Abstract
Adipose-derived stem cells (ADSCs) are a subset of mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) isolated from adipose tissue. They possess remarkable properties, including multipotency, self-renewal, and easy clinical availability. ADSCs are also capable of promoting tissue regeneration through the secretion of various cytokines, factors, and extracellular vesicles (EVs). ADSC-derived EVs (ADSC-EVs) act as intercellular signaling mediators that encapsulate a range of biomolecules. These EVs have been found to mediate the therapeutic activities of donor cells by promoting the proliferation and migration of effector cells, facilitating angiogenesis, modulating immunity, and performing other specific functions in different tissues. Compared to the donor cells themselves, ADSC-EVs offer advantages such as fewer safety concerns and more convenient transportation and storage for clinical application. As a result, these EVs have received significant attention as cell-free therapeutic agents with potential future application in regenerative medicine. In this review, we focus on recent research progress regarding regenerative medical use of ADSC-EVs across various medical conditions, including wound healing, chronic limb ischemia, angiogenesis, myocardial infarction, diabetic nephropathy, fat graft survival, bone regeneration, cartilage regeneration, tendinopathy and tendon healing, peripheral nerve regeneration, and acute lung injury, among others. We also discuss the underlying mechanisms responsible for inducing these therapeutic effects. We believe that deciphering the biological properties, therapeutic effects, and underlying mechanisms associated with ADSC-EVs will provide a foundation for developing a novel therapeutic approach in regenerative medicine.
Graphical Abstract

Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Adipose tissue, a highly versatile, dynamic and complex tissue [1,2,3], is now recognized as a vital endocrine organ that plays a crucial role in maintaining systemic metabolic homeostasis [4,5,6]. It primarily consists of mature adipocytes which make up the floating fraction, and the pelleted cellular components of the stromal vascular fraction (SVF), obtained through the conventional enzymatic isolation protocol [7, 8]. The SVF is widely acknowledged as a heterogeneous cell population composed of adipose-derived stem cells (ADSCs), preadipocytes, pericytes, endothelial precursor cells, endothelial cells, smooth muscle cells, fibroblasts, hematopoietic cells, macrophages and other immunocytes [7,8,9]. ADSCs are multipotent mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) derived from the embryonic mesoderm. Although making up only about 12–18% of the total adipose cell population [10], ADSCs are the most regeneratively active cell fraction of adipose tissue, capable of renewing their population and differentiating into multiple cell lineages, such as adipocytes, myocytes, chondrocytes, and osteocytes [11, 12]. Due to their multipotency and robust proangiogenic, proepithelial, neurotrophic, antifibrotic, antiapoptotic, and immunomodulatory effects demonstrated in numerous in vitro and in vivo studies, ADSCs have been extensively utilized in the field of regenerative medicine and cell therapy [8, 11, 13, 14]. MSCs can be directly administered to the injured area in vivo, or a novel cell-free approach utilizing extracellular vesicles (EVs) can replace live stem cells. Because the therapeutic effect of MSCs primarily relies on the autocrine/paracrine action of growth factors, immunomodulators, cytokines, and other bioactive molecules secreted by the cells and enclosed within EVs [13, 14].
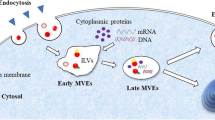
EVs are nanosized bilayer lipid membrane structures secreted by cells that carry various biomolecules from donor cells, and cannot replicate on their own [15, 16]. These biomolecular cargos include lipids, proteins, chemical compounds, multimolecular complexes, DNA, RNA (siRNA, miRNA, lncRNA, circRNA, etc.), and even intact subcellular organelles [17,18,19,20]. Revealing the details of the molecular composition, diverse structures, and unique sequences of these EV cargos through nucleic acid sequencing or mass spectrometry provides valuable insights into the metabolic state of the parent cells and positions EVs as promising clinical biomarkers [21, 22]. EVs can be released by most cell types and have been detected in a variety of solid tissues and biofluids, such as blood, breast milk, saliva, urine, semen, bile, ascites, synovial fluid, cerebrospinal fluid, and amniotic fluid, making them suitable for intercellular signal transmission [17, 23,24,25]. The uptake of EVs by recipient cells initiates intercellular signaling, which forms the basis of their therapeutic potential [26,27,28]. This process can occur through different pathways: intact EVs entering recipient cells via endocytosis mediated by receptors, clathrin-coated pits, lipid rafts, caveolae, phagocytosis and macropinocytosis; direct ligand-receptor binding triggered intracellular signaling without internalization or content release; or the release of EV contents into the cytoplasm through direct membrane fusion (Fig. 1) [27]. EV-mediated intercellular signaling has been extensively investigated in most human diseases and related biological processes, including development [29], immunity [30,31,32,33,34], virus infection [35], tissue regeneration [36,37,38,39], obesity and diabetes mellitus [40,41,42,43,44], liver diseases [45,46,47], cardiovascular disorders [48,49,50,51,52,53,54], neurodegenerative diseases [55,56,57,58,59,60], aging [61,62,63], and cancer [64,65,66,67,68,69]. In addition, the potential utility of EVs as diagnostic biomarkers [70, 71] and cell-free curative agents [72, 73] for future clinical application has also been widely explored.
Cellular biogenesis and uptake of EVs. The EV biogenesis pathways include the outward budding of plasma membrane domains to form ectosomes, and the development of endosomes to release exosomes. The EV uptake pathways include entry of intact EVs through endocytosis, direct ligand-receptor binding triggered intracellular signaling without internalization or releasing the contents, and the release of EV contents inward via direct membrane fusion
MSCs have been found to present in different tissues. Until now, the most employed human tissues as MSC-EV sources for therapeutic research and clinical trials include adipose tissue, bone marrow, and umbilical cord (Table 1) [74, 75]. Adipose tissue offers substantial advantages in its significant greater amount of clinical MSC source, resulting higher production of MSC-EVs, and the easier and less invasive surgical procedure to obtain the source tissue such as liposuction compared to other tissue sources [76, 77]. In addition, adipose-derived MSCs are reported to possess higher stability in culture conditions and lower senescence ratio by comparison [78]. Accumulating evidence suggests that ADSC-derived EVs (ADSC-EVs) possess cell therapy bioactivity similar to that of their parent cells while circumventing safety concerns associated with the administration of live stem cells [75, 79,80,81]. As a result, the number of registered clinical trials using ADSC-EVs as interventions is growing according to the ClinicalTrials.gov (Table 1, available online: http://www.clinicaltrials.gov/accessed on 23/Apr/2024). In this review, we present a concise overview of EV biogenesis and classification, with a primary emphasis on the latest advancements in tissue regenerative therapeutic potential, applications, benefits, and current limitations of ADSC-EVs in the field of regenerative medicine.
Classification and biogenesis of EVs
Although the classification of EVs may vary from time to time, the prevailing categorization is based on the biogenesis and size of vesicles, resulting in two major classes: ectosomes and exosomes [27, 82]. Ectosomes or microvesicles are characterized by their direct budding outward from the plasma membrane, with a diameter ranging from approximately 50 to 1000 nm (Fig. 1) [15, 16, 27]. The sprouting of the cell membrane is triggered by phospholipid redistribution within the bilayer, which is initiated by activation of the phospholipid crawling enzyme and facilitated by calcium-dependent degradation of the cytoskeleton that is bound to the membrane [23]. The arrestin domain-containing protein 1 (ARRDC1) plays a key role in driving cell membrane sprouting by acting as an anchor fusion molecule that facilitates the sorting of specific macromolecules into microvesicles [23, 83, 84]. ARRDC1 recruits endosomal sorting complex required for transport (ESCRT) proteins, including tumor susceptibility gene 101 (TSG101) and vacuolar protein sorting-associated protein 4 (VPS4), to the plasma membrane to promote the budding process [23, 83, 84].
In contrast, exosomes originate from endosomes and multivesicular bodies (MVBs) and are approximately 40–200 nm in diameter [16, 27, 85]. The whole formation process of exosomes is highly intricate: initially, inward budding endocytosis gives rise to early endosomes, which subsequently mature into late endosomes containing intraluminal vesicles that accumulate in the lumen under communication with the Golgi complex. Eventually, these late endosomes transform into MVBs that fuse with the cell membrane and release their contents, the intraluminal vesicles, into the extracellular space as exosomes (Fig. 1) [27, 82, 86]. Recent reports suggest that both ESCRT-dependent and ESCRT-independent sorting pathways are involved in loading MVBs with cargo during maturation [23].
Besides the two major and well-studied categories, EVs could be released through other cellular processes with different average sizes. For example, disassembly of apoptotic cells gives rise to the apoptotic body with a diameter of 800–5000 nm, which contains components and information from the dying cells and are able to deliver these to healthy recipient cells [87]. The newly discovered migrasome, with a size of 500–3000 nm, plays an important role in fields such as intercellular communication, homeostasis maintenance, embryonic development, and disease progression [88]. Their formation depends on cell migration and is closely associated with tetraspanins (TSPANs) and integrins [88]. And, the recently identified “large oncosome” has an atypical large size of 1–10 μm [89]. They are specifically originated through oncocyte plasma membrane budding with oncogenic materials carried inside, and might share biogenesis pathways with ectosomes [89].
Unfortunately, most EV isolation procedures do not separate EVs by their biogenesis mechanisms, and universal definitive molecular markers of these EV subtypes are missing. Therefore, In this review, we use the term “extracellular vesicle” to encompass various types of secreted vesicular structures as recommended [16].
Regenerative therapeutic potential of ADSC-EVs
The aforedescribed biogenesis pathways of EV load them with diverse biomolecules derived from the donor cells. As a result, these EVs mimic the function of their donor cells by initiating target signaling pathways in the recipient cells with their cargos. Substantial studies have aimed to elucidate the ADSC-EV-enclosed cargos, their respective molecular targets and the activated signaling cascades in the recipient cells, and the resulting functions within the specific context of medical conditions or diseases (Table 2). This knowledge serves as a prerequisite for designing innovative therapeutic strategies based on ADSC-EVs.
Wound healing
Acute wounds
The wound healing of skin is one of the most extensively investigated regenerative medical conditions that employs ADSC-EVs as a therapeutic intervention, showing highly promising curative outcomes according to reported findings (Table 2) [76, 128, 129]. The skin, an innate protective shield against the external environment, is constantly exposed to potential injuries, making wound healing a vital process for the survival of all higher organisms [130]. As a process that is conserved throughout evolution across species, acute wound healing occurs in four sequential and overlapping phases [130,131,132] (Fig. 2). Hemostasis begins first when blood clotting occurs to control blood loss and prevent microbial invasion. This process is followed by inflammation, which overlaps with hemostasis and involves the recruitment of proinflammatory immunocytes, such as neutrophils (initially) and then macrophages, to remove tissue debris and foreign pathogens at the injury site. Activated macrophages release a variety of growth factors and cytokines at the wound site to amplify earlier signals, thereby playing a crucial role in the healing process. Subsequently, the proliferation phase begins concurrently with inflammation, which is characterized by angiogenesis, re-epithelialization, and fibroplasia to restore the lost tissue. Fibroblasts play a pivotal role in this phase by producing important factors, including collagen, elastin, and extracellular matrix (ECM) proteins. Finally, remodeling occurs simultaneously with tissue formation through processes involving cell maturation, cell apoptosis, ECM contraction resulting from the transition of fibroblasts to myofibroblasts, and the conversion of type III collagen to type I collagen through the coordinated actions of matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) and tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases (TIMPs). The remodeling phase may last from weeks to years until the desired new tissue is ultimately regenerated [131,132,133,134] (Fig. 2).
Preparation of ADSC-EVs, the four sequential phases of wound healing, and ADSC-EV-induced promotion of wound healing. ADSC-EVs promote wound healing by enhancing cell proliferation and migration, stimulating angiogenesis, facilitating myofibroblast infiltration, promoting collagen production and deposition, accelerating re-epithelialization and tissue layer growth, as well as suppressing inflammation when it is time to move on to the next phase. Created with MedPeer (medpeer.cn)
To date, ADSCs have emerged as a promising approach for skin regeneration and wound healing owing to their remarkable abundance and accessibility compared to MSCs from other tissue sources [135, 136]. ADSC-EVs have been shown to mimic the therapeutic activity of ADSCs while offering advantages such as greater stability, easier storage, and fewer safety and ethical concerns [128]. Extensive evidence supports the role of ADSC-EVs in accelerating tissue regeneration and suppressing inflammation when it is time to move on to the next phase of wound healing at the site of injury [137] (Fig. 2). In vitro studies have demonstrated that ADSC-EVs promote cell proliferation, migration, angiogenesis, and collagen production in human dermal fibroblasts (HDFs), human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs), and human epidermal keratinocytes (HaCaT cells) through regulating signaling pathways that control these processes [113, 138, 139]. Note that in a study, the ADSC-EV-treated HDF proliferation shows an average of a 120% increase compared to the control [138]. Animal experiments consistently exhibit improved healing efficiency characterized by increased re-epithelialization, thicker tissue layers, elevated vascularization, myofibroblast infiltration, and deposition of type III collagen, consequently leading to accelerated acute wound healing [113, 138, 139]. Despite the high variability, the ADSC-EVs display an approximately 10% increase in wound closure rate compared to the control [138]. Mechanistic studies have revealed the crucial roles of the Wnt/β-catenin, the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K)/AKT, and the extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) signaling pathways, which are canonical regulators of stem cell potency, cell proliferation, survival, and growth, in mediating the ADSC-EV-driven healing process across multiple dermal cell lines [113, 139, 140]. In addition to their efficacy in excisional and incisional wounds, ADSC-EVs have shown potential in mitigating ultraviolet B (UVB)-induced skin photoaging [141]. In vivo administration of ADSC-EVs reduces skin wrinkles caused by UVB-induced photoaging in mice while increasing epidermal cell proliferation and decreasing macrophage infiltration and reactive oxygen species (ROS) levels. In vitro studies also reveal increased levels of antioxidant enzymes and decreased production of intracellular ROS in HDFs after ADSC-EV administration. This treatment enhances HDF activity, protects HDFs from UVB-induced senescence, induces HDF cell cycle arrest, and attenuates M1 macrophage polarization of RAW 264.7 cells [141]. Furthermore, ADSC-EVs have shown potential in the regeneration of skin appendages such as hair follicles, exhibiting validated phenotypes and the gene expression profile that supports the outcomes [142]. In summary, the multifaceted effects of ADSC-EVs on skin tissue repair and regeneration, similar to those of their donor cells, have been extensively acknowledged, and ongoing efforts are being made to develop optimal clinical therapies based on these effects [136, 143, 144].
