Abstract
Background
Pregnancies following assisted reproductive technology (ART) may have elevated potential risk of pregnancy loss (PL) when compared to natural conception. However, rare studies comprehensively analyzed the IVF/ICSI cycle-dependent factors for loss of clinical pregnancy. Therefore, we aimed to determine the ART subgroup-specific risks of PL throughout pregnancy and explore different risk factors for early miscarriage and late miscarriage among pregnancies conceived through ART.
Methods
A retrospective cohort study was launched in two infertility treatment centers in Nanjing and Changzhou including 5485 IVF/ICSI embryo transfer cycles with known outcomes after clinical pregnancy by the end of 2015. Cox proportional hazards regression analysis was performed to estimate the hazard ratios and their 95% confidence intervals. The associations between survival time during pregnancy and demographics and clinical characteristics of clinical pregnancies were estimated using the Kaplan-Meier method and the Log-rank test.
Results
The overall PL rate in current ART population was 12.5%. Among the 685 pregnancy loss cycles, a total of 460 ended as early miscarriage, 191 as late miscarriage. We found couples in ART pregnancies demonstrated a significantly increased risk of PL as maternal age (HR = 1.31, Ptrend < 0.001) grows. Pregnancies received controlled ovarian hyperstimulation (COH) protocol like GnRH antagonist protocol (HR = 3.49, P < 0.001) and minimal stimulation protocol (HR = 1.83, P < 0.001) had higher risk of PL than GnRH-a long protocol. Notably, in contrast to fresh cycle, women who received frozen cycle embryo had a significant increased risk of early miscarriage (P < 0.001), while frozen cycle was linked with lower risk of late miscarriage (P = 0.045). In addition, four factors (maternal age, COH protocol, cycle type and serum hCG level 14 days after transfer) had independent impact on miscarriage mainly before 12 weeks of gestational age.
Conclusions
With these findings in this study, clinicians may make it better to evaluate a patient’s risk of PL based on the maternal age at the time of treatment, COH protocol, cycle type and serum hCG level 14 days after transfer and the gestational week of the fetus, and we hope that it contributes to future study on its etiology and guide the clinical prevention and treatment.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Nearly one in six couples will encounter with fertility problems, defined as failure to achieve a clinical pregnancy for 12-month delay [1]. Steadily increasing numbers of couples are turning to assisted reproductive technology (ART) for help, such as in vitro fertilization (IVF) or intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI), conceiving and ultimately giving birth to a healthy live baby of their own. Although the clinical pregnancy rate was gradually improved over the past decade, up to 46.9% reported to Centers for Disease Control (CDC) in the United States by the end of 2012, but the rate of live birth was still low, only 38.1% [2]. Therefore, pregnancy loss (PL), including the loss of a desired pregnancy by miscarriage, stillbirth or termination for genetic indications [3], significantly threatens the rate of live-birth delivery.
The PL rate in natural conception was reported 10%-16% [4,5,6], while ART pregnancies might have increased potential probability of loss [2, 5, 7]. Data on 148,494 ART pregnancies in United States conceived from 1999 through 2002 had indicated that the PL rate in ART was up to 29% [7]. The potential risk of pregnancy loss in natural conceived conception was mainly determined by elder maternal age (≥35 years) [8], overweight or obese [9], history of abortion [4], microbial infections [10] and elevated reproductive hormones [11]. As for ART population, the elevated potential risk of loss had also been related to some potentially factors specific to women with infertility, such as fresh or frozen cycle type, uterine factor [12], polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) status [13]. However, additional unknown barriers may affect the efficiency of ART treatment and require further research. Therefore, it is essential to determine IVF/ICSI cycle-dependent factors for miscarriage and stillbirth, which has important clinical implications for the ART success rates elevation and may help understand possible mechanisms of abortion, thereby improving assisted reproduction technology and strategy.
