Abstract
Background
Anti-malarial drugs are the major focus in the prevention and treatment of malaria. Artemisinin-based combination therapy (ACT) is the WHO recommended first-line treatment for Plasmodium falciparum malaria across the endemic world. Also ACT is increasingly relied upon in treating Plasmodium vivax malaria where chloroquine is failing. The emergence of artemisinin drug-resistant parasites is a serious threat faced by global malaria control programmes. Therefore, the success of treatment and intervention strategies is highly pegged on understanding the genetic basis of resistance.
Methods
Here, resistance in P. falciparum was generated in vitro for artemisinin to produce levels above clinically relevant concentrations in vivo, and the molecular haplotypes investigated. Genomic DNA was extracted using the QIAamp mini DNA kit. DNA sequences of Pfk13, Pfcrt and Pfmdr1 genes were amplified by PCR and the amplicons were successfully sequenced. Single nucleotide polymorphisms were traced by standard bidirectional sequencing and reading the transcripts against wild-type sequences in Codon code Aligner Version 5.1 and NCBI blast.
Results
Exposure of parasite strains D6 and W2 to artemisinin resulted in a decrease in parasite susceptibility to artemisinin (W2 and D6) and lumefantrine (D6 only). The parasites exhibited elevated IC50s to multiple artemisinins, with >twofold resistance to artemisinin; however, the resistance index obtained with standard methods was noticeably less than expected for parasite lines recovered from 50 µg/ml 48 h drug pressure. The change in parasite susceptibility was associated with Pfmdr-185K mutation, a mutation never reported before. The Pfcrt-CVMNK genotype (Pfcrt codons 72–76) was retained and notably, the study did not detect any polymorphisms reported to reduce P. falciparum susceptibility in vivo in the coding sequences of the Pfk13 gene.
Discussion
This data demonstrate that P. falciparum has the capacity to develop resistance to artemisinin derivatives in vitro and that this phenotype is achieved by mutations in Pfmdr1, the genetic changes that are also underpinning lumefantrine resistance. This finding is of practical importance, because artemisinin drugs in Kenya are used in combination with lumefantrine for the treatment of malaria.
Conclusion
Artemisinin resistance phenotype as has been shown in this work, is a decrease in parasites susceptibility to artemisinin derivatives together with the parasite’s ability to recover from drug-induced dormancy after exposure to drug dosage above the in vivo clinical concentrations. The study surmises that Pfmdr1 may play a role in the anti-malarial activity of artemisinin.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Malaria is one of the most serious life-threatening protozoan diseases, classically identified by paroxysm, fever, and flu-like symptoms recurring in 48- or 72-h cycles. The World Health Organization (WHO) recommends artemisinin-based combination therapy (ACT) as the first-line treatment for falciparum malaria in all endemic regions [1]. There is already evidence of reduced susceptibility of P. falciparum to artemisinin derivatives in Southeast Asia which is manifested by the delayed parasite clearance times in vivo [2, 3]. WHO has launched an action plan to stop possibly emerging resistance at an early stage so as to protect ACT [4].
The P. falciparum multidrug resistance 1 gene (Pfmdr1), P. falciparum chloroquine resistance transporter gene (Pfcrt), and kelch13 propeller region (Pfk13) gene single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) are believed to be markers of resistance to a great number of anti-malarial drugs, including ACT [5, 6].
Increased copy number and sequence variation in Pfmdr1 at the amino acid positions N86Y, S1034, N1042 and D1246Y have been reported to interfere with the parasite susceptibility to dihydroartemisinin [7], artemisinin [8, 9], mefloquine [10], quinine [8], halofantrine [11], piperaquine [9], lumefantrine [12], amodiaquine [13] and chloroquine [14]. Recent in vitro work have strongly linked Pfmdr1 to drug transportation [15].
The Pfcrt protein has capacity to efflux peptides and glutathione [16], and transport anti-malarials besides chloroquine [17]. Its codon K76T mutation has been linked to the development of chloroquine resistance [18]. Pfcrt SNPs have also been found to be associated with the in vitro and/or in vivo parasite susceptibility to artemisinin [19], lumefantrine [20], quinine [21], mefloquine [18] and piperaquine [22].
The Pfk13 SNPs;C580Y, R539T, I543T, and Y493H were the four main alleles which were observed to be significantly involved in artemisinin resistance out of the 17 non-synonymous SNPs found in Cambodia [5]. Other genes associated with artemisinin resistance include; Pfcrt [23], P. falciparum translationally controlled tumor protein (Pftctp) gene [24], Pfmdr1, P. falciparum multidrug resistance-associated protein-1 (Pfmrp1) [9] and ABC transporters [25]. Also there are target proteins; P. falciparum calcium adenosine triphosphatase 6 (Pfatpase6) [26] and P. falciparum ubiquitin c-terminal hydrolase (Pfubcth), the orthologue of P. chabaudi ubiquitin protein-1 [27].
