazole based derivative that we have synthesized previously and here we performed density functional theory (DFT) based calculation for its molecular structure [9,10,11]. The current studied will provide more chemical information about our previously synthesized compound that has good biological activities. These current theoretical studies will further assist in the design and syntheses of better bioactive analogues of thiazole in the future. The 2-(4-oxo-3-phenyl-1,3-thiazolidin-2-yl-idene)malononitrile is a thiazole based derivative that possess several biological properties [10]. We calculated both electronic and spectroscopic properties and compared with previous experimental results of its crystal structure [9, 10, 12, 13]. From the density functional theory (DFT) based calculations we predicted its non-linear optical properties etc. that are discussed below [10]. The DFT will provide information about geometry of the molecule, different orbitals calculations like frontier molecular orbitals will provide information about the π electronic system and intramolecular charge transfer, natural bond orbitals will provide information about different bond interactions and their energies. Similarly, molecular electrostatic potential shows the reactive and non-reactive centers in the molecules while the ultra-violet visible (UV–Vis) spectrum and infra-red (IR) spectrum will also be obtained from these calculations.
Computational methods
Quantum chemical calculations
The DFT calculations for the thiazole derivative was performed with the hybrid function of B3LYP and basis set of 6-311G(d, p) [14,15,16] present in Gaussian 03 software [10, 17]. The coordinates file of the X-ray crystal structure of the thiazole derivative (compound 3) was downloaded from the online repository [10, 18]. The molecular geometry of the compound 3 was optimized through the energy minimization process without any geometrical parameters constraints [10]. The Gauss View 4.1 [19] and Chemcraft [20] softwares were used for drawing the refined structure of the compound 3 [10]. The energy minima of the optimized geometry of the selected molecule was established as there were no imaginary frequency modes. The electronic, orbital bonding and spectral properties of the selected molecule were also computed through DFT method [21,22,23]. The natural bond orbital and molecular electrostatic potential analyses for the thiazole derivative was carried out using the B3LYP/6-311G (d, P) level [14,15,16]. The NBO analyses provides the intramolecular interaction inside the thiazole derivative, stabilization energies and bond interactions. The second order perturbation energy calculation provided the donor and acceptor energies [21,22,23]. The molecular electrostatic potential analysis produced the most reactive sites in a molecule and thus it is easy to predict the electrophilic and nucleophilic attack sites.
Docking studies
The molecular docking was executed on the molecular operating environment (MOE) 2014.09 software [24,25,26]. The atomic coordinates of the human B-lactate dehydrogenase in complex with oxidized form of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide and 4-hydroxy-1,2,5-oxadiazole-3-carboxylic acid having PDB ID Number 1T2F was downloaded from protein data bank website [27]. The structure of the protein and the selected ligand was optimized, and energy minimization was performed. The binding pockets in the protein receptor were determined with site finder module of MOE [24, 25]. The efficiency of the docking program was gauged by re-docking the original ligand into the established receptor active site for the determination of root mean square deviation (RMSD) [26]. After that, the malononitrile compound 3 was docked with the receptor protein and the conformer with best docking score and free energy was selected [26, 28].
Results and discussion
Chemistry
Malononitrile was stirred with phenyl isothiocyanate in K2CO3 in dimethylfluoride to afford an intermediary anionic compound 2, which on reacting with ethyl chloroacetate forming the targeted molecule 3 [9] (Fig. 1a).
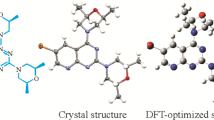
a Synthesis of thiazole derivative 3 [9]. b Optimized chemical structure of the malononitrile analogue
Optimization of the compound geometry
The optimized molecular structure bond lengths and their angles were calculated through the hybrid function of B3LYP with 6-311G(d, p) basis set as tabulated in Table 1; and compared with the experimentally determined optimized molecular structure from the literature [9, 29]. This compound possess C1 point group and its optimized structural information were compared with the crystallographic information file (CIF) [9, 10]. All the predicted geometric parameters agree with the experimental results. The bond distances of the compound 3 are a little overestimated except the C11‒C12 bond which is shorter by 0.009 Å than the experimental one [30]. The main deviations in the values of calculated from the experimental bond length and angle are 0.041 Å (S1–C) and 1.3° (O2–C9–C6), respectively [30]. The predicted values of C‒C‒C bond angle of the phenyl ring of compound 3 are in the range of 119.1‒120.3° while the experimental values are 117.9‒120.8° [10, 31]. The calculated dihedral angles of the phenyl and thiazole rings of this molecule are close to 0° showing a planar structure [10] (Fig. 1b).