Given the globally acknowledged therapeutic potential of ADSC-EVs in acute wound healing, researchers have been actively exploring strategies to enhance their bioactivity, reduce dosage frequency, and optimize clinical practice. Compared with negative control ADSC-EVs, miR-126-3p-overexpressing ADSC-EVs exhibit enhanced potential for the proliferation and migration of HDFs as well as angiogenesis in HUVECs [90]. Conversely, inhibition of either ADSC-EVs or miR-126-3p or phosphoinositide-3-kinase regulatory subunit 2 (PIK3R2), which is a regulatory subunit of PI3K and the intracellular target of miR-126-3p, results in the opposite effects. The potential of miR-126-3p-overexpressing ADSC-EVs is further verified through improvements in the wound healing rate, increased collagen deposition, and enhanced angiogenesis in a rat model [90]. In addition to bioengineering strategies, small molecules has been employed to enhance the therapeutic potential of ADSC-EVs [145]. Compared with control EVs from normal ADSCs, EVs derived from selenium-treated ADSCs lead to increased cell proliferation, migration, angiogenesis, and inflammatory suppression both in vitro and in vivo [145]. However, further investigation is needed to elucidate the underlying mechanism responsible for such improvements. Apart from their tunable therapeutic potential, as an excreted agent, EVs are rapidly eliminated by the circulation system, thus showing limited duration of efficacy at specific sites for tissue repair. Hydrogels are highly porous and loosely structured synthesized materials with excellent biocompatibility, making them an ideal choice as carriers for EVs to achieve a controlled release rate and prolonged retention time when needed [146]. For instance, the administration of Pluronic F-127 hydrogel-encapsulated human ADSC-EVs results in a reduction in dosage frequency without compromising therapeutic efficacy [147]. Compared to either subcomponent alone, the hydrogel/ADSC-EV complex enhances healing efficacy by promoting skin wound healing and re-epithelialization, stimulating collagen production, and elevating the expression of Ki67, α-smooth muscle actin (α-SMA), CD31, and skin barrier proteins while suppressing the expression of inflammatory factors [147]. To enhance the biocompatibility, a separate group of researchers employ a three-dimensional scaffold composed solely of type I collagen and platelet-rich plasma [148]. This scaffold provides natural support for cell adhesion, migration, and proliferation of keratinocytes and fibroblasts and serves as a carrier and release controller for EVs. Notably, their data demonstrate that the combination of ADSC-EVs and the scaffold effectively reduces inflammation levels and promotes cell proliferation and angiogenesis, ultimately leading to accelerated wound healing in a mouse model of full-thickness skin defects [148]. These findings have been further validated through proteomic analysis. In general, researchers’ endeavors to enhance the therapeutic efficacy and mitigate the adverse effects of ADSC-EVs through engineering approaches will significantly contribute to their global clinical application.
Skin wound healing commonly leads to scar formation, which is characterized by the absence of skin appendages and incomplete restoration of skin functionality (approximately 80% of intact skin strength), thereby causing significant aesthetic and psychological concerns [130, 132, 149]. The aberrant remodeling of the ECM and excessive collagen deposition are recognized as immediate factors contributing to scar development [149, 150]. Recent studies have indicated that ADSC-EVs play a supportive role in facilitating scarless cutaneous repair. Intravenous injection of ADSC-EVs has been shown to reduce scar size, suppress fibroblast differentiation into myofibroblasts, and increase the ratio of collagen III to collagen I, as well as the ratio of transforming growth factor-β3 (TGF-β3) to TGF-β1, in a mouse incisional wound model [151]. Furthermore, in vitro experiments on HDFs reveal that ADSC-EVs promote MMP3 expression and increase the MMP3/TIMP1 ratio by activating the ERK pathway, thereby modulating ECM remodeling [151]. Considering that myofibroblasts are the primary cell type responsible for ECM accumulation, with TGF-β signaling being a key pathway involved [150] and MMPs serving as major endopeptidases responsible for ECM degradation [152], it has been demonstrated that ADSC-EVs effectively mitigate scar formation by modulating ECM remodeling, as anticipated [151]. Moreover, scars can progress pathologically into hypertrophic scars and keloids characterized by uncontrolled fibroproliferation, the continuous accumulation of ECM and cells, and, in the case of keloids, invasion of adjacent healthy skin [150, 153, 154]. Fortunately, ADSC-EVs have also shown efficacy under both conditions. Treatment with ADSC-EVs results in reduced cell proliferation and migration in hypertrophic scar fibroblasts (HSFs), along with decreased expression of collagen proteins, interleukin-17 receptor A (IL-17RA), phosphorylated small mothers against decapentaplegic protein 2/3 (p-SMAD2/3), and increased levels of SMAD interacting protein-1 (SIP1) [95]. These effects are consistent with the accelerated wound healing and reduced hypertrophic collagen deposition observed in a mouse model. The mechanism underlying the effects of ADSC-EVs has been verified to involve the miR-192-5p/IL-17RA/SMAD axis through both overexpression and knockdown of IL-17RA [95]. In the case of keloids, ADSC-EVs have been shown to suppress collagen production and disrupt angiogenesis in keloid tissue explants [155]. In vitro tests utilizing keloid fibroblasts (KFs) demonstrate that the administration of ADSC-EVs effectively suppresses the expression of collagen I, collagen III, fibronectin, and α-SMA, as well as subsequent ECM production [155]. The leading molecular mechanisms underlying these effects are believed to involve the downregulation of the Notch 1 and TGF-β2/SMAD3 signaling pathways, concomitant with the upregulation of TGF-β3. Despite the increasing number of reports on ADSC-EV-induced attenuation of scar formation, further comprehensive investigations are imperative to elucidate the underlying mechanisms by which ADSC-EVs facilitate wound healing while inhibiting scar formation. Note that scar formation refers to the overprogression of healing process out of its physiological range, particularly the subprocesses of inflammation, cell proliferation and collagen deposition.
Chronic diabetic wounds
The fast-growing prevalence of type 2 diabetes (T2D) in recent decades has rendered this disease a formidable global health threat, afflicting approximately 537 million adults (estimated 6.7 million deaths) in 2021 and projected to increase to around 643 million by 2030 [156, 157]. The current surge entails enormous economic loss due to combined medical expenses and diminished work productivity [158]. Moreover, the occurrence of comorbidities is common in T2D patients and contributes substantially to the disease burden [159]. Taking diabetic wounds as an example, it is estimated that approximately 20% to more than 30% of patients with diabetes will develop chronic nonhealing wounds, such as diabetic foot ulcers (DFUs), during their lifespan. These wounds exhibit considerable recurrence rates of up to 40% within one year and 65% within five years, with no reliable predictive methods currently available [158]. Additionally, more than 70% of DFU patients will ultimately require lower limb amputation, imposing a heavy financial burden and severe impairment to patients’ quality of life [160].
Diabetes impedes the healing process by disrupting each phase of wound healing mentioned earlier (Fig. 2). The intricate underlying etiology involves hyperglycemia, hemoglobin glycation, impaired neutrophil function, dysregulated macrophage polarization and function, sustained production of proinflammatory cytokines, impaired angiogenesis, reduced fibroblast and keratinocyte proliferation and migration, compromised growth factor production, decreased cytokine production, downregulated MMPs production, neuropathy, and nitrous oxide blockade [133, 158, 160]. These factors orchestrate the delay of healing process, thereby making diabetes a typical condition of chronic wounds, which generally fail to progress through the normal healing process and show no signs of healing in four weeks [131, 133]. In contrast to the acute wounds described above, which typically show signs of healing in less than four weeks following the normal progression of wound healing, chronic wounds are generally characterized by elevated bacterial levels caused by hyperglycemia along with high inflammatory cytokine levels, increased protease and ROS levels, a degraded nonfunctional ECM, reduced mitogenic activity, and enhanced cell senescence [131, 132, 158]. Despite these challenges posed by the complex pathology of chronic diabetic wounds, accumulating evidence suggests that ADSC-EVs have the potential to improve chronic diabetic wound healing through mechanisms similar to those in acute wounds [157].
The effects of ADSC-EVs on chronic diabetic wounds include facilitating cell proliferation and migration, inhibiting apoptosis, enhancing re-epithelialization and angiogenesis, reducing ROS levels, and suppressing inflammation, as evidenced by recent studies [116, 121, 161,162,163,164] (Fig. 2). Multiple molecular signaling pathways responsible for these beneficial effects have been identified since ADSC-EVs are essentially a heterogeneous collection of diverse biomolecules encapsulated within a lipid membrane that can activate versatile signaling cascades. Moreover, different research groups may focus on distinct aspects of this treatment. The depicted signaling pathways include: the PI3K/AKT pathway as a key regulator of cell proliferation and survival [121, 164], the Fas/Fas ligand (FasL) pathway as an initiator of cell death [161], the sirtuin 3 (SIRT3)/superoxide dismutase 2 (SOD2) axis as a scavenger of ROS [162], the TGF-β1/SMAD3 pathway as a crucial mediator of tissue repair and immune response [163], and the hypoxia-inducible factor-1α (HIF-1α) as a key factor in angiogenesis and immunomodulation [116]. These ongoing efforts to explore the efficacy and molecular mechanisms underlying ADSC-EV treatment for chronic diabetic wounds will serve as the cornerstone for potential medical intervention against this intractable condition.
Similar to acute wounds, bioengineered ADSC-EVs have gained popularity and reliability in addressing refractory chronic diabetic wounds with enhanced efficacy. Compared with control EVs, HIF-1α-overexpressing ADSC-EVs improve the wound healing rate and quality in a diabetic nude mouse model [122]. In vitro experiments in HDFs demonstrate increased expression of multiple growth factors and collagen proteins, which appears to be induced by the upregulation of PI3K/AKT pathway, which is crucial for cell proliferation and survival [122]. In diabetes, elevated oxidative stress plays a key role in the progression of complications and impairs the healing process of diabetic wounds [133]. Nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (NRF2) effectively eliminates ROS and protects cells against oxidative stress by inducing the transcription of numerous antioxidants and cytoprotective genes through activation of the NRF2/antioxidant response element (ARE) complex. Therefore, EVs derived from ADSCs overexpressing NRF2 significantly improve diabetic wound healing by reducing the ulcerated area and inflammation, promoting cell proliferation, granulation tissue formation and angiogenesis, and upregulating growth factor expression while attenuating oxidative stress-related protein expression [123, 165]. In addition to protein-coding genes, microRNAs (miRNAs) are extensively employed for engineering ADSC-EVs to enhance their therapeutic activity. MiRNAs can be transfected as DNA constructs, overexpressed in ADSC cells and loaded into ADSC-EVs by the donor cells themselves [96], or directly electroporated into isolated ADSC-EVs as miRNA mimics [166]. Both strategies have been validated to yield positive outcomes in the treatment of chronic diabetic wounds. EVs secreted from miR-132-overexpressing ADSCs promote diabetic wound healing by upregulating angiogenesis, collagen deposition, and ECM fibronectin accumulation and attenuating local inflammation through nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) signaling-mediated M2 macrophage polarization [96]. ADSC-EVs loaded with miR-21-5p via electroporation show similar accelerated healing rate in diabetes-associated wound models [166]. Circular RNAs (circRNAs), another type of noncoding RNA with significant biological functions, often act as sponges for miRNAs to prevent them from binding to their downstream target mRNAs [167]. This machinery has been utilized to enhance the therapeutic potential of ADSC-EVs. Circ_0001052-overexpressing ADSC-EVs promote angiogenesis in DFUs by sequestering miR-106a-5p, thereby disinhibiting the translation of its downstream target fibroblast growth factor-4 (FGF4), which is known to be involved in embryonic development, cell proliferation and differentiation [119]. As expected, published data have confirmed the improved therapeutic effects of these modified EVs on DFUs [119]. A similar approach has been reported for another circRNA, circ_0000250 [120]. The overexpression of circ_0000250 in ADSC-EVs results in enhanced healing in diabetic mice through the induction of autophagy mediated by the miR-128-3p/SIRT1 axis since epidermal SIRT1 is responsible for the modulation of inflammation, wound healing and cell migration [120]. In general, the application of bioengineering techniques to modify ADSC-EVs has demonstrated remarkable accessibility and potency in the treatment of chronic wounds associated with diabetes, thereby enabling robust and personalized therapy in future clinical settings.
In addition to their application in acute wounds, hydrogels and other scaffolds have also been combined with ADSC-EVs for localized and sustained release in treating chronic diabetic wounds. Hydrogels can serve as carriers for ADSC-EVs only, exerting therapeutic effects through the hypoxia-induced circ-Snhg11/miR-144-3p/NRF2/HIF-1α axis [117], which is identical by mechanism to that achieved by administering ADSC-EVs alone [116]. Alternatively, it can be dual-loaded with ADSC-EVs and an additional small chemical compound such as metformin to achieve synergistic efficacy [168]. Extensive efforts have been devoted to developing hydrogels into versatile platforms with multifunctional capabilities beyond mere EV delivery, including injectability, self-healing properties, antibacterial activity, and pH-responsive EV release, among others [169, 170]. These studies explicitly demonstrate significantly enhanced healing efficiency of multifunctional hydrogel-incorporated ADSC-EVs in full-thickness cutaneous wounds of diabetic models compared to those treated with either EVs or hydrogels alone [169, 170]. In addition to conventional hydrogels, alternative scaffolds, such as cell sheets and acellular fibers or membranes, have been applied as carriers of ADSC-EVs for combating chronic diabetic wounds. Studies have demonstrated that transplantation of ADSC sheets derived from rat epididymal adipose tissue enhances wound healing in diabetic rats [171]. Then, further studies have combined IRF1-overexpressing ADSC-EVs with ADSC sheets, resulting in further improvements in wound healing via the IRF1/miR-16-5p/SP5 axis [124]. Moreover, acellular amniotic membranes and functional micro/nanofibers composed of phosphoethanolamine phospholipid-grafted poly-L-lactic acid have been assessed as delivery platforms for ADSC-EVs in diabetic wound therapy. Both exhibit enhanced healing potential in diabetic models, characterized by augmented cell proliferation and migration, angiogenesis, collagen production and deposition, M2 macrophage polarization, and reduced inflammation, accompanied by the modulation of associated marker genes [172, 173]. As evidenced by these studies and similar ones, the continuous development and application of novel biomaterials will strongly facilitate the realization of ADSC-EV-based cell-free stem cell therapy.
Chronic limb ischemia
Lower extremity peripheral arterial disease (PAD) can progress into chronic critical limb ischemia, which is characterized by intractable rest foot pain, gangrene, and tissue necrosis [174]. Chronic limb ischemia is a prevalent comorbidity in diabetic patients and frequently leads to chronic diabetic wounds (ulcers) and limb amputation due to inadequate tissue perfusion and dysfunctional revascularization [175].
