Abstract
Background
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is a common endocrine disorder determined by polygenic traits as well as environmental factors. Lower vitamin D levels have been detected in PCOS women and related to hormone and metabolic disturbances. Vitamin D acts in tissues through the vitamin D receptor (VDR). VDR gene variants have been associated with worse metabolic profile in the general population. We investigated the genotype and haplotype distribution of the Bsm-I (rs1544410), Apa-I (rs7975232), and Taq-I (rs731236) VDR gene polymorphisms in PCOS and non-hirsute women from southern Brazil. We further investigated the associations of these gene variants and their haplotypes with PCOS, vitamin D levels, and metabolic abnormalities, including the metabolic syndrome (MetS).
Methods
A group of 191 women with PCOS (Rotterdam criteria) and 100 non-hirsute controls with regular ovulatory cycles were genotyped for all polymorphisms by real-time PCR, with allelic discrimination assays. MetS and the cutoffs for its isolated components were defined in accordance with the Joint Scientific Statement.
Results
Women with PCOS were younger and had significantly higher BMI and total testosterone levels than controls (p < 0.05). The frequency of MetS in PCOS and controls was 26.5% and 4.8% respectively. The CC genotype of Apa-I entailed higher risk of MetS in PCOS (OR: 2.133; 95% CI 1.020–4.464, p = 0.042), and was associated with higher systolic blood pressure (p = 0.009), total cholesterol (p = 0.040), and LDL-cholesterol (p = 0.038) in both PCOS and control groups (two-way ANOVA). The frequencies of VDR haplotypes were similar in PCOS and control women.
Conclusions
The present results suggest that the Apa-I variant in VDR gene may be associated with MetS in southern Brazilian women with PCOS, and with blood pressure, total cholesterol, and LDL-c in women with and without PCOS.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is a common endocrine disorder affecting 9 to 18% of women of reproductive age according to different diagnostic criteria [1,2,3]. While its etiology remains unclear, PCOS is considered a polygenic and multifactorial disease, with metabolic, endocrine, and reproductive alterations [4]. In PCOS women, evidence suggests that vitamin D levels may be decreased and related to hormone and metabolic disturbances [5, 6].
The vitamin D receptor (VDR) is expressed in many tissues and organs (such as those involved in calcium homeostasis mechanisms), in glucose metabolism, and in the reproductive system [7], and modulates vitamin D action in these systems. VDR gene (ID: 7421) polymorphisms have been investigated in PCOS as well as in disturbances of androgen secretion. A previous study has suggested an association between VDR gene variants and precocious pubarche (PP) [8]; in turn, data on PCOS risk are controversial, with a relationship between VDR gene variants and PCOS detected by some [9,10,11,12] but not all studies [13,14,15]. Regarding endocrine characteristics, VDR gene polymorphism has been associated with total testosterone in PCOS and PP populations [8, 13], with estradiol levels in PP girls [8], and with metabolic abnormalities in different non-PCOS populations [16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23].
Therefore, the aims of the present study were to assess the genotypic and allelic distribution of Bsm-I (rs1544410), Apa-I (rs7975232) and Taq-I (rs731236) polymorphisms of the VDR gene and to determine whether these gene variants are associated with 25-hydroxyvitamin D [25(OH)D] levels and with metabolic abnormalities, including MetS, in women with PCOS in comparison to non-hirsute, ovulatory control women.
Methods
Patients
This is a cross-sectional study including 191 patients with PCOS and 100 non-hirsute women with regular, ovulatory cycles, recruited by advertisement in the local media. The characteristics of the study sample have been described elsewhere [24]. PCOS was diagnosed according to Rotterdam criteria [25]. Neither PCOS nor control participants had received any drugs known to interfere with hormone levels (such as oral contraceptive pills, antiandrogens, metformin, fibrates, or statins) for at least 3 months before the study. The exclusion criteria were pregnancy and liver or kidney disease. Approval for this study was obtained from the Institutional Review Board and the local Ethics Committee at Hospital de Clínicas de Porto Alegre. Written informed consent was obtained from every subject.
Study protocol
Anthropometric measurements included body mass index (BMI) and waist circumference (measured at the midpoint between the lower rib margin and the iliac crest). Blood pressure was measured after a 10-min rest, with the patient seated, with both feet on the floor and the arm supported at heart level. Two measurements were obtained 10 min apart using an Omron HEM-742INT automatic blood pressure monitor (Rio de Janeiro, Brazil) with the correct cuff size for the arm diameter [26,27,28,29]. MetS and the cutoffs for its isolated components were defined in accordance with the Joint Scientific Statement [30].
