Abstract
Purpose
Immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICI) are then backbone in the therapy of metastatic renal cell carcinoma (RCC). The aim of this analysis was to explore the different expression of the ICI PD-L1, BTLA, and TIM-3 at the different tumor locations of the invasion front and the tumor center.
Methods
Large-area sections of the tumor center and invasion front of 44 stage pT1–4 clear cell RCCs were examined immunohistochemically using antibodies against BTLA, TIM-3, and PD-L1 and subsequently correlated with clinicopathologic data.
Results
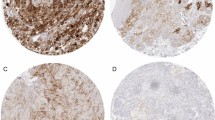
TIM-3 was most strongly expressed at the invasion front (mean ± SD: 84.1 ± 46.6, p = 0.094). BTLA expression was highest in normal tissue, with weak staining in the tumor center and at the invasion front [110.2 vs. 18.6 (p < 0.001) vs. 32.2 (p = 0.248)]. PD-L1 was weakly expressed at the tumor center (n = 5/44) and at the invasion front (n = 5/44). Correlation with clinicopathological parameters revealed significantly higher BTLA expression in ≥ T3 tumors compared to T1/2 tumors (tumor center p = 0.009; invasion front p = 0.005). BTLA-positive tumors at the tumor center correlated with worse CSS (median 48.46 vs. 68.91 months, HR 4.43, p = 0.061). PD-L1 expression was associated with worse CSS (median 1.66 vs. 4.5 years, HR 1.63, p = 0.652). For TIM-3, there were no significant associations with clinicopathological parameters and survival.
Conclusion
The present results show heterogeneous intratumoral and intertumoral expression of the investigated checkpoint receptors PD-L1, BTLA, and TIM-3. In the clinical practice tumor sampling should include different tumor locations, and multiple inhibition of different checkpoint receptors seems reasonable to increase the therapeutic success.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ljungberg B, Albiges L, Abu-Ghanem Y, Bedke J, Capitanio U, Dabestani S, Fernández-Pello S, Giles RH, Hofmann F, Hora M et al (2022) European Association of Urology guidelines on Renal Cell Carcinoma: the 2022 update. Eur Urol 82:399–410
Bedke J, Albiges L, Capitanio U, Giles RH, Hora M, Lam TB, Ljungberg B, Marconi L, Klatte T, Volpe A et al (2021) The 2021 Updated European Association of Urology Guidelines on Renal Cell Carcinoma: immune checkpoint inhibitor-based combination therapies for treatment-naive metastatic clear-cell renal cell carcinoma are standard of care. Eur Urol 80:393–397
Iwai Y, Ishida M, Tanaka Y, Okazaki T, Honjo T, Minato N (2002) Involvement of PD-L1 on tumor cells in the escape from host immune system and tumor immunotherapy by PD-L1 blockade. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 99:12293–12297
Lee CH, Motzer RJ (2016) Immune checkpoint therapy in renal cell carcinoma. Cancer J 22:92–95
Shen M, Chen G, Xie Q, Li X, Xu H, Wang H, Zhao S (2020) Association between PD-L1 expression and the prognosis and clinicopathologic features of renal cell carcinoma: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Urol Int 104:533–541
Gerlinger M, Horswell S, Larkin J, Rowan AJ, Salm MP, Varela I, Fisher R, McGranahan N, Matthews N, Santos CR et al (2014) Genomic architecture and evolution of clear cell renal cell carcinomas defined by multiregion sequencing. Nat Genet 46:225–233
Zhao Y, Fu X, Lopez JI, Rowan A, Au L, Fendler A, Hazell S, Xu H, Horswell S, Shepherd STC et al (2021) Selection of metastasis competent subclones in the tumour interior. Nat Ecol Evol 5:1033–1045
Petrova V, Annicchiarico-Petruzzelli M, Melino G, Amelio I (2018) The hypoxic tumour microenvironment. Oncogenesis 7:10
Hoefflin R, Lahrmann B, Warsow G, Hübschmann D, Spath C, Walter B, Chen X, Hofer L, Macher-Goeppinger S, Tolstov Y et al (2016) Spatial niche formation but not malignant progression is a driving force for intratumoural heterogeneity. Nat Commun 7:ncomms11845
Fisel P, Kruck S, Winter S, Bedke J, Hennenlotter J, Nies AT, Scharpf M, Fend F, Stenzl A, Schwab M, Schaeffeler E (2013) DNA methylation of the SLC16A3 promoter regulates expression of the human lactate transporter MCT4 in renal cancer with consequences for clinical outcome. Clin Cancer Res 19:5170–5181
Motzer RJ, Escudier B, McDermott DF, George S, Hammers HJ, Srinivas S, Tykodi SS, Sosman JA, Procopio G, Plimack ER et al (2015) Nivolumab versus everolimus in advanced renal-cell carcinoma. N Engl J Med 373:1803–1813