The cornerstone of chronic limb ischemia treatment lies in revascularization or angiogenesis [174], which is supported by ADSC-EV administration (Fig. 2, 3). One study shows that ADSC-EVs promote cell proliferation, migration, and tube formation while reducing cell apoptosis in high glucose-conditioned HUVECs [125]. Additionally, they enhance blood perfusion, microvessel density, and muscle structural integrity in diabetic mice. The healing potential may be attributed to the upregulation of endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS)/AKT/ERK/P-38 signaling pathways, along with the downregulation of activator protein-1 (AP-1)/ROS/NACHT-, leucine-rich repeat (LRR)- and pyrin domain (PYD)-containing protein 3 (NLRP3)/apoptosis-associated speck-like protein containing a CARD (ASC)/caspase-1/interleukin-1β (IL-1β) [125]. Furthermore, glyoxalase-1 (GLO-1) overexpression in ADSC-EVs further enhances their therapeutic potential [125]. Another study reveals that ADSC-EVs can polarize M1 macrophages toward an M2-like phenotype, characterized by reduced secretion of proinflammatory cytokines and increased production of proangiogenic factors [176]. This M2-like polarization promotes endothelial cell proliferation, migration, and tube formation. These effects have been verified in mouse hindlimb ischemia models with a Matrigel plug assay. Moreover, EVs from hypoxia-treated ADSCs exhibit even greater M2-like polarization and therapeutic potential [176]. Elevated levels of miR-21 and colony stimulating factor-1 (CSF-1)/CSF-1 receptor (CSF-1R) appear to play a pivotal role in initiating these beneficial effects [176]. These studies highlight the healing efficacy of ADSC-EVs on chronic limb ischemia while revealing their clinical potential for angiogenic therapy.
Regenerative medical conditions that are affected by ADSC-EVs and the major mechanisms of tissue regenerative efficacy. The recent advances in the regenerative medical use of ADSC-EVs focus mainly on these listed conditions. And, the most common primary mechanisms of tissue regenerative effects involve stimulated cell proliferation, migration and angiogenesis, and suppressed inflammation. Created with MedPeer (medpeer.cn)
Angiogenesis
Angiogenesis plays a critical role in wound healing and is essential for the treatment of ischemia and other tissue regeneration failures. Conventional cytokine-based angiogenic therapies utilizing growth factors such as vascular endothelial growth factors (VEGFs) and FGFs have demonstrated limited efficacy in clinical practice [177, 178]. Consequently, researchers have recently shifted their focus toward ADSC-based stem cell therapy and more advantageous ADSC-EV-based cell-free approach due to the ability of ADSCs to differentiate into endothelial cells or pericyte-like cells and to secrete proangiogenic growth factors and EVs [177].
Extensive efforts have been made to elucidate the correlation between angiogenesis and ADSC-EV administration, as well as the underlying mechanisms involved. Numerous studies have validated the positive impact of ADSC-EVs on angiogenesis [94, 98, 99, 101, 179,180,181] (Fig. 2, 3). Specifically, ADSC-EVs have been demonstrated to enhance endothelial cell proliferation, migration, and tube formation, as evidenced by increased vessel length and number of junctions and branches. These effects are attributed to the upregulation of growth factors and receptors such as VEGFs and their receptors, epidermal growth factor (EGF), platelet-derived growth factors (PDGFs), and FGFs, as well as proliferation markers, including cyclin proteins. In vivo studies in rodents have consistently shown improved neovascularization or angiogenesis along with accelerated wound closure due to enhanced re-epithelialization and collagen deposition. The therapeutic effects are mediated through exosomal miRNA-initiated signaling pathways involving axes of the miR-486-5p/SP5/cyclin D2 [94], the miR-126/sprouty-related EVH1 domain containing 1 (SPRED1)/ERK1/2 [98], the miR-125a/Drosophila delta-like 4 homolog (DLL4) [99], and the miR-31/factor-inhibiting HIF-1 (FIH1)/HIF-1α [101]. Interestingly, both hypoxia and metabolic conditions of ADSCs have been shown to influence the proangiogenic potential of derived EVs [98, 181]. Notably, compared with normoxic ADSC-EVs, hypoxic ADSC-EVs exhibit enhanced proliferation, migration and tube formation in HUVECs and improved neovascularization in a mouse model [181]. These therapeutic benefits are attributed to increased levels of growth factors and receptors, such as VEGF, EGF, FGF, VEGF-R2, and VEGF-R3, and chemokines, including monocyte chemotactic protein 2 (MCP-2) and MCP-4 [181]. However, obesity or hypertrophy can impair the proangiogenic potential of ADSC-EVs. Compared with those from lean individuals, EVs derived from ADSCs isolated from individuals with obesity exhibit attenuated potential for inducing endothelial cell proliferation, migration, and overall angiogenesis [98]. This impairment is associated with a reduction in exosomal miR-126 [98]. Moreover, treatment with palmitic acid induces ADSCs to generate EVs that recapitulate the cargo of obesity-associated ADSC-EVs. Additionally, high glucose-treatment further decreases the miR-126 level enclosed in ADSC-EVs, along with attenuated angiogenic potential [98]. Note that the angiogenic potential of ADSC-EVs is influenced not only by the composition of the culture media but also by the type of cell culture. It has been reported that EVs derived from 3D-spheroid-cultured ADSCs exhibit superior potency in promoting angiogenesis in HUVECs compared to those obtained from 2D monolayer-cultured cells [180]. Because the 3D-culturing resembles the natural local microenvironment of tissue in vivo, hopefully EVs directly extracted from adipose tissue may display higher regenerative potency [182]. Reported data have demonstrated the therapeutic efficacy of adipose tissue-derived EVs (AT-EVs) [183, 184]. However, AT-EVs cannot be strictly termed as ADSC-EVs, since the adipose tissue is composed of multiple cell types including ADSCs and others such as mature adipocytes and macrophages. And, ADSCs make up only around 12–18% but the most regeneratively active fraction of the total adipose cell population [10]. Therefore, further investigation is needed to compare the therapeutic potency of these two kinds of EVs. In conclusion, recent research has highlighted the potential of ADSC-EVs for future clinical applications in treating diseases related to ischemia and angiogenic failure, which are the leading causes of limb disability, necrosis, and amputation.
Myocardial infarction
Myocardial infarction (MI), commonly referred to as heart attack, is a severe medical condition characterized by the damage or death of myocardial tissue due to prolonged blockage of blood flow to that specific area of heart [185]. The pathology underlying this occlusion involves atherosclerosis, an inflammatory process leading to the narrowing and hardening of arteries with the buildup of plaque, thereby impeding blood circulation [186]. This progression arises from chronic inflammation and manifests as the accumulation of cholesterol, lipids, and other substances on the vascular wall [187]. Plaque rupture triggers clot formation, obstructing blood supply to cardiac muscle. Immediate management strategies for MI aim at promptly restoring blood flow through invasive procedures such as percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) and coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG) or pharmacological interventions. Long-term management encompasses lifestyle modifications and medications targeting risk reduction for future cardiovascular events while promoting tissue repair following MI damage; herein lies the potential role of ADSC-EVs.
According to the available references, the therapeutic potential of ADSC-EVs has been demonstrated in ameliorating MI injury by promoting cardiac angiogenesis, inhibiting cardiomyocyte apoptosis, and improving myocardial function [102, 188, 189] (Fig. 3). ADSC-EVs have shown efficacy in reducing obesity, enhancing insulin sensitivity, and maintaining metabolic homeostasis in obese mice, indicating their potential for alleviating metabolic disorders associated with MI [137]. Moreover, the aforementioned promotion of wound healing and vascularization by ADSC-EVs suggests their potential for addressing tissue damage related to MI [123]. Various signaling pathways are involved in mediating these therapeutic effects. It has been reported that ADSC-EVs promote cardiac regeneration and inhibit post-MI adverse remodeling through activation of the PI3K/AKT pathway. The PI3K/STAT3 pathway has also been implicated in modulating macrophage polarization to ameliorate cardiac fibrosis in infarcted hearts [190]. Additionally, EV-encapsulated miR-205, miR-196a-5p, miR-425-5p, and miR-31 (via the miR-31/FIH1/HIF-1α axis) have been identified as crucial initiators of cardiac angiogenic pathways underlying the attenuation of MI injury and the promotion of cardiac function recovery by ADSC-EVs [102, 188, 189]. Furthermore, miR-146a-overexpressing ADSC-EVs effectively attenuate acute MI-induced myocardial damage through downregulation of early growth response factor 1 (EGR1) and subsequent reversal of Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4)/NF-κB signal activation [191, 192]. Collectively, these studies suggest that ADSC-EVs could be a valuable therapeutic tool for addressing the aftermath of MI, offering potential benefits in promoting cardiac regeneration, attenuating MI injury, and improving myocardial function.
Diabetic nephropathy
Diabetic nephropathy is a severe complication of diabetes characterized by persistent albuminuria, a decrease in renal function, and increased cardiovascular morbidity and mortality [193]. It is the primary cause of chronic kidney disease in patients who are receiving renal replacement therapy [193]. The incidence of diabetic nephropathy is increasing concomitantly with the global surge in cases of diabetes mellitus [194].
Recent investigations have revealed that ADSC-EVs can mitigate pathological symptoms such as increased urine protein levels, serum creatinine (Scr) levels, blood urea nitrogen (BUN) levels, and podocyte apoptosis. This is achieved through the promotion of autophagy flux, reduction of inflammation, and attenuation of ROS levels [103, 105, 195]. The underlying signaling pathways responsible for these effects have been identified as the Kelch-like ECH-associated protein 1 (KEAP1)/NRF2/family with sequence similarity 129, member B (FAM129B) pathway [195] and the exosomal miR-26a-5p/TLR4/NF-κB pathway [105], leading to inflammatory inhibition. Additionally, the exosomal miR-486/SMAD1/mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) pathway [103] functions to activate autophagy. In conclusion, the therapeutic potential of ADSC-EVs in diabetic nephropathy is promising as a novel therapeutic strategy (Fig. 3).
Fat graft survival
Autologous fat grafting is a procedure in which adipose tissue is removed from one anatomical site and subsequently transplanted to another area within the same individual, with the aim of augmenting or restoring soft tissue volume [196]. This technique has garnered considerable attention in both aesthetic and reconstructive medicine due to its extensive applicability in facial and hand rejuvenation, breast augmentation and reconstruction, and body contouring [197,198,199]. Nevertheless, the primary obstacle impeding further advance and widespread adoption of fat grafting lies in the unpredictable resorption rates and low survival rates of the transplanted fat [197]. These challenges are believed to stem primarily from inadequate neovascularization post-transplantation [199]. Addressing these issues is crucial for enhancing the predictability and success rates of autologous fat grafting.
ADSCs have been demonstrated to play a regenerative role and facilitate the proliferation, migration, and secretion of fibroblasts and keratinocytes, thereby contributing to the replenishment and augmentation of soft tissues [200]. Co-transplantation of autologous adipose tissue with human ADSCs has been shown to enhance fat graft retention by promoting neovascularization and angiogenesis primarily through paracrine mechanisms [201, 202]. Considering that ADSC-EVs retain the therapeutic properties of ADSCs while offering certain advantages over live cells, as previously mentioned, researchers have investigated the effects of administering ADSC-EVs in fat grafting procedures and accumulated evidence supporting their significant involvement in promoting fat graft survival and adipose tissue regeneration (Fig. 3). When introduced into fat grafts, these EVs are capable of increasing neovascularization and graft retention, inhibiting fibrosis and necrosis, and inducing M2 polarization while suppressing M1 polarization and graft inflammation [198]. Further studies have indicated that ADSC-EVs can enhance fat graft retention rates by stimulating endothelial cell angiogenesis and facilitating ADSC adipogenesis through enhanced cell proliferation and migration, along with modulating the expression of marker genes [197, 199, 203, 204]. The underlying mechanisms responsible for these effects involve the modulation of various signaling pathways, such as the Wnt/β-catenin pathway [197, 204]. These findings underscore the potential utility of ADSC-EVs as a promising strategy for enhancing fat graft survival and adipose tissue regeneration.
Bone regeneration
The skeletal system plays a fundamental role in providing structural support, safeguarding vital organs, and facilitating movement. Bone regeneration and repair are indispensable for maintaining skeletal integrity, mobility, and overall physiological function following traumatic injuries, degenerative diseases or surgical interventions. This intricate biological process involves numerous cellular and molecular events that are critical for addressing medical conditions such as fractures, osteoporosis, bone defects, and orthopedic surgeries [205].
According to recent publications, researchers have demonstrated the crucial role of ADSC-EVs in promoting bone regeneration (Fig. 3). ADSC-EVs activate the proliferation, migration and osteogenesis of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells (BMSCs), stimulate angiogenesis in HUVECs, and induce M2 polarization while inhibiting the osteoclastogenesis of RAW264.7 macrophages [107, 206, 207]. Enhanced bone formation in animal models of bone defects has validated the osteogenic effect of these EVs [106, 107, 206]. The therapeutic potential of ADSC-EVs in bone regeneration and repair is mediated via various signaling pathways. One critical pathway that plays a key role in the promotion of osteogenesis by ADSC-EVs is the PI3K/AKT pathway [164, 190], leading to improved osteogenic effects and bone regeneration [208]. Furthermore, ADSC-EV-enclosed cytokines such as osteoprotegerin (OPG) and miRNAs such as miR-21-5p and let-7b-5p have been reported to hamper osteoclastogenesis by downregulating genes associated with bone resorption, suggesting the potential therapeutic use of ADSC-EVs in the treatment of osteoporosis [107]. To effectively utilize ADSC-EVs for bone regeneration, several application strategies have been proposed. These include genetic modifications of ADSCs to enhance the potency of derived EVs [209], engineering of the membrane protein of ADSC-EVs to improve their homing and retention capacities [206], and the use of biomaterial scaffolds or hydrogels to help immobilize the EVs and introduce extra osteoinductive factors to the healing site [207, 208, 210, 211]. The integration of different engineering strategies to maximize the bone regenerative efficiency of ADSC-EVs has also been evaluated. The hydrogel-encapsulated ADSC-EVs with overexpressed miR-375 enhance bone regenerative capacity with a slow and controlled release in a rat model of bone defect [106]. Challenges in the application of ADSC-EVs for bone regeneration may include the need for understanding the interactions between ADSC-EVs and the host environment, standardization of procedures for their use, and further investigations to optimize their effectiveness and delivery methods. In general, these findings support the significant therapeutic potential of ADSC-EVs in bone regeneration and repair and emphasize the need for future research to fully elucidate the underlying mechanisms and optimize their clinical application.