The identification of the genetic determinants will be cornerstone for understanding the molecular basis of artemisinin drug resistance and will, therefore, provide basic evidence for molecular surveillance of drug-resistant P. falciparum strains for epidemiological surveys. This study reports an assessment of anti-malarial resistance marker polymorphisms in Pfmdr1, Pfcrt, and Pfk13 genes in chloroquine resistant W2 and chloroquine sensitive D6 lines cultured in presence of artemisinin.
Methods
Study site
The study was carried out at the Centre for Biotechnology Research and Development (CBRD) malaria laboratory, Kenya Medical Research Institute (KEMRI) Headquarters, Nairobi, Kenya.
Parasite cultures
Two P. falciparum laboratory clones, W2 (Indochina) and D6 (Sierra Leone) were cultivated by standard methods, as described by Trager and Jensen [28] with some modifications described by Benoit-Vical et al. [29]. Continuous routine cultures were maintained at 1–5 % parasitaemia in complete medium containing 12.5 % heat inactivated human serum (blood type A, AB and O pooled) and in O+ human erythrocytes. Haematocrit was adjusted to 6 % O+ type RBCs of the 5 ml total culture volume. The choice of the two parasite lines (D6 and W2) was made in the anticipation that different genetic backgrounds of the parasites may provide a wider span of genetic determinants during the in vitro evolution by artemisinin selection.
Development of resistant parasite lines
Artemisinin resistance was induced in P. falciparum W2 and D6 lines as described by Oduola et al. [30]. Plasmodium falciparum W2 and D6 lines were cultured under increasing artemisinin pressure in stepwise increments over 450 days. The starting concentration of artemisinin was 10 µg/ml for the two parasite clones (W2 and D6). Then, increments were in escalations of 10, 20, 30, 40 and 50 µg/ml, with an exposure time of 48 h at each increment.
The drug pressure cycle started with the addition of artemisinin to asynchronous cultures with 4–8 % parasitaemia. The 12.5 % human-serum-supplemented growth medium (RPMI Medium 1640; Gibco®), with or without artemisinin, was changed after 24 h. The artemisinin pressure was removed after 48 h, the time at which parasite morphology was degraded and growth was significantly reduced. The medium containing artemisinin was discarded and parasites washed twice with drug free wash media. Then, drug-free culture medium supplemented with 12.5 % human-serum was added to cultures, which were incubated at 37 °C until parasite growth and morphology became normal.
A parasite was considered “tolerant” to a particular artemisinin concentration when the recovery phase occurred within 48 h. The artemisinin exposure time was between 42 and 173 days so as to reduce the recovery time to below 48 h for the W2 and D6 lines at each increment. This was considered as a cycle of artemisinin pressure. At this point, artemisinin pressure was resumed with the consecutive higher artemisinin concentration in the increment to culture which has attained ≥5 % parasitaemia. During adaptation, parasite was frozen and the procedure was resumed from the cryopreserved stocks to maintain this phenotype.
Bulk culture of W2 cycle 5 culture A at 50 µg/ml artemisinin (W2 c5A), D6 cycle 3 culture A at 30 µg/ml artemisinin (D6 c3A) and D6 cycle 5 culture A at 50 µg/ml artemisinin (D6 c5A) parasites was cloned by limiting dilution for 35 days to give W2 cycle 5 sub-culture B (W2 c5B), D6 cycle 3 sub-culture B (D6 c3B) and D6 cycle 5 sub-culture B (D6 c5B), respectively. However, W2 cycle 3 culture A at 30 µg/ml artemisinin (W2 c3A) was not cloned. The samples of these cultures were collected and stored in extraction buffer for further analysis. Artemisinin together with other conventional anti-malarials [dihydroartemisinin (DHA), artemisinin (QHS), artesunate (AS), artemether (AM), chloroquine diphosphate (CQ), lumefantrine (LUM) and piperaquine phosphate (PIP)], susceptibilities were assayed by measuring the inhibition of [3H] hypoxanthine uptake in a sterile technique [31], as described herein.
