Abstract
Background
Clear cell Renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC) is an immunogenic tumor. B7 family members, such as CTLA-4, PD-1, and PD-L1, are the main components of immune checkpoints that regulate various immune responses. Specifically, B7-H3 regulates T cell-mediated immune responses against cancer. This study aimed to analyze the association between B7-H3 and CTLA-4 expression and the prognostic factors of ccRCC to provide a basis for their potential use as predictive factors and in immunotherapy.
Methods
Formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded specimens were obtained from 244 ccRCC patients, and B7-H3, CTLA-4, and PD-L1 expressions were evaluated using immunohistochemical staining.
Results
B7-H3 and CTLA-4 were positive in 73 (29.9%) and 57 (23.4%) of the 244 patients, respectively. B7-H3 expression was significantly associated with PD-L1 expression (P < 0.0001); however, CTLA-4 expression was not (P = 0.842). Kaplan–Meier analysis showed that positive B7-H3 expression was associated with poor progression-free survival (PFS) (P < 0.0001), whereas CTLA-4 expression was not (P = 0.457). Multivariate analysis revealed that B7-H3 was correlated with poor PFS (P = 0.031), whereas CTLA-4 was not (P = 0.173).
Conclusions
To the best of our knowledge, this study is the first to investigate B7-H3 and PD-L1 expression and survival in ccRCC. B7-H3 expression is an independent prognostic factor for ccRCC. Furthermore, multiple immune cell inhibitory targets, such as B7-H3 and PD-L1, can be used for therapeutic tumor regression in a clinical setting.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC) accounts for 85% of renal cell carcinoma (RCC) tumors and is an immunogenic and proangiogenic cancer [1,2,3]. The dysfunction of immune cells, including tumor-associated macrophages, natural killer cells, antitumor cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs), dendritic cells, and macrophages, and cytokine and chemokine action in tumor and stroma cells are essential to the pathogenesis of ccRCC [4].
ccRCC is an immunosensitive carcinoma that responds to immune checkpoint inhibitors [5,6,7] and is highly resistant to chemotherapy and radiotherapy [8, 9]. Therefore, immunotherapy is used as a major treatment for ccRCC.
B7 family T-cell costimulatory molecules play essential roles in modulating immune cell activation, function, and fate [10, 11]. B7 family members, such as CTLA-4, PD-1, and PD-L1, are the main components of the immune checkpoints, which positively or negatively regulate various immune responses. PD-L1 recognizes and attaches to the PD-1 of T cells, deactivating the T cells. Thus, PD-L1 on the surface of cancer cells prevents T cells from attacking them. PD-L1 is highly expressed in various carcinomas, and its expression is associated with a poor prognosis; thus, PD-L1 is used as a major immunotherapy target [12,13,14]. B7-H3 plays a role in regulating the T cell-mediated immune response against cancer. Recent evidence has shown that B7-H3 expression is positively associated with the density of FOXP3 + -regulated T cells, which infiltrate tumors [15].
CTLA-4 is expressed on the surface of T cells and binds to the B7 of antigen-presenting cells, inhibiting the activation signal of T cells. CTLA-4 is a negative regulator of T-cell immune function, as it stops potentially autoreactive T cells at the initial stage of naive T-cell activation, typically in the lymph nodes [16, 17].
Among the immune system participants introduced, PD-L1 is widely used as a biomarker. We aimed to discover a sensitive marker that can predict cancer prognosis and be applied to improve immunotherapy. The high correlations between the expression of B7-H3 and CTLA-4 and cancer cell activity can be used to evaluate their potential usefulness as prognostic predictors or immunotherapy targets.
Therefore, this study aimed to investigate the association between the expression of B7-H3 and CTLA-4 and the patterns and prognostic factors of ccRCC to provide a theoretical basis for the use of B7-H3 and CTLA-4 as predictive factors for ccRCC prognosis and as targets in ccRCC immunotherapy.
Methods
Patient selection
In total, 244 ccRCC patients treated with partial or total nephrectomy at Pusan National University Yangsan Hospital (Yangsan, Korea) between 2011 and 2017 were enrolled. Pathological diagnoses were made by genitourinary pathologists (H.J.L., J.H.L) and four medical students from the School of Medicine, Pusan National University. All patients were pathologically evaluated using the International Society of Urological Pathology/World Health Organization 2016 grading and pathological staging system.