Cartilage regeneration
The significance of cartilage lies in its pivotal role in maintaining joint health and mobility and the subsequent impacts on overall quality of life. Articular cartilage serves as a crucial structural component within the skeletal system, providing a smooth and lubricated surface for joint movement and load distribution. Therefore, the regeneration and repair of articular cartilage are imperative for preventing the progression of osteoarthritis, which affects a substantial number of individuals, along with other joint-related disorders [212].
Multiple studies have demonstrated the capacity of ADSC-EVs to promote the proliferation, migration, chondrogenic differentiation, and osteogenic differentiation of BMSCs [213, 214]. Compared to bone marrow- and synovium-derived MSC-EVs, adipose-derived MSC-EVs display superior regenerative efficacy for cartilage and bone in a mouse model [213]. The therapeutic potential of ADSC-EVs has been assessed in the context of not only osteochondral regeneration but also osteoarthritis. In both in vitro and in vivo models of inflammatory osteoarthritis, ADSC-EVs are found to stimulate chondrogenesis while reducing cartilage degeneration and suppressing inflammation. Consistent modulation of marker genes are also verified associating with chondrocyte viability, cartilage matrix homeostasis, macrophage polarization, and inflammatory suppression [214,215,216]. The activation of specific signaling pathways, such as the Wnt/β-catenin, PI3K/AKT, the adenosine 5’-monophosphate (AMP)-activated protein kinase (AMPK), and the MAPK-ERK/1/2 pathways, has been implicated in mediating these therapeutic effects [213, 216]. Supported by an increasing body of evidence, the ability of ADSC-EVs to promote chondrogenesis while decreasing cartilage lesions and inhibiting inflammation holds promise for the development of innovative regenerative therapies for cartilage-related disorders (Fig. 3).
Tendinopathy and tendon healing
Tendinopathy is a prevalent musculoskeletal disorder characterized by a dysregulated collagen matrix, chronic low-grade inflammation and tissue degeneration, resulting in activity-related chronic pain and functional decline [217]. The etiology of tendinopathy is multifactorial, involving extrinsic conditions such as trauma and chronic overuse, as well as intrinsic conditions such as obesity, inflammation, and genetics [217, 218]. It poses a significant burden on healthcare systems and represents a common cause of pain and disability among athletes and sedentary individuals [219]. The limited regenerative capacity of tendons, in conjunction with the intricate pathology of tendinopathy, emphasizes the criticality of understanding the underlying mechanisms and developing efficacious therapeutic strategies for treating tendon injuries and disorders.
Recent studies have highlighted the therapeutic potential of ADSC-EVs in tissue regeneration, specifically in the healing of traumatized Achilles tendons [220, 221]. The promotion of Achilles tendon regeneration and repair by ADSC-EVs is characterized by enhanced proliferation and migration of tendon stem cells, along with increased viability, reduced senescence, and elevated collagen production in tenocytes. These effects are mediated through specific signaling pathways, including the SMAD1/5/9 and SMAD2/3 pathways [222], as well as the nicotinamide phosphoribosyltransferase (NAMPT)/SIRT1/peroxisome proliferator activated receptor γ (PPARγ)/PPARγ coactivator 1-α (PGC1-α) pathway [127]. Furthermore, ADSC-EVs exhibit anti-inflammatory effects by suppressing M1 macrophage polarization while stimulating M2 macrophage polarization. This dual action makes them promising therapeutic agents for promoting both tendon regeneration and inflammatory suppression in Achilles tendinopathy [104, 127, 222]. Moreover, the potential of ADSC-EVs for rotator cuff tendon regeneration and repair has been evaluated [223,224,225,226]. Administration of ADSC-EVs has been shown to enhance collagen deposition, promote tendon maturation and myofiber regeneration, improve histological and biomechanical properties, and reduce tendon degeneration, atrophy, and fatty infiltration in animal models of supraspinatus and infraspinatus tendon injury [223,224,225]. Similarly, immunomodulation characterized by augmented M2 polarization and attenuated M1 polarization has also been observed during these therapeutic interventions [223, 226]. In summary, there is substantial evidence supporting the therapeutic potential of ADSC-EVs in tendinopathy and tendon healing (Fig. 3). These studies collectively demonstrate their potential for improving regenerative capacity while mitigating inflammation in both the Achilles and rotator cuff tendons, thereby highlighting their significant promise as a therapeutic agent within the field of regenerative medicine.
Peripheral nerve regeneration
The peripheral nervous system is responsible for transmitting signals between the central nervous system and the rest of the body. Injuries to peripheral nerves can arise from various forms of damage or trauma, leading to a range of debilitating symptoms, such as sensory loss, muscle weakness, numbness, tingling, and chronic pain characterized by sharp, burning, or throbbing sensations. These impairments significantly impact an individual’s ability to carry out daily activities and may result in long-term disability [227, 228]. Consequently, promoting effective peripheral nerve regeneration holds immense medical significance in addressing these challenges and enhancing patient outcomes.
Recently, research has demonstrated the endocytosis-mediated internalization of ADSC-EVs by Schwann cells, which originate from the neural crest and play a primary role in axonal myelination within the peripheral nervous system [229, 230]. Myelination is essential for facilitating rapid nerve impulse conduction [229]. Numerous studies have highlighted the therapeutic potential of ADSC-EVs in promoting peripheral nerve regeneration post-injury through various mechanisms, such as cell proliferation, migration, myelination, neurotrophic factor secretion, and autophagy induction in Schwann cells [109, 230,231,232]. Consistently, animal experiments administering ADSC-EVs to rats with sciatic nerve injuries have shown enhanced regeneration of both the myelin sheath and axons and improved restoration of denervated muscle atrophy via optimized Schwann cell function [109, 231, 232]. Additionally, ADSC-EVs have been demonstrated to facilitate the recovery of erectile function following cavernous nerve injury, further emphasizing their potential application in treating peripheral nerve injuries [233]. Furthermore, ADSC-EV-encapsulated miRNA is found to promote Schwann cell proliferation and migration via the miR-22-3p/phosphatase and tensin homolog deleted on chromosome 10 (PTEN)/AKT/mTOR axis [110]. Another ADSC-EV-miRNA is reported to induce Schwann cell autophagy through the miR-26b/karyopherin subunit α-2 (KPNA2) axis [109]. These investigations elucidate the underlying molecular machinery governing the efficacy of ADSC-EVs in peripheral nerve regeneration. Overall, these findings provide valuable insights into the role of ADSC-EVs in promoting peripheral nerve regeneration and functional recovery while supporting their potential clinical application in treating peripheral nerve injuries (Fig. 3).
Acute lung injury
Acute lung injury (ALI), also known as acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) in its severe form, is a prevalent and life-threatening pulmonary disease characterized by acute alveolar damage, pronounced inflammation, heightened vascular permeability, and substantial protein-rich pulmonary edema, leading to reduced lung compliance, impaired gas exchange, hypoxemia and respiratory failure [234, 235]. The pathogenesis of ALI primarily involves disruption of the lung endothelial and epithelial barriers induced by acute inflammation [234]. ADSC-EVs have been demonstrated to ameliorate ALI through mechanisms that include immunomodulation of alveolar macrophages and protection of the pulmonary endothelial barrier. In the recent pandemic of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), approximately 15–30% of people hospitalized with COVID-19 will develop COVID-19 associated ARDS (CARDS) [236, 237]. The therapeutic effects of MSC-EVs including ADSC-EVs in COVID-19 are currently being assessed with dozens of clinical trials (Table 1).
It has been demonstrated that the administration of ADSC-EVs in alveolar macrophages results in decreased secretion of inflammatory cytokines and increased production of anti-inflammatory cytokines [19, 238]. And, the transfer of mitochondrial components derived from donor cells through EVs plays a significant role in mediating these therapeutic effects when internalized by recipient alveolar macrophages. This internalization leads to an increase in mtDNA levels, mitochondrial membrane potential, mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation (OXPHOS) activity, and ATP generation while relieving mitochondrial ROS stress [19]. In vivo assessments in mice with cecal ligation and puncture (CLP)-induced ALI have consistently revealed anti-inflammatory outcomes, such as reduced macrophage aggregation, downregulated pro-inflammatory cytokines, and alleviated pulmonary edema and vascular leakage, which are associated with improved survival rates [238]. In addition, the administration of ADSC-EVs has been shown to facilitate recovery from pulmonary microvascular endothelial cell (PMVEC) injury. These EVs effectively inhibit excessive inflammatory response-induced ROS accumulation; cell damage, including apoptosis and ferroptosis; tight junction damage; and high permeability of PMVECs [111, 239]. Furthermore, ADSC-EVs protect against cigarette smoke-induced chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) [240] and silicosis [241] by regulating macrophages and suppressing inflammation. Moreover, they have shown efficacy in treating ventilator-induced lung injury (VILI) by repairing the pulmonary endothelial barrier and ameliorating the inflammatory response [242]. In conclusion, these findings strongly support the immunomodulatory and pulmonary endothelial cell protective properties of ADSC-EVs in the context of ALI and related conditions (Fig. 3). These findings underscore the potential therapeutic efficacy of ADSC-EVs as a promising intervention for these diseases, necessitating further investigations to understand the underlying mechanisms and optimize strategies for future clinical application.
Other regenerative medical conditions affected by ADSC-EVs
In addition to their effects on the aforementioned diseases, ADSC-EVs have also displayed therapeutic potential in various medical conditions that require tissue regeneration and immunomodulation (Fig. 3). According to the latest literature available to the authors, ADSC-EVs ameliorate hepatic ischemia–reperfusion injury [243], skeletal muscle injury [126, 244], diabetic [245, 246] or non-diabetic [247] erectile dysfunction, and thin endometrium-induced infertility [248], primarily through the activation of tissue regeneration characterized by enhanced cell proliferation, differentiation, angiogenesis, reduced apoptosis, and modulated production of cell factors regulating these processes. Additionally, ADSC-EV-mediated inflammatory suppression has been reported as a major underlying mechanism for treating atopic dermatitis [249, 250], sepsis [251, 252], and atherosclerosis-induced vascular lesions [253], along with other conditions of immunosuppression failure listed in this review. In these contexts, ADSC-EVs downregulate the expression of inflammatory cytokines while decreasing immunocyte infiltration and reducing ROS accumulation. They also inhibit macrophage M1 polarization while stimulating M2 polarization [249,250,251,252,253]. Furthermore, ADSC-EVs exhibit antifibrotic effects on hepatic fibrosis by reducing fibrotic collagen deposition and liver inflammation while restoring liver function [112, 254, 255]. Moreover, ADSC-EVs have been found to protect against metabolic disturbance and alleviate polycystic ovary syndrome by maintaining liver metabolic homeostasis [108]. Collectively, these studies highlight the versatile applications of ADSC-EVs in promoting tissue regeneration and reducing inflammation and fibrosis while maintaining metabolic homeostasis, thus strongly supporting their role as a promising therapeutic strategy in regenerative medicine.
Conclusions and perspectives
ADSCs have gained recognition for their significant potential in regenerative medicine due to their ability to differentiate into various cell lineages and exert autocrine/paracrine effects through the secretion of growth factors, cytokines, chemokines, miRNAs, proteins, and diverse important mediators enclosed in EVs [75]. Utilizing ADSC-derived EVs offers several advantages, including ease of transportation and storage, low immunogenicity, and no potential tumorigenicity, while preserving the therapeutic activity of donor ADSCs [200]. The reviewed studies have demonstrated that ADSC-EVs represent a novel therapeutic approach in the field of regenerative medicine due to their pivotal roles in various biological processes, such as cell proliferation, migration, angiogenesis, apoptosis, tissue regeneration, and immunomodulation [78]. They have been applied to the afore-listed regenerative medical conditions and have shown the most promising outcomes in skin wounds, scars, bone injuries, and fat grafting associated with plastic and cosmetic surgery. Utilizing adipose tissue as the source of MSCs provides numerous advantages, including abundant clinical source availability, resulting high EV yields, and easier and less invasive surgical technique to obtain the adipose tissue compared to other tissue sources, which is uniquely convenient for plastic surgeons and researchers since plastic surgeons frequently perform liposuction and autologous fat transplantation [76].
However, several notable challenges still need to be addressed before the clinical application of ADSC-EVs can be realized. Currently, the clinical translation of ADSC-EVs is hindered by limitations such as insufficient understanding of the mechanisms and interactions between ADSC-EVs and the host environments; variations in EV contents and bioactivities across tissues, individuals and their metabolic states; less-optimized therapeutic efficiency and delivery methods; an absence of standardized protocols and automatic workflows specific for adipose tissue and ADSC isolation, large-scale production, transport and preservation; a lack of quality control for EV sources; and the inadequate standards for the characterization of EV products [75, 79, 256]. Please note that adipose tissue is dynamically and deeply associated with and regulating the systemic metabolic homeostasis [1], which could potentially augment the variation of EV contents across individuals and their metabolic states. For example, ADSC-EVs collected from normal individuals and individuals with obesity might show inconsistent efficacies [98]. As a result, further studies, engineering optimizations, and the establishment of these procedures and standards, with a specific consideration of donor metabolic states, will be essential for facilitating the transition of ADSC-EV therapy to clinical practice [256]. Overall, the therapeutic potential of ADSC-EVs in tissue regeneration is strongly supported by their pro-proliferative, proangiogenic, regenerative, and immunomodulatory properties. The future clinical applications of these EVs hold great promise for addressing diverse medical conditions and advancing regenerative medicine.
Data availability
No datasets were generated or analysed during the current study.
