Abstract
Background
Pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) is a life-threatening chronic cardiopulmonary disease. However, there is a paucity of studies that reflect the available biomarkers from separate gene expression profiles in PAH.
Methods
The GSE131793 and GSE113439 datasets were combined for subsequent analyses, and batch effects were removed. Bioinformatic analysis was then performed to identify differentially expressed genes (DEGs). Weighted gene co-expression network analysis (WGCNA) and a protein-protein interaction (PPI) network analysis were then used to further filter the hub genes. Functional enrichment analysis of the intersection genes was performed using Gene Ontology (GO), Disease Ontology (DO), Kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes (KEGG) and gene set enrichment analysis (GSEA). The expression level and diagnostic value of hub gene expression in pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) patients were also analyzed in the validation datasets GSE53408 and GSE22356. In addition, target gene expression was validated in the lungs of a monocrotaline (MCT)-induced pulmonary hypertension (PH) rat model and in the serum of PAH patients.
Results
A total of 914 differentially expressed genes (DEGs) were identified, with 722 upregulated and 192 downregulated genes. The key module relevant to PAH was selected using WGCNA. By combining the DEGs and the key module of WGCNA, 807 genes were selected. Furthermore, protein–protein interaction (PPI) network analysis identified HSP90AA1, CD8A, HIF1A, CXCL8, EPRS1, POLR2B, TFRC, and PTGS2 as hub genes. The GSE53408 and GSE22356 datasets were used to evaluate the expression of TFRC, which also showed robust diagnostic value. According to GSEA enrichment analysis, PAH-relevant biological functions and pathways were enriched in patients with high TFRC levels. Furthermore, TFRC expression was found to be upregulated in the lung tissues of our experimental PH rat model compared to those of the controls, and the same conclusion was reached in the serum of the PAH patients.
Conclusions
According to our bioinformatics analysis, the observed increase of TFRC in the lung tissue of human PAH patients, as indicated by transcriptomic data, is consistent with the alterations observed in PAH patients and rodent models. These data suggest that TFRC may serve as a potential biomarker for PAH.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) is a complex and progressive disorder characterized by elevated pulmonary arterial pressure leading to right ventricular failure [1]. Although numerous targeted therapies for PAH have been developed to effectively alleviate symptoms, this serious disease remains associated with a poor prognosis. The five-year survival rate for newly diagnosed patients is only 61.2% [2]. Early diagnosis of PAH is important for patients, therefore, there is an urgent need to identify the potential mechanism of PAH and to identify related biomarkers.
Recent advancements in bioinformatics have enabled a more nuanced understanding of the molecular basis of PAH [3,4,5]. Bioinformatic analysis methods can aid in identifying candidate genes related to the development of PAH, offering valuable guidance for diagnostic or prognostic biomarkers and therapeutic targets [6, 7]. However, many current studies only make theoretical predictions without experimentally validating of their reliability [5, 8].
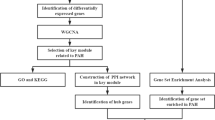
We first merged the PAH microarray data from the public Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) databases GSE131793 and GSE113439, to eliminate differences between batches. After evaluating the quality of the raw data, differentially expressed genes (DEGs) were identified using the limma package in R software version 4.3.2(http://www.r-project.org/). The development of co-expression networks has facilitated the creation of network-based gene screening methods, which can be used to identify potential biomarkers and therapeutic targets [9]. WGCNA was employed to identify genes that were associated with the clinical phenotype. The previously mentioned DEGs, which overlap with the key modules of WGCNA, were utilized for the purpose of performing functional and pathway enrichment analysis through the use of GO, DO, KEGG, and GSEA. Subsequently, a protein-protein interaction (PPI) network was constructed using these genes. Subsequently, the hub genes were identified through the use of Cytoscape software. The PPI network was intersected with the top 20 hub genes of the biological network analysis with four algorithms, resulting in the selection of 8 genes: HSP90AA1, CD8A, HIF1A, CXCL8, EPRS1, POLR2B, TFRC, and PTGS2. After the verification of two independent datasets and experimental validation, TFRC was identified as a potential molecular biomarker in PAH. The following section outlines the materials and methods used in this study.