Laboratory measurements
All samples were obtained between the 2nd and 10th days of the menstrual cycle, or on any day if the patient was amenorrheic, between 8:00 and 10:00 am, after a 12-h overnight fast. Blood samples were drawn from an antecubital vein for determination of hormone levels. Blood samples were also collected for genomic DNA extraction.
Total cholesterol, high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-c), triglycerides, and glucose levels were determined by colorimetric-enzymatic methods (Bayer 1650 Advia System). LDL-cholesterol (LDL-c) was determined indirectly with the formula total cholesterol – HDL-c – triglycerides/5. Total testosterone levels were measured by chemiluminescence (Siemens Advia Centaur XP), with a sensitivity of 0.10 ng/mL and intra- and interassay coefficients of variation (CVs) of 3.3 and 7.5% respectively. Plasma insulin and sex hormone–binding globulin (SHBG) levels were measured by chemiluminescence (Siemens Advia Centaur XP), with a sensitivity of 0.50 U/mL and 0.035 nmol/L, respectively, with intra-assay CV < 3% and interassay CV < 5%. The free androgen index (FAI) was calculated as testosterone (nmol/L)/SHBG (nmol/L) × 100. The homeostasis model assessment index (HOMA index) was calculated by multiplying insulin (μIU/mL) by glucose (mmol/L) and dividing this product by 22.5 [31]. 25(OH)D levels were measured in a subset of 102 women (54 PCOS and 48 controls) by chemiluminescence (Liaison, DiaSorin), with intra-assay and interassay CV of 7.7 and 10.9% respectively.
Genotype analysis
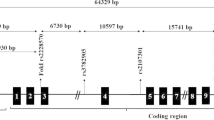
Genomic DNA was extracted from peripheral blood leukocytes [32]. The DNA samples were diluted to 2 ng/mL. Molecular genotyping was performed through real-time polymerase chain reaction (7500 Fast Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction System, Applied Biosystems, CA, USA), using the allelic discrimination assay with TaqMan MGB primers and probes (Applied Biosystems, CA, USA).
For genotyping the single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) Apa-I and Taq-I, the following were added: TaqMan Master mix (2.5 μL), TaqMan assay (0.25 μL), and H2O (1.25 μL), for a final volume of 4 μL per sample, followed by addition of 1μLof DNA for a total reaction volume of 5 μL. To genotype SNP Bsm-I, TaqMan Master mix (5.0 μL), TaqMan assay (0.50 μL), and H2O (3.5 μL) were added for a final volume of 9 μL per sample, and 1 μL of DNA was added for a total reaction volume of 10 μL. Reaction conditions for all polymorphisms were: 10 min at 95 °C after 50 cycles of denaturation at 95 °C (15 s) and annealing at 60 °C (1 min). Endpoint fluorescent readings were performed in the 7500 Fast System Sequence Detection Software version 1.4 environment. The internal quality of genotype data was assessed by typing 10% of blinded samples in duplicate.
Statistical analysis
Sample size estimation was based on the study by Al-Daghri et al. [16], which found an association between Apa-I variants of the VDR gene and higher blood pressure in MetS in female and male control subjects. Therefore, considering a difference of 3.9 mmHg in blood pressure between Apa-I genotypes [CC or CA + AA], an alpha of 5%, and a beta of 80%, the sample size was estimated as 91 PCOS women for each genotype.
The Shapiro-Wilk normality test and descriptive statistics were used to evaluate the distribution of data. Results are presented as means ± standard deviation or percentages. Non-Gaussian variables were log-transformed for statistical analysis and reported after being back-transformed into their original units of measure. Comparisons between means were analyzed by the unpaired two-tailed Student’s t-test. Two-way ANOVA was used for testing the interaction between diagnosis and genotype groups. Categorical variables and the agreement of genotype frequencies with Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium for each SNP were analyzed using the Pearson chi-square test (χ2). Odds ratios (OR) and 95% confidence intervals (95%CI) were obtained using χ2 risk estimate. Lewontin’s D’ statistic for linkage disequilibrium was calculated for each pair of polymorphisms. Haplotypes were inferred using the Phase 2.1 program, which uses Bayesian statistics. Data were considered as statistically significant at p < 0.05. The Statistical Package for the Social Sciences v. 24 (SPSS, Chicago, IL) was used for the analyses.