Abbreviations
- ACVR2A:
-
Activin A receptor Type 2A
- ADSC:
-
Adipose-derived stem cell
- ADSC-EV:
-
Adipose-derived stem cell (ADSC)-derived extracellular vesicle (EV)
- ALI:
-
Acute lung injury
- AMPK:
-
Adenosine 5’-monophosphate (AMP)-activated protein kinase
- AP-1:
-
Activator protein-1
- ARDS:
-
Acute respiratory distress syndrome
- ARE:
-
Antioxidant response element
- ARRDC1:
-
Arrestin domain-containing protein 1
- ASC:
-
Apoptosis-associated speck-like protein containing a CARD
- α-SMA:
-
α-Smooth muscle actin
- AT-EV:
-
Adipose tissue-derived extracellular vesicle (EV)
- BMSC:
-
Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cell
- BTG2:
-
B-cell translocation gene 2
- BUN:
-
Blood urea nitrogen
- CABG:
-
Coronary artery bypass grafting
- CARDS:
-
COVID-19 associated acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS)
- CCL1:
-
C–C motif chemokine ligand 1
- CircRNA:
-
Circular RNA
- CLP:
-
Cecal ligation and puncture
- COPD:
-
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
- COVID-19:
-
Coronavirus disease 2019
- CSF-1:
-
Colony stimulating factor-1
- CSF-1R:
-
Colony stimulating factor (CSF)-1 receptor
- DFU:
-
Diabetic foot ulcer
- DLL4:
-
Drosophila delta-like 4 homolog
- ECM:
-
Extracellular matrix
- EGF:
-
Epidermal growth factor
- EGFR:
-
Epidermal growth factor receptor
- EGR1:
-
Early growth response factor 1
- eNOS:
-
Endothelial Nitric oxide synthase
- ERK:
-
Extracellular signal-regulated kinase
- ESCRT:
-
Endosomal sorting complex required for transport
- EV:
-
Extracellular vesicle
- FAM129B:
-
Family with sequence similarity 129, member B
- FasL:
-
Fas ligand
- FGF:
-
Fibroblast growth factor
- FIH1:
-
Factor-inhibiting hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF)-1
- GLO-1:
-
Glyoxalase-1
- HaCaT cells:
-
Cultured human keratinocytes
- HDF:
-
Human dermal fibroblast
- HIF-1α:
-
Hypoxia-inducible factor-1α
- HSF:
-
Hypertrophic scar fibroblast
- HUVEC:
-
Human umbilical vein endothelial cell
- IL-1β:
-
Interleukin-1β
- IL-17RA:
-
Interleukin-17 receptor A
- IRS1:
-
Insulin receptor substrate 1
- KEAP1:
-
Kelch-like ECH-associated protein 1
- KF:
-
Keloid fibroblast
- KPNA2:
-
Karyopherin subunit α-2
- MCP:
-
Monocyte chemotactic protein
- MI:
-
Myocardial infarction
- miRNA:
-
MicroRNA
- MMP:
-
Matrix metalloproteinase
- MSC:
-
Mesenchymal stem cell
- MSC-EV:
-
Mesenchymal stem cell (MSC)-derived extracellular vesicle (EV)
- mTOR:
-
Mammalian Target of rapamycin
- MVB:
-
Multivesicular body
- NAMPT:
-
Nicotinamide phosphoribosyltransferase
- NF-κB:
-
Nuclear factor-κB
- NLRP3:
-
NACHT-, leucine-rich repeat (LRR)- and pyrin domain (PYD)-containing protein 3
- NRF2:
-
Nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2
- NRG1:
-
Neuregulin 1
- OPG:
-
Osteoprotegerin
- OXPHOS:
-
Oxidative phosphorylation
- P38MAPK:
-
P38 mitogen activated protein kinase
- PAD:
-
Peripheral arterial disease
- PAQR3:
-
Progestin and adipoQ receptor family member 3
- PCI:
-
Percutaneous coronary intervention
- PDGF:
-
Platelet-derived growth factor
- PGC1-α:
-
PPARγ coactivator 1-α
- PI3K:
-
Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase
- PIK3R2:
-
Phosphoinositide-3-kinase regulatory subunit 2
- PMVEC:
-
Pulmonary microvascular endothelial cell
- PPARγ:
-
Peroxisome proliferator activated receptor γ
- PTEN:
-
Phosphatase and tensin homolog deleted on chromosome 10
- ROS:
-
Reactive oxygen species
- RUNX3:
-
RUNX family transcription factor 3
- Scr:
-
Serum creatinine
- SIP1:
-
Small mothers against decapentaplegic protein (SMAD)-interacting protein-1
- SIRT3:
-
Sirtuin 3
- SMAD:
-
Small mothers against decapentaplegic protein
- SOD2:
-
Superoxide dismutase 2
- SPRED1:
-
Sprouty-related EVH1 domain containing 1
- SUFU:
-
SUFU negative regulator of Hedgehog signaling
- SVF:
-
Stromal vascular fraction
- T2D:
-
Type 2 diabetes
- TGF-β:
-
Transforming growth factor-β
- TIMP:
-
Tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases
- TLR4:
-
Toll-like receptor 4
- TSG101:
-
Tumor susceptibility gene 101
- TSPAN:
-
Tetraspanin
- TWIST1:
-
Twist basic helix-loop-helix transcription factor 1
- UVB:
-
Ultraviolet B
- VEGF:
-
Vascular endothelial growth factor
- VILI:
-
Ventilator-induced lung injury
- VPS4:
-
Vacuolar protein sorting-associated protein 4
References
Cypess AM. Reassessing human adipose tissue. N Engl J Med. 2022;386:768–79.
Morigny P, Boucher J, Arner P, Langin D. Lipid and glucose metabolism in white adipocytes: pathways, dysfunction and therapeutics. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2021;17:276–95.
Kahn CR, Wang G, Lee KY. Altered adipose tissue and adipocyte function in the pathogenesis of metabolic syndrome. J Clin Invest. 2019;129:3990–4000.
Tseng Y-H. Adipose tissue in communication: within and without. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2023;19:70–1.
Mei R, Qin W, Zheng Y, Wan Z, Liu L. Role of adipose tissue derived exosomes in metabolic disease. Front Endocrinol. 2022;13: 873865.
Galic S, Oakhill JS, Steinberg GR. Adipose tissue as an endocrine organ. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2010;316:129–39.
Bora P, Majumdar AS. Adipose tissue-derived stromal vascular fraction in regenerative medicine: a brief review on biology and translation. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2017;8:145.
Al-Ghadban S, Bunnell BA. Adipose tissue-derived stem cells: immunomodulatory effects and therapeutic potential. Physiology. 2020;35:125–33.
Bourin P, Bunnell BA, Casteilla L, Dominici M, Katz AJ, March KL, et al. Stromal cells from the adipose tissue-derived stromal vascular fraction and culture expanded adipose tissue-derived stromal/stem cells: a joint statement of the international federation for adipose therapeutics and science (IFATS) and the international society for cellular therapy (ISCT). Cytotherapy. 2013;15:641–8.
Lenz M, Arts ICW, Peeters RLM, de Kok TM, Ertaylan G. Adipose tissue in health and disease through the lens of its building blocks. Sci Rep. 2020;10:10433.
Mazini L, Rochette L, Admou B, Amal S, Malka G. Hopes and limits of adipose-derived stem cells (ADSCs) and mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) in wound healing. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21:1306.
Tang QQ, Lane MD. Adipogenesis: from stem cell to adipocyte. Annu Rev Biochem. 2012;81:715–36.
Bacakova L, Zarubova J, Travnickova M, Musilkova J, Pajorova J, Slepicka P, et al. Stem cells: their source, potency and use in regenerative therapies with focus on adipose-derived stem cells—a review. Biotechnol Adv. 2018;36:1111–26.
Argentati C, Morena F, Bazzucchi M, Armentano I, Emiliani C, Martino S. Adipose stem cell translational applications: from bench-to-bedside. Int J Mol Sci. 2018;19:3475.
Shah R, Patel T, Freedman JE. Circulating extracellular vesicles in human disease. N Engl J Med. 2018;379:958–66.
Welsh JA, Goberdhan DCI, O’Driscoll L, Buzas EI, Blenkiron C, Bussolati B, et al. Minimal information for studies of extracellular vesicles (MISEV2023): from basic to advanced approaches. J Extracell Vesicles. 2024;13: e12404.
Li C-J, Fang Q-H, Liu M-L, Lin J-N. Current understanding of the role of adipose-derived extracellular vesicles in metabolic homeostasis and diseases: communication from the distance between cells/tissues. Theranostics. 2020;10:7422–35.
Crewe C, Funcke J-B, Li S, Joffin N, Gliniak CM, Ghaben AL, et al. Extracellular vesicle-based interorgan transport of mitochondria from energetically stressed adipocytes. Cell Metab. 2021;33:1853-1868.e11.
Xia L, Zhang C, Lv N, Liang Z, Ma T, Cheng H, et al. AdMSC-derived exosomes alleviate acute lung injury via transferring mitochondrial component to improve homeostasis of alveolar macrophages. Theranostics. 2022;12:2928–47.
Rosina M, Ceci V, Turchi R, Chuan L, Borcherding N, Sciarretta F, et al. Ejection of damaged mitochondria and their removal by macrophages ensure efficient thermogenesis in brown adipose tissue. Cell Metab. 2022;34:533-548.e12.
Wu Q, Fu S, Xiao H, Du J, Cheng F, Wan S, et al. Advances in extracellular vesicle nanotechnology for precision theranostics. Adv Sci. 2023;10: e2204814.
Xu Z, Chen Y, Ma L, Chen Y, Liu J, Guo Y, et al. Role of exosomal non-coding RNAs from tumor cells and tumor-associated macrophages in the tumor microenvironment. Mol Ther. 2022;30:3133–54.
Wu P, Zhang B, Ocansey DKW, Xu W, Qian H. Extracellular vesicles: a bright star of nanomedicine. Biomaterials. 2021;269: 120467.
Pelissier Vatter FA, Cioffi M, Hanna SJ, Castarede I, Caielli S, Pascual V, et al. Extracellular vesicle- and particle-mediated communication shapes innate and adaptive immune responses. J Exp Med. 2021;218: e20202579.
Isaac R, Reis FCG, Ying W, Olefsky JM. Exosomes as mediators of intercellular crosstalk in metabolism. Cell Metab. 2021;33:1744–62.
Gurung S, Perocheau D, Touramanidou L, Baruteau J. The exosome journey: from biogenesis to uptake and intracellular signalling. Cell Commun Signal. 2021;19:47.
Kalluri R, LeBleu VS. The biology, function, and biomedical applications of exosomes. Science. 2020. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aau6977.
Cheng L, Hill AF. Therapeutically harnessing extracellular vesicles. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2022;21:379–99.
Melnik BC, Stremmel W, Weiskirchen R, John SM, Schmitz G. Exosome-derived microRNAs of human milk and their effects on infant health and development. Biomolecules. 2021;11:851.
Buzas EI. The roles of extracellular vesicles in the immune system. Nat Rev Immunol. 2023;23:236–50.
Tang D, Cao F, Yan C, Fang K, Ma J, Gao L, et al. Extracellular vesicle/macrophage axis: potential targets for inflammatory disease intervention. Front Immunol. 2022;13: 705472.
Noonin C, Thongboonkerd V. Exosome-inflammasome crosstalk and their roles in inflammatory responses. Theranostics. 2021;11:4436–51.
Tang T-T, Wang B, Lv L-L, Liu B-C. Extracellular vesicle-based nanotherapeutics: emerging frontiers in anti-inflammatory therapy. Theranostics. 2020;10:8111–29.
Ocansey DKW, Zhang L, Wang Y, Yan Y, Qian H, Zhang X, et al. Exosome-mediated effects and applications in inflammatory bowel disease. Biol Rev Camb Philos Soc. 2020;95:1287–307.
Peng Y, Yang Y, Li Y, Shi T, Luan Y, Yin C. Exosome and virus infection. Front Immunol. 2023;14:1154217.
Roefs MT, Sluijter JPG, Vader P. Extracellular vesicle-associated proteins in tissue repair. Trend Cell Biol. 2020;30:990–1013.
Todorova D, Simoncini S, Lacroix R, Sabatier F, Dignat-George F. Extracellular vesicles in angiogenesis. Circ Res. 2017;120:1658–73.
Hade MD, Suire CN, Suo Z. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes: applications in regenerative medicine. Cells. 2021;10:1959.
Tsiapalis D, O’Driscoll L. Mesenchymal stem cell derived extracellular vesicles for tissue engineering and regenerative medicine applications. Cells. 2020;9:991.
Soltani S, Mansouri K, Parvaneh S, Thakor AS, Pociot F, Yarani R. Diabetes complications and extracellular vesicle therapy. Rev Endocr Metab Disord. 2022;23:357–85.
Castaño C, Novials A, Párrizas M. Exosomes and diabetes. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2019;35: e3107.
Brandao BB, Lino M, Kahn CR. Extracellular miRNAs as mediators of obesity-associated disease. J Physiol. 2022;600:1155–69.
Kita S, Maeda N, Shimomura I. Interorgan communication by exosomes, adipose tissue, and adiponectin in metabolic syndrome. J Clin Invest. 2019;129:4041–9.
Akbar N, Azzimato V, Choudhury RP, Aouadi M. Extracellular vesicles in metabolic disease. Diabetologia. 2019;62:2179–87.
Sun J, Zhang D, Li Y. Extracellular vesicles in pathogenesis and treatment of metabolic associated fatty liver disease. Front Physiol. 2022;13: 909518.
Thietart S, Rautou P-E. Extracellular vesicles as biomarkers in liver diseases: a clinician’s point of view. J Hepatol. 2020;73:1507–25.
Szabo G, Momen-Heravi F. Extracellular vesicles in liver disease and potential as biomarkers and therapeutic targets. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2017;14:455–66.
Saheera S, Jani VP, Witwer KW, Kutty S. Extracellular vesicle interplay in cardiovascular pathophysiology. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2021;320:H1749–61.
Charla E, Mercer J, Maffia P, Nicklin SA. Extracellular vesicle signalling in atherosclerosis. Cell Signal. 2020;75: 109751.
Davidson SM, Yellon DM. Exosomes and cardioprotection—a critical analysis. Mol Asp Med. 2018;60:104–14.
Heo J, Kang H. Exosome-based treatment for atherosclerosis. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23:1002.
Zhao S, Wang H, Xu H, Tan Y, Zhang C, Zeng Q, et al. Targeting the microRNAs in exosome: a potential therapeutic strategy for alleviation of diabetes-related cardiovascular complication. Pharmacol Res. 2021;173: 105868.
Wang C, Li Z, Liu Y, Yuan L. Exosomes in atherosclerosis: performers, bystanders, biomarkers, and therapeutic targets. Theranostics. 2021;11:3996–4010.
de Abreu RC, Fernandes H, da Costa Martins PA, Sahoo S, Emanueli C, Ferreira L. Native and bioengineered extracellular vesicles for cardiovascular therapeutics. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2020;17:685–97.
Zhang T, Ma S, Lv J, Wang X, Afewerky HK, Li H, et al. The emerging role of exosomes in alzheimer’s disease. Ageing Res Rev. 2021;68: 101321.
Guo M, Hao Y, Feng Y, Li H, Mao Y, Dong Q, et al. Microglial exosomes in neurodegenerative disease. Front Mol Neurosci. 2021;14: 630808.
Upadhya R, Zingg W, Shetty S, Shetty AK. Astrocyte-derived extracellular vesicles: neuroreparative properties and role in the pathogenesis of neurodegenerative disorders. J Control Releas. 2020;323:225–39.
Peng C, Trojanowski JQ, Lee VMY. Protein transmission in neurodegenerative disease. Nat Rev Neurol. 2020;16:199–212.
Hill AF. Extracellular vesicles and neurodegenerative diseases. J Neurosci. 2019;39:9269–73.
Xu M, Feng T, Liu B, Qiu F, Xu Y, Zhao Y, et al. Engineered exosomes: desirable target-tracking characteristics for cerebrovascular and neurodegenerative disease therapies. Theranostics. 2021;11:8926–44.