Natural atomic charge on the molecule
The charge distribution over a molecule has pivotal role in quantum chemistry. The atomic charges are related to the electronic density, charge distribution and dipole moment of a compound. The natural atomic charges (NAC) computed through DFT at the different atomic positions are tabulated in Table 2. The studied molecule has oxygen, nitrogen and sulfur-heteroatoms. The O and N-atoms are the most electronegative atomic spots in the malononitrile analogue [33]. In contrast, the S-atom is electropositive. The calculated natural atomic charge for the two N-sites of the nitrile groups (N3 and N4) are approximately equivalent [33]. While the NAC at the thiazole nitrogen atom is more negative than the N-atoms of the nitrile group. In the present compound 3, all the H-atoms are electropositive whereas the aliphatic protons (H7 and H8) are more positively charged than the aromatic ones [33]. The NAC on the aliphatic and aromatic protons are 0.2437 and 0.2080–0.2146, respectively. Most of the aromatic C-atoms are electronegative except C14 as this carbon bonded to the high electronegative N5-atom [34]. The most electropositive C-atom in the molecule is the carbonyl carbon [32].
Molecular electrostatic potential
The distribution of charge and its related properties of compounds can be obtained through the 3D electrostatic potential maps. The electrostatic potential map was produced by overlapping the Van der Waal’s radii of each atoms present in the compound 3 so that it reveals the charged surface and thus one can visualize the morphological properties of the molecule [10, 35, 36]. Through these maps, we can forecast the reactive spots for electrophilic as well as the nucleophilic attack during the chemical reactions [10, 37, 38]. The malononitrile derivative electrostatic potential map was predicted through the same DFT hybrid function and basis set as other parameters were measured and is presented in Fig. 2. The charged surface map in Fig. 2 showed that the negative regions (red) contain the N3 and N4 atoms of the nitrile group, showing that these N-sites are the hot spots for electrophilic attack. While the blue regions in Fig. 2 represent the positive regions that contain the area of H7, H8 and C6-atoms of the compound 3 and are the hot spot of nucleophilic attacks. These results gave information about how compound 3 interact with receptor active sites.
Nonlinear optical properties
The nonlinear optical materials are important for photonic communications due to its use light for data transmission and thus are an actively used in industry nowadays [39,40,41]. Many organic based compounds are used in photonic communication instruments due to their superior polarizability (α0) and lower energy gap (ΔE) between their highest occupied and lowest unoccupied molecular orbitals [40,41,42]. Here the α0 and ΔE values of the thiazole based malononitrile derivative are 162.89 Bohr3 and 4.6905 eV, while the polarizability value is approximately six times that of urea. Based on our calculations it has lower ΔE than urea. Thus, this thiazole based compound has superior nonlinear optical qualities than the reference molecules [33, 43, 44].
Frontier molecular orbitals (FMOs) of the malononitrile analogue
The electronic densities of FMOs are helpful in predicting the reactive positions and different reaction types for a π-electron systems containing molecules [33, 43]. Further, the energies of the two types of orbitals (EHOMO and ELUMO) and their ΔE of a molecule showed its inherent chemical reactivity and intramolecular charge transfer (ICT) capacities [32, 45,46,47,48]. The ΔE for the FMOs of the thiazole based compound 3 was calculated through the hybrid function of B3LYP/6‒311G (d, p) and its FMOs picture is presented in Fig. 3 [32]. It was observed that the molecular orbitals level are delocalized over the five member ring of the compound and the C10–C11–C–N π-electronic systems. The EHOMO is − 6.9947 eV while ELUMO is − 2.3043 eV. The orbitals ΔE signifies a lower energy electronic transition with a value of 4.6905 eV for the thiazole based compound under study. This ICT of electron transition happens due to π–π* excitations. The 40 spin allowed singlet–singlet electronic transitions predicted are tabulated in Additional file 1: Table S1 and the electronic spectrum is presented in Additional file 1: Figure S4 [49]. Experimentally there are two intense electronic transition bands that are observed at 249 nm and 296 nm. On the basis of DFT calculations, these electronic spectral bands were observed at 237.9 nm (f = 0.1618) and 276.4 nm (f = 0.3408) on the spectrum and these can be assigned to the excitation from H-3 → L (94%) and H → L (95%) respectively.
Electronic density surface plots at ground state for the FMOs of thiazole based malononitrile analogue. The molecular orbitals level are delocalized over the five member thiazole ring and the attached cyanate groups. Green represent negative values of the orbital overlap, dark red represents positive values of the orbitals overlap [50]
Natural bond orbital (NBO) analysis
The stabilization energies E(2) for the relevant intra-molecular charge transfer contacts were calculated through the NBO method (Table 3) [51, 52]. The different types of interactions between filled and empty orbitals in a complex molecule can be used to measure the intra-molecular electronic density delocalization. A larger stabilization energy showed high rate of electronic exchange between donor and acceptor NBOs, i.e. higher the amount of conjugation inside the molecule [53]. The second-order perturbation theory is used to describe the energetics of such interactions [10, 54, 55]. The intramolecular charge transfer exchange as a result of the orbital overlap between π → π*, n → σ* and n → π* orbitals helps in stabilization of the molecular system up to 23.30, 30.63 and 52.48 kcal/mol respectively, which are due to BD(2)C17–C19 → BD*(2)C14–C15, LP(2)O2 → BD*(1)N5–C9 and LP(1)N5 → BD*(2)C10–C11 ICT interactions, respectively [10]. These predicted results showed that there is strong electronic density spread from LP(1)N5 to the nearby C10–C11π*-NBO. Further, there is a π → π* electron delocalization between the nitrile group π-system to the nearby π*-NBO of the C10–C11 bond in this thiazole based compound.