Results
Clinical, hormonal, and metabolic features
The clinical, hormonal and metabolic characteristics of the studied population have been previously described [24]. Women with PCOS were younger than controls (22.9 ± 6.7 vs. 25.2 ± 7.7 years, p = 0.013), and presented higher BMI (29.7 ± 6.4 vs. 27.0 ± 6.1 kg/m2, p = 0.001) and higher frequency of overweight/obesity (p = 0.002) and of MetS (p < 0.001). PCOS participants also had significantly higher total testosterone and FAI, as well as lower SHBG (p < 0.001), than controls (Table 1). Vitamin D levels were similar in PCOS and controls (p = 0.985).
When only the PCOS group was analyzed, the presence of MetS (p = 0.018), glucose ≥100 mg/dL (p = 0.025), waist circumference ≥ 88 cm (p = 0.040) and triglycerides ≥150 mg/dL (p = 0.011) were linked to lower vitamin D levels (Table 2).
VDR gene polymorphisms
All the three studied polymorphisms were in Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium, and over 98% (n = 287) of the sample were effectively genotyped. Genotype and allele frequencies of VDR gene variants are presented in Table 3. The genotype and allele distribution of all three polymorphisms was similar in PCOS and control groups.
Figure 1 shows the frequency of MetS in PCOS participants according to Apa-I genotypes. Individuals with the CC genotype had higher risk of MetS vs. the CA + AA genotype (OR: 2.133; 95% CI 1.020–4.464, p = 0.042). The CC genotype was also associated with higher systolic blood pressure (p = 0.009), total cholesterol (p = 0.040) and LDL-c (p = 0.038) in both PCOS and control groups. There was no interaction between genotypes and PCOS or control groups (p > 0.05) (Table 4).
The Bsm-I (G → A) polymorphism was in almost complete linkage disequilibrium with the Apa-I (C → A) polymorphism (|D’| = 1.00; r2 = 1.00), and in partial linkage disequilibrium with Taq-I (A → G) (|D’| = 0.75; r2 = 0.21). Apa-I (C → A) was also in partial linkage disequilibrium with Taq-I (A → G) (|D’| = 0.87; r2 = 0.35). Eight haplotypes were inferred in the sample: AAA, AAG, ACA, ACG, GAA, GAG, GCA, and GCG, with frequencies of 0.022, 0.340, 0.015, 0.004, 0.192, 0.019, 0.393, and 0.015 respectively. The first letter of each haplotype refers to Bsm-I, the second to Apa-I, and the third to Taq-I. Taking into consideration the results of individual polymorphism analyses, haplotypes were grouped according to the presence of the C allele of Apa-I (ACA + ACG + GCA + GCG vs. AAA + AAG + GAA + GAG). The frequency of combined haplotypes was similar in PCOS and control groups (p = 0.332).
Discussion
In the present study, despite the similar vitamin D levels detected in PCOS and control participants, the CC genotype of Apa-I SNP of the VDR gene was specifically related to higher risk of MetS in PCOS participants. Moreover, this same genotype was associated with higher blood pressure, total cholesterol, and LDL-c in both PCOS and control participants. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first report to show an association between Apa-I VDR gene polymorphism and MetS in a PCOS population. This observation is relevant because it may help explain the meaning of vitamin D level variation, which may not play a role per se, but rather reflect a putative gene-environment interaction in different populations.
The few available studies analyzing the influence of Apa-I VDR gene polymorphisms on metabolic variables in PCOS women have reported no association with insulin resistance [10, 13] or glucose and lipid abnormalities [10]. However, data from non-PCOS populations suggest that metabolic abnormalities, such as obesity, insulin resistance, low HDL-c, and type 2 diabetes are associated with the VDR gene [16,17,18,19,20,21]. In this sense, a recent meta-analysis comprising 9232 participants showed that the association between insulin resistance-related diseases and Apa-I and Bsm-I VDR gene variants was more pronounced in dark-pigmented Caucasians and Asians than in Caucasians with white skin. In the sub-group analysis, Bsm-I (GG genotype) was associated with MetS, and the Apa-I variant (CC genotype) was associated with insulin resistance-related diseases in a population living in a mid-latitude zone (30°–60°) [23], which is also the case of the present population (30°01′59”S).