Miscarriage or spontaneous abortion (SA) is defined as the spontaneous loss of a pregnancy during the first 24 completed weeks of gestational age and it accounted for 80% of fetal losses. Early miscarriage refers to pregnancy loss before 12 weeks of gestational age, while late miscarriage occurs between 12 weeks and 24 weeks [10]. Previous studies revealed that causative factors differed in early miscarriages and late miscarriages, and most early miscarriages resulted from aneuploidy that was greatly influenced by total parental age [14], while late miscarriages were attributed to antiphospholipid syndrome, congenital uterine anomalies, cervical weakness, infection and placental insufficiency [15]. Although many studies have assessed risk factors for early miscarriage in ART pregnancies [12, 16, 17], rare large scale studies have explored the risk factor differences between early SA and late SA among pregnancies conceived through ART. This led us to investigate different risk factors between them, which may be applied to counsel ART pregnant women about their risk time period of SA and help clarify the pathogenesis of miscarriage in order to guide the clinical prevention and ART effective treatment. In addition, previous studies utilizing cross-sectional data only discussed the relation of risk factors and miscarriages, but these studies did not explain the effect of time on ART outcomes.
Therefore, the objectives of current study were to examine PL rates and IVF/ICSI cycle-dependent factors influencing live birth probability as pregnancy progresses on specific subgroups by survival analysis method and investigate the different risks of early miscarriage and late miscarriage after following IVF/ICSI treatment.
Methods
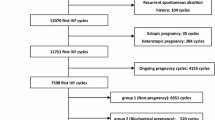
By the end of 2015, a total of 5856 embryo transfer (ET) cycles carried out and resulted in clinical pregnancies in Reproductive Medicine Center of the Affiliated Nanjing Maternity and Child Health Hospital of Nanjing Medical University (Nanjing) and Reproductive Medicine Center of the Affiliated Changzhou Maternity and Child Health Care Hospital of Nanjing Medical University (Changzhou). We restricted the analysis to cycles with records about final pregnancy outcome (pregnancy loss or live-birth). We excluded donor/preimplantation genetic diagnosis (PGD)/preimplantation genetic screening (PGS) cycles (N = 2) and natural ET cycles (N = 18). In addition, cycles were excluded if patients were diagnosed with abnormal karyotypes (N = 23) or uterine anomalies like fibroids, persistent müllerian duct syndrome or asherman syndrome (N = 87). 241 cycles were excluded because of missing data of gestational weeks. After all exclusions, 4165 cycles in Nanjing and 1320 in Changzhou were available for analysis.
Detailed information on maternal and paternal characteristics, ART treatment procedures were collected from the electronic medical records of the two reproductive centers. The pregnancy outcomes were obtained from the follow-up database. Pregnancy was defined as positive serum human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) level on day 14 after oocyte retrieval, and clinical pregnancy referred to visualization of a gestational sac on ultrasound 3-4weeks after positive hCG test. The gestational week was equal to survival months during pregnancy.
The risk factors for pregnancy loss investigated in this study were maternal age, maternal BMI (body mass index, kg/m2), paternal BMI, infertility type, controlled ovarian hyperstimulation (COH) protocol, the total gonadotropin (Gn) dose, fertilization methods, cycle type, no. of embryos transferred, cleavage-stage embryo or blastocyst, serum hCG level 14 days after transfer (IU/L).
Maternal age, maternal BMI, paternal BMI and no. of embryos transferred were categorized for the clarity of data analysis. Maternal age was divided into four subgroups (<30 years, 30-35 years, 36-40 years, >40years). Maternal BMI and paternal BMI subgroups were: <18.5 kg/m2, 18.5-24.9 kg/m2, 25-28 kg/m2, >28 kg/m2. Primary infertility was defined as the inability to achieve a clinical pregnancy after 12 months of unprotected and regular sexual intercourse when a woman has never conceived, while secondary infertility was the incapability to conceive in a couple who have had at least one successful clinical pregnancy previously. Three subgroups of no. of embryos transferred were: Group 1(1 embryo transferred), Group 2 (2 embryos transferred) and Group 3 (3 embryos transferred). Depending on the usage of a gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonist (GnRH-a) versus antagonist analogue, GnRH analogue ART protocols are classified as GnRH-a or GnRH antagonist protocols. Among the various GnRH-a protocols, including long, short and rolonged protocol, GnRH-a long protocol is the most conventional protocol. Another protocol utilizes the usage of clomiphene citrate (CC) in combination with Gn, which is termed minimal stimulation protocol. Thus, COH protocols were divided into six categories in this study, including GnRH-a long protocol, GnRH-a short protocol, GnRH antagonist protocol, minimal stimulation protocol, GnRH-a rolonged protocol and other protocol. Besides among them, GnRH antagonist protocol was not utilized in Changzhou, and they only transferred cleavage-stage embryos. 2 days and 3 days embryo before transfer belong to cleavage-stage embryo, while 5 days and 6 days embryo before transfer belong to blastocyst.