Vibrational spectrum analyses
The IR vibrational spectrum of the malononitrile analogue were computed through the same hybrid function and basis set as described previously and the vibrational modes were assigned through visual inspection through the GaussView software [10, 17, 56]. The comparison between theoretically computed and the experimental vibrational band frequencies of the compound 3 are tabulated in Additional file 1: Table S2 and the IR spectrum is shown in Fig. 5 [10]. The Additional file 1: Table S2 showed that there is close resemblance between the two IR vibrational frequencies [10, 57].
Aromatic C–H bending vibrations
The thiazole ring of the malononitrile derivative posseses the carbon–hydrogen stretching vibrations in 3100–3000 cm−1 region [10, 58]. In this study, the IR band recognized for the C–H stretching vibrations at 3042 cm−1 is present at 3097–3070 cm−1 [10, 59]. The in-plane and out-of-plane ring C–H bending vibrations bands are predicted in the region 1400–1000 and 1000–600 cm−1 respectively [10, 60, 61]. The DFT analyses also showed that the in-plane bending modes are at 1475, 1438, 1305, 1158, 1148, 1128, 1067 and 1013 cm−1 (exp. 1461, 1291, 1157 and 1024 cm−1) [10]. Few of the in-plane C–H bending vibrational modes mixed with other bands [62]. On other hand, the out-of-plane bending modes for C–H are present at 980–904, 817, 739 and 684 cm−1 (exp. 991, 911, 791 and 698 cm−1) [10]. Thus our theoretical calculated C–H vibrational frequencies agree very well with experimental data.
Aliphatic C–H vibrations of the thiazole ring
The compound under investigation has one methylene group at the thiazole ring. It will therefore exhibits two aliphatic C–H stretching vibration at lower frequencies in the spectrum than those of the aromatic C–H ring vibrations [63,64,65]. Both the symmetric and asymmetric stretching vibrations of the CH2 group are present at 3027 (exp. 2997 cm−1) and 2979 cm−1 (exp. 2944 cm−1), in the computed vibrational spectrum [62, 66, 67]. The theoretically computed CH2 scissoring, wagging, twisting and rocking vibrations are present at 1410 cm−1 (exp. 1384 cm−1), 1285 cm−1 (exp. 1234 cm−1), 1109 cm−1 and 888 cm−1 (exp. 886 cm−1), respectively [10, 64].
C≡N vibrations
Generally the nitrile stretching vibration is present at 2250 ± 10 cm−1 in saturated nitriles or in olefinic nitriles where no conjugation exists between the nitrile and the olefinic group [68, 69]. While in conjugated nitrile, the band moves to lower frequency of 2225 ± 7 cm−1 [69, 70]. Here in this molecule, there are two nitrile groups attached to the C=C so the symmetric and asymmetric υC≡N modes are predicted at 2251 and 2241 cm−1 [71]. In agreement with literature, the υC≡N mode observed experimentally at 2215 cm−1. In the IR spectrum of this compound 3, the symmetric and asymmetric δC–C≡N modes were predicted at 602 and 462 cm−1 (exp. 468 cm−1), respectively. Furthermore, the nitrile group out-of-plane torsion mode has a predicted at 454 cm−1 (exp. 453 cm−1) [10, 64, 65, 72].
C=O, C=C and C–S vibrations
In compounds that have aromaticity, the C=C stretching vibrations is mostly present at 1600–1500 cm−1 [63, 73]. In the current system, these stretching vibrations are predicted at 1587–1438 cm−1 while experimentally observed at 1597–1461 cm−1 [10]. We also found that the aromatic rings breathing modes are at 987 cm−1 (exp. 999 cm−1) [10]. We noted, the υ(C10=C11) stretching mode at 1520 cm−1 while experimentally it is observed at 1527 cm−1 [10]. The malononitrile analogue showed intense carbonyl vibration observed experimentally at 1745 cm−1 (calc. 1769 cm−1). The thiazole ring C–S stretching vibrational frequency mode is calculated at 758 cm−1 while it is experimentally noted at 757 cm−1 [69].
Molecular docking
Lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) has an active role in the metabolism of lactate during normal physiological process [74, 75]. The high levels of lactate are associated in different ways to several types of human cancers, as cancerous cells have increased metabolism [75]. The increase level of lactate ion may directly contributes to tumor growth and progression [75]. Molecular docking was conducted to find out the interaction of 2-(4-oxo-3-phenylthiazolidin-2-ylidene) malononitrile with the lactate dehydrogenase enzyme. The malononitrile derivative has good affinity for the LDH enzyme showing a total free energy of − 4.6 kcal/mol on its interaction. It is clearly the cyano moiety that is the highly active group in the malononitrile by making two hydrogen acceptor interactions with Arg 106 with − 3.0 kcal/mol and one hydrogen acceptor interaction with Thr 248 with − 1.6 kcal/mol (Figs. 4, 5).
