Abstract
N6-methyl-adenosine (m6A) is the most prevalent modification on mRNAs and long noncoding RNAs (lnRNAs) in higher eukaryotes. Modulation of m6A relies on m6A writers, erasers and readers. m6A modification contributes to diverse fundamental biological functions at the molecular, cellular, and physiological levels. The dysregulation of m6A modification has been implicated in various human diseases. Thus, m6A modification has now become a research hotspot for its potential therapeutic applications in the treatment of various cancers and diseases. The immune system is essential to provide defense against infections and cancers. This review summarizes the current knowledge about the roles of m6A in regulating immune cell functions and immune responses.
Video abstract
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
The first modification in DNA nucleotides was discovered in 1948 [1] and since then the “epigenetics” research field has developed and evolved. Over time, the contributions of epigenetics in almost all cellular functions through regulation of gene expression became evident. Our knowledge has extended to post-translational protein modifications which are now well recognized to control the proteins’ fate. In contrast to DNA and proteins, RNA was considered to be less important and thought to merely be a transitional element bridging the information stored in the DNA and the synthesized proteins [2].
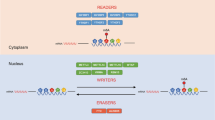
It was later on discovered that 70–90% of the human genome is transcribed into RNA but only 1–3% of the transcriptome actually bears the blueprint for the synthesis of proteins [2]. It was not until the 1980s when light was shed upon the functions of RNA molecules, other than coding for a peptide. Since the emergence of next-generation sequencing (NGS) technology, research was shifted extensively towards the epitranscriptome which represents the biochemical base modifications of a cell’s RNA transcripts that are not genetically encoded in the RNA sequence [2, 3]. So far, more than 100 RNA modifications have been identified in different types of RNA [4]. Those modifications modulate nearly all aspects of RNA metabolism and the associated physiological processes making them a key component of the post-transcriptional gene regulatory landscape [2, 3]. Among these RNA modifications, the N6-methyladenosine (m6A) (Fig. 1) represents the most prevailing post-transcriptional modification in eukaryotic RNA transcripts as well as long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs) [5].
Serendipitously discovered in 1974 [6, 7], the m6A modification refers to the post-transcriptional methylation of the mRNA adenine base at the nitrogen-6 position [8]. After the emergence of antibody-based immunoprecipitation followed by high-throughput m6A sequencing (MeRIP–Seq), it was revealed that human mRNA transcripts are punctuated by m6A at highly conserved and specific sites, particularly in the vicinity of stop codons, at the 3′ untranslated regions (3' UTRs), and in consensus sequences within long exons [9]. There are two slightly differing consensus motifs proposed in which m6A occurs: DR m6A CH [10] and RR m6A CH [11, 12] (with D = G, A, or U; R = G or A; and H = C, A, or U).
m6A modification modulates RNA secondary structure/folding. These m6A—derived alterations of target RNA structures are directly conveyed to their fates, functions and metabolism. These include (a) altering the mRNA splicing pattern, thereby potentially changing the distribution of splice isoforms of the transcript depending on the tissue or organ, (b) modulating the intracellular distribution and localization of mRNA by affecting nuclear export/retention, (c) influencing the potential for translation; or (d) impacting the stability of the transcript affecting its decay rate [8]. Moreover, m6A modification on chromosome-associated regulatory RNAs (carRNAs), which include promoter-associated RNAs (paRNA), enhancer RNAs (eRNA), and repeat RNAs, regulate chromatin accessibility and downstream transcription [13]. m6A could make the chromatin more or less accessible, thus increase or decrease transcription and translation [14,15,16,17]. m6A methylation also modulates the status of histone methylation or acetylation, and subsequently, histone modification can tune gene expression [13]. Any of these processes consequently leaves a print on the potential of translation, thereby affecting both the nature and quantity of the various produced protein isoforms. These molecular effects are then conveyed to the cellular level by influencing cell metabolism, circadian rhythm [18], cell differentiation [19,20,21,22], reprogramming, state transitions and stress responses [20, 23, 24], thus shaping cell function and identity. These effects are sequentially echoed to the organism’s physiology [3, 25]. Thus, a disturbance in the balance of m6A modifications can result in abnormalities in transcripts and proteins levels which are associated with various diseases and types of cancers [2, 26,27,28,29,30].
The immune system is the human body’s defense weapon against microbes and cancers. Through immunological surveillance, the immune system uses different mechanisms to recognize and combat the broad range of pathogens it encounters. This monitoring process of the immune system is also extended to the detection of virally infected, stressed, transformed and malignant cells making the immune system a key player in fighting infections and cancers [4].
m6A modification adds another layer of regulation to the already sophisticated gene expression regulation pathways in mammals. Extensive research has been carried out on the regulatory roles of m6A in stem cells and cancer cells. However, only little is known about the role of m6A in the immune system. In this review, we summarize the recent findings on the impact of m6A in different types of immune cells.
Protein factors involved in cellular m6A methylation
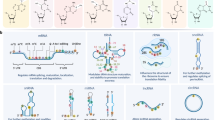
Adenosine methylation is a dynamic and reversible process that is orchestrated by extremely conserved methyltransferases (“writers”) and demethylases (“erasers”). Together, the writers and erasers shape the cellular ‘epitranscriptome’. The methyl code is decrypted by a cluster of m6A readers which sequentially direct the fate of the modified transcripts. The dynamic interplay between the writers, erasers and readers create the methylated transcriptome and dictate the prevalence, distribution and the m6A-dependent functions on RNA [3, 8]. Recently, with the development of advanced m6A detection methods [31, 32], scientists began to unveil the full repertoire of m6A proteins and how they finely contribute to the tuning of mRNA and lncRNA regulation.
m6A writers—adenosine methyltransferases
The m6A modification is catalyzed by the m6A writer complex inside the nucleus, which consists of the enzymatically active methyltransferase-like 3 (METTL3) protein and some interacting proteins. METTL3 was the first identified of all core writer components, first reported in 1994 as an S-Adenosyl methionine-binding protein with methyltransferase capacity. Known interaction partners of METTL3 are: METTL14, Wilms' tumor 1-associating protein (WTAP), KIAA1429 and RNA-binding motif protein 15 (RBM15). METTL3 activity was also detected in the cytoplasm where it acted to promote translation independent of its methyl transferase activity [9]. METTL14 doesn’t catalyze methyl-group transfer. Rather, it forms a stable heterodimer with METTL3 in a stoichiometric 1:1 ratio and acts as the RNA binding platform which binds to substrate mRNA to enhance the enzymatic activity of METTL3. Separately, METTL3 and METTL14 show comparable weak methyltransferase activity in vitro; synergistically, they exhibit a much higher catalytic activity [2, 27, 33].