Statistical methods
Demographics and clinical characteristics of pregnancies conceived through ART were calculated by chi-square test. The distributions of continuous variables were evaluated by using Wilcox-test. The associations between survival time during pregnancy and demographics and clinical characteristics of clinical pregnancies were estimated using the Kaplan-Meier method and the Log-rank test. Cox proportional hazards regression analysis was performed to estimate the hazard ratio (HR) and 95% confidence interval (CI). P values were given for two-sided tests and statistical significance was defined by P < 0.05. Superscript asterisk (*) was added after P values with significnce in Tables. Pregnancy survival curves were constructed by the Kaplan-Meier method [18]. Pregnancies were right-censored at completion of the 26th week, because above 98% pregnancy loss were occurred before the 26th week while all of live births occurred between 26 and 42 weeks’ gestation. All the statistical analyses were carried out by R software (Version 3.0.2, 2013-09-25; R Foundation for Statistical Computing, http://www.cran.r-project.org/).
Results
Demographics and clinical characteristics of clinical pregnancies
Table 1 summarized demographics and clinical characteristics of clinical pregnancies conceived through ART and compared the differences of these demographics and clinical characteristics between Nanjing and Changzhou. We found that compared with clinical pregnancies in Nanjing, those in Changzhou had significantly higher maternal age (30.42±4.03 vs. 29.89±4.03, P < 0.001), and serum hCG level 14 days after transfer (861.75±568.97 vs. 619.49±470.08, P < 0.001), lower the total Gn dose in cycle (1728.88±788.45 vs. 1833.67±613.50, P < 0.001). The mean of total Gn dose in cycle and serum HCG level 14 days after transfer were 1808.01 IU and 695.30 IU/L respectively, thereby setting as the cutoff values. Besides, there were statistically highly significant distribution differences of six COH protocols, fertilization methods, cycle type, no. of embryos transferred and cleavage-stage embryo or blastocyst among pregnancies between Nanjing and Changzhou (all P < 0.001), whereas no difference of infertility type , maternal BMI and paternal BMI were found.
Factors influencing live birth probability throughout gestational weeks
As shown in Table 2, the overall rate of pregnancy loss in IVF/ICSI clinical pregnancies was 12.5% (685/5485). Maternal age, maternal BMI, COH protocol, cycle type, no. of embryos transferred and cleavage-stage embryo or blastocyst were significantly associated with the survival time during pregnancy by log-rank test after adjusted by maternal age (all log-rank P < 0.05, data not shown).
We found couples in ART pregnancies demonstrated a significantly increased risk of PL as maternal age (HR=1.31, 95% CI=1.17-1.45, Ptrend<0.001) grows when age was divided into four subgroups. Moreover, compared with women <30 years old, those aged 36-40 years (HR=1.63, 95% CI=1.28-2.08, P < 0.001) and older than 40 years (HR=4.14, 95% CI=2.63-6.52, P < 0.001) had significantly shorter survival pregnancy weeks. Besides, obese women (BMI≥28, HR=1.52, 95% CI=1.11-2.10, P = 0.010) tended to have higher risk of PL compared with the normal BMI group (BMI=18.5-25), yet there was significant heterogeneity for maternal BMI (BMI≥28) in two reproductive medicine centers (Nanjing and Changzhou) based on heterogeneity test (P for heterogeneity test was 0.02) (Additional file 1: Table S1). What’s more, pregnancies received COH protocol like GnRH antagonist protocol (HR=3.49, 95% CI=2.46-4.94, P < 0.001) and minimal stimulation protocol (HR=1.83, 95% CI=1.31-2.54, P < 0.001) had higher risk of PL than GnRH-a long protocol.