Materials and methods
Microarray data analysis and identification of differentially expressed genes
The gene expression datasets GSE131793 [10], GSE113439 [11], GSE53408 [12] and GSE22356 [13] were selected for this study. All gene expression microarray data were obtained from the GEO database in the form of a standardized and quality-controlled gene expression matrix (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo/). The GSE131793 dataset included 10 samples each from PAH patients and normal controls. The GSE113439 dataset comprises 15 PAH samples and 11 control samples. The GSE53408 and GSE22356 datasets were selected as the validation sets, which contain 12 PAH samples and 11 control samples and 18 PAH samples and 20 control samples, respectively. The GSE131793 and GSE113439 microarray datasets were integrated as training datasets after excluding inter-batch variation using the Surrogate variable analysis (SVA) package [14]. Two-dimensional principal component analysis (PCA) was employed to illustrate the disparity between the pre- and post-SVA batch groups. Data normalization and background correction were performed using the robust multiarray average (RMA) method. The microarray probes were annotated using annotation files, resulting in the removal of any gene probes that were not aligned to a specific gene. In the event that multiple probes represented the same gene symbol, the average value was used as a representative measurement. Gene screening for differential expression was conducted using the “limma” package, applying a significance threshold of P < 0.05 and a |log2 fold change (FC)|> 0.5. The ggplot2 package [15]was used to generate a volcano plot of the DEGs, and the pheatmap package was utilized to construct a heat map of the DEGs.
Modules identified to be related to PAH via WGCNA analysis
The WGCNA tool in R was used to construct a weighted co-expression network of the merged datasets [9]. To build the scale-free network, the pickSoftThreshold function was utilized to select soft powers b = 10. An adjacency matrix was generated, which was then transformed into a topological overlap matrix (TOM) and the corresponding dissimilarity matrix(1-TOM). A hierarchical clustering tree diagram of the 1-TOM matrix was constructed in order to classify similar gene expressions patterns into different gene co-expression modules. To identify additional functional modules in the co-expression network, module-trait associations between modules and clinical feature information were calculated based on previously conducted studies with the intention of identifying those modules that demonstrated high correlation coefficients with clinical features. To identify key differentially expressed genes (DEGs), the online tool (https://bioinfogp.cnb.csic.es/tools/venny/) was used to construct Venn diagrams demonstrating the intersection of DEGs and key modules.
Methodology for enrichment analysis
Gene Ontology (GO), disease ontology (DO), gene set enrichment analysis (GSEA) and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) were used for enrichment analysis. The analysis used the ‘clusterProfiler‘ [16] and ‘DOSE‘ [17] packages to perform GO, KEGG, and DO enrichment analyses, with a significance threshold of P < 0.05.
Protein-protein Interaction (PPI) Network Construction and Analysis
To investigate protein-protein interactions among the differentially expressed genes (DEGs) identified in our study, we utilized the STRING database (https://string-db.org/). The network was processed using Cytoscape software version 3.8.2 (https://www.cytoscape.org) for visualization and analysis. The top 20 hub genes identified by biological network analysis with four algorithms via the CytoHubba Cytoscape plugin.