WTAP is an essential component of the writer complex. As it lacks methyltransferase domains, it acts as an adaptor protein translocating the METTL3-METTL14 complex to mRNA. Likewise, RBM15 and RBM15B interact with METTL3 in a WTAP-dependent way using their RNA-binding domains enabling the writer complex to bind to specific mRNAs. KIAA1429 is another accessory component associated with the writer complex. KIAA1429, also known as, protein virilizer homolog VIRMA, was reported to guide the METTL3-METTL14 heterodimer to mRNA for region-selective m6A methylation. METTL16 was recently described as a methyltransferase exerting its functions independently of the m6A writer complex surrounding METTL3 [2, 27, 33].
m6A erasers—demethylases
Fat mass and obesity-associated protein (FTO) and alkylated DNA repair protein alkB homologue 5 (ALKBH5) are the two m6A demethylases identified to date [25, 34]. Both proteins are members of the AlkB family, each displaying distinct subcellular and tissue distributions. FTO is readily detected in both the nucleus and the cytosol [6]; however, ALKBH5 is markedly enriched in the nucleus. Hence, this implies that FTO is capable of targeting mature RNAs regulating cytosolic mRNA processing events and ALKBH5 may target nuclear mRNAs where it can regulate export and metabolism of mRNA [27, 33]. It was reported that inactivating ALKBH5 increased total m6A mRNA levels and this was accompanied by accelerated nuclear export and accumulation of mRNA in the cytoplasm [35]. Consistent with these findings, a lack in m6A slowed down nuclear export, delaying the nuclear exit and elongating nuclear retention times [18]. The enzymes’ tissue distribution is another difference between the two enzymes. FTO is broadly expressed in all adult and fetal tissues and highly enriched in brain tissue [36], whereas ALKBH5 is mostly expressed in testes and at substantially lower levels in other tissues [35]. This might suggest that ALKBH5 imparts its demethylase activity in tissues that lack FTO and vice versa [6]. FTO was the first m6A eraser identified several decades ago [36]. FTO was first reported to associate with increased body mass and obesity in humans [37, 38]. Overexpression of FTO in mice led to decreased total m6A levels accompanied with increased food intake, body weight and fat mass [25].
m6A readers— m6A RNA binding proteins
The m6A modifications are recognized by m6A readers and investigating them has shed light on the role of m6A in RNA processing [27]. The m6A modifications are predominantly read either by proteins that are members of the YT521-B homology domain-containing family (YTHDF) and interact with m6A sites via their YTH domains or by the eukaryotic initiation factor 3 (eIF3) [31]. YTH-containing reader proteins include YTH N6-methyladenosine RNA binding proteins 1/2/3 (YTHDF1, YTHDF2, YTHDF3) and YTH Domain-Containing Protein 1 (YTHDC1) which have a conserved m6A-binding pocket [3]. YTHDF1 recruits m6A‐containing transcripts to ribosomes by interacting with translation initiation factors, thereby promoting translation [31]. However, the m6A sites on a transcript seem to be decisive on its fate; whereas methylation within transcripts’ UTRs promoted translation, methylation within coding regions attenuates translation [39].
In contrast, YTHDF2 speeds up the degradation of 3' UTR m6A-modified mRNA transcripts by either interfering with the binding of mRNA stabilizing proteins or by recruiting proteins, which target mRNAs to processing bodies (the cellular sites of mRNA decay) [6, 40].
It was revealed that both the YTHDF1 and YTHDF2 m6A readers share a similar set of target transcripts and cooperate harmoniously. Interestingly, YTHDF1 binds to mRNA in the early stage of its life to promote translation as long as the protein is required. YTHDF2 then associates with the transcripts after their cellular duties are accomplished to alter their stability and sentence them to decay [3, 25]. A study demonstrated that m6A methylation appeared to promote the protein expression of one transcript and to downregulate another. They then explained that the former transcript was a target of YTHDF1 and the latter was a target for YTHDF2 [41].
On the other hand, m6A might also stabilize mRNAs by binding to certain reader proteins that encourage transcript stability preventing their degradation and naturally increasing their expression [42, 43]. Recently, a study stated that insulin-like growth factor 2 mRNA-binding proteins (IGF2BPs, including IGF2BP1/2/3) could also recognize m6A modifications, and can be considered as a distinct family of m6A readers. IGF2BPs exhibits mRNA – stability promoting functions in an m6A-dependent manner in contrast to the mRNA-decay-promoting function of YTHDF2 [44].
YTHDF3, cooperating with YTHDF1 and YTHDF2, can regulate mRNA translation and mediate mRNA decay, respectively [27]. Last but not least, YTHDC1 is the main reader of nuclear m6A modifications. It’s present in both nucleus and cytoplasm and is characterized as a modulator of mRNA splicing events. Additionally, the heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein (hnRNP), another m6A reader, binds to m6A-containing pre-mRNAs and has been shown to affect alternative splicing [2]. eIF3 is a central player in the recruitment of the pre-initiation complex (PIC) to mRNA and the initiation of translation [45]. \* MERGEFORMAT Fig. 2 summarizes the key players involved in the cellular m6A methylation events.
The dynamics of the m6A methylome. The methylated adenosine group is colored yellow. m6A writers, erasers and readers are the protein factors involved in the cellular m6A methylation event. m6A writers catalyze the covalent conversion of Adenosine (A) to m6A on target RNAs. FTO and ALKBH5 are m6A erasers that reverse the methylation. A diverse set of m6A readers selectively bind m6A and mediate post-transcriptional processes on m6A-containing RNA including ① alternative splicing ② nuclear export and RNA localization ③ mRNA degradation ④ 7-Methylguanosine cap-dependent translation ⑤ 7-Methylguanosine cap-independent translation ⑥ and mRNA stabilization
m6A and the innate immune response
The m6A methylation events appear to be integral in the functioning of the innate immune response. Studies demonstrate that m6A modification tightly controls various innate immune responses such as the expression of interferons (IFNs), inflammatory responses, and macrophages and dendritic cells homeostasis. m6A can either improve the immune response against pathogens and viruses or tame the immune response to prevent aggressive immunopathological damage [46].
m 6 A in NK cells
NK cells are innate immune lymphocytes with natural cytotoxicity and cytokine-producing effector functions. It was discovered that m6A methylation acts a positive regulator of NK cell antitumor and antiviral activities. Upon activation by cytokines, tumors, and virus infection, YTHDF2 is upregulated in NK cells. YTHDF2 maintains NK cell homeostasis, maturation and IL-15–mediated NK survival. IL-15 is a crucial regulator of NK cell development, survival and effector functions by forming a STAT5–YTHDF2 positive feedback loop. YTHDF2 deficiency in NK cells impairs NK cell antitumor and antiviral activity in vivo. Tardbp (TAR DNA-binding protein 43 [TDP-43]) transcript is m6A methylated serving as an YTHDF2 binding target. Tardbp is involved in NK cell proliferation and survival. YTHDF2 regulates NK cell proliferation through modulating the mRNA stability of Tardbp and consequently its expression [47]. It was also revealed that METTL3 expression is positively correlated with levels of effector molecules in NK cells and NK effector functions. The mRNA encoding SHP-2 is m6A modified. METTL3-mediated m6A methylation of SHP-2 promotes its expression, thus mediating the activation of AKT-mTOR and MAPK-ERK signaling pathways in response to IL-15 stimulation. METTL3 depletion in NK cells impairs NK homeostasis, renders NK cells hypo-responsive to IL-15 and hinders NK cell infiltration and function in the tumor microenvironment (TME). Mice conditionally deficient for METTL3 in NK cells exhibited aggressive tumor progression, suppressed effector functions of NK cells and shortened survival time. These findings show that METTL3-mediated m6A methylation safeguards the homeostasis and tumor immunosurveillance of NK cells [48]. Investigating the biological roles of m6A modifications in NK cells will open a path to exploit NK power in antitumor immunity.
m 6 A in Dendritic cells
Dendritic cells (DCs) are antigen-presenting cells that initiate an immune response by activating T cells, thus bridging between the innate and adaptive immune systems. A study reported that m6A installed by METTL3 is crucial for DCs maturation and activation, thus m6A serves as a positive regulator. CD40, CD80, and the toll-like receptor (TLR) signaling adaptor protein (TIRAP) are crucial molecules in DCs for inducing T cell activation. METTL3-mediated m6A of these transcripts enhanced their translation in DCs via YTHDF1, thus promoting DCs activation and stimulating DC-mediated T cell activation [49]. Additionally, CCR7 chemokine receptor stimulation induces DCs migration toward draining lymph nodes. This is important for the initiation of protective immunity and maintenance of immune homeostasis. A long non-coding RNA, lnc-Dpf3, hinders the CCR7-induced DC migration and inflammatory response via inhibiting HIF1α-dependent glycolysis in DCs, therefore inhibiting their migratory capacity. m6A-modified lnc-Dpf3 could be degraded when it’s recognized by YTHDF2. CCR7 stimulation upregulates lncDpf3 transcripts by removing m6A, preventing RNA degradation. This negative feedback inhibition via lnc-Dpf3 is vital to prevent exaggerated CCR7-mediated DC migration, therefore prevents amplified adaptive immune responses and inflammatory injuries, maintaining immune balance [50].