Cycle type was significantly associated with the survival time during pregnancy by Cox analysis adjusted for maternal age as well (Log-rank P < 0.001). Notable, the risk of loss increased after frozen cycles (HR=1.30, 95% CI=1.11-1.53, P = 0.001). However, heterogeneity was also significant for cycle type (P = 0.011) between two reproductive medicine centers (Nanjing and Changzhou). After two and three embryos transfer, couples demonstrated 29% (HR=0.71, 95% CI=056-0.90, P = 0.005) and 33% (HR=0.67, 95% CI=0.49-0.91, P = 0.010) decreased risk of PL than those after one embryos transfer. And, a significant locus-dosage effect was detected between three groups and risk of PL (adjusted HR=0.81, 95% CI=0.69-0.96, Ptrend=0.012). In addition, pregnancies after blastocyst transfer had higher risk than those after cleavage-stage embryo transfer after accounting for maternal age (HR=1.10, 95% CI=1.01-1.19, P = 0.030). However, after stratification analysis, we found only cleavage-stage embryos were transferred in Changzhou and the difference was no more significant. Moreover, on day 14 after transfer, women with hCG≥695.30 IU/L had an HR of 0.36 (95% CI=0.29-0.45, P < 0.001) compared to those with hCG lower than 695.30 IU/L.
To get insight into the independent effects of characteristics and clinical features of pregnancies on survival time during ART pregnancy, we performed stepwise backward Cox proportional hazard analysis. As shown in Table 3, four independent factors were determined, including maternal age (compared with maternal age<30, P = 0.027 for maternal age between 36 and 40 years, P < 0.001 for maternal age>40 years), COH protocol (compared with GnRH-a long protocol, P value<0.001 for both GnRH antagonist protocol and mini-stimulation protocol), cycle type (P = 0.030) and serum hCG level 14 days after transfer (P < 0.001). Kaplan-Meier plots of live birth by maternal age, COH protocol, cycle type and serum hCG level 14 days after transfer were shown in Fig. 1.
Risk factors for early miscarriage and late miscarriage
In Table 4, among the 685 pregnancy loss cycles, a total of 460 ended as early SA, 191 as late SA. The rate of early miscarriage in ART clinical pregnancies was 8.4% (460/5485) while the rate of late miscarriage in ART clinical pregnancies after 12 weeks of gestational age was 3.8% (191/5025). Of those clinical pregnancies, women aged 36-40 years (HR=2.14, 95% CI=1.62-2.83, P < 0.001) and over 40 years (HR=6.04, 95% CI=3.76-9.69, P < 0.001) were more likely to encounter early pregnancy loss in contrast to those younger than 30 years old. Besides, treated by GnRH antagonist and minimal stimulation COH protocol (both P < 0.001), blastocyst transferred (P = 0.006), and frozen embryo transferred (P < 0.001) were more likely to encounter early pregnancy loss. What’s more, there was a significant decrease of risk of early SA in pregnancies after two embryos transferred compared with those following one embryo transfer (P < 0.001). Serum hCG level at higher level on day 14 after transfer was linked with a significant 78% and 32% decreased risk of early SA and late SA (P < 0.001). Moreover, maternal BMI≥28 had a positive impact on late PL rather than early PL. Notably, in contrast to fresh cycle, women who received frozen cycle embryo had a significant decrease of risk of late SA (P = 0.045), while frozen cycle was linked with higher risk of early PL. After stepwise backward Cox proportional hazard analysis, we found that maternal age, COH protocol, cycle type and hCG level 14 days after transfer had independent effects on live birth probability of ART clinical pregnancies before 12 weeks of gestational age (In Table 5). However, none of factors for PL investigated in this study had independent effects on late miscarriage (data not shown).
Discussion
This retrospective cohort study on the risk of PL throughout ART pregnancy included 5485 ART clinical pregnancies with data of gestational weeks, 685 of which suffered pregnancy loss. The main findings of this study were that maternal age, COH protocol, cycle type and hCG level 14 days after transfer significantly affected the reproductive pregnancy loss of ART population. Besides, the incidence of PL decreased as pregnancy progresses, early SA therefore occurred more frequently than the late one. To our knowledge, this is the first retrospective cohort study to extensively explore the different risk factors of early miscarriage and late miscarriage after IVF/ICSI.