Yin Y, Chen H, Wang Y, Zhang L, Wang X. Roles of extracellular vesicles in the aging microenvironment and age-related diseases. J Extracell Vesicles. 2021;10: e12154.
Du S, Ling H, Guo Z, Cao Q, Song C. Roles of exosomal miRNA in vascular aging. Pharmacol Res. 2021;165: 105278.
Picca A, Guerra F, Calvani R, Bucci C, Lo Monaco MR, Bentivoglio AR, et al. Mitochondrial dysfunction and aging: insights from the analysis of extracellular vesicles. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20:805.
Han Q-F, Li W-J, Hu K-S, Gao J, Zhai W-L, Yang J-H, et al. Exosome biogenesis: machinery, regulation, and therapeutic implications in cancer. Mol Cancer. 2022;21:207.
Yang E, Wang X, Gong Z, Yu M, Wu H, Zhang D. Exosome-mediated metabolic reprogramming: the emerging role in tumor microenvironment remodeling and its influence on cancer progression. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2020;5:242.
Mashouri L, Yousefi H, Aref AR, Ahadi AM, Molaei F, Alahari SK. Exosomes: composition, biogenesis, and mechanisms in cancer metastasis and drug resistance. Mol Cancer. 2019;18:75.
Weng Z, Zhang B, Wu C, Yu F, Han B, Li B, et al. Therapeutic roles of mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles in cancer. J Hematol Oncol. 2021;14:136.
Xu Z, Zeng S, Gong Z, Yan Y. Exosome-based immunotherapy: a promising approach for cancer treatment. Mol Cancer. 2020;19:160.
Dai J, Su Y, Zhong S, Cong L, Liu B, Yang J, et al. Exosomes: key players in cancer and potential therapeutic strategy. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2020;5:145.
Mori MA, Ludwig RG, Garcia-Martin R, Brandão BB, Kahn CR. Extracellular miRNAs: from biomarkers to mediators of physiology and disease. Cell Metab. 2019;30:656–73.
Kourembanas S. Exosomes: vehicles of intercellular signaling, biomarkers, and vectors of cell therapy. Annu Rev Physiol. 2015;77:13–27.
Takahashi Y, Takakura Y. Extracellular vesicle-based therapeutics: extracellular vesicles as therapeutic targets and agents. Pharmacol Ther. 2023;242: 108352.
Murphy DE, de Jong OG, Brouwer M, Wood MJ, Lavieu G, Schiffelers RM, et al. Extracellular vesicle-based therapeutics: natural versus engineered targeting and trafficking. Exp Mol Med. 2019;51:1–12.
Wang Z-G, He Z-Y, Liang S, Yang Q, Cheng P, Chen A-M. Comprehensive proteomic analysis of exosomes derived from human bone marrow, adipose tissue, and umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2020;11:511.
Zhou C, Zhang B, Yang Y, Jiang Q, Li T, Gong J, et al. Stem cell-derived exosomes: emerging therapeutic opportunities for wound healing. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2023;14:107.
Xiong M, Zhang Q, Hu W, Zhao C, Lv W, Yi Y, et al. Exosomes from adipose-derived stem cells: the emerging roles and applications in tissue regeneration of plastic and cosmetic surgery. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020;8: 574223.
Pomatto M, Gai C, Negro F, Cedrino M, Grange C, Ceccotti E, et al. Differential therapeutic effect of extracellular vesicles derived by bone marrow and adipose mesenchymal stem cells on wound healing of diabetic ulcers and correlation to their cargoes. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22:3851.
Alonso-Alonso ML, García-Posadas L, Diebold Y. Extracellular vesicles from human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells: a review of common cargos. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2022;18:854–901.
Kou M, Huang L, Yang J, Chiang Z, Chen S, Liu J, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles for immunomodulation and regeneration: a next generation therapeutic tool? Cell Death Dis. 2022;13:580.
Jafarinia M, Alsahebfosoul F, Salehi H, Eskandari N, Ganjalikhani-Hakemi M. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles: a novel cell-free therapy. Immunol Invest. 2020;49:758–80.
Trzyna A, Banaś-Ząbczyk A. Adipose-derived stem cells secretome and its potential application in “stem cell-free therapy.” Biomolecules. 2021;11:878.
Yang S, Li X. Recent advances in extracellular vesicles enriched with non-coding RNAs related to cancers. Gene Diseas. 2018;5:36–42.
Maas SLN, Breakefield XO, Weaver AM. Extracellular vesicles: unique intercellular delivery vehicles. Trends Cell Biol. 2017;27:172–88.
Wang Q, Yu J, Kadungure T, Beyene J, Zhang H, Lu Q. ARMMs as a versatile platform for intracellular delivery of macromolecules. Nat Commun. 2018;9:960.
Pegtel DM, Gould SJ. Exosomes. Annu Rev Biochem. 2019;88:487–514.
van Niel G, D’Angelo G, Raposo G. Shedding light on the cell biology of extracellular vesicles. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2018;19:213–28.
Xu X, Lai Y, Hua Z-C. Apoptosis and apoptotic body: disease message and therapeutic target potentials. 2019. Biosci Rep. https://doi.org/10.1042/BSR20180992.
Zhang X, Yao L, Meng Y, Li B, Yang Y, Gao F. Migrasome: a new functional extracellular vesicle. Cell Death Discov. 2023;9:381.
Minciacchi VR, Freeman MR, Di Vizio D. Extracellular vesicles in cancer: exosomes, microvesicles and the emerging role of large oncosomes. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2015;40:41–51.
Ma J, Zhang Z, Wang Y, Shen H. Investigation of miR-126-3p loaded on adipose stem cell-derived exosomes for wound healing of full-thickness skin defects. Exp Dermatol. 2022;31:362–74.
Pi L, Yang L, Fang B-R, Meng X-X, Qian L. Exosomal microRNA-125a-3p from human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells promotes angiogenesis of wound healing through inhibiting PTEN. Mol Cell Biochem. 2022;477:115–27.
Yang C, Luo L, Bai X, Shen K, Liu K, Wang J, et al. Highly-expressed micoRNA-21 in adipose derived stem cell exosomes can enhance the migration and proliferation of the HaCaT cells by increasing the MMP-9 expression through the PI3K/AKT pathway. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2020;681: 108259.
Cao G, Chen B, Zhang X, Chen H. Human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomal microrna-19b promotes the healing of skin wounds through modulation of the CCL1/TGF-β signaling axis. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2020;13:957–71.
Lu Y, Wen H, Huang J, Liao P, Liao H, Tu J, et al. Extracellular vesicle-enclosed miR-486-5p mediates wound healing with adipose-derived stem cells by promoting angiogenesis. J Cell Mol Med. 2020;24:9590–604.
Li Y, Zhang J, Shi J, Liu K, Wang X, Jia Y, et al. Exosomes derived from human adipose mesenchymal stem cells attenuate hypertrophic scar fibrosis by miR-192-5p/IL-17RA/smad axis. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021;12:221.
Ge L, Wang K, Lin H, Tao E, Xia W, Wang F, et al. Engineered exosomes derived from miR-132-overexpresssing adipose stem cells promoted diabetic wound healing and skin reconstruction. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2023;11:1129538.
Zheng Z, Liu L, Zhan Y, Yu S, Kang T. Adipose-derived stem cell-derived microvesicle-released miR-210 promoted proliferation, migration and invasion of endothelial cells by regulating RUNX3. Cell Cycle. 2018;17:1026–33.
Togliatto G, Dentelli P, Gili M, Gallo S, Deregibus C, Biglieri E, et al. Obesity reduces the pro-angiogenic potential of adipose tissue stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles (EVs) by impairing miR-126 content: impact on clinical applications. Int J Obes. 2016;40:102–11.
Liang X, Zhang L, Wang S, Han Q, Zhao RC. Exosomes secreted by mesenchymal stem cells promote endothelial cell angiogenesis by transferring miR-125a. J Cell Sci. 2016;129:2182–9.
Xu F, Xiang Q, Huang J, Chen Q, Yu N, Long X, et al. Exosomal miR-423-5p mediates the proangiogenic activity of human adipose-derived stem cells by targeting sufu. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019;10:106.
Kang T, Jones TM, Naddell C, Bacanamwo M, Calvert JW, Thompson WE, et al. Adipose-derived stem cells induce angiogenesis via microvesicle transport of miRNA-31. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2016;5:440–50.
Zhu D, Wang Y, Thomas M, McLaughlin K, Oguljahan B, Henderson J, et al. Exosomes from adipose-derived stem cells alleviate myocardial infarction via microRNA-31/FIH1/HIF-1α pathway. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2022;162:10–9.
Jin J, Shi Y, Gong J, Zhao L, Li Y, He Q, et al. Exosome secreted from adipose-derived stem cells attenuates diabetic nephropathy by promoting autophagy flux and inhibiting apoptosis in podocyte. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019;10:95.
Shen H, Lane RA. Extracellular vesicles from primed adipose-derived stem cells enhance achilles tendon repair by reducing inflammation and promoting intrinsic healing. Stem Cells. 2023;41:617–27.
Duan Y, Luo Q, Wang Y, Ma Y, Chen F, Zhu X, et al. Adipose mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles containing microRNA-26a-5p target TLR4 and protect against diabetic nephropathy. J Biol Chem. 2020;295:12868–84.
Chen S, Tang Y, Liu Y, Zhang P, Lv L, Zhang X, et al. Exosomes derived from miR-375-overexpressing human adipose mesenchymal stem cells promote bone regeneration. Cell Prolif. 2019;52: e12669.
Lee KS, Lee J, Kim HK, Yeom SH, Woo CH, Jung YJ, et al. Extracellular vesicles from adipose tissue-derived stem cells alleviate osteoporosis through osteoprotegerin and miR-21-5p. J Extracell Vesicles. 2021;10: e12152.
Cao M, Zhao Y, Chen T, Zhao Z, Zhang B, Yuan C, et al. Adipose mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomal microRNAs ameliorate polycystic ovary syndrome by protecting against metabolic disturbances. Biomaterials. 2022;288: 121739.
Yin G, Yu B, Liu C, Lin Y, Xie Z, Hu Y, et al. Exosomes produced by adipose-derived stem cells inhibit schwann cells autophagy and promote the regeneration of the myelin sheath. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2021;132: 105921.
Yang J, Wang B, Wang Y, Feng C, Chen L, Liu Y, et al. Exosomes derived from adipose mesenchymal stem cells carrying miRNA-22-3p promote schwann cells proliferation and migration through downregulation of PTEN. Dis Markers. 2022;2022:7071877.
Shen K, Wang X, Wang Y, Jia Y, Zhang Y, Wang K, et al. miR-125b-5p in adipose derived stem cells exosome alleviates pulmonary microvascular endothelial cells ferroptosis via keap1/Nrf2/GPX4 in sepsis lung injury. Redox Biol. 2023;62: 102655.
Du Z, Wu T, Liu L, Luo B, Wei C. Extracellular vesicles-derived miR-150-5p secreted by adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells inhibits CXCL1 expression to attenuate hepatic fibrosis. J Cell Mol Med. 2021;25:701–15.
Qian L, Pi L, Fang B-R, Meng X-X. Adipose mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes accelerate skin wound healing via the lncRNA H19/miR-19b/SOX9 axis. Lab Invest. 2021;101:1254–66.
He L, Zhu C, Jia J, Hao X-Y, Yu X-Y, Liu X-Y, et al. ADSC-exos containing MALAT1 promotes wound healing by targeting miR-124 through activating Wnt/β-catenin pathway. 2020. Biosci Rep. https://doi.org/10.1042/BSR20192549.
Qiu J, Shu C, Li X, Ye C, Zhang W-C. Exosomes from linc00511-overexpressing ADSCs accelerates angiogenesis in diabetic foot ulcers healing by suppressing PAQR3-induced twist1 degradation. Diabet Res Clin Pract. 2021;180: 109032.
Shi R, Jin Y, Zhao S, Yuan H, Shi J, Zhao H. Hypoxic ADSC-derived exosomes enhance wound healing in diabetic mice via delivery of circ-Snhg11 and induction of M2-like macrophage polarization. Biomed Pharmacother. 2022;153: 113463.
Hu N, Cai Z, Jiang X, Wang C, Tang T, Xu T, et al. Hypoxia-pretreated ADSC-derived exosome-embedded hydrogels promote angiogenesis and accelerate diabetic wound healing. Acta Biomater. 2023;157:175–86.
Wang Z, Feng C, Liu H, Meng T, Huang W, Long X, et al. Hypoxic pretreatment of adipose-derived stem cells accelerates diabetic wound healing via circ-gcap14 and HIF-1α/VEGF mediated angiopoiesis. Int J Stem Cells. 2021;14:447–54.
Liang Z-H, Pan N-F, Lin S-S, Qiu Z-Y, Liang P, Wang J, et al. Exosomes from mmu_circ_0001052-modified adipose-derived stem cells promote angiogenesis of DFU via miR-106a-5p and FGF4/p38MAPK pathway. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2022;13:336.
Shi R, Jin Y, Hu W, Lian W, Cao C, Han S, et al. Exosomes derived from mmu_circ_0000250-modified adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells promote wound healing in diabetic mice by inducing miR-128-3p/SIRT1-mediated autophagy. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2020;318:C848–56.
Ren S, Chen J, Guo J, Liu Y, Xiong H, Jing B, et al. Exosomes from adipose stem cells promote diabetic wound healing through the eHSP90/LRP1/AKT axis. Cells. 2022;11:3229.
Wang J, Wu H, Zhao Y, Qin Y, Zhang Y, Pang H, et al. Extracellular vesicles from HIF-1α-overexpressing adipose-derived stem cells restore diabetic wounds through accelerated fibroblast proliferation and migration. Int J Nanomed. 2021;16:7943–57.
Li X, Xie X, Lian W, Shi R, Han S, Zhang H, et al. Exosomes from adipose-derived stem cells overexpressing Nrf2 accelerate cutaneous wound healing by promoting vascularization in a diabetic foot ulcer rat model. Exp Mol Med. 2018;50:1–14.
Wu M, Tu J, Huang J, Wen H, Zeng Y, Lu Y. Exosomal IRF1-loaded rat adipose-derived stem cell sheet contributes to wound healing in the diabetic foot ulcers. Mol Med. 2023;29:60.
Zhang X, Jiang Y, Huang Q, Wu Z, Pu H, Xu Z, et al. Exosomes derived from adipose-derived stem cells overexpressing glyoxalase-1 protect endothelial cells and enhance angiogenesis in type 2 diabetic mice with limb ischemia. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021;12:403.