While a functional role of VDR gene polymorphisms has not yet been established, the association between Apa-I gene variant and MetS observed in the present study could be assumed to be linked to disturbed VDR gene expression [33]. The Apa-I polymorphism is located at the 3′ untranslated region (3′ UTR) of the VDR gene, which has been recognized as being involved in the modulation of gene expression, especially through the regulation of mRNA stability and efficiency of protein translation [34]. Moreover, the methylation levels of the VDR gene appear to be altered according to race and presence of the polymorphisms of the 3’UTR region of the gene [35]. Additionally, Apa-I is in strong linkage disequilibrium with other VDR gene polymorphisms in different populations [22, 36], which may be contributing to the general transcriptional activity of VDR in different biological processes. Importantly, the VDR gene regulates more than 200 genes, and mediates most effects of vitamin D on gene expression via formation of a heterodimer with the retinoid X receptor molecule, which binds to promoter regions of many target genes [37, 38].
In our study, lower 25(OH)D levels were associated with MetS and with its isolated components in PCOS women, such as higher glucose, waist circumference and triglycerides. In this sense, the present results are in agreement with a meta-analysis reporting that women with PCOS and vitamin D deficiency are more likely to have dysglycemia compared to those without vitamin D deficiency [5], and that in women with both PCOS and MetS, vitamin D levels are lower than in women with PCOS and without MetS [39].
Similar vitamin D levels were detected in the present study in PCOS and control participants regardless of the presence of Apa-I SNP. Interestingly, while two meta-analyses [5, 6] comprising 3182 and 2262 women respectively showed that serum 25(OH)D concentrations were lower in PCOS compared to controls, the reported standardized mean difference between the groups in both studies seems of little clinical relevance – only 0.74 ng/mL (95%IC: -1.26 to − 0.22) [5] and 0.64 ng/mL (95%IC: -1.12 to − 0.15) [6]. In turn, the fact that our PCOS patients with MetS had lower vitamin D levels and higher frequency of CC polymorphism compared to those without MetS suggests that the Apa-I gene variant might impact vitamin D levels in PCOS with MetS. In fact, vitamin D status is influenced by many factors, especially dietary pattern, season, and genetic traits [40]. A better understanding of the genetic factors that may be involved in vitamin D level variation and metabolic disturbances could shed some light on hypothetical gene-environment interactions of vitamin D. Further studies with larger PCOS populations and higher proportion of MetS are needed in order to confirm this hypothesis.
We did not find any association between genotypes or haplotypes of VDR gene variants in PCOS participants. Only a few studies are available in the literature assessing VDR gene polymorphism and risk of PCOS, with uncertain conclusions, which vary according to the studied sample. While some studies show an association between at least one VDR gene polymorphism and PCOS [9,10,11,12, 41], others report similar distributions of Bsm-I, Apa-I and Taq-I polymorphisms in PCOS and control women [13,14,15]. Also, regarding haplotypes of VDR gene variants, no definitive data are available, with few reports of distinct haplotypes of VDR gene polymorphisms presenting slightly higher frequency in PCOS women when compared to controls [10, 12, 14]. These unclear data may be, at least in part, attributed to ethnic differences in the studied populations and to the polygenic condition of PCOS. Yet, other studies have reported an association of VDR gene polymorphisms with PP [8] and diabetes [42,43,44,45].
One strength of our study is the focus on a less well represented ethnic group, PCOS women from southern Brazil, with assessment of gene variants which may be contributing to this polygenic and multifactorial disease. Furthermore, we evaluated polymorphisms found in a genomic position that plays an important role in the modulation of gene expression. Limitations of the present study are the relatively small sample size of 291 participants (191 PCOS and 100 controls) and the low frequency of MetS in the control group, precluding complementary analyses correlating VDR gene polymorphisms and MetS in that group. In addition, further studies on functional evaluation of VDR SNPs are needed in order to deepen the understanding of findings.
Conclusions
Our results indicate that Bsm-I, Apa-I, and Taq-I polymorphisms in VDR gene are not related to PCOS. However, there seems to be an association of the CC genotype of Apa-I with MetS in PCOS women, and with blood pressure, total cholesterol, and LDL-c in women with and without PCOS. Despite the similarity in the vitamin D levels of PCOS and control participants, our study suggests that Apa-I impacts vitamin D levels in PCOS with MetS.