The negative effect of maternal reproductive age on the risk of PL has been consistently reported and studied in previous studies [19, 20]. Age of the female is the most important risk factor in determining pregnancy success rates both in natural conception and after ART [4]. It is partly because of obvious decline in ovarian germ cells supply, decrease in oocyte quality and ultimately leading to ovarian reproductive failure [21]. In this study, women>40 years old had approximately 37.7% PL rate, and they showed significant decline in survival probability of ART clinical pregnancies progressed to a live birth compared with those <30 years old. Some studies suggested that the decreased fecundity and fertility rate occurred due in part to decreased follicle reserves [22] and increased aneuploidy [23] in the older female. In addition, chromosome abnormality decreases as pregnancy progresses and occurs mostly before 12 weeks of pregnancy [14], which makes the association of older parental age with early SA credible. Now, pre-implantation genetic screening of embryos prior to transfer may reduce early pregnancy wastage resulting from aneuploidy, but safety and risks of the technology need further investigation.
Controlled ovarian hyperstimulation is a fundamental step of IVF/ICSI and over time IVF techniques have developed to satisfy the needs of fertility patients and the improvement of ART success rate. The present results suggest that for the purpose of increasing survival probabilities of ART pregnancies, the GnRH-a long protocol is a better option for IVF/ICSI stimulation compared to GnRH antagonist and minimal stimulation protocol. Using Gn and CC in ART cycles is associated with chromosomal abnormalities in an IVF embryo and subsequent early miscarriage after transfer [24]. Moreover, patients with poor ovarian reserve prefer considering minimal stimulation protocol, and GnRH antagonist protocols are applied to "poor responders" and women at high-risk of developing OHSS, thus oocyte/embryo quality and development was inferior to that of the agonist group. However, data from earlier studies don’t support the finding and indicate that the usage of GnRH antagonist is not associated with reduction of the likelihood of achieving live birth, compared with GnRH-a protocols [25]. Therefore, further investigation is needed to clarify the matter and future developments have to be focused on the optimization of COH protocols.
As for the association of cycle type and the occurrence of PL, we found the rate of loss, especially early miscarriage, increased after frozen IVF/ICSI cycles. We considered that embryo may inevitably be damaged by cryopreservation technology, which may damage the ability of embryo development and thus result in abortion. However, a meta-analysis showed that this difference did not reach statistical significance [26], and even in a multicenter randomized trial, the opposite result showed in infertile women with PCOS [27]. Thus, it is necessary to examine the effect of hormone level. To our surprise, frozen embryos after implantation showed significant lower late SA probability compared to fresh ones in our findings, which was consistent with the two multicenter randomized trials involving infertile women with the PCOS and ovulatory women [27, 28]. However, after stepwise backward Cox proportional hazard analysis, this different was no more significant, which could be due to difference in cryopreservation protocols, freezing day (cleavage-stage or blastocyst), number or quality of frozen embryos transferred.
Serum hCG has been used to be the main endocrine determinant of ongoing pregnancy, and then whether serum hCG level measured on the 14th day after transfer is sufficient in predicting final live birth outcomes needs to be confirmed. It was a significant observation in our findings that the hCG level of live birth was markedly higher than that of PL especially early abortion, which was agreement with another study that estimates the cutoff value of 50 IU/L (75% sensitivity, 81% specificity, P < 0.001) to predict ongoing pregnancy [29] as well. However, no hCG cutoff level had a sensitivity or specificity of 100% for pregnancies, making it essential to continue routine monitoring of ART pregnancy outcomes.
In addition to the above, we found BMI, freezing day (cleavage-stage or blastocyst) and no. of embryos transferred affected PL, but the three factors were not significant any more after stepwise COX regression. The incidence of PL progressively ascended as maternal BMI categories increased, which is consistent with a recent study [30]. And the association of female obesity (BMI>28 kg/m2) with a significant decreased possibility of ART baby’s survival after 12 weeks of gestational age was another interesting observation. It is suggested that maternal obesity can impair embryo development and the mechanism that Stella insufficiency in oocytes mediates developmental defects in early embryos has been elucidated in a recent study [31]. Besides, it is explained that the higher risk in subjects with high BMI may be due to the action of a hormone named leptin, which is produced predominantly in the adipose tissue [32].