Pharmacophore studies
The pharmacophore analyses was done with the MOE software package (version 2014.010) using the default settings. The different conformers production for the under test ligand was carried out using the conformational analysis algorithm, present in the MOE software package [76]. Pharmacophore modeling tools determine the different chemical properties and spatial arrangement in three dimensions that are essential for interaction between ligand and its receptor and thus for the drug action. Pharmacophore models can be generated from the structural data of protein–ligand complexes as well as from ligands when no receptor information is available and also from the receptor structure when no ligands are available. The generated models are usually used for virtual screening of online libraries of compounds that are the potentially active molecules. Also, the pharmacophoric feature may represent a specific property and is not necessarily related to a particular chemical structure; but different chemical groups may share the same property and possesses the same feature (Fig. 6 and Table 4) [77, 78].
Conclusions
The chemical structure of the 2-(4-oxo-3-phenylthiazolidin-2-ylidene) malononitrile was optimized through the hybrid B3LYP method and 6-311G (d, p) basis set. The predicted geometrical parameters of the malononitrile derivative agree well with the previous experimental results. From this study it was observed that this malononitrile compound has superior non-linear optical properties than urea. Thus, it can be used in photonic communication instruments.
Abbreviations
- DFT:
-
density functional theory
- B3LYP:
-
Becke, 3-parameter, Lee–Yang–Parr
- CIF:
-
crystallographic information file
- MOE:
-
molecular operating environment
- PDB:
-
protein data bank
- RMSD:
-
root mean square deviation
- K2CO3 :
-
potassium carbonate
- HOMO:
-
highest occupied molecular orbitals
- LUMO:
-
lowest unoccupied molecular orbitals
- NBO:
-
natural bond orbitals
- NAC:
-
natural atomic charge
- FMO:
-
frontier molecular orbital
- eV:
-
electron volt
- MEP:
-
molecular electrostatic potential
- ICT:
-
intramolecular charge transfer
References
Rouf A, Tanyeli C (2015) Bioactive thiazole and benzothiazole derivatives. Eur J Med Chem 97:911–927
Cheney ML, Weyna DR, Shan N, Hanna M, Wojtas L, Zaworotko MJ (2010) Supramolecular architectures of meloxicam carboxylic acid cocrystals, a crystal engineering case study. Cryst Growth Des 10:4401–4413. https://doi.org/10.1021/cg100514g
Knadler MP, Bergstrom RF, Callaghan JT, Rubin A (1986) Nizatidine, an H2-blocker. Its metabolism and disposition in man. Drug Metab Dispos 14:175–182
Ozcengiz G, Demain AL (2013) Recent advances in the biosynthesis of penicillins, cephalosporins and clavams and its regulation. Biotechnol Adv 31:287–311
Robinson HJ, Phares HF, Graessle OE (1978) The toxicological and antifungal properties of thiabendazole. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 1:471–476. https://doi.org/10.1016/0147-6513(78)90015-5
Álvarez G, Varela J, Cruces E, Fernández M, Gabay M, Leal SM, Escobar P, Sanabria L, Serna E, Torres S, Thiel SJF, Yaluff G, De Bilbao NIV, Cerecetto H, González M (2015) Identification of a new amide-containing thiazole as a drug candidate for treatment of Chagas’ disease. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 59:1398–1404. https://doi.org/10.1128/AAC.03814-14
Gangolf M, Czerniecki J, Radermecker M, Detry O, Nisolle M, Jouan C, Martin D, Chantraine F, Lakaye B, Wins P, Grisar T, Bettendorff L (2010) Thiamine status in humans and content of phosphorylated thiamine derivatives in biopsies and cultured cells. PLoS ONE 5:e13616. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0013616
Zhang Y, Li P, Fan X, Jin L (2014) Crystal structure of (Z)-2-hydroxy-N′-(4-oxo-1,3-thiazolidin-2-ylidene)benzohydrazide. Acta Crystallogr Sect E Struct Rep Online 70:o1167. https://doi.org/10.1107/s1600536814022351
Farhat MF, El-Saghier AMM, Makhlouf MA, Kreddan KM, Elmezoughi AB (2007) Ketene N,S-acetals in heterocyclic synthesis: part 1: synthesis of N-phenyl-2-ylidene and 2,5-diylidene-4-thiazolidinone derivatives. J Sulfur Chem 28:563–572. https://doi.org/10.1080/17415990701586823
Barakat A, Soliman SM, Al-Majid AM, Lotfy G, Ghabbour HA, Fun HK, Yousuf S, Choudhary MI, Wadood A (2015) Synthesis and structure investigation of novel pyrimidine-2,4,6-trione derivatives of highly potential biological activity as anti-diabetic agent. J Mol Struct 1098:365–376. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molstruc.2015.06.037