On the other hand, recent reports show that m6A plays a negative role in the antitumor immune response specifically in the cross-presentation of tumor antigens for priming T cells by DCs [51]. Antitumor immunity is spontaneously generated by tumor neoantigens, but still, despite expression of neoantigens, tumors can still evade immune recognition. YTHDF1 readers in dendritic cells (DCs) recognize m6A -modified mRNAs encoding lysosomal proteases. They subsequently facilitate the translation of lysosomal proteases, enzymes that destroy proteins in phagosomes, thus destroy antigens, quashing thereby the cross-presentation of engulfed tumor neoantigens by DCs. This is considered one mechanism of immune evasion. Depletion of YTHDF1 in DCs in mouse models enhances cross-presentation of tumor antigens, promotes their cross-priming with CD8+ T and increases the infiltration of neoantigen-specific CD8+ T cells in the tumor microenvironment, thus enhancing antitumor immunity. Therefore, it was proposed that YTHDF1 could be a target for immunotherapy [51].
It is well known that nucleic acids can trigger the innate immune response via activation of endosomal toll-like receptors (TLRs), RIG-like receptors and cytosolic DNA sensors. Interestingly, it was also noticed that DCs treated with m6A-modified RNAs, produce significantly less cytokines and activation markers than when exposed to unmodified RNAs, suggesting that m6A impedes DCs activation. DCs and TLR-expressing cells can better detect and respond to unmodified RNAs as means of selectively responding to invading bacteria or necrotic tissue. However, they are not activated by mammalian total RNA which is m6A-abundant. It was also thought by some researchers that the presence of m6A in some viruses serve the virus in evading the host immune system [52]. Another study reported that the Influenza and Rous sarcoma viruses harbor m6A-modified-RNAs, and these are unable to elicit antiviral innate immune signaling and induce IFN expression [53]. Similar results were reported when the role of m6A in innate immunity induced by exogenous circular RNAs (circRNAs) was investigated. circRNAs prevail in eukaryotic cells and viral genomes. Foreign circRNAs are powerful adjuvants to induce antigen-specific T cell activation, anti-tumor immunity in vivo and antibody production. Mammalian cells possess innate immunity to detect foreign exogenous circRNAs. It was reported that m6A-modified human circRNAs suppress the innate immunization against “self” circRNAs, apparently protected by the m6A modification. On the other hand, unmodified circRNAs increase interferon production [54].
m 6 A in Macrophages
Macrophages, serving as the first line of host defense, are the scavenger cells of the innate immune system playing significant roles in autophagy by engulfing worn-out cells and other cellular debris. They also act as antigen presenting cells and secretory cells that produce a variety of cytokines vital to the host immune defense against infection [4]. m6A modification was also reported to play a role in macrophage functions.
Investigating the m6A regulatory enzymes during macrophage polarization revealed that METTL3 is upregulated during M1 polarization of mouse macrophages. Depending on their genetic background and environmental stimuli, macrophages can be polarized to one of two phenotypes, either M1 or M2, based on in vitro model systems [55]. M1 macrophages are tumoricidal, produce interferon γ (IFN-γ) with proinflammatory activity, and have a high capacity for antigen presentation and T cell activation. M2 macrophages are of a protumoral phenotype and produce interleukin-4 (IL-4) with anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressive function. Alterations in macrophage polarization between M1 and M2 phenotypes control various physiological and pathological processes. It must be kept in mind that strict M1 and M2 macrophages almost certainly do not exist in vivo since macrophages are exposed to a plethora of stimuli that result in different macrophage cell surface markers and different functions [56]. METTL3 methylates an important player in M1 macrophage polarization, STAT1 mRNA, thus upregulating its expression. METTL3 knockdown markedly reduced M1 and stimulated M2 macrophage polarization. This implies that METTL3 might play an important role in anti-inflammatory therapies [55]. Similarly, another study indicated that m6A and METTL3 expression levels were up‐regulated in lipopolysaccharide (LPS)‐stimulated human dental pulp cells (HDPCs) in dental pulp inflammation. In response to LPS, NF-κB and MAPK pathways are activated in macrophages, which further induce the expression of various proinflammatory cytokines, such as TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6. Dental pulp inflammation is an inflammatory disease characterized by accumulation of inflammatory mediators. It can progress to pulp necrosis and periapical diseases, which are mainly due to a bacterial infection acting as a major pathogenic factor. METTL3 deletion decreases the expression of inflammatory cytokines and suppresses the activation of Nuclear Factor kappa B (NF-κB) and MAPK signaling pathway in LPS-induced HDPCs. METTL3 was found to modulate the alternative splicing of MyD88, a splice variant of MyD88 that inhibits inflammatory cytokine production. m6A inhibition significantly increases MyD88S mRNA levels which consequently inhibits proinflammatory cytokines production. This suggests that METTL3 modulates LPS-induced inflammatory response of HDPCs by regulating alternative splicing of MyD88 in HDPCs [57].
Consistently, m6A modification also has a positive regulatory role in macrophage activation. Macrophage Toll-like Receptors (TLRs) play a vital role in sensing invading pathogens. TLR4, induce type I interferons and inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-α and IL-6. IL-1 receptor–associated kinase 3 (IRAK3), also known as IRAKM, is a negative regulator of TLR signaling pathways. The transcripts of IRAKM gene are highly m6A-modified. METTL3 deficiency led to the loss of m6A modification on IRAKM mRNA, leading to slowing down decay rate and therefore the suppression of TLR signaling–mediated macrophage activation. Loss of METTL3 promotes tumor growth, increased susceptibility to bacterial infection in vivo and reduced TNF-α secretion by macrophages in vitro. This concludes that METTL3 deficiency inhibits macrophage activation by inducing a negative regulator of the TLR signaling pathway. These findings implicate the m6A machinery as a potential cancer immunotherapy target [58]. Supporting these results, another study demonstrated that METTL3 deletion in macrophages promotes tumorigenesis and metastasis by enhancing tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs) and T regulatory (Treg) cells infiltration into the tumor microenvironment (TME). Most tumors shape the TME by recruiting TAMs and Tregs, which induce an immunosuppressive TME. METTL3 deficiency impairs the YTHDF1- mediated translation of SPRED2 mRNA, an m6A target gene. This enhances the activation of NF-kB and STAT3 through the ERK pathway in METTL3-depleted macrophages, leading to increased tumor growth and metastasis [59].