Establishment of the MCT-induced PH mouse model
This study adhered to the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals (revised in 1996) of the United States National Institutes of Health (publication no. 85–23), and it received approval from the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of Jilin University, Changchun, China. The study employed Sprague-Dawley rats, weighing between 180 and 220 g and six weeks of age. The rats were obtained from Vital River Laboratories Co., Ltd., Beijing, China. A total of 16 males were housed in a specific pathogen-free environment with a 12-hour light/dark cycle, a temperature of 25 ± 2 °C, and a humidity of 50% ± 5%. The animals were permitted to acclimate for two weeks before the experimental commenced. The rats were randomly allocated to two groups: a PAH model group that received a single subcutaneous injection of 60 mg/kg MCT (Sigma, St. Louis, MO, USA, n = 8), and a control group that was administered saline (n = 8). Following a three-week interval, all rats were weighed and anesthetized with a dose of 60 ml/kg chloral hydrate to prepare them for the subsequent assessments of the development of pulmonary arterial hypertension.
Hemodynamic measurement, tissue collection, and histopathological analysis
To assess the right ventricular systolic pressure (RVSP) in rats, a polyethylene catheter was carefully inserted into the right ventricle via the right jugular vein and connected to a force transducer for accurate measurements. Following these measurements, the rats were euthanized, and their hearts and lungs were promptly collected for further analysis. Right ventricular hypertrophy (RVH) was quantified as the ratio of the weight of the right ventricle to the combined weight of the left ventricle and septum (RV/LV + S). Additionally, the right lung was immediately snap-frozen in liquid nitrogen for biochemical and molecular analysis. A portion of the harvested lungs was fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde, embedded in paraffin, and sectioned into 4-µm-thick slices. Selected sections were then stained with hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) and elastin van gieson (EVG) following established protocols to assess morphological changes. The external and internal diameters of the pulmonary arteries were meticulously measured using Image-Pro Plus software (Media Cybernetics, USA). Arterial wall thickness was calculated using the following formula: percentage wall thickness = [(external diameter − internal diameter)/external diameter] × 100. This metric provides a quantifiable measure of vascular remodeling, a key pathological feature in PAH.
Quantitative PCR (qRT-PCR) analysis
The mRNA expression levels were quantitatively analyzed by the ABI Prism Fast 7500 system using the SYBR Green real-time quantitative PCR kit (SYBR; TOYOBO, Japan). The △△Ct method was used to calculate gene expression relative to the that of housekeeping gene. Primer sequences for RT-PCR were as follows: TFRC, forward primer: GGATCAAGCCAGATCAGCAT; reverse primer: CTCATCTGCAGCCAGTTTCA; GAPDH, forward primer: AAGCCCATCACCATCTTCCA; reverse primer: ATGGCATGGACTGTGGTCAT.
Protein extraction and western blot analysis
Tissue samples were processed after the specified treatment time using radioimmunoprecipitation assay (RIPA) lysis buffer from Applygen (Beijing, China) supplemented with a complete protease inhibitor cocktail and a phosphatase inhibitor cocktail (both from Roche, Basel, Switzerland) and loading buffer (Applygen, Beijing, China). Lysates were then frozen at -80 °C until further use. For protein analysis, cell lysates containing 20 µg of total protein were subjected to reducing SDS-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (PAGE). After electrophoresis, the proteins were transferred to polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) membranes. These membranes were blocked to prevent nonspecific binding and then probed overnight at 4 °C with rabbit monoclonal antibodies against TFRC (Abcam, ab269513, at a dilution of 1:1000) or to glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) (Abcam, ab181602, at a dilution of 1:5000). The membranes were washed three times with TBST and incubated with horseradish peroxidase-conjugated secondary antibody for one hour at room temperature. After rinsing, the membranes were developed with enhanced chemiluminescent substrate (No. WBKLS0500, Millipore). ImageJ was used to analyze band intensities.