[3H] hypoxanthine incorporation assays
Plasmodium falciparum growth was determined by measuring incorporation of the nucleic acid precursor [3H] hypoxanthine in the parasites genomic DNA. Test compounds were diluted in DMSO (except CQ; diluted in water) and diluted to >0.2 % DMSO. 25 µl of screening medium was added to each well (except row B) in a 96-well flat-bottom micro-culture plate (Costar®, Corning Incorported, NY, USA). Fifty microlitre of dissolved compounds, containing four times the highest test concentration, were added to wells of row B in duplicates. Two times serial drug dilutions were prepared using a multichannel pipette. Twenty five microlitre of drug solution were taken from wells of row B and transferred, after mixing, to wells of row C and so forth down to row H (a 64-fold range dilution). The 25 µl of diluent removed from wells of row H were discarded. Two hundred microlitre of infected erythrocytes (1.5 % haematocrit and 0.5 % parasitaemia) were then added to each well except for wells A9–A12, to which, 200 µl of uninfected RBCs (diluted in screening medium to 1.5 % haematocrit) were added as a negative control.
The plates were incubated at 37 °C in a chamber gassed by a medical grade gas mixture of 92 % N2, 3 % O2, and 5 % CO2 at 95 % humidity. After a 48-h incubation period, 25 µl of [3H] hypoxanthine working solution was added by pulsing to each well (0.5 µCi per well).
Plates were incubated for an additional 18 h period then frozen at negative 20 °C. After thawing, the content of the plates was harvested onto glass-fiber filter mats (A 1450-421; Perkin Elmer) using a Betaplate cell harvester (1295-004 Betaplate; Wallac Perkin Elmer) and dried in an oven.
The oven-dried filter mats were drenched in 10 ml of scintillation fluid (Beta Scintilla®, Perkin Elmer, Schwerzenbach, CH) in a plastic foil (1450-432; Perkin Elmer) and the [3H] hypoxanthine incorporation was measured in terms of counts per minute (cpm) using a Betaplate liquid scintillation counter (1205 Betaplate; Wallac Perkin Elmer).
The result of each well was recorded as counts per minute and expressed as percentage of the untreated (positive) control (wells A1–A8; cultures without test compound). The negative control was used for background subtraction. IC50s (drug concentration at which 50 % of [3H] hypoxanthine incorporation was inhibited compared to drug-free controls) were estimated by linear interpolation [32].
Data analysis was done using Graph Pad Prism software, version 5 (Graph Pad Software, Inc.), and the concentrations of the drugs that inhibited parasite growth by 50 % (IC50) were obtained by nonlinear regression analysis of the inhibition of uptake values and log-transformed concentration values.
Genomic DNA isolation
The genomic DNA was extracted from 1 to 2 ml aliquots of parasite cultures by using the QIAamp mini DNA kit (Qiagen, Germany) as per the manufacturer’s specifications and eluted in 50 µl of AE elution buffer. Non-template control samples were obtained by using un-parasitized red blood cells in each extraction. The untreated parasites (i.e., no drug pressure, W2 and D6) samples, cultured for the same period of 450 days, were used as the positive controls.
Sequencing of the Pfmdr1, Pfcrt and Pfk13 genes
The Pfmdr1 (PFE1150w), Pfcrt (MAL7P1.27), and Pfk13 (PlasmoDB identifier PF3D7_1218300) genes were amplified from genomic DNA using polymerase chain reaction (PCR). The primers used for PCR and sequencing of the genes are shown in Table 1. The double-strand sequencing of PCR products was performed by Macrogen laboratory (Netherlands). Sequences were analysed by the BLAST programme in ncbi. Multiple nucleotide sequence alignment and analysis of the reported gene 3D7 in PlasmoDB DB and Pfmdr1, Pfcrt, and Pfk13 sequenced genes was done using the Codon code Aligner version 5.1 and MEGA 6 to identify specific single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) combinations (standard bidirectional sequencing and reading).
Nucleotide sequence accession numbers
The DNA sequences of representative samples showing mutant types were submitted to Gen-Bank and assigned accession numbers KU236713 and KU236714.
Results
Discontinuous drug pressure generates P. falciparum lines tolerant to increased levels artemisinin in vitro
The IC50 values of artemisinin for the parental parasite lines W2 and D6 were determined by [3H] hypoxanthine incorporation susceptibility assays [31], which were 2.85 ng/ml for W2 and 3.06 ng/ml for D6 (Table 2). As the parasites became adapted to gradually increased concentrations of artemisinin, the two lines became increasingly less susceptible to the drugs, artemisinin (QHS), dihydroartemisinin (DHA), artesunate (AS) and lumefantrine (LMF) (for D6 only), but more susceptible to CQ (Table 2).
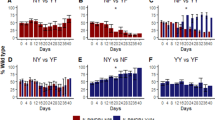
W2 c5B after W2 was the most tolerant strain produced from the assay described above, which was treated with artemisinin at a level that surpassed what would typically be found in plasma of malaria patients treated with artemisinin (Fig. 1). This produced W2 parasites that tolerated 50 µg/ml artemisinin for 48 h.