Abbreviations
- 25(OH)D:
-
25-hydroxyvitamin D
- BMI:
-
Body mass index
- BP:
-
Blood pressure
- CV:
-
Coefficient of variation
- DBP:
-
Diastolic blood pressure
- FAI:
-
Free androgen index
- Glu:
-
Glucose
- HDL-c:
-
High-density lipoprotein cholesterol
- HOMA:
-
Homeostasis model assessment index
- LDL-c:
-
Low-density lipoprotein cholesterol
- MetS:
-
Metabolic syndrome
- PCOS:
-
Polycystic ovary syndrome
- PCR:
-
Polymerase chain reaction
- PP:
-
Precocious pubarche
- SBP:
-
Systolic blood pressure
- SHBG:
-
Sex hormone–binding globulin
- SNP:
-
Single nucleotide polymorphism
- TC:
-
Total cholesterol
- Trig:
-
Triglyceride
- TT:
-
Total testosterone
- VDR:
-
Vitamin D receptor
- WC:
-
Waist circumference
References
Azziz R, Woods KS, Reyna R, Key TJ, Knochenhauer ES, Yildiz BO. The prevalence and features of the polycystic ovary syndrome in an unselected population. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2004;89:2745–9.
Asuncion M, Calvo RM, San Millan JL, Sancho J, Avila S, Escobar-Morreale HF. A prospective study of the prevalence of the polycystic ovary syndrome in unselected Caucasian women from Spain. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2000;85:2434–8.
March WA, Moore VM, Willson KJ, Phillips DIW, Norman RJ, Davies MJ. The prevalence of polycystic ovary syndrome in a community sample assessed under contrasting diagnostic criteria. Hum Reprod. 2010;25:544–51.
De Leo V, Musacchio MC, Cappelli V, Massaro MG, Morgante G, Petraglia F. Genetic, hormonal and metabolic aspects of PCOS: an update. Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2016;14:38.
He CL, Lin ZM, Robb SW, Ezeamama AE. Serum vitamin D levels and polycystic ovary syndrome: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Nutrients. 2015;7:4555–77.
Bacopoulou F, Kolias E, Efthymiou V, Antonopoulos CN, Charmandari E. Vitamin D predictors in polycystic ovary syndrome: a meta-analysis. Eur J Clin Investig. 2017;47:746–55.
Palomer X, Gonzalez-Clemente JM, Blanco-Vaca F, Mauricio D. Role of vitamin D in the pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2008;10:185–97.
Santos BR, Mascarenhas LP, Satler F, Boguszewski MC, Spritzer PM. Vitamin D receptor gene polymorphisms and sex steroid secretion in girls with precocious pubarche in southern Brazil: a pilot study. J Endocrinol Investig. 2012;35:725–9.
Mahmoudi T. Genetic variation in the vitamin D receptor and polycystic ovary syndrome risk. Fertil Steril. 2009;92:1381–3.
El-Shal AS, Shalaby SM, Aly NM, Rashad NM, Abdelaziz AM. Genetic variation in the vitamin D receptor gene and vitamin D serum levels in Egyptian women with polycystic ovary syndrome. Mol Biol Rep. 2013;40:6063–73.
Mahmoudi T, Majidzadeh-A K, Farahani H, Mirakhorli M, Dabiri R, Nobakht H, et al. Association of vitamin D receptor gene variants with polycystic ovary syndrome: a case control study. Int J Reprod Biomed (Yazd). 2015;13(12):793–800.
Siddamalla S, Reddy TV, Govatati S, Erram N, Deenadayal M, Shivaji S, et al. Vitamin D receptor gene polymorphisms and risk of polycystic ovary syndrome in south Indian women. Gynecol Endocrinol. 2017;3:1–5.
Wehr E, Trummer O, Giuliani A, Gruber HJ, Pieber TR, Obermayer-Pietsch B. Vitamin D-associated polymorphisms are related to insulin resistance and vitamin D deficiency in polycystic ovary syndrome. Eur J Endocrinol. 2011;164:741–9.
Dasgupta S, Dutta J, Annamaneni S, Kudugunti N, Battini MR. Association of vitamin D receptor gene polymorphisms with polycystic ovary syndrome among Indian women. Indian J Med Res. 2015;142:276–85.