In our finding, more than one embryo transfer was a protective factor of fetal loss in ART pregnancies after accounting for maternal age and the association of two embryos transfer with a significant decreased risk of early loss is an interesting observation. Although the results of a previous study also suggested that live birth and pregnancy rates following single embryo transfer were lower than those following double embryo transfer, so are the chances of multiple pregnancy including twins [33]. Multiple gestations lead to an increased risk of complications in both the fetuses and the mothers, so the optimal and recommended choice is the limit to the number of embryos to transfer [34].
This study was limited by some data availability as there is no routine ART surveillance system. We could not have data of other PL risk factors like microbial infections to resolve existing data gap. Secondly, the data covered in the article derived from two centers in Nanjing and Changzhou, so we would not obtain sufficient and identical characteristics and clinical features of pregnancies for lack data of some variables in either of centers. Lastly, in this retrospective cohort study, we could not investigate the mechanism of miscarriage during pregnancy weeks and the sample size is not enough, so the large-scale prospective cohort study should be carried out to in China.
Conclusions
In conclusion, the ultimate aim of assisted reproductive medicine practitioners would still be the improvement of IVF/ICSI efficacy in terms of take-home-baby rates. Therefore, with these findings in this study, clinicians may make it better to evaluate an infertile couple’s risk of PL based on the maternal age at the time of treatment, COH protocol, cycle type and serum hCG level 14 days after transfer and the gestational week of the fetus. Additionally, these factors had significant impact on miscarriage mainly before 12 weeks of gestational age. Hopefully, these findings may offer some suggestions of population risks of pregnancy loss for reproductive health epidemiologists and contribute to future study on its etiology.
Abbreviations
- ART:
-
Assisted reproductive technology
- BMI:
-
Body mass index
- CC:
-
Clomiphene citrate
- CDC:
-
Centers for Disease Control
- CI:
-
Confidence interval
- COH:
-
Controlled ovarian hyperstimulation
- ET:
-
Embryo transfer
- Gn:
-
Gonadotropin
- GnRH-a:
-
Gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonist
- hCG:
-
Human chorionic gonadotropin
- HR:
-
Hazard ratio
- ICSI:
-
Intracytoplasmic sperm injection
- IVF:
-
In vitro fertilization
- PCOS:
-
Polycystic ovarian syndrome
- PGD:
-
Preimplantation genetic diagnosis
- PGS:
-
Preimplantation genetic screening
- PL:
-
Pregnancy loss
- SA:
-
Spontaneous abortion
References
Boivin J, Bunting L, Collins JA, Nygren KG. International estimates of infertility prevalence and treatment-seeking: potential need and demand for infertility medical care. Hum Reprod. 2007;22:1506–12.
Sunderam S, Kissin DM, Crawford SB, Folger SG, Jamieson DJ, Warner L, Barfield WD. Centers for Disease C, Prevention. Assisted Reproductive Technology Surveillance - United States, 2012. MMWR Surveill Summ. 2015;64:1–29.
Robinson GE. Pregnancy loss. Best Pract Res Clin Obstet Gynaecol. 2014;28:169–78.
Nybo Andersen AM, Wohlfahrt J, Christens P, Olsen J, Melbye M. Maternal age and fetal loss: population based register linkage study. BMJ. 2000;320:1708–12.
Wang JX, Norman RJ, Wilcox AJ. Incidence of spontaneous abortion among pregnancies produced by assisted reproductive technology. Hum Reprod. 2004;19:272–7.
Assefa N, Berhane Y, Worku A. Pregnancy rates and pregnancy loss in eastern Ethiopia. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 2013;92:642–7.
Farr SL, Schieve LA, Jamieson DJ. Pregnancy loss among pregnancies conceived through assisted reproductive technology, United States, 1999-2002. Am J Epidemiol. 2007;165:1380–8.
Buck Louis GM, Sapra KJ, Schisterman EF, Lynch CD, Maisog JM, Grantz KL, Sundaram R. Lifestyle and pregnancy loss in a contemporary cohort of women recruited before conception: the LIFE study. Fertil Steril. 2016;106:180–8.
Delabaere A, Huchon C, Deffieux X, Beucher G, Gallot V, Nedellec S, Vialard F, Carcopino X, Quibel T, Subtil D, et al. Epidemiology of loss pregnancy. J Gynecol Obstet Biol Reprod (Paris). 2014;43:764–75.