Changes in the index of resistance. Changes in the index of resistance (ratio of the IC50 for the resistant progeny to the IC50 for the parental line) to various drugs during the adaptation of the P. falciparum lines W2 and D6 to artemisinin. QHS artemisinin, DHA dihydroartemisinin, CQ chloroquine diphosphate, PIP piperaquine phosphate, AM artemether, AS artesunate, LMF lumefantrine. There was >twofold resistance increase to artemisinin and its derivatives
The adaptation pattern observed was similar, a marked reduction in artemisinin susceptibility when the parasites became adapted to 50 µg/ml (Fig. 2), a phenotype manifested the selected progenies progressing normally through the erythrocytic stages of the lifecycle, with no substantial differences in growth from the parental lines in the absence of artemisinin pressure.
Resistant phenotype was due to polymorphism in Pfmdr1 gene
Key polymorphic regions of the Pfmdr1 gene that covered codons 86 and 184 were sequenced successfully in the parental and resistant progenies. Mutations N86Y was observed in the parental W2 parasite lines, while D6 parasites had “wild-type” Pfmdr1. Interestingly the parental parasites and their respective progenies had Y184 codon but I185K mutation was reported as a novel polymorphism. The amino acid codons at these positions are shown in Table 3.
Codons 72–76 of Pfcrt
The wild-type Pfcrt allele, encoding CVMNK at codons 72–76 of the crt protein was confirmed as present in both D6 (one sample of the one sequenced, D6 isolate) and its tolerant progenies (four samples of the four sequenced, D6 c3A, D6 c3B, D6 c5A and D6 c5B), but W2 (one sample of the one sequenced, W2 isolate) and its subsequent progenies (three samples of the three sequenced, W2 c3A, W2 c5A and W2 c5B) harboured the CVIET allele.
Pfk13 propeller
The changes in amino acid sequences at codon C580Y, R539T, I543T, and Y493H as has been reported by Ariey et al. [5], were not detected in either parent lines W2 and D6 or their artemisinin tolerant progenies and all the coding sequences were “wild type”.
Discussion
There are several drawbacks to ACT as the current strategy, despite its success over the last decade. The WHO [33] currently endorses five combinations artemether-lumefantrine, dihydroartemisinin–piperaquine phosphate, artesunate-amodiaquine, artesunate-mefloquine, and artesunate–pyronaridine. ACT is a highly used anti-malarial, creating a substantial selection advantage for parasites to evolve resistance independently with a precipitous decline in the artemisinin susceptibility.
In 2014, the number of courses treatment using various artemisinin-based combinations increased from 11 million in 2005 to 337 million [34], but the mechanisms by which artemisinin act is still under investigation. Deducing molecular genetics on its resistance is paramount for determining treatment strategies, mapping the spread of resistance and guiding elimination [27, 35, 36]. For the new tools for resistance surveillance to be validated a better understanding of the mechanisms of artemisinin resistance is needed. These tools are essential in guiding national treatment policies and helping in designing and deploying new drug combinations that may counter the emergence and spread of resistance.
In the present study, the discontinuous method of inducing resistance/tolerance to artemisinin in W2 and D6 lines of P. falciparum was used [30]. In agreement with other study [36], the in vitro developed artemisinin-tolerant parasites could not grow permanently under artemisinin pressure. Hence resistance to artemisinin is different from resistance to other conventional anti-malarial drugs, such as amodiaquine. The culmination of in vitro resistance as used here in, is the ability for parasites to survive pharmacologically relevant exposure of artemisinin (levels considered clinically relevant in vivo) over many generations and by major increases in the IC50. After conducting the [3H] hypoxanthine incorporation susceptibility assays, it was found that resistant parasites showed the greatest tolerance for artemisinin (W2 c5B and D6 c5B). The study hypothesized a reduced susceptibility to this drug, because it was used to induce resistance in these strains. The discontinuous drug pressure selection scheme is supposedly to have been the key to success in selecting the tolerant lines [30]. After adapting, the parasites were able to tolerate as much as 50 µg/ml of artemisinin for 48 h without noticeable changes in growth rate or morphology. The results also showed resistant parasites generally had decreased susceptibility to artemisinin, but were more susceptible to CQ, which is in agreement with other studies [7, 37, 38]. There was a significant degree of cross-resistance to various other artemisinin derivatives, including artemether, artesunate, and dihydroartemisinin which were not utilized in the generation of resistance in those particular lines. This highlights that, it is possible to select resistance in a drug-sensitive background (D6) African isolate, in antagonism to conclusion from other studies in which it was stated that multiple resistance phenotypes must pre-exist [39, 40].