Havel JJ, Chowell D, Chan TA (2019) The evolving landscape of biomarkers for checkpoint inhibitor immunotherapy. Nat Rev Cancer 19:133–150
Snyder A, Makarov V, Merghoub T, Yuan J, Zaretsky JM, Desrichard A, Walsh LA, Postow MA, Wong P, Ho TS et al (2014) Genetic basis for clinical response to CTLA-4 blockade in melanoma. N Engl J Med 371:2189–2199
Le DT, Durham JN, Smith KN, Wang H, Bartlett BR, Aulakh LK, Lu S, Kemberling H, Wilt C, Luber BS et al (2017) Mismatch repair deficiency predicts response of solid tumors to PD-1 blockade. Science 357:409–413
Samstein RM, Lee CH, Shoushtari AN, Hellmann MD, Shen R, Janjigian YY, Barron DA, Zehir A, Jordan EJ, Omuro A et al (2019) Tumor mutational load predicts survival after immunotherapy across multiple cancer types. Nat Genet 51:202–206
McDermott DF, Huseni MA, Atkins MB, Motzer RJ, Rini BI, Escudier B, Fong L, Joseph RW, Pal SK, Reeves JA et al (2018) Clinical activity and molecular correlates of response to atezolizumab alone or in combination with bevacizumab versus sunitinib in renal cell carcinoma. Nat Med 24:749–757
Gerlinger M, Rowan AJ, Horswell S, Math M, Larkin J, Endesfelder D, Gronroos E, Martinez P, Matthews N, Stewart A et al (2012) Intratumor heterogeneity and branched evolution revealed by multiregion sequencing. N Engl J Med 366:883–892
Golkaram M, Kuo F, Gupta S, Carlo MI, Salmans ML, Vijayaraghavan R, Tang C, Makarov V, Rappold P, Blum KA et al (2022) Spatiotemporal evolution of the clear cell renal cell carcinoma microenvironment links intra-tumoral heterogeneity to immune escape. Genome Med 14:143
Krishna C, DiNatale RG, Kuo F, Srivastava RM, Vuong L, Chowell D, Gupta S, Vanderbilt C, Purohit TA, Liu M et al (2021) Single-cell sequencing links multiregional immune landscapes and tissue-resident T cells in ccRCC to tumor topology and therapy efficacy. Cancer Cell 39:662-677.e666
Li R, Ferdinand JR, Loudon KW, Bowyer GS, Laidlaw S, Muyas F, Mamanova L, Neves JB, Bolt L, Fasouli ES et al (2022) Mapping single-cell transcriptomes in the intra-tumoral and associated territories of kidney cancer. Cancer Cell 40:1583-1599.e1510
Fourcade J, Sun Z, Pagliano O, Guillaume P, Luescher IF, Sander C, Kirkwood JM, Olive D, Kuchroo V, Zarour HM (2012) CD8(+) T cells specific for tumor antigens can be rendered dysfunctional by the tumor microenvironment through upregulation of the inhibitory receptors BTLA and PD-1. Cancer Res 72:887–896
Kim PS, Ahmed R (2010) Features of responding T cells in cancer and chronic infection. Curr Opin Immunol 22:223–230
Pardoll DM (2012) The blockade of immune checkpoints in cancer immunotherapy. Nat Rev Cancer 12:252–264
Hurchla MA, Sedy JR, Gavrieli M, Drake CG, Murphy TL, Murphy KM (2005) B and T lymphocyte attenuator exhibits structural and expression polymorphisms and is highly Induced in anergic CD4+ T cells. J Immunol 174:3377–3385
Chen YL, Lin HW, Chien CL, Lai YL, Sun WZ, Chen CA, Cheng WF (2019) BTLA blockade enhances Cancer therapy by inhibiting IL-6/IL-10-induced CD19(high) B lymphocytes. J Immunother Cancer 7:313
Watanabe N, Gavrieli M, Sedy JR, Yang J, Fallarino F, Loftin SK, Hurchla MA, Zimmerman N, Sim J, Zang X et al (2003) BTLA is a lymphocyte inhibitory receptor with similarities to CTLA-4 and PD-1. Nat Immunol 4:670–679
Świderska J, Kozłowski M, Gaur M, Pius-Sadowska E, Kwiatkowski S, Machaliński B, Cymbaluk-Płoska A (2022) Clinical significance of BTLA, CD27, CD70, CD28 and CD80 as diagnostic and prognostic markers in ovarian cancer. Diagnostics (Basel) 12:251
Zhang X, Yin X, Zhang H, Sun G, Yang Y, Chen J, Shu K, Zhao J, Zhao P, Chen N et al (2019) Differential expression of TIM-3 between primary and metastatic sites in renal cell carcinoma. BMC Cancer 19:49
Zhou E, Huang Q, Wang J, Fang C, Yang L, Zhu M, Chen J, Chen L, Dong M (2015) Up-regulation of Tim-3 is associated with poor prognosis of patients with colon cancer. Int J Clin Exp Pathol 8:8018–8027
Yuan J, Jiang B, Zhao H, Huang Q (2014) Prognostic implication of TIM-3 in clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Neoplasma 61:35–40
Yang M, Yu Q, Liu J, Fu W, Cao Y, Yu L, Shao S, Wang X, Niu H, Wang Y (2015) T-cell immunoglobulin mucin-3 expression in bladder urothelial carcinoma: clinicopathologic correlations and association with survival. J Surg Oncol 112:430–435
Piao YR, Piao LZ, Zhu LH, Jin ZH, Dong XZ (2013) Prognostic value of T cell immunoglobulin mucin-3 in prostate cancer. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev 14:3897–3901