Giakoumelou S, Wheelhouse N, Cuschieri K, Entrican G, Howie SE, Horne AW. The role of infection in miscarriage. Hum Reprod Update. 2016;22:116–33.
Negro R, Schwartz A, Gismondi R, Tinelli A, Mangieri T, Stagnaro-Green A. Increased pregnancy loss rate in thyroid antibody negative women with TSH levels between 2.5 and 5.0 in the first trimester of pregnancy. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2010;95:E44–8.
Hipp H, Crawford S, Kawwass JF, Chang J, Kissin DM, Jamieson DJ. First trimester pregnancy loss after fresh and frozen in vitro fertilization cycles. Fertil Steril. 2016;105:722–8.
Wang JX, Davies MJ, Norman RJ. Polycystic ovarian syndrome and the risk of spontaneous abortion following assisted reproductive technology treatment. Hum Reprod. 2001;16:2606–9.
Jia CW, Wang L, Lan YL, Song R, Zhou LY, Yu L, Yang Y, Liang Y, Li Y, Ma YM, Wang SY. Aneuploidy in Early Miscarriage and its Related Factors. Chin Med J (Engl). 2015;]:2772–2776.
McNamee KM, Dawood F, Farquharson RG. Mid-trimester pregnancy loss. Obstet Gynecol Clin N Am. 2014;41:87–102.
Winter E, Wang J, Davies MJ, Norman R. Early pregnancy loss following assisted reproductive technology treatment. Hum Reprod. 2002;17:3220–3.
Chen CD, Chiang YT, Yang PK, Chen MJ, Chang CH, Yang YS, Chen SU. Frequency of low serum LH is associated with increased early pregnancy loss in IVF/ICSI cycles. Reprod BioMed Online. 2016;33:449–57.
Abd ElHafeez S, Torino C, D'Arrigo G, Bolignano D, Provenzano F, Mattace-Raso F, Zoccali C, Tripepi G. An overview on standard statistical methods for assessing exposure-outcome link in survival analysis (part II): the Kaplan-Meier analysis and the cox regression method. Aging Clin Exp Res. 2012;24:203–6.
Spandorfer SD, Davis OK, Barmat LI, Chung PH, Rosenwaks Z. Relationship between maternal age and aneuploidy in in vitro fertilization pregnancy loss. Fertil Steril. 2004;81:1265–9.
Khalil A, Syngelaki A, Maiz N, Zinevich Y, Nicolaides KH. Maternal age and adverse pregnancy outcome: a cohort study. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 2013;42:634–43.
Baird DT, Collins J, Egozcue J, Evers LH, Gianaroli L, Leridon H, Sunde A, Templeton A, Van Steirteghem A, Cohen J, et al. Fertility and ageing. Hum Reprod Update. 2005;11:261–76.
Ziebe S, Loft A, Petersen JH, Andersen AG, Lindenberg S, Petersen K, Andersen AN. Embryo quality and developmental potential is compromised by age. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 2001;80:169–74.
Franasiak JM, Forman EJ, Hong KH, Werner MD, Upham KM, Treff NR, Scott RT Jr. The nature of aneuploidy with increasing age of the female partner: a review of 15,169 consecutive trophectoderm biopsies evaluated with comprehensive chromosomal screening. Fertil Steril. 2014;101:656–63. e651
Shoham Z, Zosmer A, Insler V. Early miscarriage and fetal malformations after induction of ovulation (by clomiphene citrate and/or human menotropins), in vitro fertilization, and gamete intrafallopian transfer. Fertil Steril. 1991;55:1–11.
Lambalk CB, Banga FR, Huirne JA, Toftager M, Pinborg A, Homburg R, van der Veen F, van Wely M. GnRH antagonist versus long agonist protocols in IVF: a systematic review and meta-analysis accounting for patient type. Hum Reprod Update. 2017;23:560–79.
Roque M, Lattes K, Serra S, Sola I, Geber S, Carreras R, Checa MA. Fresh embryo transfer versus frozen embryo transfer in in vitro fertilization cycles: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Fertil Steril. 2013;99:156–62.
Chen ZJ, Shi Y, Sun Y, Zhang B, Liang X, Cao Y, Yang J, Liu J, Wei D, Weng N, et al. Fresh versus frozen embryos for infertility in the polycystic ovary syndrome. N Engl J Med. 2016;375:523–33.