Immunohistochemical analysis
Immunohistochemistry was performed using formalin-fixed tissue samples obtained for the pathological diagnosis of ccRCC. High-density tissue microarrays (TMAs) were constructed using 244 ccRCC tissue samples. Each tumor was represented by 2 mm two cores for the highest and most common grade areas (total of 488 cores). A primary antibodies against B7-H3 (sc-376,769; Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Dallas, TX, USA) and CTLA-4 (ab237712; Abcam, Cambridge, MA, USA) were used. Sections were immunostained for B7-H3 with an anti-B7-H3 mouse monoclonal antibody (1:500) and for CTLA-4 with an anti-CTLA-4 rabbit monoclonal antibody (1:100).
Tumors were scored as positive, demonstrating membranous immune reactivity at low- and high-power magnifications. The B7-H3 immunostained samples were subdivided into two groups according to the macroscopic expression ratio (< 50% and ≥ 50%) on the TMA slides, regarded as negative and positive, respectively. The CTLA-4 immunostained samples were divided into two groups according to the macroscopic expression ratio (< 5% and ≥ 5%) on the TMA slides, regarded as negative and positive, respectively. PD-L1 expression was mainly confined to the tumor cell membrane. PD-L1 tumor positivity was defined as ≥5% tumor cell membrane staining [12].
Statistical analysis
The relationship between clinical and pathological features was evaluated using the χ2 test. The PFS rate was estimated using the Kaplan–Meier method for univariate analysis and the Cox proportional hazards regression model for multivariate analysis. PFS was defined as the duration between the date of surgery and the date of recurrence or metastasis. Statistical analyses were performed using Statistical Package for the Social Sciences version 19.0 (SPSS, Inc., Chicago, IL, USA).
Results
Patient characteristics
The patient cohort consisted of 183 male and 61 female study participants, with a median age of 61 years (range, 27–88 years). None of the patients had a history of malignancy. The follow-up was 1–138 months, and the median PFS was 77 months (Table 1).
B7-H3 and CTLA-4 expression in ccRCC
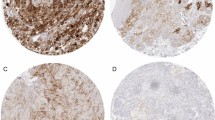
Of the 244 patients, B7-H3 (CD276) expression was positive in 73 (29.9%) (Fig. 1A) but negative in 171 (70.1%) (Fig. 1B), and CTLA-4 expression was positive in 57 patients (23.4%) but negative in 187 patients (76.6%) (Fig. 1D). The expression of B7-H3 and CTLA-4 were correlated (χ2 test, P = 0.031, Table 2).
Morphological features and immunohistochemistry
B7-H3 expression was associated with a sarcomatoid pattern (P = 0.001, Table 2) (Fig. 2), whereas CTLA-4 expression was not (P = 0.769). Moreover, B7-H3 expression was associated with necrosis (P = 0.04), whereas CTLA-4 expression was not (P = 0.162).
Comparison between B7-H3 and CTLA-4 expression and PD-L1 expression
χ2 tests revealed that relationships exist between PD-L1, B7-H3, and CTLA-4 expressions in the ccRCC cohort. B7-H3 expression was significantly associated with PD-L1 expression (P < 0.0001, Table 2) (Fig. 1C). However, CTLA-4 expression was not (P = 0.842).
Relationship between B7-H3 and CTLA-4 expression and metastasis
B7-H3 positive staining was associated with metastasis (P = 0.007, Table 2). Similarly, a χ2 test was performed to determine the relationship between CTLA-4 and metastasis. No relationship was observed between the degree of CTLA-4 staining and metastasis (P = 0.118).
Association between CTLA-4 and B7-H3 expression and PFS in ccRCC patients
Kaplan–Meier analysis indicated that positive B7-H3 expression was associated with poor PFS (P < 0.0001) (Fig. 3A), whereas CTLA-4 expression was not (P = 0.457; Fig. 3B). Similarly, multivariate analysis revealed that B7-H3 was correlated with poor PFS (P = 0.031), whereas CTLA-4 was not (P = 0.173) (Table 3).