It can be concluded from the previous studies in macrophages that METTL3 is crucial for macrophage activation and for initiating a pro-inflammatory cascade or exerting a tumoricidal role. Depleting METTL3 in macrophages hindered macrophage activation, promoted anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressive activities and encouraged tumor growth and metastasis. In contrast, the m6A reader, YTHDF2, plays a negative regulatory role in LPS-mediated inflammatory responses of macrophages. YTHDF2 depletion results in the upregulated expression and stability of MAP2K4 and MAP4K4 mRNAs, upstream molecules in the LPS-induced inflammatory response, which promote the expression of proinflammatory cytokines. Thus, YTHDF2 can be another likely target for anti-inflammatory therapies [60].
m6A and the adaptive immune response
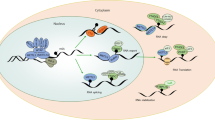
There are two types of lymphocytes critical for the adaptive immune response, T-lymphocytes (T cells) and B-lymphocytes (B cells). They originate from stem cells in the bone marrow and differentiate in the central lymphoid organs. T cells mediate the cellular immune response and B cells produce antibodies in humoral immune responses [4].
m 6 A modification in T cells
D2-like Dopamine (DA) receptors, which are highly influenced by m6A modification events, are not only expressed in the brain but also in T cells. They contribute to the regulation of T-lymphocyte function and development in the thymus thus linking m6A modification with normal T lymphocytes development and immune responses [61, 62].
In a study by Li et al., it was shown that m6A methylation on mRNA controls T cell homeostasis. Depletion of METTL3 in mouse T cells upsets T cell homeostasis and differentiation. T cells fail to undergo homeostatic expansion and remain in the naive state for up to 12 weeks. m6A mRNA methylation targets the IL-7/STAT5/SOCS pathways, which represent an important signal axis in the maintenance of T cell proliferation and differentiation. Deleting METTL3 decreased methylation of the Suppressors of Cytokine Signaling (SOCS) family genes transcripts, which encode the IL-7/STAT signaling inhibitory proteins. These hindered the mRNA decay and increased mRNAs, mRNA half-life and SOCS protein expression in naive T cells. The amplified activity of the SOCS family consequently inhibited IL-7-mediated STAT5 activation and suppressed T cell homeostatic proliferation and differentiation. This means that m6A is essential for inducing decay of SOCS mRNAs, in order for T cells to escape the naïve state in response to IL-7/STAT signaling [63]. Building up on the previous study, researchers quantified RNA dynamics in T cells, using bioinformatic analysis, to reveal how transcripts are regulated by m6A. In the context of T cell homeostasis, m6A depletion is reported to globally slow down the rates of all stages of the RNA life cycle by delaying RNA synthesis rates, impairing RNA processing rates and hindering SOCS mRNA decay rates. All these effects may directly or indirectly upset T cell differentiation [64]. Interestingly, these findings suggest that T cell-targeted delivery of m6A modifying agents could be an eminent step in cancer immunotherapy [31, 63, 65].
Likewise, research on regulatory T cells showed how m6A plays a role in their function. Regulatory T cells are a subpopulation of CD4+ T cells that act to reduce inflammation, suppress the immune response and reduce autoimmunity [66]. m6A is critical to sustain the suppressive functions of Tregs. Decreased m6A portrayed a similar scenario as observed in CD4+ naïve T cells. Low m6A led to a loss in Tregs suppressive functions where SOCS activity increased, inhibiting the IL2-STAT5 pathway, which is critical for the Treg cell functions. When Tregs with depleted m6A were co-cultured with naïve CD4+ T cells, it was revealed that naïve T cells exerted faster proliferation due to complete lack of suppressive action of Tregs. Moreover, METTL3-knockout mice develop severe systemic autoimmune diseases. It was suggested that since Tregs alleviate the tumor-killing functions of CD8+ T cells in the tumor microenvironment, the selective reduction of m6A in tumor-infiltrated Tregs may be advantageous in combination with other methods of cancer immunotherapy [67].
Follicular helper T (Tfh) are a unique CD4+ T cell subset and have an eminent role in the formation of germinal centers (GCs) and mediating humoral immunity. Inducible costimulator (icos) is crucial for Tfh development. GAPDH, a glycolytic enzyme, is a key player in regulating Tfh cell development, acting as an epigenetic regulator. GAPDH alters the METTL3/METTL14-mediated m6A modification on icos mRNA during the initiation of Tfh cells. It negatively controls icos gene expression, by promoting icos mRNA degradation via the m6A modification on icos mRNA, thus suppressing Tfh development [68].
m 6 A modification in B cells
The role of m6A in B cells is still under-explored. It was reported that m6A methylation is vital in early B cells development as it induces IL-7 mediated pro-B cell proliferation as well as the transitioning from large-pre B cells to small- pre-B cells. Deletion of METTL14 severely impairs both processes and causes defects in gene expression important for B cell development [69].
The effects of m6A modifications on T cells and B cells have extensive implications in the adaptive immune response and surely have an impact in the development and progression of various immune-related diseases. \* MERGEFORMAT Fig. 3 shows a summary of some m6A regulatory pathways in some immune cells.
m 6 A and antiviral immunity
Recent research has demonstrated that the m6A machinery is involved in the host response to viral infection, playing either a pro-viral or an anti-viral role.
m6A modification can suppress the antiviral innate immune system by targeting type I interferons. The mRNA of IFN-β, the main type I interferon in non-immune cells that drives the type I interferon response, is m6A modified. m6A decorating the IFN-β dictates the fast turnover of interferon mRNAs consequently facilitating viral propagation. IFN-β transcripts were stabilized following repression of METTL3 or YTHDF2. Deletion of METTL3 or YTHDF2 reader led to an increase in the induction of interferon-stimulated genes following a viral infection or after stimulation with an inactivated virus. Consequently, propagation of different viruses was suppressed in an interferon-signaling-dependent manner [70]. Moreover, YTHDF3 also suppresses IFN response by upregulating FOXO3 translation. FOXO3 acts as the IFN transcription repressor [71]. These findings suggest that m6A serves as a negative regulator of interferon response, thus the antiviral response. Another finding shows that m6A acts as a negative regulator for the Rig-like receptors (RLR)-mediated sensing pathway of the Vesicular Stomatitis Virus (VSV) dsRNA. Upon VSV infection, METTL3 increases m6A on virus-derived transcripts and decreases viral dsRNA formation, thus reducing the virus-sensing efficacy of RLRs and attenuating the antiviral immune signaling. METTL3 depletion in the monocytes of a murine model protects the mice against VSV infection, enhances type I IFN expression and speeds up VSV clearance [72].
On the contrary, other studies reported that m6A is vital for the antiviral innate immune response. m6A modification plays a critical role in increasing the IFN release in macrophage- mediated antiviral immunity. DEAD-box (DDX) helicase members have been verified to sense viral RNAs, thus are crucial for the initiation of antiviral innate immunity. However, one of the nuclear DDX family members, DDX46 was shown to negatively regulate the production of type I interferon after viral infection. It does this by recruiting ALKBH5 to demethylate some m6A-modified antiviral transcripts. This enforces the nuclear retention of antiviral transcripts, preventing their translation and hindering interferon production in the infected macrophages. This might help to prevent the over activation of antiviral innate responses. In vivo knockdown of DDX46 enhances macrophage-mediated antiviral response [73]. Coincidentally, another study revealed that m6A modification augments the IFN- mediated antiviral immune response by encouraging the translation of certain IFN-stimulated genes (ISGs) [74]. Upon viral infection, m6A writer, WTAP, is degraded via the ubiquitination- proteasome pathway. This reduces m6A levels on the IFN‐regulatory factor 3 (IRF3) and interferon alpha/beta receptor subunit 1 (IFNAR1) mRNAs, which are transcripts crucial for IFN-derived antiviral response. Consequently, their translation is suppressed, thereby blocking IFN‐I‐mediated antiviral responses. Thus, m6A induced by WTAP is essential to maintain the protein abundance of IRF3 and IFNAR1, thus sustaining the antiviral response [75].