Human subjects
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects before the study began. All research procedures were conducted in accordance with the tenets of the Declaration of Helsinki. Ethical approval for research involving human subjects was also obtained from the Ethics Committee of the China-Japan Union Hospital of Jilin University. Fifteen treatment-naive IPAH patients were enrolled at the China-Japan Union Hospital of Jilin University from June 2020 to January 2022. The diagnosis of IPAH was confirmed by right heart catheterization according to the guidelines [18]. Fifteen age- and sex-matched healthy subjects were enrolled as control subjects. Clinical characteristics included age, body mass index (BMI), 6-minute walk distance (6MWD), N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP), mean pulmonary arterial pressure (mPAP), and pulmonary vascular resistance (PVR). Blood was collected from the cubital vein in the morning under fasting conditions. Blood samples were collected in EDTA VACUETTE and centrifuged at 6,000 rpm for 10 min at 4 °C. Plasma was separated immediately and stored in liquid nitrogen at -80 °C until use.
Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) of clinical blood samples
Serum levels were determined using a human TFRC ELISA kit (ab272469; Abcam) according to the manufacturer’s protocol.
Statistical analysis
Statistical analysis of the data was performed using R software (version 3.6.3) and GraphPad Prism software (version 8.0.0). The receiver operating curve (ROC) was used to assess the efficacy of the model, and the area under the curve (AUC) was used to assess the efficacy of the model. Statistical analysis of anatomical structure measurements and gene expression at the mRNA or protein level was performed using GraphPad Prism software. Student’s t-test and one-way ANOVA were used to compare two and multiple groups, respectively. A value of P < 0.05 was considered to indicate statistical significance. All the data are expressed as the mean ± SEM.
Results
DEG-recognition results
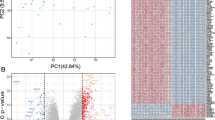
A two-dimensional PCA clustering plot was generated to illustrate the distinctions between the batches before and after the introduction of GSE131793 and GSE113439 (Fig. 1A and B). The analysis revealed marked clustering of the two samples once batch discrepancies were resolved. In total, 914 differentially expressed genes (DEGs), comprising 722 upregulated and 192 downregulated genes were identified, as depicted in the volcano plot (Fig. 1C) and heatmap (Fig. 1D), respectively. The complete list of DEGs is available in the supplementary materials (Table S1).
Differential genes and batch-to-batch differences. (A) PCA before and (B) after correction. (C) Volcano map showing the differential gene. Red and blue represent up- and downregulated genes, and gray represents no significant difference. (D) Heat map showing the 914 up- and downregulated genes. The two colors represent different trends; the darker the color, the more prominent the trend
Weighted correlation network analysis
Pearson’s correlation coefficient was used to cluster the samples, and a sample clustering tree was constructed accordingly (Fig. 2A). A final power of 10 was chosen as the soft-thresholding parameter to ensure that the network was scale-free (Fig. 2B). Next, the adjacency matrix was constructed and the TOM was constructed. Finally, 10 modules were identified based on average hierarchical clustering and dynamic tree clipping. The correlation between each module and two clinical features was evaluated and visualized by a heatmap of module-trait relationships (Fig. 2C), which showed that the turquoise module had high correlations with PAH (r = 0.68, P < 0.001). Therefore, it was selected as the clinically important module for follow-up analysis. The turquoise module contained 3208 genes (Table S2). Venn diagrams showed that 807 genes could be obtained from the DEGs and WGCNA (Fig. 2D, Table S3).
Weighted gene correlation network analysis. (A) Genes with similar expression patterns were clustered, different colors represent different gene clusters, gray modules represent genes not assigned to any of the modules. (B) Optimal soft threshold power. (C) Heat map of module-trait correlations. The color red indicates a positive correlation with the phenotype, while the color blue indicates a negative correlation. (D) Venn diagrams between DEGs and turquoise module
Conclusion of the functional enrichment analysis
Our GO enrichment analysis revealed that the genes were enriched in biological processes (BP) such as ribosome biogenesis and muscle contraction, cellular response to heat, response to manganese ion, positive regulation of rRNA processing. The enrichment in cell component (CC) included nuclear speck, cell leading edge, centriole, centriolar satellite, and preribosome. Furthermore, the molecular function (MF) category showed significant enrichment in functions such as ATP hydrolysis activity, GTPase binding, catalytic activity acting on DNA, helicase activity, and ATP-dependent activity acting on DNA, marking the top five differentially enriched genes in this segment (Fig. 3A). Kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes (KEGG) revealed a significant enrichment in gene sets associated with proteoglycans in cancer, regulation of actin cytoskeleton, lipid and atherosclerosis, focal adhesion and NOD-like receptor signaling pathway (Fig. 3B). In addition, our comparative enrichment analysis between the disease group and the control group suggested that pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) may contribute to disorders within the cardiovascular system and systemic diseases, such as myocardial infraction, atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease, pulmonary hypertension, atherosclerosis (Fig. 3C).