Figliolini F, Ranghino A, Grange C, Cedrino M, Tapparo M, Cavallari C, et al. Extracellular vesicles from adipose stem cells prevent muscle damage and inflammation in a mouse model of hind limb ischemia: role of neuregulin-1. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2020;40:239–54.
Wu G, Su Q, Li J, Xue C, Zhu J, Cai Q, et al. NAMPT encapsulated by extracellular vesicles from young adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells treated tendinopathy in a “one-stone-two-birds” manner. J Nanobiotechnol. 2023;21:7.
Jia Q, Zhao H, Wang Y, Cen Y, Zhang Z. Mechanisms and applications of adipose-derived stem cell-extracellular vesicles in the inflammation of wound healing. Front Immunol. 2023;14:1214757.
Surowiecka A, Chrapusta A, Klimeczek-Chrapusta M, Korzeniowski T, Drukała J, Strużyna J. Mesenchymal stem cells in burn wound management. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23:15339.
Takeo M, Lee W, Ito M. Wound healing and skin regeneration. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2015;5: a023267.
Spear M. Acute or chronic? what’s the difference? Plast Surg Nurs. 2013;33:98–100.
Morton LM, Phillips TJ. Wound healing and treating wounds: differential diagnosis and evaluation of chronic wounds. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2016. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaad.2015.08.068.
Patel S, Srivastava S, Singh MR, Singh D. Mechanistic insight into diabetic wounds: Pathogenesis, molecular targets and treatment strategies to pace wound healing. Biomed Pharmacother. 2019;112: 108615.
Singh MR, Saraf S, Vyas A, Jain V, Singh D. Innovative approaches in wound healing: trajectory and advances. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol. 2013;41:202–12.
Frazier T, Alarcon A, Wu X, Mohiuddin OA, Motherwell JM, Carlsson AH, et al. Clinical translational potential in skin wound regeneration for adipose-derived, blood-derived, and cellulose materials: cells, exosomes, and hydrogels. Biomolecules. 2020;10:E1373.
Jo H, Brito S, Kwak BM, Park S, Lee M-G, Bin B-H. Applications of mesenchymal stem cells in skin regeneration and rejuvenation. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22:2410.
Zhao H, Shang Q, Pan Z, Bai Y, Li Z, Zhang H, et al. Exosomes from adipose-derived stem cells attenuate adipose inflammation and obesity through polarizing M2 macrophages and beiging in white adipose tissue. Diabetes. 2018;67:235–47.
Lee JH, Won YJ, Kim H, Choi M, Lee E, Ryoou B, et al. Adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes promote wound healing and tissue regeneration. Int J Mol Sci. 2023;24:10434.
Ren S, Chen J, Duscher D, Liu Y, Guo G, Kang Y, et al. Microvesicles from human adipose stem cells promote wound healing by optimizing cellular functions via AKT and ERK signaling pathways. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019;10:47.
Ma T, Fu B, Yang X, Xiao Y, Pan M. Adipose mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes promote cell proliferation, migration, and inhibit cell apoptosis via Wnt/β-catenin signaling in cutaneous wound healing. J Cell Biochem. 2019;120:10847–54.
Xu P, Xin Y, Zhang Z, Zou X, Xue K, Zhang H, et al. Extracellular vesicles from adipose-derived stem cells ameliorate ultraviolet B-induced skin photoaging by attenuating reactive oxygen species production and inflammation. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2020;11:264.
Wu J, Yang Q, Wu S, Yuan R, Zhao X, Li Y, et al. Adipose-derived stem cell exosomes promoted hair regeneration. Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2021;18:685–91.
Ma J, Yong L, Lei P, Li H, Fang Y, Wang L, et al. Advances in microRNA from adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosome: focusing on wound healing. J Mater Chem B. 2022;10:9565–77.
An Y, Lin S, Tan X, Zhu S, Nie F, Zhen Y, et al. Exosomes from adipose-derived stem cells and application to skin wound healing. Cell Prolif. 2021;54: e12993.
Heo JS. Selenium-stimulated exosomes enhance wound healing by modulating inflammation and angiogenesis. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23:11543.
Ju Y, Hu Y, Yang P, Xie X, Fang B. Extracellular vesicle-loaded hydrogels for tissue repair and regeneration. Mater Today Bio. 2023;18: 100522.
Zhou Y, Zhang XL, Lu ST, Zhang NY, Zhang HJ, Zhang J, et al. Human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomes encapsulated in pluronic F127 hydrogel promote wound healing and regeneration. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2022;13:407.
Wang Y, Zhang Y, Li T, Shen K, Wang KJ, Tian C, et al. Adipose mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes promote keratinocytes and fibroblasts embedded in collagen/platelet-rich plasma scaffold and accelerate wound healing. Adv Mater. 2023. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.202303642.
Monavarian M, Kader S, Moeinzadeh S, Jabbari E. Regenerative scar-free skin wound healing. Tissue Eng Part B Rev. 2019;25:294–311.
Macarak EJ, Wermuth PJ, Rosenbloom J, Uitto J. Keloid disorder: fibroblast differentiation and gene expression profile in fibrotic skin diseases. Exp Dermatol. 2021;30:132–45.
Wang L, Hu L, Zhou X, Xiong Z, Zhang C, Shehada HMA, et al. Exosomes secreted by human adipose mesenchymal stem cells promote scarless cutaneous repair by regulating extracellular matrix remodelling. Sci Rep. 2017;7:13321.
Bonnans C, Chou J, Werb Z. Remodelling the extracellular matrix in development and disease. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2014;15:786–801.
Wang Z-C, Zhao W-Y, Cao Y, Liu Y-Q, Sun Q, Shi P, et al. The roles of inflammation in keloid and hypertrophic scars. Front Immunol. 2020;11: 603187.
Huang C, Ogawa R. Systemic factors that shape cutaneous pathological scarring. FASEB J. 2020;34:13171–84.
Li J, Li Z, Wang S, Bi J, Huo R. Exosomes from human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells inhibit production of extracellular matrix in keloid fibroblasts via downregulating transforming growth factor-β2 and Notch-1 expression. Bioengineered. 2022;13:8515–25.
Sun H, Saeedi P, Karuranga S, Pinkepank M, Ogurtsova K, Duncan BB, et al. IDF diabetes atlas: global, regional and country-level diabetes prevalence estimates for 2021 and projections for 2045. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2022;183: 109119.
Deng H, Chen Y. The role of adipose-derived stem cells-derived extracellular vesicles in the treatment of diabetic foot ulcer: trends and prospects. Front Endocrinol. 2022;13: 902130.
Burgess JL, Wyant WA, Abdo Abujamra B, Kirsner RS, Jozic I. Diabetic wound-healing science. Medicina. 2021;57:1072.
Eilat-Tsanani S, Margalit A, Golan LN. Occurrence of comorbidities in newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes patients and their impact after 11 years’ follow-up. Sci Rep. 2021;11:11071.
Glover K, Stratakos AC, Varadi A, Lamprou DA. 3D scaffolds in the treatment of diabetic foot ulcers: new trends vs conventional approaches. Int J Pharm. 2021;599: 120423.
Wang J-W, Zhu Y-Z, Ouyang J-Y, Nie J-Y, Wang Z-H, Wu S, et al. Adipose-derived stem cell extracellular vesicles improve wound closure and angiogenesis in diabetic mice. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2023;151:331–42.
Zhang Y, Bai X, Shen K, Luo L, Zhao M, Xu C, et al. Exosomes derived from adipose mesenchymal stem cells promote diabetic chronic wound healing through SIRT3/SOD2. Cells. 2022;11:2568.
Hsu H-H, Wang AYL, Loh CYY, Pai AA, Kao H-K. Therapeutic potential of exosomes derived from diabetic adipose stem cells in cutaneous wound healing of db/db mice. Pharmaceutics. 2022;14:1206.
Wang J, Wu H, Peng Y, Zhao Y, Qin Y, Zhang Y, et al. Hypoxia adipose stem cell-derived exosomes promote high-quality healing of diabetic wound involves activation of PI3K/Akt pathways. J Nanobiotechnol. 2021;19:202.
Long M, Rojo de la Vega M, Wen Q, Bharara M, Jiang T, Zhang R, et al. An essential role of NRF2 in diabetic wound healing. Diabetes. 2016. https://doi.org/10.2337/db15-0564.
Lv Q, Deng J, Chen Y, Wang Y, Liu B, Liu J. Engineered human adipose stem-cell-derived exosomes loaded with miR-21-5p to promote diabetic cutaneous wound healing. Mol Pharm. 2020;17:1723–33.
Kristensen LS, Andersen MS, Stagsted LVW, Ebbesen KK, Hansen TB, Kjems J. The biogenesis, biology and characterization of circular RNAs. Nat Rev Genet. 2019;20:675–91.
Zhang Y, Li M, Wang Y, Han F, Shen K, Luo L, et al. Exosome/metformin-loaded self-healing conductive hydrogel rescues microvascular dysfunction and promotes chronic diabetic wound healing by inhibiting mitochondrial fission. Bioact Mater. 2023;26:323–36.
Wang M, Wang C, Chen M, Xi Y, Cheng W, Mao C, et al. Efficient angiogenesis-based diabetic wound healing/skin reconstruction through bioactive antibacterial adhesive ultraviolet shielding nanodressing with exosome release. ACS Nano. 2019;13:10279–93.
Wang C, Wang M, Xu T, Zhang X, Lin C, Gao W, et al. Engineering bioactive self-healing antibacterial exosomes hydrogel for promoting chronic diabetic wound healing and complete skin regeneration. Theranostics. 2019;9:65–76.
Kato Y, Iwata T, Washio K, Yoshida T, Kuroda H, Morikawa S, et al. Creation and transplantation of an adipose-derived stem cell (ASC) sheet in a diabetic wound-healing model. J Vis Exp. 2017. https://doi.org/10.3791/54539-v.
Xiao S, Xiao C, Miao Y, Wang J, Chen R, Fan Z, et al. Human acellular amniotic membrane incorporating exosomes from adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells promotes diabetic wound healing. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021;12:255.
Li J, Yan S, Han W, Dong Z, Li J, Wu Q, et al. Phospholipid-grafted PLLA electrospun micro/nanofibers immobilized with small extracellular vesicles from rat adipose mesenchymal stem cells promote wound healing in diabetic rats. Regen Biomater. 2022. https://doi.org/10.1093/rb/rbac071.
Farber A, Eberhardt RT. The current state of critical limb ischemia: a systematic review. JAMA Surg. 2016;151:1070–7.
Huerta CT, Voza FA, Ortiz YY, Liu Z-J, Velazquez OC. Mesenchymal stem cell-based therapy for non-healing wounds due to chronic limb-threatening ischemia: a review of preclinical and clinical studies. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2023;10:1113982.
Zhu D, Johnson TK, Wang Y, Thomas M, Huynh K, Yang Q, et al. Macrophage M2 polarization induced by exosomes from adipose-derived stem cells contributes to the exosomal proangiogenic effect on mouse ischemic hindlimb. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2020;11:162.
Rautiainen S, Laaksonen T, Koivuniemi R. Angiogenic effects and crosstalk of adipose-derived mesenchymal stem/stromal cells and their extracellular vesicles with endothelial cells. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22:10890.
Zhao L, Johnson T, Liu D. Therapeutic angiogenesis of adipose-derived stem cells for ischemic diseases. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2017;8:125.
Gangadaran P, Rajendran RL, Oh JM, Oh EJ, Hong CM, Chung HY, et al. Identification of angiogenic cargo in extracellular vesicles secreted from human adipose tissue-derived stem cells and induction of angiogenesis in vitro and in vivo. Pharmaceutics. 2021;13:495.
Chance TC, Herzig MC, Christy BA, Delavan C, Rathbone CR, Cap AP, et al. Human mesenchymal stromal cell source and culture conditions influence extracellular vesicle angiogenic and metabolic effects on human endothelial cells in vitro. J Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2020;89:S100–8.
Han Y, Ren J, Bai Y, Pei X, Han Y. Exosomes from hypoxia-treated human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells enhance angiogenesis through VEGF/VEGF-R. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2019;109:59–68.
Li S-R, Man Q-W, Gao X, Lin H, Wang J, Su F-C, et al. Tissue-derived extracellular vesicles in cancers and non-cancer diseases: present and future. J Extracell Vesicles. 2021;10: e12175.
Huang J, Wang L, Tian W. Small extracellular vesicles derived from adipose tissue prevent bisphosphonate-related osteonecrosis of the jaw by promoting angiogenesis. Int J Nanomed. 2021;16:3161–72.
Dong J, Wu B, Tian W. Human adipose tissue-derived small extracellular vesicles promote soft tissue repair through modulating M1-to-M2 polarization of macrophages. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2023;14:67.
Thygesen K, Alpert JS, White HD. Joint ESC/ACCF/AHA/WHF task force for the redefinition of myocardial infarction universal definition of myocardial infarction. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2007. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jacc.2007.09.011.
Weber C, Noels H. Atherosclerosis: current pathogenesis and therapeutic options. Nat Med. 2011;17:1410–22.
Chan CKW, Zhang L, Cheng CK, Yang H, Huang Y, Tian XY, et al. Recent advances in managing atherosclerosis via nanomedicine. Small. 2018. https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.201702793.
Wang T, Li T, Niu X, Hu L, Cheng J, Guo D, et al. ADSC-derived exosomes attenuate myocardial infarction injury by promoting miR-205-mediated cardiac angiogenesis. Biol Direct. 2023;18:6.
de Almeida Oliveira NC, Neri EA, Silva CM, Valadão IC, Fonseca-Alaniz MH, Zogbi C, et al. Multicellular regulation of miR-196a-5p and miR-425-5 from adipose stem cell-derived exosomes and cardiac repair. Clin Sci. 2022;136:1281–301.
Lee T-M, Harn H-J, Chiou T-W, Chuang M-H, Chen C-H, Chuang C-H, et al. Preconditioned adipose-derived stem cells ameliorate cardiac fibrosis by regulating macrophage polarization in infarcted rat hearts through the PI3K/STAT3 pathway. Lab Invest. 2019;99:634–47.
Hong P, Yang H, Wu Y, Li K, Tang Z. The functions and clinical application potential of exosomes derived from adipose mesenchymal stem cells: a comprehensive review. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019;10:242.
Pan J, Alimujiang M, Chen Q, Shi H, Luo X. Exosomes derived from miR-146a-modified adipose-derived stem cells attenuate acute myocardial infarction-induced myocardial damage via downregulation of early growth response factor 1. J Cell Biochem. 2019;120:4433–43.
Gross JL, de Azevedo MJ, Silveiro SP, Canani LH, Caramori ML, Zelmanovitz T. Diabetic nephropathy: diagnosis, prevention, and treatment. Diabetes Care. 2005;28:164–76.