m6A levels also were found to be upregulated in primary human foreskin fibroblasts upon infection with human cytomegalovirus (HCMV), exhibiting a pro-viral role by activating viral propagation. Post infection, in METTL3-depleted cells, the decreased m6A leads to increased mRNA stability of Interferon- β (IFN-β) and sustained IFN-β production. This prompts an intense antiviral response to block HCMV growth [70]. Consistently, METTL14 depletion enhanced IFN expression and reduced viral propagation, but ALKBH5 depletion had an opposite effect [76]. Moreover, a proviral role of m6A machinery has also been observed with influenza A virus. Though the mechanism is unknown, it is assumed that YTHDF2 promotes the degradation of antiviral transcripts [77]. Additionally, m6A modification of the SARS-CoV-2 genome was investigated in regulating the innate immune response. Depleting METTL3 decreases m6A in SARS-CoV-2 and host genes, and this subsequently enhances the downstream innate immune signaling and inflammatory gene expression towards the virus. This shows that m6A has a pro-viral role suppressing the innate immune signaling [78]. Similarly, another study also reported that RBM15, a methyltransferase, was significantly elevated in SARS-CoV-2 infected patients, as well as positively correlated with disease severity. RBM15 elevated m6A modifications of multi-target genes thus negatively regulated host immune response to SARS-CoV-2. These findings indicate that RBM15 can serve as a target for the treatment COVID-19 [79]. HIV-1 infection of the human CD4 + T cells triggers a massive increase in m6A in both host and viral mRNAs. m6A on the viral transcripts positively correlate with HIV-1 viral replication, where m6A is vital for the export of viral mRNAs from T cell nuclei and subsequently viral replication. Silencing m6A writers decreases HIV-1 replication and silencing m6A erasers increased HIV-1 replication [80]. Consistently, YTHDF overexpression enhanced HIV-1 protein and RNA expression, propagating virus replication in CD4 + T cells. YTHDF downregulation reversed this effect. These results suggest that m6A writers and readers have pro-viral roles [81]. Conversely, another study showed that YTHDF readers recognize m6A-modified HIV-1 RNA and inhibit HIV-1 infection in CD4 + cells by decreasing HIV-1 reverse transcription. Knocking down YTHDF proteins had opposite effects. This implies that YTHDF can also act as a negative regulator of the HIV-1 replication, indicating that the m6A-mediated functions in regulating HIV-1 infection depend on different stages of the viral life cycle [82, 83].
The function of m6A modifications in the oncogenic human DNA virus Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (KSHV) remains controversial. m6A levels were reported to be significantly increased in B cells infected with KSHV. METTL3 and YTHDF2 functioned in a pro-viral manner and depleting them significantly reduced virion production in KSHV infected B cells [84]. Additionally, YTHDC1 encourages KSHV lytic replication by facilitating the splicing of the replication transcription activator (RTA) [85]. On the other hand, a study reported that YTHDF2 impairs KSHV replication by degrading KSHV viral transcripts [86]. Interestingly, m6A can be a novel target to develop new KSHV antiviral therapies.
To sum up, it is clear that m6A is neither consistently pro-viral nor anti-viral. Instead, it regulates many aspects of viral replication and the immune response signaling pathways by modulating specific RNAs according to the cell type [87].
Conclusion
Recently, m6A modification is becoming one of the hot spots of life sciences gaining vast attention of RNA biologists because of its various functional implications [29]. The dynamic interplay between the methyl writers, readers and erasers creates an optimally methylated transcriptome that dictate the m6A-dependent functions and fate of RNA [3]. m6A can modulate the mRNA life cycle transcriptionally and post-transcriptionally, which include pre-mRNA processing, export, translation and decay processes.
It was noted that m6A could affect diseases by regulating the immune system, unfolding the curtains on the link between m6A and immunotherapy. Targeting the m6A modification could enhance the patient’s own immune system to fight against progressive cancers and other diseases. Thus, m6A could be potential pharmacological targets [33, 88].
In this review, we summarized some recent findings of m6A modification in immune cells. In general, we concluded that the role of m6A in various immune cells is controversial. Interestingly, m6A can potentially exert dual opposite effects on the fate of methylated transcripts. The fate of m6A modified transcripts is dictated by several factors. One factor is governed by which type of reader protein recognizes and binds to the transcript at which time point. Different readers may target different set of transcripts but sometimes, different readers may preferentially bind to diverse regions within the same transcripts or may even compete on the same region within the same transcript. Therefore, to better understand the m6A mediated regulation of mRNA transcripts, it is important to know which regions of the transcripts are m6A modified and which readers bind to the modified sections [89]. Another factor is that m6A regulatory proteins may function differently in different cell context by regulating different sets of targets, concluding that m6A regulation is of cell heterogeneity [90]. Thus, it is not unusual that an m6A writer and an eraser may exert the same result in a given type of pathological condition, probably through targeting distinct sets of genes [29]. Alternatively, they may also regulate the same set of target genes and cause similar biological effects via different mechanisms [89], so each case must be analyzed individually. The greatest challenge is that m6A is a dynamic and reversible modification, so pinpointing the exact modification sites and the key transcripts regulated by m6A is difficult. Moreover, any manipulation of m6A to manipulate the immune response will be difficult and will need to be specifically targeted.
How and when are m6A regulatory proteins involved in the methylation event? How do they interact with one another? Do the roles of m6A work in concert or are antagonistic in different immune cells? In other words, can the effect of m6A in the different immune cells result in a general immunosuppressant or an immunostimulant effect? How and why do m6A regulators mediate specific gene expression regulation? All these questions are still unresolved. We anticipate that more extensive research on m6A in immune cells and the immune response will open the door for exploiting immune cells in novel therapeutic strategies including cancer immunotherapy, antiviral, anti-inflammatory and autoimmune disease therapies.
Availability of data and materials
Not applicable.
Abbreviations
- 3' UTR :
-
3' Untranslated Region
- ALKBH5:
-
Alkylated DNA repair protein alkB homologue 5
- AML:
-
Acute myeloid leukemia
- DA:
-
Dopamine
- DC :
-
Dendritic cell
- DDX:
-
DEAD-box
- DLBCL:
-
Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma
- FTO:
-
Fat mass and obesity-associated protein
- GSCs:
-
Glioblastoma stem cells
- HCC:
-
Hepatocellular carcinoma
- HCMV:
-
Human cytomegalovirus
- IFN:
-
Interferon
- IGF2BPs:
-
Insulin-like growth factor 2 mRNA-binding proteins
- IL:
-
Interleukin
- IRAK3:
-
IL-1 receptor–associated kinase 3
- KIAA1429:
-
Protein virilizer homolog VIRMA
- KSHV:
-
Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus
- LPS:
-
Lipopolysaccharide
- METTL3:
-
Methyltransferase-like 3
- NK cells:
-
Natural Killer cells
- NSCLC:
-
Non-small-cell lung carcinoma
- PEDF:
-
Pigment epithelium-derived factor
- PIC:
-
Pre-initiation complex
- piRNAs:
-
PIWI-interacting RNAs
- RTA:
-
Replication transcription activator
- SOCS:
-
Suppressors of cytokine signaling
- Tfh:
-
Follicular helper T
- TIRAP:
-
TLR signaling adaptor protein
- TLR:
-
Toll-like receptor
- TME:
-
Tumor microenvironment
- TNF:
-
Tumor necrosis factor
- WTAP:
-
Wilms' tumor 1-associating protein
- YTHDF:
-
YT521-B homology domain-containing family
References
Hotchkiss RD. The quantitative separation of purines, pyrimidines, and nucleosides by paper chromatography. J Biol Chem [Internet]. 1948;175(1):315–32.