PPI network establishment and central genes identification
The database facilitates the analysis of both physical and functional gene interactions. A protein-protein interaction (PPI) network was constructed by integrating 807 overlapping genes. The CytoNCA plug-in was used to analyze the topology of the network and to identify central genes within it. To obtain a more reliable results, four algorithms were used to calculate the degree of connectivity of the overlapping genes. We selected the top 20 genes in each algorithm, such as those related to degree centrality, (Fig. 4A), betweenness centrality (Fig. 4B), bottleneck centrality (Fig. 4C), and stress centrality (Fig. 4D). The results of the 4 algorithms were then intersected. Eight hub genes (HSP90AA1, CD8A, HIF1A, CXCL8, EPRS1, POLR2B, TFRC, and PTGS2 were identified (Fig. 4E).
Establishment of protein-protein interaction (PPI) network and hub genes identification. The top 20 hub genes with the highest degree of clustering identified by the four algorithms of the cytoHubba analysis. (A) degree centrality, (B) betweenness centrality, (C) bottleneck centrality and (D) stress centrality (E) Venn diagram of results from four algorithms
Verification of Hub gene expression
The expression levels of the hub genes were further evaluated in the validation set. The box plots showed that the expression levels of the hub genes were different in the training set (Fig. 5A) and the validation sets GSE53408 and GSE22356 (Fig. 5B and C). HSP90AA1, HIF1A, CXCL8, EPRS1, POLR2B, TFRC, and PTGS2 were genes that showed significantly higher expression, and CD8A was significantly lower in the PAH group than in the control group in the training set and the validation set GSE53408. While transferrin receptor (TFRC) was then the only gene still differentially highly expressed in the GSE22356 validation set, considering that we selected TFRC as the key gene for further analysis.
Enrichment in the high-TFRC group and its validation
GSEA (Fig. 6A-B) revealed that the majority of genes in PAH samples with high TFRC levels were enriched in the following biological processes: cell cycle checkpoint signaling, chromosome separation, templated DNA replication, mitotic sister chromatid segregation, and nuclear chromosome segregation. Additionally, pathways involved in cell cycle, ferroptosis, NF-κB signaling, NOD-like receptor signaling, nucleocytoplasmic transport, ribosome biogenesis in eukaryotes, and TNF signaling were also enriched in the high-TFRC PAH group. Since cell proliferation and inflammatory infiltration are hallmarks of PAH pathogenesis, both functional and pathway enrichment analyses suggest a potential role for TFRC in the setting of PAH. We also used the ROC in the validation dataset to further verify the diagnostic efficacy of the target gene shown in the figures in the validation cohorts, TFRC was obtained and examined in GSE53408 and GSE22356, which TFRC was also upregulated, and the AUC reached 0.8788 (Fig. 6C) and 0.7056 (Fig. 6D), respectively. This finding suggested that the expression of TFRC could discriminate PAH patients from controls.
The functional and pathway enrichment from PAH patients with high TFRC and diagnostic power of TFRC. (A) The GSEA analysis showing biological processes enriched in high TFRC group versus low TFRC group in training dataset. (B) The KEGG analysis displaying biological pathways enriched in high TFRC group versus low TFRC group in training dataset. (C) The ROC curve of validation cohort in dataset GSE53408, (D) The ROC curve of validation cohort in dataset GSE22356.