Das M, Zhu C, Kuchroo VK (2017) Tim-3 and its role in regulating anti-tumor immunity. Immunol Rev 276:97–111
Gleason MK, Lenvik TR, McCullar V, Felices M, O’Brien MS, Cooley SA, Verneris MR, Cichocki F, Holman CJ, Panoskaltsis-Mortari A et al (2012) Tim-3 is an inducible human natural killer cell receptor that enhances interferon gamma production in response to galectin-9. Blood 119:3064–3072
Gorman JV, Starbeck-Miller G, Pham NL, Traver GL, Rothman PB, Harty JT, Colgan JD (2014) Tim-3 directly enhances CD8 T cell responses to acute Listeria monocytogenes infection. J Immunol 192:3133–3142
Lee J, Su EW, Zhu C, Hainline S, Phuah J, Moroco JA, Smithgall TE, Kuchroo VK, Kane LP (2011) Phosphotyrosine-dependent coupling of Tim-3 to T-cell receptor signaling pathways. Mol Cell Biol 31:3963–3974
Nakae S, Iikura M, Suto H, Akiba H, Umetsu DT, Dekruyff RH, Saito H, Galli SJ (2007) TIM-1 and TIM-3 enhancement of Th2 cytokine production by mast cells. Blood 110:2565–2568
Reig Ò, Marin M, Jimenez N, Pare L, Galvan P, Mallofre C, Prat A, Mellado B (2018) Immune-related expression profiles and sunitinib response in metastatic clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC). J Clin Oncol 36:e16579
Wherry EJ, Kurachi M (2015) Molecular and cellular insights into T cell exhaustion. Nat Rev Immunol 15:486–499
Iacovelli R, Nolè F, Verri E, Renne G, Paglino C, Santoni M, Cossu Rocca M, Giglione P, Aurilio G, Cullurà D et al (2016) Prognostic role of PD-L1 expression in renal cell carcinoma. A systematic review and meta-analysis. Target Oncol 11:143–148
Xu F, Xu L, Wang Q, An G, Feng G, Liu F (2015) Clinicopathological and prognostic value of programmed death ligand-1 (PD-L1) in renal cell carcinoma: a meta-analysis. Int J Clin Exp Med 8:14595–14603
Jilaveanu LB, Shuch B, Zito CR, Parisi F, Barr M, Kluger Y, Chen L, Kluger HM (2014) PD-L1 expression in clear cell renal cell carcinoma: an analysis of nephrectomy and sites of metastases. J Cancer 5:166–172
Ning XH, Gong YQ, He SM, Li T, Wang JY, Peng SH, Chen JC, Liu JY, Qi NN, Guo YL, Gong K (2017) Higher programmed cell death 1 ligand 1 (PD-L1) mRNA level in clear cell renal cell carcinomas is associated with a favorable outcome due to the active immune responses in tumor tissues. Oncotarget 8:3355–3363
Nunes-Xavier CE, Angulo JC, Pulido R, López JI (2019) A Critical Insight into the Clinical Translation of PD-1/PD-L1 Blockade therapy in clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Curr Urol Rep 20:1
Funding
MS and ES were in part supported by the Robert Bosch Stiftung Stuttgart, Germany.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
VS: Protocol/project development, Data collection or management, Data analysis, Manuscript writing; BA: Data collection or management, Data analysis; SR: Review & editing; AS: Review & editing, Supervision; MS: Review & editing, Supervision; ES: Review & editing; Supervision; JB: Protocol/project development, Review & editing, Project administration.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
JB reports institutional research grants as local principal investigator from BMS, Ipsen, MSD, Pfizer, Roche, Astellas, AstraZeneca, Eisai, Nektar, Novartis, Seagen; consulting fees from Apogepha, Astellas, AstraZeneca, BMS, Eisai, Ipsen, Janssen, Merck Serono, MSD, Pfizer, Roche, Speakers' bureau fees from Astellas, BMS, Ipsen, Merck Serono, MSD, Pfizer, Roche and Seagen; travel support from Merck and steering committee member for BMS, MSD, Pfizer and Seagen. SR: honoraria for speaker, advisory role: Astellas, Bayer, Pfizer, Merck. AS: consultancies, honoraria, or study participation from Bayer, BMS, Immatics, Novartis, Pfizer, and Roche. The remaining authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethical approval
The study was conducted according to the guidelines of the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by the Ethics Committee of the University of Tuebingen (565/2020/BO).
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Stühler, V., Alemi, B., Rausch, S. et al. Analysis of the immunological markers BTLA, TIM-3, and PD-L1 at the invasion front and tumor center in clear cell renal cell carcinoma. World J Urol 42, 53 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00345-023-04721-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00345-023-04721-4