These artemisinin-tolerant parasites provided a unique resource for the study of the artemisinin resistance mechanism(s) and modes of action based on analysis of SNPs in Pfmdr1, Pfk13 and haplotypes in Pfcrt. The rationale for considering using these three genes were (i) that a relationship between SNPs in Pfmdr1 and ACT has been reported, suggesting that Pfmdr1-N86 or -184F was selected in reinfections after artemether-lumefantrine treatment; and moreover, Pfcrt-76K and Pfmdr1-N86 were selected by artemether-lumefantrine in recurrent infections [20]. Pfmdr1 and Pfcrt were selected for chloroquine resistance and they also both have been reported to be associated with in vitro reduced susceptibility to artesunate and amodiaquine [41]. (ii) Genome association studies strongly suggested a locus on P. falciparum chromosome 13 gene PF3D7_1343700 (bases 1,724,817–1,726,997, PlasmoDB 11.1) to artemisinin resistance and mutations discovered in the Pfk13 were strongly linked to artemisinin resistance [5].
It is well known that Pfmdr1 is associated with drug resistance in Asia [7, 38]. Pfmdr1 encode protein of the ATP binding cassette (ABC) transporter superfamily encoding P-glycoprotein homologue-1 [42], which are localized to the parasite food vacuole membrane or plasma membrane and can decrease intracellular drug accumulation by pumping out drugs.
SNPs at codons 86, 184, and 1246 of the Pfmdr1 gene has been suspected to be the markers of changes in parasite susceptibility to various drugs, including ACT [43]. This shows that monitoring of changes in prevalence of SNPs in the Pfmdr1 gene may serve as an early warning tool to selection of P. falciparum tolerant/resistant to ACT [44].
In the two artemisinin-tolerant parasite lines used in the present study, the decrease in parasite susceptibility to the drug was associated with substitution of mutation at codon Y184F for I185K. This conforms with other studies where sequence variation and increase in copy number in Pfmdr1 were reported to interfere with the parasite susceptibility to dihydroartemisinin [7] and artemisinin [9]. This is because; the mutation at codon Y184F was not detected in the two studies. However, other studies have shown a relationship between SNPs in Pfmdr1 and ACT drugs, in that Pfmdr1-N86 or -184F was selected in reinfections and Pfcrt-K76 and the Pfmdr1-N86 in recurrent infections after artemether-lumefantrine treatment [20].
It is established that ACT can select for particular alleles of two genes, Pfmdr1 and Pfcrt, which are firmly associated with resistance to the 4-aminoquinolines chloroquine and amodiaquine. The Pfcrt gene that encodes a 424-amino acid integral 10 trans-membrane domains protein is a transporter present in the parasite digestive vacuole membrane.
In this work, it was observed that Pfcrt-CVMNK were the favoured haplotypes. This can be attributed to compensatory mutation at C350R in a different study, which was shown to explain the seemingly discordant chloroquine response in Pfcrt-CVIET haplotype [45]. This may suggest the benefit of the two wild-type genes, Pfmdr1-N86 Y184 and Pfcrt-CVMNK, was enhanced by the presence of artemisinin.
Ariey et al. [5] linked artemisinin resistance in P. falciparum to slow clearance rates in patients which he strongly associated with single point mutations in the “propeller” domain of the P. falciparum kelch protein gene on chromosome 13 (kelch13) (PlasmoDB identifier PF3D7_1218300). 17 mutations in the propeller region are linked to artemisinin drug resistance. The Pfk13 gene is well conserved across Plasmodium species and is thought to mediate protein–protein interactions [5].WHO included Pfk13 mutations (Y493H, I543T, R539T, C580Y and M476I) in the new working definition for suspected artemisinin resistance in August 2014 [46]. The present study did not detect any polymorphisms reported elsewhere to reduce P. falciparum susceptibility in vivo in the coding sequences of the Pfk13 gene.
Although it is clear that Pfmdr1 may play a significant role in artemisinin resistance, some studies also demonstrated that changes in susceptibility to mefloquine or halofantrine could be achieved without changes in the expression level or allelic type of Pfmdr1 [47, 48], suggesting a possible involvement of other genes and/or mechanisms of sustaining resistance in these parasites, including transient changes in gene expression.