Increased TFRC expression in the experimental PH model
We successfully established a PAH rodent model, with a significantly greater right ventricular systolic pressure (RVSP) (38.41 ± 4.75 mmHg vs. 20.86 ± 4.61 mmHg) in the PAH group than in the control group (p < 0.001) (Fig. 7A). In additional, there was a significant increase in right ventricular hypertrophy (RVH), as evidenced by the RV/LV + S ratio, which was 32.97% ± 6.48% in the MCT-treated rats versus 22.36% ± 5.01% in the control group (p < 0.05) (Fig. 7B). In addition, the media wall of pulmonary arteries in PH mice was significantly greater than that in control mice (Fig. 7C-D).
Establishment of MCT induced PH mouse model. (A) RVSP and (B) RV/(LV + S) were assessed in MCT-induced PH rats or control (n = 8/group). (C) Representative images of H&E and EVG staining of lung tissues in two group. Black asterisk indicates lumen of pulmonary artery. Scale bar = 30 mm. (D) Quantification of media thickness of small pulmonary arterioles (E) The mRNA expression level of TFRC relative to GAPDH were examined in lung tissues from MCT-induced PH mice or control. (n = 5/group). (F) Representative Western blots and quantification of TFRC and GAPDH in the lungs of MCT- induced rats and controls. RVSP = right ventricular systematic pressure; RV/(LV + S) = right ventricular/(left ventricular + septum). Data represent mean ± SEM. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01 compared to control, as analyzed by unpaired t test or Mann-Whitney test as appropriate
The mRNA expression of the target gene was then examined in the lung tissue of PH rats. TFRC was significantly upregulated in the lungs of the PH model (Fig. 7E). TFRC was also selected for verification at the protein level. The results show that, the protein expression of TFRC in the lungs of PH rats was approximately 1.5 times that in the lungs of PH rats. (Fig. 7F).
Validation of TFRC in clinical samples
Based on the above bioinformatics analysis and experimental verification, we found that TFRC was the only target gene whose expression was consistently upregulated in the PAH group. Therefore, we selected TFRC for further experimental validation. First, we collected blood samples from 15 IPAH patients and 15 healthy controls to determine the serum TFRC concentration. The clinical characteristics are displayed in Table 1. We found that the serum TFRC concentration was much higher in IPAH patients than in healthy controls (Fig. 8A). The ability of TFRC levels to diagnose PAH was evaluated using ROC curve analysis, which showed that an AUC value of 0.7511 demonstrated high predictive efficiency of TFRC as a diagnostic biomarker (Fig. 8B).
Discussion
Pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) is a severe pulmonary vascular disease characterized by pulmonary vascular proliferation and extracellular matrix remodeling, the causes of which are multifactorial [19,20,21,22]. Although great progress has been made in understanding PAH, there is still a lack of effective ways to diagnose and treat it. Fortunately, with the development of high-throughput technologies, more novel biomarkers and therapeutic targets for PAH are emerging [23]. Integrated bioinformatics analyses are increasingly being used to discover new genes involved in PAH, potential diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers, underlying mechanisms and therapeutic targets [6, 24, 25].
In this study, 914 DEGs were identified from the PAH expression profile obtained from the public GEO database after differential analysis. WGCNA was used to identify genes associated with clinical phenotypes. GO, KEGG and GSEA revealed significant enrichment of DEGs in several pathways associated with PAH. DO enrichment analysis more clearly revealed the occurrence of cardiovascular diseases, including atherosclerosis, arteriosclerotic cardiovascular disease, coronary artery disease, atherosclerosis and pulmonary artery hypertension. The TFRC was selected for further investigation based on validation in validation datasets and validation in animal experiments. Consistent with the predicted results, the mRNA and protein expression levels of TFRC were found to be elevated not only in PAH rodent models but also in the serum of PAH patients.