Shi Y, Sun Y, Hao C, Zhang H, Wei D, Zhang Y, Zhu Y, Deng X, Qi X, Li H, et al. Transfer of fresh versus frozen embryos in ovulatory women. N Engl J Med. 2018;378:126–36.
Urbancsek J, Hauzman E, Fedorcsak P, Halmos A, Devenyi N, Papp Z. Serum human chorionic gonadotropin measurements may predict pregnancy outcome and multiple gestation after in vitro fertilization. Fertil Steril. 2002;78:540–2.
Provost MP, Acharya KS, Acharya CR, Yeh JS, Steward RG, Eaton JL, Goldfarb JM, Muasher SJ. Pregnancy outcomes decline with increasing body mass index: analysis of 239,127 fresh autologous in vitro fertilization cycles from the 2008-2010 Society for Assisted Reproductive Technology registry. Fertil Steril. 2016;105:663–9.
Han L, Ren C, Li L, Li X, Ge J, Wang H, Miao YL, Guo X, Moley KH, Shu W, Wang Q. Embryonic defects induced by maternal obesity in mice derive from Stella insufficiency in oocytes. Nat Genet. 2018;50:432–42.
Mitchell M, Armstrong DT, Robker RL, Norman RJ. Adipokines: implications for female fertility and obesity. Reproduction. 2005;130:583–97.
McLernon DJ, Harrild K, Bergh C, Davies MJ, de Neubourg D, Dumoulin JC, Gerris J, Kremer JA, Martikainen H, Mol BW, et al. Clinical effectiveness of elective single versus double embryo transfer: meta-analysis of individual patient data from randomised trials. BMJ. 2010;341:c6945.
Practice Committee of the American Society for Reproductive Medicine. Electronic address Aao, Practice Committee of the Society for Assisted Reproductive T. Guidance on the limits to the number of embryos to transfer: a committee opinion. Fertil Steril. 2017;107:901–3.
Acknowledgements
The authors thank all of medics in Reproductive Medicine Center of the Affiliated Nanjing Maternity and Child Health Hospital of Nanjing Medical University and Reproductive Medicine Center of the Affiliated Changzhou Maternity and Child Health Care Hospital of Nanjing Medical University for recording all the data in this study through the years.
Funding
Supported by National Key Research & Development Program (2016YFC1000200, 2016YFC1000204), the State Key Program of National Natural Science of China (31530047), Science Foundation for Distinguished Young Scholars in Jiangsu (BK20160046), National Natural Science Foundation of China (81602927), Cheung Kong Scholars Programme of China, the QingLan Project of the Jiangsu Province, Jiangsu Specially-Appointed Professor project, Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions (PAPD), Clinical medicine research fund of the Chinese medical association (17020420711), Innovation fund of state key laboratory of reproductive medicine (SKLRM-GC201802), Top-notch Academic Programs Project of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions (PPZY2015A067), Jiangsu Provincial Medical Youth Talent (QNRC2016304), and Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province (BK20161031).
Availability of data and materials
The datasets used and analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
LH and JD contributed to conception and design. HL contributed to analysis and interpretation of data, drafting and revising the article. JZ, MC, YW, FW, FL and XC contributed to acquisition of data. JZ, HM, GJ, HS, LC, XL and ZH contributed to revising the article critically for important intellectual content. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
All methods and information collection protocols were approved by Nanjing Medical University and were carried out in accordance with the approved guidelines. Our research has gotten the waiver from institutional review board for the medical record review for selective variable analysis in the Affiliated Nanjing Maternity and Child Health Hospital of Nanjing Medical University, and the Affiliated Changzhou Maternity and Child Health Care Hospital of Nanjing Medical University.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Additional file
Additional file 1:
Table S1. Cox analysis of risk of pregnancy loss throughout pregnancy in ART clinical pregnancies stratified by two fertility centers. (DOC 103 kb)
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated.
About this article
Cite this article
Hu, L., Du, J., Lv, H. et al. Influencing factors of pregnancy loss and survival probability of clinical pregnancies conceived through assisted reproductive technology. Reprod Biol Endocrinol 16, 74 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12958-018-0390-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12958-018-0390-6