Other work has reported lack of mutations in Pfmdr1 and Pfcrt in parasites cultured for 5 years under artemisinin derivatives in vitro, and Pfmdr1 amplification was not observed. Further, four mutations were discovered in Pfk13 (Y493H, I543T, R539T and C580Y). In the same study, 17 single K 13-propeller mutations were detected in naturally circulating parasites in Cambodia [5]. However in the present study, there was Pfmdr1 novel mutation at codon I185K and no non-synonymous mutations in Pfk13 gene. This difference can be attributed to the shorter period (450 days) of artemisinin exposure.
Conclusion
ACT is the critical tool for controlling the world’s most important parasitic disease; malaria. This necessitates research on artemisinin resistance markers for epidemiological surveys in malaria endemic regions. This work has demonstrated that resistance to artemisinin can be induced in P. falciparum in vitro. Although long-term stability studies at high levels of drug exposure have not been completed; this data suggest that stable artemisinin tolerance was selected for by multiple pulse exposures to drug over time. This is reflected in the substitution of Pfmdr1 Y184F mutation for I185K. Clearly, more studies are required to identify the mechanism(s) by which resistance to artemisinin emerges and to find molecular genetic markers that can be used for epidemiological studies to track the possible emergence of artemisinin resistance.
Recommendations
High artemisinin resistant lines should be selected and probably to a line which can grow continuously under artemisinin pressure. Thereafter, the investigations into artemisinin resistance markers mainly targeting the implicated genes Pfk13, Pfmdr1 and Pfubcth associated with reduction in drug efficacy should be performed. Structured studies that mitigate confounding factors such as multiple clonal infections in a variety of crossing experiments should be investigated in vivo. This is because in the laboratory, the effect of the mutation is determined in only one genetic background but a wide variety of backgrounds are found in the field due to recombination.
References
White NJ. Qinghaosu (artemisinin): the price of success. Science. 2008;320:330–4.
Dondorp AM, Nosten F, Yi P, Das D, Phyo AP, Tarning J, et al. Artemisinin resistance in Plasmodium falciparum malaria. N Engl J Med. 2009;361:455–67.
Wongsrichanalai C, Pickard AL, Wernsdorfer WH, Meshnick SR. Epidemiology of drug-resistant malaria. Lancet Infect Dis. 2002;2:209–18.
Burr W. WHO to develop plan to curb artemisinin resistance. Can Med Assoc J. 2011;183:E81–2.
Ariey F, Witkowski B, Amaratunga C, Beghain J, Langlois A-C, Khim N, et al. A molecular marker of artemisinin-resistant Plasmodium falciparum malaria. Nature. 2014;505:50–5.
Kavishe RA, Paulo P, Kaaya RD, Kalinga A, van Zwetselaar M, Chilongola J, et al. Surveillance of artemether-lumefantrine associated Plasmodium falciparum multidrug resistance protein-1 gene polymorphisms in Tanzania. Malar J. 2014;13:264.
Price RN, Uhlemann AC, Brockman A, McGready R, Ashley E, Phaipun L, et al. Mefloquine resistance in Plasmodium falciparum and increased pfmdr1 gene copy number. Lancet. 2004;364:438–47.
Reed MB, Saliba KJ, Caruana SR, Kirk K, Cowman AF. Pgh1 modulates sensitivity and resistance to multiple antimalarials in Plasmodium falciparum. Nature. 2000;403:906–9.
Veiga MI, Ferreira PE, Jornhagen L, Malmberg M, Kone A, Schmidt BA, et al. Novel polymorphisms in Plasmodium falciparum ABC transporter genes are associated with major ACT antimalarial drug resistance. PLoS One. 2011;6:e20212.
Dondorp AM, Yeung S, White L, Nguon C, Day NP, Socheat D, et al. Artemisinin resistance: current status and scenarios for containment. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2010;8:272–80.
Sidhu ABS, Uhlemann AC, Valderramos SG, Valderramos JC, Krishna S, Fidock DA. Decreasing pfmdr1 copy number in Plasmodium falciparum malaria heightens susceptibility to mefloquine, lumefantrine, halofantrine, quinine, and artemisinin. J Infect Dis. 2006;194:528–35.
Malmberg M, Ngasala B, Ferreira PE, Larsson E, Jovel I, Hjalmarsson A, et al. Temporal trends of molecular markers associated with artemether-lumefantrine tolerance/resistance in Bagamoyo district, Tanzania. Malar J. 2013;12:103.
Holmgren G, Hamrin J, Svärd J, Mårtensson A, Gil JP, Björkman A. Selection of pfmdr1 mutations after amodiaquine monotherapy and amodiaquine plus artemisinin combination therapy in East Africa. Infect Genet Evol. 2007;7:562–9.