Naseem S, Khalid M, Tahir MN, Halim MA, Braga AAC, Naseer MM, Shafiq Z (2017) Synthesis, structural, DFT studies, docking and antibacterial activity of a xanthene based hydrazone ligand. J Mol Struct 1143:235–244. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molstruc.2017.04.093
Sakka OK, Fleita DH, Harrison WTA (2013) 2-(4-Oxo-3-phenyl-1,3-thiazolidin-2-ylidene)malononitrile. Acta Crystallogr E Struct Rep Online 69:o350. https://doi.org/10.1107/s160053681300216x
Ahmad MS, Khalid M, Shaheen MA, Tahir MN, Khan MU, Braga AAC, Shad HA (2018) Synthesis and XRD, FT-IR vibrational, UV–vis, and nonlinear optical exploration of novel tetra substituted imidazole derivatives: a synergistic experimental-computational analysis. J Phys Chem Solids 115:265–276. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpcs.2017.12.054
Curtiss LA, Raghavachari K, Trucks GW, Pople JA (1991) Gaussian-2 theory for molecular-energies of 1st-row and 2nd-row compounds. J Chem Phys 94:7221–7230
McGrath MP, Radom L (1991) Extension of Gaussian-1 (G1) theory to bromine-containing molecules. J Chem Phys. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.460367
Curtiss LA, McGrath MP, Blaudeau JP, Davis NE, Binning RC, Radom L (1995) Extension of Gaussian-2 theory to molecules containing third-row atoms Ga-Kr. J Chem Phys. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.470438
Frisch MJ, Trucks GW, Schlegel HB, Scuseria GE, Robb MA, Cheeseman JR, Montgomery JAJ, Vreven T, Kudin KN, Burant JC, Millam JM, Iyengar SS, Tomasi J, Barone V, Mennucci B, Cossi M, Scalmani G, Rega N, Petersson GA, Nakatsuji H, Hada M, Ehara M, Toyota K, Fukuda R, Hasegawa J, Ishida M, Nakajima T, Honda Y, Kitao O, Nakai H, Klene M, Li X, Knox JE, Hratchian HP, Cross JB, Bakken V, Adamo C, Jaramillo J, Gomperts R, Stratmann RE, Yazyev O, Austin AJ, Cammi R, Pomelli C, Ochterski JW, Ayala PY, Morokuma K, Voth GA, Salvador P, Dannenberg JJ, Zakrzewski VG, Dapprich S, Daniels AD, Strain MC, Farkas O, Malick DK, Rabuck AD, Raghavachari K, Foresman JB, Ortiz JV, Cui Q, Baboul AG, Clifford S, Cioslowski J, Stefanov BB, Liu G, Liashenko A, Piskorz P, Komaromi I, Martin RL, Fox DJ, Keith T, Al-Laham MA, Peng CY, Nanayakkara A, Challacombe M, Gill PMW, Johnson B, Chen W, Wong MW, Gonzalez C, Pople JA (2004) Gaussian 03, Revision C.02, vol 24. Gaussian Inc, Wallingford. ISBN 9788578110796
Akkurt M, El-Saghier AM, Younes SH, Horton PN, Albayati MR (2013) 2-(4-Oxo-3-phenyl-1,3-thia-zolidin-2-yl-idene)propanedi-nitrile. Acta Crystallogr E Struct 69:o1313. https://doi.org/10.1107/s1600536813018308
Frisch A, Nielsen AB, Holder AJ (2000) Gaussview users manual. Gaussian Inc., Wallingford
Zhurko GA, Zhurko DA (2017) Chemcraft. Lite Version Build 08. Available online: http://www.chemcraftprog.com/
Laurent AD, Jacquemin D (2013) TD-DFT benchmarks: a review. Int J Quantum Chem 113:2019–2039
Glendening ED, Badenhoop JK, Reed AD, Carpenter JE, Weinhold F (1996) NBO 3.1. Theoretical Chemistry Institute, University of Wisconsin, Madison, WI
Ghiasuddin, Akram M, Adeel M, Khalid M, Tahir MN, Khan MU, Asghar MA, Ullah MA, Iqbal M (2018) A combined experimental and computational study of 3-bromo-5-(2,5-difluorophenyl) pyridine and 3,5-bis(naphthalen-1-yl)pyridine: insight into the synthesis, spectroscopic, single crystal XRD, electronic, nonlinear optical and biological properties. J Mol Struct 1160:129–141. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molstruc.2018.01.100
MOE (Molecular Operating Environment) (2009), Vol 2009.10 Re. Available online: http://www.chemcomp.com
Chemical Computing Group Inc (2004) Molecular operating environment (MOE). Sci Comput Instrum 22:32. https://doi.org/10.1017/cbo9781107415324.004
Gomha SM, Abbas IM, Elneairy MAA, Mahmoud ME, Mabrouk BKA (2017) Synthesis, molecular docking and pharmacological study of pyrimidothiadiazinones and its bis-derivatives. Lett Drug Des Discov 14:434–443
Cameron A, Read J, Tranter R, Winter VJ, Sessions RB, Brady RL, Vivas L, Easton A, Kendrick H, Croft SL, Barros D, Lavandera JL, Martin JJ, Risco F, Garcia-Ochoa S, Gamo FJ, Sanz L, Leon L, Ruiz JR, Gabarro RFG (2004) Identification and activity of a series of azole-based compounds with lactate dehydrogenase-directed anti-malarial activity. J Biol Chem 279:31429–31439. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.m402433200
Khan MU, Khalid M, Ibrahim M, Braga AAC, Safdar M, Al-Saadi AA, Janjua MRSA (2018) First theoretical framework of triphenylamine–dicyanovinylene-based nonlinear optical dyes: structural modification of π-linkers. J Phys Chem C 122:4009–4018. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jpcc.7b12293