Jedrzejuk D, Laczmanski L, Milewicz A, Kuliczkowska-Plaksej J, Lenarcik-Kabza A, Hirnle L, et al. Classic PCOS phenotype is not associated with deficiency of endogenous vitamin D and VDR genepolymorphisms rs731236 (TaqI), rs7975232 (ApaI), rs1544410 (BsmI), rs10735810 (FokI): a case-control study of lower Silesian women. Gynecol Endocrinol. 2015;31:976–9.
Al-Daghri NM, Al-Attas OS, Alkharfy KM, Khan N, Mohammed AK, Vinodson B, et al. Association of VDR-gene variants with factors related to the metabolic syndrome, type 2 diabetes and vitamin D deficiency. Gene. 2014;542:129–33.
Hitman GA, Mannan N, McDermott MF, Aganna E, Ogunkolade BW, Hales CN, et al. Vitamin D receptor gene polymorphisms influence insulin secretion in Bangladeshi Asians. Diabetes. 1998;47:688–90.
Bienertová-Vašků J, Zlámal F, Pohořalá A, Mikeš O, Goldbergová-Pávková M, Novák J, Šplíchal Z, Pikhart H. Allelic variants in vitamin D receptor gene are associated with adiposity measures in the central-European population. BMC Medical Genetics. 2017;18:90–99.
Alvarez JA, Ashraf A. Role of vitamin D in insulin secretion and insulin sensitivity for glucose homeostasis. Int J Endocrinol. 2010;92:1344–9.
Oh JY, Barrett-Connor E. Association between vitamin D receptor polymorphism and type 2 diabetes or metabolic syndrome in community-dwelling older adults: the rancho Bernardo study. Metabolism. 2002;51:356–9.
Ortlepp JR, Metrikat J, Albrecht M, von Korff A, Hanrath P, Hoffmann R. The vitamin D receptor gene variant and physical activity predicts fasting glucose levels in healthy young men. Diabet Med. 2003;20:451–4.
Santos BR, Mascarenhas LPG, Satler F, Boguszewski MCS, Spritzer PM. Vitamin D deficiency in girls from South Brazil: a cross-sectional study on prevalence and association with vitamin D receptor gene variants. BMC Pediatr. 2012;12:62–8.
Han FF, Lv YL, Gong LL, Liu H, Wan ZR, Liu LH. VDR gene variation and insulin resistance related diseases. Lipids Health Dis. 2017;16(1):157.
Santos BR, Lecke SB, Spritzer PM. Genetic variant in vitamin D-binding protein is associated with metabolic syndrome and lower 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels in polycystic ovary syndrome: a cross-sectional study. PLoS One. 2017;12:e0173695.
Group REA-SPCW. Revised 2003 consensus on diagnostic criteria and long-term health risks related to polycystic ovary syndrome. Fertil Steril. 2004;81:19–25.
Toscani M, Mighavacca R, Sisson de Castro JA, Spritzer PM. Estimation of truncal adiposity using waist circumference or the sum of trunk skinfolds: a pilot study for insulin resistance screening in hirsute patients with or without polycystic ovary syndrome. Metabolism. 2007;56:992–7.
Graff SK, Mario FM, Alves BC, Spritzer PM. Dietary glycemic index is associated with less favorable anthropometric and metabolic profiles in polycystic ovary syndrome women with different phenotypes. Fertil Steril. 2013;100:1081–8.
Di Domenico K, Wiltgen D, Nickel FJ, Magalhaes JA, Moraes RS, Spritzer PM. Cardiac autonomic modulation in polycystic ovary syndrome: does the phenotype matter? Fertil Steril. 2013;99:286–92.
Ramos RB, Spritzer PMFTO. Gene variants are not associated with polycystic ovary syndrome in women from southern Brazil. Gene. 2015;560:25–9.
Alberti K, Eckel RH, Grundy SM, Zimmet PZ, Cleeman JI, Donato KA, et al. Harmonizing the metabolic syndrome a joint interim statement of the international diabetes federation task force on epidemiology and prevention; National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute; American Heart Association; world heart federation; international atherosclerosis society; and International Association for the Study of obesity. Circulation. 2009;120:1640–5.
Wallace TM, Levy JC, Matthews DR. Use and abuse of HOMA modeling. Diabetes Care. 2004;27:1487–95.
Miller SA, Dykes DD, Polesky HF. A simple salting out procedure for extracting DNA from human nucleated cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988;16:1215.