Barnes DA, Foote SJ, Galatis D, Kemp DJ, Cowman AF. Selection for high-level chloroquine resistance results in deamplification of the pfmdr1 gene and increased sensitivity to mefloquine in Plasmodium falciparum. EMBO J. 1992;11:3067.
Sanchez CP, Mayer S, Nurhasanah A, Stein WD, Lanzer M. Genetic linkage analyses redefine the roles of PfCRT and PfMDR1 in drug accumulation and susceptibility in Plasmodium falciparum. Mol Microbiol. 2011;82:865–78.
Patzewitz E-M, Salcedo-Sora JE, Wong EH, Sethia S, Stocks PA, Maughan SC, et al. Glutathione transport: a new role for PfCRT in chloroquine resistance. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2013;19:683–95.
Bellanca S, Summers RL, Meyrath M, Dave A, Nash MN, Dittmer M, et al. Multiple drugs compete for transport via the Plasmodium falciparum chloroquine resistance transporter at distinct but interdependent sites. J Biol Chem. 2014;289:36336–51.
Sidhu ABS, Verdier-Pinard D, Fidock DA. Chloroquine resistance in Plasmodium falciparum malaria parasites conferred by pfcrt mutations. Science. 2002;298:210–3.
Cooper RA, Hartwig CL, Ferdig MT. pfcrt is more than the Plasmodium falciparum chloroquine resistance gene: a functional and evolutionary perspective. Acta Trop. 2005;94:170–80.
Sisowath C, Petersen I, Veiga MI, Mårtensson A, Premji Z, Björkman A, et al. In vivo selection of Plasmodium falciparum parasites carrying the chloroquine-susceptible pfcrt K76 allele after treatment with artemether-lumefantrine in Africa. J Infect Dis. 2009;199:750–7.
Ferdig MT, Cooper RA, Mu J, Deng B, Joy DA, Su X, et al. Dissecting the loci of low-level quinine resistance in malaria parasites. Mol Microbiol. 2004;52:985–97.
Eastman RT, Fidock DA. Artemisinin-based combination therapies: a vital tool in efforts to eliminate malaria. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2009;7:864–74.
Valderramos SG, Valderramos JC, Musset L, Purcell LA, Mercereau-Puijalon O, Legrand E, et al. Identification of a mutant PfCRT-mediated chloroquine tolerance phenotype in Plasmodium falciparum. PLoS Pathog. 2010;6:e1000887.
Eichhorn T, Winter D, Büchele B, Dirdjaja N, Frank M, Lehmann WD, et al. Molecular interaction of artemisinin with translationally controlled tumor protein (TCTP) of Plasmodium falciparum. Biochem Pharmacol. 2013;85:38–45.
Anderson TJ, Nair S, Qin H, Singlam S, Brockman A, Paiphun L, et al. Are transporter genes other than the chloroquine resistance locus (pfcrt) and multidrug resistance gene (pfmdr) associated with antimalarial drug resistance? Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2005;49:2180–8.
Krishna S, Pulcini S, Fatih F, Staines H. Artemisinins and the biological basis for the PfATP6/SERCA hypothesis. Trends Parasitol. 2010;26:517–23.
Hunt P, Martinelli A, Modrzynska K, Borges S, Creasey A, Rodrigues L, et al. Experimental evolution, genetic analysis and genome re-sequencing reveal the mutation conferring artemisinin resistance in an isogenic lineage of malaria parasites. BMC Genom. 2010;11:499.
Trager W, Jensen JB. Human malaria parasites in continuous culture. Science. 1976;193:673–5.
Benoit-Vical F, Lelievre J, Berry A, Deymier C, Dechy-Cabaret O, Cazelles J, et al. Trioxaquines are new antimalarial agents active on all erythrocytic forms, including gametocytes. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2007;51:1463–72.
Oduola AM, Milhous WK, Weatherly NF, Bowdre JH, Desjardins RE. Plasmodium falciparum: induction of resistance to mefloquine in cloned strains by continuous drug exposure in vitro. Exp Parasitol. 1988;67:354–60.
Desjardins RE, Canfield CJ, Haynes JD, Chulay JD. Quantitative assessment of antimalarial activity in vitro by a semiautomated microdilution technique. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1979;16:710–8.
Huber W, Koella JC. A comparison of three methods of estimating EC50 in studies of drug resistance of malaria parasites. Acta Trop. 1993;55:257–61.
Reyburn H, et al. New WHO guidelines for the treatment of malaria. BMJ. 2010;340:c2637. http://www.bmj.com/content/340/bmj.c2637.short. Accessed 6 Dec 2015.
WHO. World malaria report. 2014. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2015. http://www.who.int/malaria/visual-refresh/en/html.