Kurt M, Yurdakul M (2005) Molecular structure and vibrational spectra of lepidine and 2-chlorolepidine by density functional theory and ab initio Hartree–Fock calculations. J Mol Struct THEOCHEM 730:59–67
Mabkhot YN, Aldawsari FD, Al-showiman SS, Barakat A, Soliman SM, Choudhary MI, Yousuf S, Mubarak MS, Hadda TB (2015) Novel enaminone derived from thieno [2, 3-b] thiene: synthesis, x-ray crystal structure, HOMO, LUMO, NBO analyses and biological activity. Chem Cent J 9:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13065-015-0100-9
Kurt M, Yurdakul M, Yurdakul Ş (2004) Molecular structure and vibrational spectra of 3-chloro-4-methyl aniline by density functional theory and ab initio Hartree–Fock calculations. J Mol Struct THEOCHEM 711:25–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.theochem.2004.07.034
Barakat A, Al-Majid AM, Soliman SM, Mabkhot YN, Ali M, Ghabbour HA, Fun H-K, Wadood A (2015) Structural and spectral investigations of the recently synthesized chalcone (E)-3-mesityl-1-(naphthalen-2-yl) prop-2-en-1-one, a potential chemotherapeutic agent. Chem Cent J 9:35. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13065-015-0112-5
Barakat A, Al-Najjar HJ, Al-Majid AM, Soliman SM, Mabkhot YN, Ghabbour HA, Fun HK (2015) Synthesis and molecular characterization of 5,5′-((2,4-dichlorophenyl)methylene)bis(1,3-dimethylpyrimidine-2,4,6(1H,3H,5H)-trione). J Mol Struct 1084:207–215. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molstruc.2014.12.030
Islam MS, Barakat A, Al-Majid AM, Soliman SM, Ghabbour HA, Fun HK (2015) Crystal structure of 7,11-bis(2,4-dichlorophenyl)-2,4-dimethyl-2,4- diazaspiro[5.5]undecane -1,3,5,9-tetraone and its computational studies. J Chem Sci 127:2039–2050. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12039-015-0969-9
Mottishaw JD, Erck AR, Kramer JH, Sun H, Koppang M (2015) Electrostatic potential maps and natural bond orbital analysis: visualization and conceptualization of reactivity in Sangers reagent. J Chem Educ 92:1846–1852. https://doi.org/10.1021/ed5006344
Hinze SR, Williamson VM, Deslongchamps G, Shultz MJ, Williamson KC, Rapp DN (2013) Textbook treatments of electrostatic potential maps in general and organic chemistry. J Chem Educ 90:1275–1281. https://doi.org/10.1021/ed300395e
Politzer P, Murray JS (1996) Relationships of electrostatic potentials to intrinsic molecular properties, vol 3. Elsevier, Amsterdam. ISBN 9780444823533
Scrocco E, Tomasi J (1979) Electronic molecular structure, reactivity and intermolecular forces: an euristic interpretation by means of electrostatic molecular potentials. Adv Quantum Chem 11:115–193. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0065-3276(08)60236-1
Suresh S, Ramanand A, Jayaraman D, Mani P (2012) Review on theoretical aspect of nonlinear optics. Rev Adv Mater Sci 30:175–183
Geskin VM, Lambert C, Brédas JL (2003) Origin of high second- and third-order nonlinear optical response in ammonio/borato diphenylpolyene zwitterions: the remarkable role of polarized aromatic groups. J Am Chem Soc 125:15651–15658. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja035862p
Abbotto A, Beverina L, Manfredi N, Pagani GA, Archetti G, Kuball H-G, Wittenburg C, Heck J, Holtmann J (2009) Second-order nonlinear optical activity of dipolar chromophores based on pyrrole-hydrazono donor moieties. Chem Eur J 15(6175–6185):S6175/1–S6175/11. https://doi.org/10.1002/chem.200900287
Waskasi MM, Hashemianzadeh SM, Mostajabi Sarhangi O, Harzandi AP (2012) Computational model of hydrogen production by Coumarin-dye-sensitized water splitting to absorb the visible light in a local electric field. Energy Convers Manag 62:154–164. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enconman.2012.03.014
Fukui K, Yonezawa T, Shingu H (1952) A molecular orbital theory of reactivity in aromatic hydrocarbons. J Chem Phys 20:722–725. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1700523
Kato S (2000) Perspective on “A molecular orbital theory of reactivity in aromatic hydrocarbons”. Theor Chem Acc Theory Comput Model 103:219–220. https://doi.org/10.1007/s002149900031
Suresh DM, Sajan D, Diao Y-P, Němec I, Hubert Joe I, Bena Jothy V (2013) Structural conformations and density functional study on the intramolecular charge transfer based on vibrational spectra of 2,4-dihydroxy-N′-(4-methoxybenzylidene)benzohydrazide. Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc 110:157–168. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2013.01.067