La Marra F, Stinco G, Buligan C, Chiriacò G, Serraino D, Di Loreto C, et al. Immunohistochemical evaluation of vitamin D receptor (VDR) expression in cutaneous melanoma tissues and four VDR gene polymorphisms. Cancer Biol Med. 2017;14:162–75.
Ogunkolade BW, Boucher BJ, Prahl JM, Bustin SA, Burrin JM, Noonan K, et al. Vitamin D receptor (VDR) mRNA and VDR protein levels in relation to vitamin D status, insulin secretory capacity, and VDR genotype in Bangladeshi Asians. Diabetes. 2002;51:2294–300.
Meyer V, Saccone DS, Tugizimana F, Asani FF, Jeffery TJ, Bornman L. Methylation of the vitamin D receptor (VDR) gene, together with genetic variation, race, and environment influence the signaling efficacy of the toll-like receptor 2/1-VDR pathway. Front Immunol. 2017;8:1048.
Uitterlinden AG, Fang Y, Van Meurs JB, Pols HA, Van Leeuwen JP. Genetics and biology of vitamin D receptor polymorphisms. Gene. 2004;338:143–56.
Pike JW, Meyer MB. The vitamin D receptor: new paradigms for the regulation of gene expression by 1,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D-3. Endocrinol Metab Clin N Am. 2010;39:255–69.
Dilworth FJ, Chambon P. Nuclear receptors coordinate the activities of chromatin remodeling complexes and coactivators to facilitate initiation of transcription. Oncogene. 2001;20:3047–54.
Joham AE, Teede HJ, Cassar S, Stepto NK, Strauss BJ, Harrison CL, et al. Vitamin D in polycystic ovary syndrome: relationship to obesity and insulin resistance. Mol Nutr Food Res. 2016;60:110–8.
Bahrami A, Sadeghnia HR, Tabatabaeizadeh SA, Bahrami-Taghanaki H, Behboodi N, Esmaeili H, Ferns GA, Mobarhan MG, Avan A. Genetic and epigenetic factors influencing vitamin D status. J Cell Physiol. 2018;233:4033–43.
Bagheri M, Abdi Rad I, Hosseini Jazani N, Nanbakhsh F. Vitamin D receptor TaqI gene variant in exon 9 and polycystic ovary syndrome risk. Int J Fertil Steril. 2013;7:116–21.
San-Pedro JI, Bilbao JR, De Nanclares GP, Vitoria JC, Martul P, Castano L. Heterogeneity of vitamin D receptor gene association with celiac disease and type 1 diabetes mellitus. Autoimmunity. 2005;38:439–44.
Ramos-Lopez E, Jansen T, Ivaskevicius V, Kahles H, Klepzig C, Oldenburg J, et al. Protection from type 1 diabetes by vitamin D receptor haplotypes. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2006;1079:327–34.
Panierakis C, Goulielmos G, Mamoulakis D, Petraki E, Papavasiliou E, Galanakis E. Vitamin D receptor gene polymorphisms and susceptibility to type 1 diabetes in Crete, Greece. Clin Immunol. 2009;133:276–81.
Kamel MM, Fouad SA, Salaheldin O, Abd El-Razek AA, Abd El-Fatah AI. Impact of vitamin D receptor gene polymorphisms in pathogenesis of Type-1 diabetes mellitus. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2014;7:5505–10.
Funding
This work was supported by grants from Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico/Brazilian National Institute of Hormones and Women’s Health (CNPq/INCT 465482/2014–7) and Coordenacão de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior (CAPES, Post-doc grant to BRS). The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
Availability of data and materials
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this manuscript and in a previous publication
(Santos BR, et al. PLoS One. 2017;12(3):e0173695. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0173695).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
BRS and PMS were involved in the conception and design of the study, BRS, SBL and PMS were involved in data collection and analysis. BRS and PMS drafted the article. All the authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The study was approved by the Institutional Review Board and the local Ethics Committee at Hospital de Clínicas de Porto Alegre (FIPE-HCPA 340/2004). Written informed consent was obtained from every subject.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated.
About this article
Cite this article
Santos, B.R., Lecke, S.B. & Spritzer, P.M. Apa-I polymorphism in VDR gene is related to metabolic syndrome in polycystic ovary syndrome: a cross-sectional study. Reprod Biol Endocrinol 16, 38 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12958-018-0355-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12958-018-0355-9