Jacob R, Zander S, Gutschner T. The dark side of the epitranscriptome: Chemical modifications in long non-coding rnas. Int J Mol Sci. 2017;18(11):2387.
Zhao BS, Roundtree IA, He C. Post-transcriptional gene regulation by mRNA modifications. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2016;18(1):31–42.
Liu C, Yang Z, Li R, Wu Y, Chi M, Gao S, et al. Potential roles of N6-methyladenosine (m6A) in immune cells. J Transl Med [Internet]. 2021;19(1):251. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12967-021-02918-y.
Lewis CJT, Pan T, Kalsotra A. RNA modifications and structures cooperate to guide RNA–protein interactions. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol [Internet]. 2017;18(3):202–10.
Meyer KD, Jaffrey SR. The dynamic epitranscriptome: N6-methyladenosine and gene expression control. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2014;15(5):313–26.
Huang J, Yin P. Structural Insights into N6-methyladenosine (m6A) modification in the transcriptome. Genomics Proteomics Bioinforma [Internet]. 2018;16(2):85–98. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gpb.2018.03.001.
Edupuganti RR, Geiger S, Lindeboom RGH, Shi H, Hsu PJ, Lu Z, et al. N6-methyladenosine (m6A) recruits and repels proteins to regulate mRNA homeostasis. Nat Struct Mol Biol [Internet]. 2017;24(10):870–8.
Lin S, Choe J, Du P, Triboulet R, Gregory RI. The m 6 A methyltransferase METTL3 promotes translation in human cancer cells. Mol Cell [Internet]. 2016;62(3):335–45.
Linder B, Grozhik AV, Olarerin-George AO, Meydan C, Mason CE, Jaffrey SR. Single-nucleotide-resolution mapping of m6A and m6Am throughout the transcriptome. Nat Methods [Internet]. 2015;12(8):767–72.
Wei C-M, Moss B. Nucleotide sequences at the N 6 -methyladenosine sites of HeLa cell messenger ribonucleic acid. Biochemistry [Internet]. 1977;16(8):1672–6. https://doi.org/10.1021/bi00627a023.
Csepany T, Lin A, Baldick CJ, Beemon K. Sequence specificity of mRNA N6-adenosine methyltransferase. J Biol Chem [Internet]. 1990;265(33):20117–22.
Zhao Y, Chen Y, Jin M, Wang J. The crosstalk between m 6 A RNA methylation and other epigenetic regulators: A novel perspective in epigenetic remodeling. Theranostics [Internet]. 2021;11(9):4549–66.
Kan RL, Chen J, Sallam T. Crosstalk between epitranscriptomic and epigenetic mechanisms in gene regulation. Trends Genet [Internet]. 2022;38(2):182–93.
Liu J, Dou X, Chen C, Chen C, Liu C, Xu MM, et al. N 6 -methyladenosine of chromosome-associated regulatory RNA regulates chromatin state and transcription. Science (80- ) [Internet]. 2020;367(6477): 580–6. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aay6018.
Chen C, Liu W, Guo J, Liu Y, Liu X, Liu J, et al. Nuclear m6A reader YTHDC1 regulates the scaffold function of LINE1 RNA in mouse ESCs and early embryos. Protein Cell [Internet]. 2022;13(6):470–1. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13238-021-00853-8.
He C, Lan F. RNA m6A meets transposable elements and chromatin. Protein Cell [Internet]. 2021;12(12):906–10. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13238-021-00859-2.
Fustin J-M, Doi M, Yamaguchi Y, Hida H, Nishimura S, Yoshida M, et al. RNA-methylation-dependent RNA processing controls the speed of the circadian clock. Cell [Internet]. 2013;155(4):793–806.
Batista PJ, Molinie B, Wang J, Qu K, Zhang J, Li L, et al. m6A RNA Modification controls cell fate transition in mammalian embryonic stem cells. Cell Stem Cell [Internet]. 2014;15(6):707–19.
Zhang C, Samanta D, Lu H, Bullen JW, Zhang H, Chen I, et al. Hypoxia induces the breast cancer stem cell phenotype by HIF-dependent and ALKBH5-mediated m 6 A-demethylation of NANOG mRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci [Internet]. 2016;113(14):E2047–56. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1602883113.
Geula S, Moshitch-Moshkovitz S, Dominissini D, Mansour AA, Kol N, Salmon-Divon M, et al. m 6 A mRNA methylation facilitates resolution of naïve pluripotency toward differentiation. Science (80- ) [Internet]. 2015;347(6225):1002–6. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1261417.
Wang Y, Li Y, Toth JI, Petroski MD, Zhang Z, Zhao JC. N6-methyladenosine modification destabilizes developmental regulators in embryonic stem cells. Nat Cell Biol [Internet]. 2014;16(2):191–8.
Schwartz S, Agarwala SD, Mumbach MR, Jovanovic M, Mertins P, Shishkin A, et al. High-resolution mapping reveals a conserved, widespread, dynamic mRNA methylation program in yeast meiosis. Cell [Internet]. 2013;155(6):1409–21.
Wang X, Zhao BS, Roundtree IA, Lu Z, Han D, Ma H, et al. N6-methyladenosine modulates messenger RNA translation efficiency. Cell [Internet]. 2015;161(6):1388–99.
Maity A, Das B. N 6-methyladenosine modification in mRNA : machinery, function and implications for health and diseases. FEBS J [Internet]. 2016;283(9):1607–30. https://doi.org/10.1111/febs.13614.
Cai X, Wang X, Cao C, Gao Y, Zhang S, Yang Z, et al. HBXIP-elevated methyltransferase METTL3 promotes the progression of breast cancer via inhibiting tumor suppressor let-7g. Cancer Lett [Internet]. 2018;415:11–9.
Yang Y, Hsu PJ, Chen YS, Yang YG. Dynamic transcriptomic m6A decoration: Writers, erasers, readers and functions in RNA metabolism. Cell Res [Internet]. 2018;28(6):616–24. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41422-018-0040-8.
Niu Y, Lin Z, Wan A, Chen H, Liang H, Sun L, et al. RNA N6-methyladenosine demethylase FTO promotes breast tumor progression through inhibiting BNIP3. Mol Cancer [Internet]. 2019;18(1):46. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-019-1004-4.
Wu L, Wu D, Ning J, Liu W, Zhang D. Changes of N6-methyladenosine modulators promote breast cancer progression. BMC Cancer [Internet]. 2019;19(1):326. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12885-019-5538-z.
Zhang S, Zhao BS, Zhou A, Lin K, Zheng S, Lu Z, et al. m 6 A demethylase ALKBH5 maintains tumorigenicity of glioblastoma stem-like cells by sustaining FOXM1 expression and cell proliferation program. Cancer Cell [Internet]. 2017;31(4):591-606.e6.
Zhang C, Fu J, Zhou Y. A review in research progress concerning m6A methylation and immunoregulation. Front Immunol [Internet]. 2019;10(APR). https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2019.00922/full.
Sun T, Wu R, Ming L. The role of m6A RNA methylation in cancer. Biomed Pharmacother [Internet]. 2019;112:108613.
Niu Y, Wan A, Lin Z, Lu X, Wan G. N6-Methyladenosine modification: a novel pharmacological target for anti-cancer drug development. Acta Pharm Sin B [Internet]. 2018;8(6):833–43.