Anderson TJ, Nair S, Nkhoma S, Williams JT, Imwong M, Yi P, et al. High heritability of malaria parasite clearance rate indicates a genetic basis for artemisinin resistance in western Cambodia. J Infect Dis. 2010;201:1326–30.
Witkowski B, Lelièvre J, Barragán MJL, Laurent V, Su X, Berry A, et al. Increased tolerance to artemisinin in Plasmodium falciparum is mediated by a quiescence mechanism. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2010;54:1872–7.
Chavchich M, Gerena L, Peters J, Chen N, Cheng Q, Kyle DE. Role of pfmdr1 amplification and expression in induction of resistance to artemisinin derivatives in Plasmodium falciparum. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2010;54:2455–64.
Pickard AL, Wongsrichanalai C, Purfield A, Kamwendo D, Emery K, Zalewski C, et al. Resistance to antimalarials in Southeast Asia and genetic polymorphisms in pfmdr1. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2003;47:2418–23.
Rathod PK, McErlean T, Lee P-C. Variations in frequencies of drug resistance in Plasmodium falciparum. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1997;94:9389–93.
Afonso A, Hunt P, Cheesman S, Alves AC, Cunha CV, Do Rosário V, et al. Malaria parasites can develop stable resistance to artemisinin but lack mutations in candidate genes atp6 (encoding the sarcoplasmic and endoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ ATPase), tctp, mdr1, and cg10. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2006;50:480–9.
Danquah I, Coulibaly B, Meissner P, Petruschke I, Müller O, Mockenhaupt FP. Selection of pfmdr1 and pfcrt alleles in amodiaquine treatment failure in north-western Burkina Faso. Acta Trop. 2010;114:63–6.
Rosenthal PJ. The interplay between drug resistance and fitness in malaria parasites. Mol Microbiol. 2013;89:1025–38.
Humphreys GS, Merinopoulos I, Ahmed J, Whitty CJM, Mutabingwa TK, Sutherland CJ, et al. Amodiaquine and artemether-lumefantrine select distinct alleles of the Plasmodium falciparum mdr1 gene in Tanzanian children treated for uncomplicated malaria. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2007;51:991–7.
Lekana-Douki JB, Boutamba SDD, Zatra R, Edou SEZ, Ekomy H, Bisvigou U, et al. Increased prevalence of the Plasmodium falciparum Pfmdr1 86N genotype among field isolates from Franceville, Gabon after replacement of chloroquine by artemether–lumefantrine and artesunate–mefloquine. Infect Genet Evol. 2011;11:512–7.
Sibley CH, Lane KD. Fusion of field studies and the laboratory solves a puzzle in antimalarial resistance. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2015;112:11432–3.
Lin Z, Zaw M. Molecular determinants of artemisinin resistance in k13 gene of Plasmodium falciparum. Br Microbiol Res J. 2015;9:1–11.
Lim AS, Galatis D, Cowman AF. Plasmodium falciparum: amplification and overexpression of pfmdr1 is not necessary for increased mefloquine resistance. Exp Parasitol. 1996;83:295–303.
Ritchie GY, Mungthin M, Green JE, Bray PG, Hawley SR, Ward SA. In vitro selection of halofantrine resistance in Plasmodium falciparum is not associated with increased expression of Pgh1. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1996;83:35–46.
Authors’ contributions
JNK was the principal investigator for the study, initiated, mapped the design, supervised and assisted in data analysis and manuscript review. FTK supervised the project activities, laboratory experiments and provided guidance on the analysis plan and manuscript review. DK initiated, mapped the designed, supervised and manuscript review. JK supervised the project; assisted in data analysis and manuscript review. MJN initiated, contributed to the study design, performed all experiments, analysed the data and wrote the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Acknowledgements
We would like to express our gratitude to all the administrative authorities the Director KEMRI and the entire staff of the Centre for Biotechnology Research and Development (CBRD) malaria laboratory, KEMRI in Nairobi.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The study was approved by Scientific Ethical Review Committee (SERU), in Kenya Medical Research Institute, KEMRI (SERU/CBRD/132/3127). The blood for obtaining host red blood cells (RBCs) and human sera was obtained upon signed acceptance of informed consent terms and conditions by the participant.
Funding
This work was supported by the AFRICA-ai-JAPAN Project through the ICMoB (Innovation Centre for Molecular Biology and Biochemistry) and JKUAT research project and extension office.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated.
About this article
Cite this article
Njokah, M.J., Kang’ethe, J.N., Kinyua, J. et al. In vitro selection of Plasmodium falciparum Pfcrt and Pfmdr1 variants by artemisinin. Malar J 15, 381 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12936-016-1443-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12936-016-1443-y