TFRC is a cell surface receptor that plays a key role in the uptake and regulation of iron ions [26]. During cell proliferation, the demand for iron typically increases. This is due to the necessity of synthesizing more DNA and performing other metabolic activities [27]. Iron is a cofactor for numerous oxidoreductase enzymes that play pivotal roles in DNA replication and repair, as well as in other cellular metabolic processes [26]. In the event of rapid cell proliferation, local or systemic iron deficiency can occur if there is an insufficient supply of iron in the body or if the cells are unable to absorb and utilize iron efficiently [28]. Abnormal TFRC expression has been associated with a variety of diseases, including iron metabolism disorders, certain types of anemia, and cancer [29,30,31]. TFRC expression is significantly greater in many types of cancer cells because these cells require more iron to support rapid growth [32,33,34]. TFRC expression is regulated by cellular iron levels to maintain a homeostatic balance of iron ions. When intracellular iron levels are low, TFRC expression increases, promoting greater iron uptake; conversely, TFRC expression decreases when iron is abundant [35, 36].
On the other hand, iron is a key factor in the function of many immune cells [37], and TFRC plays an important role in regulating iron homeostasis in immune cells. For example, TFRC is particularly important for the function of macrophages and T cells [38]. Recently, the TFRC has been identified as a prognostic biomarker. It is correlated with immune infiltration in breast cancer [39]. Furthermore, TFRC expression in induced sputum correlates positively with proinflammatory M1 macrophage numbers and asthma severity [40]. TFRC in cardiomyocytes promotes heart failure by inducing macrophage infiltration and activation through regulating Ccl2 expression mediated by HIF-1α and STAT3 [41]. Macrophages accumulate in large numbers around the pulmonary arteries during the early stages of pulmonary hypertension and influence the inflammatory state and remodeling of the pulmonary vasculature by activating multiple signaling pathways and cytokines (e.g., HIF-1, IL-6, etc.) [42, 43]. It has been observed in several experimental models that altering the M1/M2 ratio of macrophages may have an effect on the severity of pulmonary hypertension [44]. Whether TFRC is associated with macrophage activation in PAH remains to be investigated.
Pulmonary hypertension (PH) is a disease associated with vascular remodeling and smooth muscle cell proliferation [45]. Studies have shown that abnormal iron metabolism is common in patients with pulmonary hypertension [46]. Patients may be iron deficient, although the underlying mechanism is not fully understood. Iron deficiency may affect cell proliferation and vascular remodeling by affecting intracellular oxygen-sensing pathways, which in turn may affect cell proliferation and vascular remodeling [47]. An imbalance in iron homeostasis (both iron deficiency and iron overload) can aggravate certain pathologies. For example, iron deficiency can affect the ability of cells to transport and use oxygen, which in turn affects their metabolic state and ability to proliferate [48].Taken together, pulmonary artery smooth muscle cells may be challenged by increased iron requirements during proliferation, particularly in diseases such as pulmonary hypertension, which involves significant cell proliferation and vascular remodeling. Iron deficiency may affect the function of these cells and the progression of disease; TFRC activity is critical for cell proliferation and differentiation, especially during periods of high iron demand. Therefore, understanding the role of iron metabolism in pulmonary hypertension may have important implications for the treatment and management of this disease.
In our study, GSEA analysis revealed that the majority of genes in PAH samples with high TFRC were enriched in the following biological processes: cell cycle checkpoint signaling, chromosome separation, templated DNA replication, mitotic sister chromatid segregation, and nuclear chromosome segregation. GSEA analysis also showed the pathways involved cell cycle, ferroptosis, NF-kappa B signaling pathway, the NOD-like receptor signaling pathway, nucleocytoplasmic transport, ribosome biogenesis in eukaryotes and the TNF signaling pathway. High TFRC gene sets are associate with iron metabolism, inflammation and cell proliferation. These are important pathological processes in pulmonary hypertension. The proliferation and remodeling of cells in the pulmonary arteries, driven by disrupted cell cycle and chromosome handling, are critical in the progression of PH [49]. Thus, targeting these pathways might offer therapeutic avenues for managing or treating pulmonary hypertension.