Progression-free survival (PFS) curves of RCC patients in the B7-H3 and CTLA-4-positive and -negative groups (Kaplan–Meier). The cases were divided into two groups showing positive or negative B7-H3 (A) and CTLA-4 (B) expression. The patients with positive B7-H3 expression showed poorer overall survival (P < 0.001) (A)
Discussion
ccRCC is recognized as an immunogenic tumor. Many studies have focused on immune-based approaches to ccRCC treatment. B7-H3 is a member of the B7 family of immune regulatory proteins that regulate T cell-mediated immune responses and is speculated to control tumor aggressiveness in various cancer types [18, 19]. Given its recent discovery, the regulatory mechanisms of B7-H3 are ill-understood. B7-H3 mRNA expression has been found in multiple human tissues and cell lines, such as prostate cancer, non-small-cell lung carcinoma, and RCC [20], and B7-H3 has been implicated as a potential inhibitor of T-cell activity [21]. B7-H3 has been noted to be expressed by dendritic cells and related with suppressive activity by contacting with CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells [22]. B7-H3 ligand expression may be regulated by tumor microenvironment, and is supported by differential B7-H3 expression with different tumor types [23].
The expression of B7-H3 in tumor vascular endothelium and its clinical significance are gradually becoming important [24, 25]. B7-H3 could act as potent new cancer vessel-specific carrier to deliver antiangiogenic agents, and could help predict the clinical outcome of using different targeted agents in the treatment of ccRCC [26, 27].
The immunohistochemical staining of B7-H3 and CTLA-4 in 244 concurrent ccRCC cases treated with partial or total nephrectomy at Pusan National University (Yangsan, Korea) between 2011 and 2017 was conducted and analyzed. Our study has three main findings. First, one of the most important purposes of this study was to determine the correlation between the expression of the B7-H3 family members and ccRCC progression. Patients who were B7-H3 immunohistochemistry positive exhibited poor PFS (P < 0.001). In this study, a correlation was observed between the expression of the B7-H3 family members and necrosis, sarcomatoid pattern, and metastasis. Second, no correlation was observed between CTLA-4 expression and ccRCC progression. There were no correlations between CTLA-4 and necrosis, sarcomatoid pattern and metastasis. Third, B7-H3 expression was associated with PD-L1 expression, whereas CTLA-4 expression was not. Given that B7-H3 was correlated with poor prognosis in RCC, performing B7-H3 immunohistochemistry analysis will be useful in evaluating the prognosis of ccRCC patients.
This study is relevant as B7-H3 is a promising target for future immunotherapies. Immunotherapy using the B7-H3 pathway is effective when chemotherapy and radiotherapy are performed simultaneously. Additionally, the study findings will help elucidate the relationship between the B7-H3 pathway and cancer progression and ultimately facilitate the treatment of ccRCC.
CTLA-4 expression was not associated with ccRCC prognosis in this study, and the immunological processes mediated by CTLA-4 have not yet been clarified [28, 29]. Some studies have suggested that CTLA-4 expression positively correlates with cancer severity and prognosis [30]. We need to include more cases and further studies would help clarify the relationship between CTLA-4 and ccRCC.
Conclusions
To the best of our knowledge, this study is the first to investigate the correlation between B7-H3 and PD-L1 expression and survival in ccRCC. B7-H3 expression is an independent prognostic factor for ccRCC. Furthermore, multiple immune cell inhibitory targets, such as B7-H3 and PD-L1, can be used for therapeutic tumor regression in a clinical setting.
Availability of data and materials
The dataset supporting the conclusions of this article is included within the article.
Change history
16 May 2023
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1186/s13000-023-01356-2
Abbreviations
- RCC:
-
Renal cell carcinoma
- ccRCC:
-
Clear cell renal cell carcinoma
- ISUP:
-
International Society of Urological Pathology
- CTLs:
-
Cytotoxic T lymphocytes
- TMAs:
-
Tissue microarrays
- PFS:
-
Progression-free survival
References
Liu XD, Hoang A, Zhou L, Kalra S, Yetil A, Sun M, et al. Resistance to antiangiogenic therapy is associated with an immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment in metastatic renal cell carcinoma. Cancer Immunol Res. 2015;3:1017–29. https://doi.org/10.1158/2326-6066.CIR-14-0244.