Ravikumar C, Joe IH, Jayakumar VS (2008) Charge transfer interactions and nonlinear optical properties of push–pull chromophore benzaldehyde phenylhydrazone: a vibrational approach. Chem Phys Lett 460:552–558. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cplett.2008.06.047
Saranya G, Kolandaivel P, Senthilkumar K (2013) Opto-electronic properties of low band gap fused-ring thieno[3,4-b]pyrazine analogues—a theoretical study. Mol Phys 111:3036–3046. https://doi.org/10.1080/00268976.2013.766368
Vijayan N, Rani N, Bhagavannarayana G, Haranath D, Jayabharathi J, Wahab MA, Das S (2012) Optical, elemental and structural analyses of acetoacetanilide single crystals for nonlinear optical applications. Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc 93:75–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2012.02.077
Wazzan NA (2016) Charge transfer complexes between 2-, 3-and 4-aminopyridines and some π-acceptors in the gas phase and in chloroform: DFT calculations. J Theor Comput Chem 15:1650029. https://doi.org/10.1142/s0219633616500292
Wu C, De Visscher A, Gates DI (2017) Molecular interactions between 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium tetrafluoroborate and model naphthenic acids: a DFT study. J Mol Liq 243:462–471
Chamundeeswari SPV, Samuel ERJJ, Sundaraganesan N (2011) Theoretical and experimental studies on 2-(2-methyl-5-nitro-1-imidazolyl)ethanol. Eur J Chem 2:136–145. https://doi.org/10.5155/eurjchem.2.2.136-145.169
Barakat A, Islam MS, Al-Majid AM, Ghabbour HA, Yousuf S, Ashraf M, Shaikh NN, Iqbal Choudhary M, Khalil R, Ul-Haq Z (2016) Synthesis of pyrimidine-2,4,6-trione derivatives: anti-oxidant, anti-cancer, α-glucosidase, β-glucuronidase inhibition and their molecular docking studies. Bioorg Chem 68:72–79. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bioorg.2016.07.009
Sebastian S, Sundaraganesan N (2010) The spectroscopic (FT-IR, FT-IR gas phase, FT-Raman and UV) and NBO analysis of 4-Hydroxypiperidine by density functional method. Spectrochim Acta Mol Biomol Spectrosc. 75:941–952. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2009.11.030
Hubert Joe I, Kostova I, Ravikumar C, Amalanathan M, Pînzaru SC (2009) Theoretical and vibrational spectral investigation of sodium salt of acenocoumarol. J Raman Spectrosc 40:1033–1038. https://doi.org/10.1002/jrs.2226
Helgaker T, Jørgensen P, Olsen J (2000) Molecular electronic-structure theory. Wiley, New York. ISBN 9781118531471
Krishnakumar V, Prabavathi N (2008) Simulation of IR and Raman spectral based on scaled DFT force fields: a case study of 2-amino 4-hydroxy 6-trifluoromethylpyrimidine, with emphasis on band assignment. Spectrochim Acta Mol Biomol Spectrosc 71:449–457. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2007.12.033
Mirzaei M (2010) A computational NMR study of boron phosphide nanotubes. Zeitschrift fur Naturforsch A J Phys Sci. 65:844–848. https://doi.org/10.1515/zna-2010-1010
Varsanyi G (1974) Vibrational spectra of 700 benzene derivatives, vol I, II. AkademiciKiaclo, Budapest
Barakat A, Al-Najjar HJ, Al-Majid AM, Soliman SM, Mabkhot YN, Shaik MR, Ghabbour HA, Fun HK (2015) Synthesis, NMR, FT-IR, X-ray structural characterization, DFT analysis and isomerism aspects of 5-(2,6-dichlorobenzylidene)pyrimidine-2,4,6(1H,3H,5H)-trione. Spectrochim Acta Mol Biomol Spectrosc 147:107–116. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2015.03.016
Varsányi G (2012) Vibrational spectra of benzene derivatives. Academic Press, New York. ISBN 0323150667
Nyquist RA, Kagel RO (1971) Handbook of infrared and Raman spectra of inorganic compounds and organic salts. Academic Press, New York. ISBN 9780125234504
El-Faham A, Soliman SM, Osman SM, Ghabbour HA, Siddiqui MRH, Fun HK, Albericio F (2016) One pot synthesis, molecular structure and spectroscopic studies (X-ray, IR, NMR, UV-Vis) of novel 2-(4,6-dimethoxy-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl) amino acid ester derivatives. Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc 159:184–198. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2016.01.051
Sponer J, Hobza P (1996) DNA base amino groups and their role in molecular interactions: Ab initio and preliminary density functional theory calculations. Int J Quantum Chem 57:959–970. https://doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1097-461X(1996)57:5%3c959:AID-QUA16%3e3.0.CO;2-S
Soliman SM, Hagar M, Ibid F, El Ashry ESH (2015) Experimental and theoretical spectroscopic studies, HOMO-LUMO, NBO analyses and thione-thiol tautomerism of a new hybrid of 1,3,4-oxadiazole-thione with quinazolin-4-one. Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc 145:270–279. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2015.01.061