Holoch D, Moazed D. RNA-mediated epigenetic regulation of gene expression. Nat Rev Genet [Internet]. 2015;16(2):71–84.
Zheng G, Dahl JA, Niu Y, Fedorcsak P, Huang C-M, Li CJ, et al. ALKBH5 Is a mammalian RNA demethylase that impacts RNA metabolism and mouse fertility. Mol Cell [Internet]. 2013;49(1):18–29.
Gerken T, Girard CA, Tung Y-CL, Webby CJ, Saudek V, Hewitson KS, et al. The Obesity-Associated FTO Gene Encodes a 2-Oxoglutarate-Dependent Nucleic Acid Demethylase. Science (80- ) [Internet]. 2007;318(5855):1469–72. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1151710.
Frayling TM, Timpson NJ, Weedon MN, Zeggini E, Freathy RM, Lindgren CM, et al. A common variant in the FTO gene is associated with body mass index and predisposes to childhood and adult obesity. Science (80- ) [Internet]. 2007;316(5826):889–94. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1141634.
Scuteri A, Sanna S, Chen W-M, Uda M, Albai G, Strait J, et al. Genome-wide association scan shows genetic variants in the FTO gene are associated with obesity-related traits. Barsh G, editor. PLoS Genet [Internet]. 2007;3(7):e115. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.0030115.
Slobodin B, Han R, Calderone V, Vrielink JAFO, Loayza-Puch F, Elkon R, et al. Transcription impacts the efficiency of mRNA translation via Co-transcriptional N6-adenosine methylation. Cell [Internet]. 2017;169(2):326–37.
Wang X, Lu Z, Gomez A, Hon GC, Yue Y, Han D, et al. N6-methyladenosine-dependent regulation of messenger RNA stability. Nature [Internet]. 2014;505(7481):117–20.
Liu JJ, Eckert MA, Harada BT, Liu S-M, Lu Z, Yu K, et al. m6A mRNA methylation regulates AKT activity to promote the proliferation and tumorigenicity of endometrial cancer. Nat Cell Biol [Internet]. 2018;20(9):1074–83.
Li T, Hu PS, Zuo Z, Lin JF, Li X, Wu QN, et al. METTL3 facilitates tumor progression via an m6A-IGF2BP2-dependent mechanism in colorectal carcinoma. Mol Cancer. 2019;18(1):1–15.
Dominissini D, Moshitch-Moshkovitz S, Schwartz S, Salmon-Divon M, Ungar L, Osenberg S, et al. Topology of the human and mouse m6A RNA methylomes revealed by m6A-seq. Nature [Internet]. 2012;485(7397):201–6.
Huang H, Weng H, Sun W, Qin X, Shi H, Wu H, et al. Recognition of RNA N6-methyladenosine by IGF2BP proteins enhances mRNA stability and translation. Nat Cell Biol [Internet]. 2018;20(3):285–95.
Ma F, Li X, Ren J, Guo R, Li Y, Liu J, et al. Downregulation of eukaryotic translation initiation factor 3b inhibited proliferation and metastasis of gastric cancer. Cell Death Dis [Internet]. 2019;10(9):623.
Zhao B, Wang W, Zhao Y, Qiao H, Gao Z, Chuai X. Regulation of Antiviral Immune Response by N6-Methyladenosine of mRNA. Front Microbiol [Internet]. 2021; https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2021.789605/full.
Ma S, Yan J, Barr T, Zhang J, Chen Z, Wang L-S, et al. The RNA m6A reader YTHDF2 controls NK cell antitumor and antiviral immunity. J Exp Med [Internet]. 2021;218(8):2021.
Song H, Song J, Cheng M, Zheng M, Wang T, Tian S, et al. METTL3-mediated m6A RNA methylation promotes the anti-tumour immunity of natural killer cells. Nat Commun [Internet]. 2021;12(1):5522.
Wang H, Hu X, Huang M, Liu J, Gu Y, Ma L, et al. Mettl3-mediated mRNA m6A methylation promotes dendritic cell activation. Nat Commun [Internet]. 2019;10(1):1898.
Liu J, Zhang X, Chen K, Cheng Y, Liu S, Xia M, et al. CCR7 chemokine receptor-inducible lnc-Dpf3 restrains dendritic cell migration by inhibiting HIF-1α-mediated glycolysis. Immunity [Internet]. 2019;50(3):600–15.
Han D, Liu J, Chen C, Dong L, Liu Y, Chang R, et al. Anti-tumour immunity controlled through mRNA m6A methylation and YTHDF1 in dendritic cells. Nature [Internet]. 2019;566(7743):270–4.
Karikó K, Buckstein M, Ni H, Weissman D. Suppression of RNA recognition by toll-like receptors: The impact of nucleoside modification and the evolutionary origin of RNA. Immunity [Internet]. 2005;23(2):165–75.
Durbin AF, Wang C, Marcotrigiano J, Gehrke L. RNAs Containing Modified Nucleotides Fail To Trigger RIG-I Conformational Changes for Innate Immune Signaling. Racaniello VR, editor. MBio [Internet]. 2016;https://doi.org/10.1128/mBio.00833-16.
Chen YG, Chen R, Ahmad S, Verma R, Kasturi SP, Amaya L, et al. N6-methyladenosine modification controls circular RNA immunity. Mol Cell. 2019;76(1):96-109.e9.
Liu Y, Liu Z, Tang H, Shen Y, Gong Z, Xie N, et al. The N 6 -methyladenosine (m 6 A)-forming enzyme METTL3 facilitates M1 macrophage polarization through the methylation of STAT1 mRNA. Am J Physiol Physiol [Internet]. 2019;317(4):C762–75. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpcell.00212.2019.
Tabas I, Bornfeldt KE. Macrophage phenotype and function in different stages of atherosclerosis. Circ Res [Internet]. 2016;118(4):653–67. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.115.306256.
Feng Z, Li Q, Meng R, Yi B, Xu Q. METTL 3 regulates alternative splicing of MyD88 upon the lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory response in human dental pulp cells. J Cell Mol Med [Internet]. 2018;22(5):2558–68. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcmm.13491.
Tong J, Wang X, Liu Y, Ren X, Wang A, Chen Z, et al. Pooled CRISPR screening identifies m 6 A as a positive regulator of macrophage activation. Sci Adv [Internet]. 2021;https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.abd4742.
Yin H, Zhang X, Yang P, Zhang X, Peng Y, Li D, et al. RNA m6A methylation orchestrates cancer growth and metastasis via macrophage reprogramming. Nat Commun [Internet]. 2021;12(1):1394.
Yu R, Li Q, Feng Z, Cai L, Xu Q. m6A Reader YTHDF2 regulates LPS-induced inflammatory response. Int J Mol Sci [Internet]. 2019;20(6):1323.
Mignini F, Sabbatini M, Capacchietti M, Amantini C, Bianchi E, Artico M, et al. T-cell subpopulations express a different pattern of dopaminergic markers in intra- and extra-thymic compartments. J Biol Regul Homeost Agents. 2013;1(27):463–75.
Huang Y, Qiu A-W, Peng Y-P, Liu Y, Huang H-W, Qiu Y-H. Roles of dopamine receptor subtypes in mediating modulation of T lymphocyte function. Neuro Endocrinol Lett [Internet]. 2010;31(6):782–91.
Li H-B, Tong J, Zhu S, Batista PJ, Duffy EE, Zhao J, et al. m6A mRNA methylation controls T cell homeostasis by targeting the IL-7/STAT5/SOCS pathways. Nature [Internet]. 2017;548(7667):338–42.