Fukuda T, Kamai T, Masuda A, Nukui A, Abe H, Arai K, et al. Higher preoperative serum levels of PD-L1 and B7-H4 are associated with invasive and metastatic potential and predictable for poor response to VEGF-targeted therapy and unfavorable prognosis of renal cell carcinoma. Cancer Med. 2016;5:1810–20. https://doi.org/10.1002/cam4.754.
Makhov P, Joshi S, Ghatalia P, Kutikov A, Uzzo RG, Kolenko VM. Resistance to systemic therapies in clear cell renal cell carcinoma: mechanisms and management strategies. Mol Cancer Ther. 2018;17:1355–64. https://doi.org/10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-17-1299.
Santoni M, Berardi R, Amantini C, Burattini L, Santini D, Santoni G, et al. Role of natural and adaptive immunity in renal cell carcinoma response to VEGFR-TKIs and mTOR inhibitor. Int J Cancer. 2014;134:2772–7. https://doi.org/10.1002/ijc.28503.
Zarrabi K, Fang C, Wu S. New treatment options for metastatic renal cell carcinoma with prior anti-angiogenesis therapy. J Hematol Oncol. 2017;10:38. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13045-016-0374-y.
Motzer RJ, Rini BI, McDermott DF, Redman BG, Kuzel TM, Harrison MR, et al. Nivolumab for metastatic renal cell carcinoma: results of a randomized phase II trial. J Clin Oncol. 2015;33:1430–7. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2014.59.0703.
Das R, Verma R, Sznol M, Boddupalli CS, Gettinger SN, Kluger H, et al. Combination therapy with anti-CTLA-4 and anti-PD-1 leads to distinct immunologic changes in vivo. J Immunol. 2015;194:950–9. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.1401686.
Goyal R, Gersbach E, Yang XJ, Rohan SM. Differential diagnosis of renal tumors with clear cytoplasm: clinical relevance of renal tumor subclassification in the era of targeted therapies and personalized medicine. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2013;137:467–80. https://doi.org/10.5858/arpa.2012-0085-RA.
Rini BI, Campbell SC, Escudier B. Renal cell carcinoma. Lancet. 2009;373:1119–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(09)60229-4.
Greenwald RJ, Freeman GJ, Sharpe AH. The B7 family revisited. Annu Rev Immunol. 2005;23:515–48. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.immunol.23.021704.115611.
Inman BA, Frigola X, Dong H, Kwon ED. Costimulation, coinhibition and cancer. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2007;7:15–30. https://doi.org/10.2174/156800907780006878.
Choueiri TK, Fay AP, Gray KP, Callea M, Ho TH, Albiges L, et al. PD-L1 expression in nonclear-cell renal cell carcinoma. Ann Oncol. 2014;25:2178–84. https://doi.org/10.1093/annonc/mdu445.
Stenzel PJ, Schindeldecker M, Tagscherer KE, Foersch S, Herpel E, Hohenfellner M, et al. Prognostic and predictive value of tumor-infiltrating leukocytes and of immune checkpoint molecules PD1 and PDL1 in clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Transl Oncol. 2020;13:336–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tranon.2019.11.002.
Joseph RW, Millis SZ, Carballido EM, Bryant D, Gatalica Z, Reddy S, et al. PD-1 and PD-L1 expression in renal cell carcinoma with sarcomatoid differentiation. Cancer Immunol Res. 2015;3:1303–7. https://doi.org/10.1158/2326-6066.CIR-15-0150.
Inamura K, Amori G, Yuasa T, Yamamoto S, Yonese J, Ishikawa Y. Relationship of B7-H3 expression in tumor cells and tumor vasculature with FOXP3+ regulatory T cells in renal cell carcinoma. Cancer Manag Res. 2019;11:7021–30. https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S209205.
Buchbinder EI, Desai A. CTLA-4 and PD-1 pathways: similarities, differences, and implications of their inhibition. Am J Clin Oncol. 2016;39:98–106. https://doi.org/10.1097/COC.0000000000000239.
Fife BT, Bluestone JA. Control of peripheral T-cell tolerance and autoimmunity via the CTLA-4 and PD-1 pathways. Immunol Rev. 2008;224:166–82. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-065X.2008.00662.x.