Tanaka N, Babazono T. Assessing genetic susceptibility to diabetic nephropathy. Nephrology. 2005;10(Suppl):S17-21.
Ren P, Qian F, Fu L, He W, He Q, Jin J, et al. Adipose-derived stem cell exosomes regulate Nrf2/Keap1 in diabetic nephropathy by targeting FAM129B. Diabetol Metab Syndr. 2023;15:149.
Strong AL, Cederna PS, Rubin JP, Coleman SR, Levi B. The current state of fat grafting: a review of harvesting, processing, and injection techniques. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2015;136:897–912.
Chen A, Tang S, He J, Li X, Peng G, Zhang H, et al. Small extracellular vesicles from human adipose-derived mesenchymal stromal cells: a potential promoter of fat graft survival. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021;12:263.
Zhu Y-Z, Zhang J, Hu X, Wang Z-H, Wu S, Yi Y-Y. Supplementation with extracellular vesicles derived from adipose-derived stem cells increases fat graft survival and browning in mice: a cell-free approach to construct beige fat from white fat grafting. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2020;145:1183–95.
Mou S, Zhou M, Li Y, Wang J, Yuan Q, Xiao P, et al. Extracellular vesicles from human adipose-derived stem cells for the improvement of angiogenesis and fat-grafting application. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2019;144:869–80.
Cai Y, Li J, Jia C, He Y, Deng C. Therapeutic applications of adipose cell-free derivatives: a review. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2020;11:312.
Cui Z, Tan Q. Bcl-2 modified adipose-derived stem cells improve the retention of fat graft. Adipocyte. 2022;11:501–9.
Suga H, Glotzbach JP, Sorkin M, Longaker MT, Gurtner GC. Paracrine mechanism of angiogenesis in adipose-derived stem cell transplantation. Ann Plast Surg. 2014;72:234–41.
Li W, Chen X, Zou F, He X. Extracellular vesicles derived from hypoxia treated human adipose stem cells increase proliferation and angiogenic differentiation in human adipose stem cells. Aesthet Surg J. 2023. https://doi.org/10.1093/asj/sjad139.
Chen K, Xiong J, Xu S, Wu M, Xue C, Wu M, et al. Adipose-derived stem cells exosomes improve fat graft survival by promoting prolipogenetic abilities through wnt/β-catenin pathway. Stem Cells Int. 2022;2022:5014895.
Majidinia M, Sadeghpour A, Yousefi B. The roles of signaling pathways in bone repair and regeneration. J Cell Physiol. 2018;233:2937–48.
Wu Q, Fu X, Li X, Li J, Han W, Wang Y. Modification of adipose mesenchymal stem cells-derived small extracellular vesicles with fibrin-targeting peptide CREKA for enhanced bone repair. Bioact Mater. 2023;20:208–20.
Li G, Zhang Y, Wu J, Yang R, Sun Q, Xu Y, et al. Adipose stem cells-derived exosomes modified gelatin sponge promotes bone regeneration. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2023;11:1096390.
Zhang J, Liu X, Li H, Chen C, Hu B, Niu X, et al. Exosomes/tricalcium phosphate combination scaffolds can enhance bone regeneration by activating the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2016;7:136.
Nan K, Zhang Y, Zhang X, Li D, Zhao Y, Jing Z, et al. Exosomes from miRNA-378-modified adipose-derived stem cells prevent glucocorticoid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head by enhancing angiogenesis and osteogenesis via targeting miR-378 negatively regulated suppressor of fused (Sufu). Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021;12:331.
Kang Y, Xu C, Meng L, Dong X, Qi M, Jiang D. Exosome-functionalized magnesium-organic framework-based scaffolds with osteogenic, angiogenic and anti-inflammatory properties for accelerated bone regeneration. Bioact Mater. 2022;18:26–41.
Li W, Liu Y, Zhang P, Tang Y, Zhou M, Jiang W, et al. Tissue-engineered bone immobilized with human adipose stem cells-derived exosomes promotes bone regeneration. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2018;10:5240–54.
Kwon H, Brown WE, Lee CA, Wang D, Paschos N, Hu JC, et al. Surgical and tissue engineering strategies for articular cartilage and meniscus repair. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2019;15:550–70.
Li Q, Yu H, Sun M, Yang P, Hu X, Ao Y, et al. The tissue origin effect of extracellular vesicles on cartilage and bone regeneration. Acta Biomater. 2021;125:253–66.
Zhao C, Chen J-Y, Peng W-M, Yuan B, Bi Q, Xu Y-J. Exosomes from adipose-derived stem cells promote chondrogenesis and suppress inflammation by upregulating miR-145 and miR-221. Mol Med Rep. 2020;21:1881–9.
Woo CH, Kim HK, Jung GY, Jung YJ, Lee KS, Yun YE, et al. Small extracellular vesicles from human adipose-derived stem cells attenuate cartilage degeneration. J Extracell Vesicles. 2020;9:1735249.
Li S, Liu J, Liu S, Jiao W, Wang X. Chitosan oligosaccharides packaged into rat adipose mesenchymal stem cells-derived extracellular vesicles facilitating cartilage injury repair and alleviating osteoarthritis. J Nanobiotechnol. 2021;19:343.
Ilaltdinov AW, Gong Y, Leong DJ, Gruson KI, Zheng D, Fung DT, et al. Advances in the development of gene therapy, noncoding RNA, and exosome-based treatments for tendinopathy. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2021;1490:3–12.
Still C, Chang W-T, Sherman SL, Sochacki KR, Dragoo JL, Qi LS. Single-cell transcriptomic profiling reveals distinct mechanical responses between normal and diseased tendon progenitor cells. Cell Rep Med. 2021;2: 100343.
Del Buono A, Battery L, Denaro V, Maccauro G, Maffulli N. Tendinopathy and inflammation: some truths. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol. 2011;24:45–50.
Chen S-H, Chen Z-Y, Lin Y-H, Chen S-H, Chou P-Y, Kao H-K, et al. Extracellular vesicles of adipose-derived stem cells promote the healing of traumatized achilles tendons. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22:12373.
Xu T, Lin Y, Yu X, Jiang G, Wang J, Xu K, et al. Comparative effects of exosomes and ectosomes isolated from adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells on achilles tendinopathy in a rat model. Am J Sport Med. 2022;50:2740–52.
Liu H, Zhang M, Shi M, Zhang T, Lu W, Yang S, et al. Adipose-derived mesenchymal stromal cell-derived exosomes promote tendon healing by activating both SMAD1/5/9 and SMAD2/3. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021;12:338.
Zhang X, Cai Z, Wu M, Huangfu X, Li J, Liu X. Adipose stem cell-derived exosomes recover impaired matrix metabolism of torn human rotator cuff tendons by maintaining tissue homeostasis. Am J Sport Med. 2021;49:899–908.
Wang C, Hu Q, Song W, Yu W, He Y. Adipose stem cell-derived exosomes decrease fatty infiltration and enhance rotator cuff healing in a rabbit model of chronic tears. Am J Sport Med. 2020;48:1456–64.
Wang C, Song W, Chen B, Liu X, He Y. Exosomes isolated from adipose-derived stem cells: a new cell-free approach to prevent the muscle degeneration associated with torn rotator cuffs. Am J Sports Med. 2019;47:3247–55.
Wang C, Zhang Y, Zhang G, Yu W, He Y. Adipose stem cell-derived exosomes ameliorate chronic rotator cuff tendinopathy by regulating macrophage polarization: from a mouse model to a study in human tissue. Am J Sport Med. 2021;49:2321–31.
Supra R, Agrawal DK. Peripheral nerve regeneration: opportunities and challenges. J Spine Res Surg. 2023;5:10–8.
Scheib J, Höke A. Advances in peripheral nerve regeneration. Nat Rev Neurol. 2013;9:668–76.
Jessen KR, Mirsky R, Lloyd AC. Schwann cells: development and role in nerve repair. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2015;7: a020487.
Haertinger M, Weiss T, Mann A, Tabi A, Brandel V, Radtke C. Adipose stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles induce proliferation of schwann cells via internalization. Cells. 2020;9:163.
Chen J, Ren S, Duscher D, Kang Y, Liu Y, Wang C, et al. Exosomes from human adipose-derived stem cells promote sciatic nerve regeneration via optimizing schwann cell function. J Cell Physiol. 2019;234:23097–110.
Bucan V, Vaslaitis D, Peck C-T, Strauß S, Vogt PM, Radtke C. Effect of exosomes from rat adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells on neurite outgrowth and sciatic nerve regeneration after crush injury. Mol Neurobiol. 2019;56:1812–24.
Li M, Lei H, Xu Y, Li H, Yang B, Yu C, et al. Exosomes derived from mesenchymal stem cells exert therapeutic effect in a rat model of cavernous nerves injury. Andrology. 2018;6:927–35.
Mowery NT, Terzian WTH, Nelson AC. Acute lung injury. Curr Probl Surg. 2020;57: 100777.
Hu Q, Zhang S, Yang Y, Yao J-Q, Tang W-F, Lyon CJ, et al. Extracellular vesicles in the pathogenesis and treatment of acute lung injury. Mil Med Res. 2022;9:61.
Attaway AH, Scheraga RG, Bhimraj A, Biehl M, Hatipoğlu U. Severe covid-19 pneumonia: pathogenesis and clinical management. BMJ. 2021;372: n436.
Torres Acosta MA, Singer BD. Pathogenesis of COVID-19-induced ARDS: implications for an ageing population. Eur Respir J. 2020;56:2002049.
Wang X, Liu D, Zhang X, Yang L, Xia Z, Zhang Q. Exosomes from adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells alleviate sepsis-induced lung injury in mice by inhibiting the secretion of IL-27 in macrophages. Cell Death Discov. 2022;8:18.
Li C, Wang M, Wang W, Li Y, Zhang D. Autophagy regulates the effects of ADSC-derived small extracellular vesicles on acute lung injury. Respir Res. 2022;23:151.
Zhu Z, Lian X, Su X, Wu W, Zeng Y, Chen X. Exosomes derived from adipose-derived stem cells alleviate cigarette smoke-induced lung inflammation and injury by inhibiting alveolar macrophages pyroptosis. Respir Res. 2022;23:5.
Bandeira E, Oliveira H, Silva JD, Menna-Barreto RFS, Takyia CM, Suk JS, et al. Therapeutic effects of adipose-tissue-derived mesenchymal stromal cells and their extracellular vesicles in experimental silicosis. Respir Res. 2018;19:104.
Yu Q, Wang D, Wen X, Tang X, Qi D, He J, et al. Adipose-derived exosomes protect the pulmonary endothelial barrier in ventilator-induced lung injury by inhibiting the TRPV4/Ca2+ signaling pathway. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2020;318:L723–41.
Piao C, Sang J, Kou Z, Wang Y, Liu T, Lu X, et al. Effects of exosomes derived from adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells on pyroptosis and regeneration of injured liver. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23:12065.
Byun S-E, Sim C, Chung Y, Kim HK, Park S, Kim DK, et al. Skeletal muscle regeneration by the exosomes of adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2021;43:1473–88.
Zhu LL, Huang X, Yu W, Chen H, Chen Y, Dai YT. Transplantation of adipose tissue-derived stem cell-derived exosomes ameliorates erectile function in diabetic rats. Andrologia. 2018. https://doi.org/10.1111/and.12871.
Chen F, Zhang H, Wang Z, Ding W, Zeng Q, Liu W, et al. Adipose-derived stem cell-derived exosomes ameliorate erectile dysfunction in a rat model of type 2 diabetes. J Sex Med. 2017;14:1084–94.
Liang L, Shen Y, Dong Z, Gu X. Photoacoustic image-guided corpus cavernosum intratunical injection of adipose stem cell-derived exosomes loaded polydopamine thermosensitive hydrogel for erectile dysfunction treatment. Bioact Mater. 2022;9:147–56.
Lin J, Wang Z, Huang J, Tang S, Saiding Q, Zhu Q, et al. Microenvironment-protected exosome-hydrogel for facilitating endometrial regeneration, fertility restoration, and live birth of offspring. Small. 2021;17: e2007235.
Shin K-O, Ha DH, Kim JO, Crumrine DA, Meyer JM, Wakefield JS, et al. Exosomes from human adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells promote epidermal barrier repair by inducing de novo synthesis of ceramides in atopic dermatitis. Cells. 2020;9:680.
Cho BS, Kim JO, Ha DH, Yi YW. Exosomes derived from human adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells alleviate atopic dermatitis. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2018;9:187.
Shen K, Jia Y, Wang X, Zhang J, Liu K, Wang J, et al. Exosomes from adipose-derived stem cells alleviate the inflammation and oxidative stress via regulating Nrf2/HO-1 axis in macrophages. Free Radic Biol Med. 2021;165:54–66.
Bai X, Li J, Li L, Liu M, Liu Y, Cao M, et al. Extracellular vesicles from adipose tissue-derived stem cells affect notch-miR148a-3p axis to regulate polarization of macrophages and alleviate sepsis in mice. Front Immunol. 2020;11:1391.
Comariţa IK, Vîlcu A, Constantin A, Procopciuc A, Safciuc F, Alexandru N, et al. Therapeutic potential of stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles on atherosclerosis-induced vascular dysfunction and its key molecular players. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022;10: 817180.
Zhang Z, Shang J, Yang Q, Dai Z, Liang Y, Lai C, et al. Exosomes derived from human adipose mesenchymal stem cells ameliorate hepatic fibrosis by inhibiting PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway and remodeling choline metabolism. J Nanobiotechnol. 2023;21:29.
Wu B, Feng J, Guo J, Wang J, Xiu G, Xu J, et al. ADSCs-derived exosomes ameliorate hepatic fibrosis by suppressing stellate cell activation and remodeling hepatocellular glutamine synthetase-mediated glutamine and ammonia homeostasis. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2022;13:494.
Liu Y, Holmes C. Tissue regeneration capacity of extracellular vesicles isolated from bone marrow-derived and adipose-derived mesenchymal stromal/stem cells. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021;9: 648098.
Funding
This research was funded by the General Project of Natural Sciences Foundation of Chongqing (grant number cstc2020jcyj-msxmX0306) and the Fundamental Research and Frontier Exploration Project of Yuzhong District, Chongqing (grant number 20180151).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Song Yang: Conceptualization, Software, Writing—original draft preparation, Graphing, Project administration, Funding acquisition; Yiran Sun: Conceptualization, Validation, Writing—review and editing, Supervision; Chenchen Yan: Software, Writing—original draft preparation, Graphing. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, S., Sun, Y. & Yan, C. Recent advances in the use of extracellular vesicles from adipose-derived stem cells for regenerative medical therapeutics. J Nanobiotechnol 22, 316 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12951-024-02603-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12951-024-02603-4