Furlan M, Galeota E, De Pretis S, Caselle M, Pelizzola M. m6A-Dependent RNA Dynamics in T Cell Differentiation. Genes (Basel) [Internet]. 2019;10(1):28.
Lou X, Wang J-J, Wei Y-Q, Sun J-J. Emerging role of RNA modification N6-methyladenosine in immune evasion. Cell Death Dis [Internet]. 2021;12(4):300.
Li MO, Rudensky AY. T cell receptor signalling in the control of regulatory T cell differentiation and function. Nat Rev Immunol [Internet]. 2016;16(4):220–33.
Tong J, Cao G, Zhang T, Sefik E, Amezcua Vesely MC, Broughton JP, et al. m6A mRNA methylation sustains treg suppressive functions. Cell Res [Internet]. 2018;28(2):253–6.
Zhu Y, Zhao Y, Zou L, Zhang D, Aki D, Liu Y-C. The E3 ligase VHL promotes follicular helper T cell differentiation via glycolytic-epigenetic control. J Exp Med [Internet]. 2019;216(7):1664–81.
Zheng Z, Zhang L, Cui X-L, Yu X, Hsu PJ, Lyu R, et al. Control of early B cell development by the RNA N6-methyladenosine methylation. Cell Rep [Internet]. 2020;31(13):107819.
Winkler R, Gillis E, Lasman L, Safra M, Geula S, Soyris C, et al. m6A modification controls the innate immune response to infection by targeting type I interferons. Nat Immunol [Internet]. 2019;20(2):173–82. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41590-018-0275-z.
Zhang Y, Wang X, Zhang X, Wang J, Ma Y, Zhang L, et al. RNA-binding protein YTHDF3 suppresses interferon-dependent antiviral responses by promoting FOXO3 translation. Proc Natl Acad Sci [Internet]. 2019;116(3):976–81. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1812536116.
Qiu W, Zhang Q, Zhang R, Lu Y, Wang X, Tian H, et al. N6-methyladenosine RNA modification suppresses antiviral innate sensing pathways via reshaping double-stranded RNA. Nat Commun [Internet]. 2021;12(1):1582.
Zheng Q, Hou J, Zhou Y, Li Z, Cao X. The RNA helicase DDX46 inhibits innate immunity by entrapping m6A-demethylated antiviral transcripts in the nucleus. Nat Immunol [Internet]. 2017;18(10):1094–103.
McFadden MJ, McIntyre ABR, Mourelatos H, Abell NS, Gokhale NS, Ipas H, et al. Post-transcriptional regulation of antiviral gene expression by N6-methyladenosine. Cell Rep [Internet]. 2021;34(9):108798.
Ge Y, Ling T, Wang Y, Jia X, Xie X, Chen R, et al. Degradation of WTAP blocks antiviral responses by reducing the m 6 A levels of IRF3 and IFNAR1 mRNA. EMBO Rep [Internet]. 2021;https://doi.org/10.15252/embr.202052101.
Rubio RM, Depledge DP, Bianco C, Thompson L, Mohr I. RNA m 6 A modification enzymes shape innate responses to DNA by regulating interferon β. Genes Dev [Internet]. 2018;32(23–24):1472–84. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.319475.118.
Courtney DG, Kennedy EM, Dumm RE, Bogerd HP, Tsai K, Heaton NS, et al. Epitranscriptomic enhancement of influenza A virus gene expression and replication. Cell Host Microbe [Internet]. 2017;22(3):377–86.
Li N, Hui H, Bray B, Gonzalez GM, Zeller M, Anderson KG, et al. METTL3 regulates viral m6A RNA modification and host cell innate immune responses during SARS-CoV-2 infection. Cell Rep [Internet]. 2021;35(6):109091.
Meng Y, Zhang Q, Wang K, Zhang X, Yang R, Bi K, et al. RBM15-mediated N6-methyladenosine modification affects COVID-19 severity by regulating the expression of multitarget genes. Cell Death Dis [Internet]. 2021;12(8):732.
Lichinchi G, Gao S, Saletore Y, Gonzalez GM, Bansal V, Wang Y, et al. Dynamics of the human and viral m6A RNA methylomes during HIV-1 infection of T cells. Nat Microbiol [Internet]. 2016;1(4):16011.
Kennedy EM, Bogerd HP, Kornepati AVR, Kang D, Ghoshal D, Marshall JB, et al. Posttranscriptional m 6 A Editing of HIV-1 mRNAs enhances viral gene expression. Cell Host Microbe [Internet]. 2016;19(5):675–85.
Tirumuru N, Zhao BS, Lu W, Lu Z, He C, Wu L. N6-methyladenosine of HIV-1 RNA regulates viral infection and HIV-1 Gag protein expression. Elife [Internet]. 2016;5. Available from: https://elifesciences.org/articles/15528
Lu W, Tirumuru N, St. Gelais C, Koneru PC, Liu C, Kvaratskhelia M, et al. N6-Methyladenosine–binding proteins suppress HIV-1 infectivity and viral production. J Biol Chem [Internet]. 2018;293(34):12992–3005.
Hesser CR, Karijolich J, Dominissini D, He C, Glaunsinger BA. N6-methyladenosine modification and the YTHDF2 reader protein play cell type specific roles in lytic viral gene expression during Kaposi’s sarcoma-associated herpesvirus infection. Dittmer DP, editor. PLOS Pathog [Internet]. 2018;14(4):e1006995. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.ppat.1006995.
Ye F, Chen ER, Nilsen TW. Kaposi’s Sarcoma-Associated Herpesvirus Utilizes and Manipulates RNA N 6 -Adenosine Methylation To Promote Lytic Replication. Longnecker RM, editor. J Virol [Internet]. 2017;https://doi.org/10.1128/JVI.00466-17.
Tan B, Gao S-J. RNA epitranscriptomics: Regulation of infection of RNA and DNA viruses by N 6 -methyladenosine (m 6 A). Rev Med Virol [Internet]. 2018;28(4):e1983. https://doi.org/10.1002/rmv.1983.
Williams GD, Gokhale NS, Horner SM. Regulation of viral infection by the RNA modification N6 -methyladenosine. Annu Rev Virol [Internet]. 2019;6(1):235–53. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-virology-092818-015559.
Couzin-Frankel J. Cancer Immunotherapy. Science (80- ) [Internet]. 2013;342(6165):1432–3. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.342.6165.1432.
Deng X, Su R, Weng H, Huang H, Li Z, Chen J. RNA N6-methyladenosine modification in cancers: current status and perspectives. Cell Res [Internet]. 2018;28(5):507–17.
Li X-C, Jin F, Wang B-Y, Yin X-J, Hong W, Tian F-J. The m6A demethylase ALKBH5 controls trophoblast invasion at the maternal-fetal interface by regulating the stability of CYR61 mRNA. Theranostics [Internet]. 2019;9(13):3853–65.
Acknowledgements
Not applicable
Funding
Open access funding provided by The Science, Technology & Innovation Funding Authority (STDF) in cooperation with The Egyptian Knowledge Bank (EKB). The Research project at the IFADO and GUC is funded by the German Federal Ministry of Education and Research and the Egyptian Science, Technology and Innovation Funding Authority (STDF) through the German-Egyptian Research Fund (GERF-REMARK Project; No.: 33603).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
R A. E wrote the manuscript. All authors have read, edited and agreed to the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Compecting interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
About this article
Cite this article
Elsabbagh, R.A., Rady, M., Watzl, C. et al. Impact of N6-methyladenosine (m6A) modification on immunity. Cell Commun Signal 20, 140 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12964-022-00939-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12964-022-00939-8