Chapoval AI, Ni J, Lau JS, Wilcox RA, Flies DB, Liu D, et al. B7-H3: a costimulatory molecule for T cell activation and IFN-gamma production. Nat Immunol. 2001;2:269–74. https://doi.org/10.1038/85339.
Wang Z, Wang Z, Zhang C, Liu X, Li G, Liu S, et al. Genetic and clinical characterization of B7-H3(CD276) expression and epigenetic regulation in diffuse brain glioma. Cancer Sci. 2018;109:2697–705. https://doi.org/10.1111/cas.13744.
Crispen PL, Sheinin Y, Roth TJ, Lohse CM, Kuntz SM, Frigola X, et al. Tumor cell and tumor vasculature expression of B7-H3 predict survival in clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 2008;14:5150–7. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-08-0536.
Ling V, Wu PW, Spaulding V, Kieleczawa J, Luxenberg D, Carreno BM, et al. Duplication of primate and rodent B7-H3 immunoglobulin V- and C-like domains: divergent history of functional redundancy and exon loss. Genomics. 2003;82:365–77. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0888-7543(03)00126-5.
Mahnke K, Ring S, Johnson TS, Schallenberg S, Schönfeld K, Storn V, et al. Induction of immunosuppressive functions of dendritic cells in vivo by CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells: role of B7-H3 expression and antigen presentation. Eur J Immunol. 2007;37:2117–26. https://doi.org/10.1002/eji.200636841.
Zang X, Allison JP. The B7 family and cancer therapy: costimulation and coinhibition. Clin Cancer Res. 2007;13:5271–9. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-07-1030.
Xie J, Sun M, Zhang D, Chen C, Lin S, Zhang G. Fibronectin enhances tumor metastasis through B7-H3 in clear cell renal cell carcinoma. FFBS Open Bio. 2021;11:2977–87. https://doi.org/10.1002/2211-5463.13280.
Zhao B, Li H, Xia Y, Wang Y, Wang Y, Shi Y, et al. Immune checkpoint of B7-H3 in cancer: from immunology to clinical immunotherapy. J Hematol Oncol. 3033;15:153 https://doi.org/10.1186/s13045-022-01364-7.
Wang G, Wu Z, Wang Y, Li X, Zhang G, Hou J. Therapy to target renal cell carcinoma using 131I-labeled B7-H3 monoclonal antibody. Oncotarget. 2016;7:24888–98. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.8550.
Qin X, Zhang H, Ye D, Dai B, Zhu Y, Shi G. B7-H3 is a new cancer-specific endothelial marker in clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Onco Targets Ther. 2013;6:1667–73. https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S53565.
Oaks MK, Hallett KM, Penwell RT, Stauber EC, Warren SJ, Tector AJ. A native soluble form of CTLA-4. Cell Immunol. 2000;201:144–53. https://doi.org/10.1006/cimm.2000.1649.
Saverino D, Brizzolara R, Simone R, Chiappori A, Milintenda-Floriani F, Pesce G, et al. Soluble CTLA-4 in autoimmune thyroid diseases: relationship with clinical status and possible role in the immune response dysregulation. Clin Immunol. 2007;123:190–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clim.2007.01.003.
Kahlmeyer A, Stöhr CG, Hartmann A, Goebell PJ, Wullich B, Wach S, et al. Expression of PD-1 and CTLA-4 are negative prognostic markers in renal cell carcinoma. J Clin Med. 2019;8:743. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8050743.
Acknowledgments
Not applicable.
Funding
This study was supported by a 2022 research grant from Pusan National University Yangsan Hospital.
This study was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea grant NRF2020R1F1A1060678 (H.J.L.)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
HJL designed and wrote the paper; JHL and YJK collected and interpreted histological under the supervision of JYN, DHS and JYK; CSH, SYK, JYP and SHS collected the clinical data; HWR, SWS and EJK analyzed the data. All authors commented on the manuscript. The manuscript was approved by all authors.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
This study was approved by the Institutional Review Board of the Pusan National University Yangsan Hospital (05–2022-167).
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
The original online version of this article was revised: the authors requested to update the affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, J.H., Kim, Y.J., Ryu, H.W. et al. B7-H3 expression is associated with high PD-L1 expression in clear cell renal cell carcinoma and predicts poor prognosis. Diagn Pathol 18, 36 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13000-023-01320-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s13000-023-01320-0