Soliman SM, Kassem TS, Badr AMA, Abou Youssef MA, Assem R (2014) Molecular structure and spectral properties of ethyl 3-quinolinecarboxylate (E3Q) and [Ag(E3Q)2(TCA)] complex (TCA = Trichloroacetate). Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc 130:453–465. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2014.04.045
Socrates G (2004) Infrared and Raman characteristic group frequencies. Wiley, New York. ISBN 978-0-470-09307-8
Colthup N, Daly L, Wiberley S (1990) Introduction to infrared and Raman spectroscopy. Academic Press, New York. ISBN 0-12-182554-X
McMurry HL, Thornton V (1952) Correlation of infrared spectra. Anal Chem 24:318–334. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac60062a018
Kitson RE, Griffith NE (1952) Infrared absorption band due to nitrile stretching vibration. J Anal Chem 24:334–337. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac60062a019
Islam MS, Al-Majid AA, Barakat A, Soliman S, Ghabbour H, Quah CK, Fun HK (2015) Synthesis, molecular structure and spectroscopic investigations of novel fluorinated spiro heterocycles. Molecules 20:8223–8241
Ebenezar J (ed) (2017) Recent trends in materials science and applications, vol 189. Springer Nature, New York. ISBN 978-3-319-44889-3
Barakat A, Ghabbour HA, Al-Majid AM, Soliman SM, Ali M, Mabkhot YN, Shaik MR, Fun HK (2015) Synthesis, spectroscopic investigations (X-ray, NMR and TD-DFT), antimicrobial activity and molecular docking of 2,6-bis(hydroxy(phenyl)methyl)cyclohexanone. Molecules 20:13240–13263. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules200713240
Dorotíková S, Plevová K, Bučinský L, Malček M, Herich P, Kucková L, Bobeničová M, Šoralová S, Kožíšek J, Fronc M, Milata V, Dvoranová D (2014) Conformational, spectroscopic, and molecular dynamics DFT study of precursors for new potential antibacterial fluoroquinolone drugs. J Phys Chem A 118:9540–9551. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp506355f
Han T, Kang D, Ji D, Wang X, Zhan W, Fu M, Xin HB, Wang JB (2013) How does cancer cell metabolism affect tumor migration and invasion? Cell Adhes Migr 7:395–403
Dhup S, Dadhich RK, Porporato PE, Sonveaux P (2012) Multiple biological activities of lactic acid in cancer: influences on tumor growth, angiogenesis and metastasis. Curr Pharm Des 18:1319–1330. https://doi.org/10.2174/138161212799504902
Radwan AA, Abdel-Mageed WM (2014) In silico studies of quinoxaline-2-carboxamide 1,4-di-N-oxide derivatives as antimycobacterial agents. Molecules 19:2247–2260. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules19022247
Papageorgiou L, Megalooikonomou V, Vlachakis D (2017) Genetic and structural study of DNA-directed RNA polymerase II of Trypanosoma brucei, towards the designing of novel antiparasitic agents. PeerJ 5:e3061. https://doi.org/10.7717/peerj.3061
Markley JL, Bax A, Arata Y, Hilbers CW, Kaptein R, Sykes BD, Wright PE, Wüthrich K (1998) Recommendations for the presentation of NMR structures of proteins and nucleic acids—IUPAC-IUBMB-IUPAB Inter-Union Task Group on the standardization of data bases of protein and nucleic acid structures determined by NMR spectroscopy. Eur J Biochem 256:1–15. https://doi.org/10.1023/a:1008290618449
Authors’ contributions
All authors contributed equally. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Acknowledgements
The authors extend their appreciation to the Deanship of Scientific Research at King Khalid University for its funding this prolific research group no.(R.G.P.2/23/40/2019).
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Availability of data and materials
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Funding
King Khalid University grant awarded to Dr. Yahia Mabkhot.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional file
Additional file 1: Table S1.
The calculated electronic transition bands of the malononitrile compound. Table S2. Comparison of the predicted and experimental frequency modes of the malononitrile analogue. Figure S1. Comparison of the predicted (upper) and experimental (lower) absorbance spectra of the thiazole based malononitrile analogue. Figure S2. The experimental (lower one) and calculated (upper one) IR spectra of the studied compound.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated.
About this article
Cite this article
Mabkhot, Y.N., Al-Showiman, S.S., Barakat, A. et al. Computational studies of 2-(4-oxo-3-phenylthiazolidin-2-ylidene)malononitrile. BMC Chemistry 13, 25 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13065-019-0542-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s13065-019-0542-6