In order to enhance the reliability of our results, we utilized two human datasets, GSE53408 and GSE22356 to validate the hub genes. The results demonstrated that, of the eight hub genes, only TFRC exhibited consistently robust high expression. It is hypothesized that this outcome may be related to the specific validation datasets that were selected. The GSE22356 dataset comprises gene expression profiles derived from peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) of patients with PAH, rather than lung tissue. TFRC has been well-established as a protein expressed on the cell surface, with the primary function of facilitating iron uptake [50]. The soluble form of TFRC can be detected in the blood, providing an assessment of the individual’s iron metabolism [51]. In contrast, the other hub genes are typically not detectable in blood. This likely explains the lack of differential expression of other hub genes observed in the GSE22356 validation cohort. However, in the validation cohort GSE53408, which also comprises lung samples, the 8 hub genes exhibited same expression changes as observed in the training set. Notably, four of the eight hub genes (HSP90AA1, HIF1A, CXCL8 and PTGS2) that were screened in this study have already been shown to play important roles in pulmonary hypertension. HSP90AA1 has been identified as a critical biomarker and therapeutic target in PAH [52,53,54]. HIF1A plays a critical role in the development and progression of pulmonary hypertension (PH) by promoting pulmonary vascular remodeling and right ventricular hypertrophy under hypoxic conditions. This protein regulates various cellular processes, such as angiogenesis, metabolism, and inflammatory responses in the lungs, which are key factors in the pathophysiology of PH [55,56,57]. CXCL8, also known as interleukin-8, plays a significant role in pulmonary hypertension (PH) by recruiting neutrophils and other immune cells to the lungs, which contributes to the inflammation and vascular remodeling observed in PH [57, 58]. PTGS2, also known as COX-2, is involved in the pathogenesis of pulmonary hypertension (PH) by mediating inflammation and contributing to vascular remodeling and pulmonary vascular smooth muscle proliferation. Inhibiting PTGS2 has been shown to have a protective effect on vascular proliferative diseases, including PH, and might be an important intervention for the prevention and treatment of this condition [59, 60]. These findings demonstrate the feasibility of our method for the identification of disease diagnostic markers and therapeutic targets.
The expression of TFRC was found to be consistent among multiple datasets of PAH lungs. This result aligns with the TFRC alteration observed in a PH mouse model and in PAH patients. The results showed a significant increase in the serum TFRC in PAH patients, and the ROC curve showed an AUC of 0.751. This finding suggested that TFRC could be used as a molecular target for the diagnosis of PAH. This study is the first to demonstrate that TFRC can be used as a clinically predictive molecular target in PAH.
Our study has several limitations. (1) The number of patients included in the study was limited. Future larger prospective studies should be conducted to determine the significance of TFRC in PAH; (2) this study did not elucidate the role and mechanism of TFRC in vascular remodeling in PAH; and (3) we only used the MCT-induced PAH mouse model. In the future, we will establish a hypoxia + SU5416-induced rat PAH model to improve the reliability of the results.
In conclusion, the results of this study indicate that TFRC may be associated with PAH. Furthermore, targeting TFRC may represent a promising strategy for the diagnosis and treatment of PAH.
Data availability
No datasets were generated or analysed during the current study.
Abbreviations
- PAH:
-
Pulmonary arterial hypertension
- DEGs:
-
Differentially expressed genes
- WGCNA:
-
Weighted gene co-expression network analysis
- PPI:
-
Protein-protein interaction
- GO:
-
Gene Ontology
- GSEA:
-
Gene set enrichment analysis
- GEO:
-
Gene expression omnibus
- RMA:
-
Robust multiarray average
- SVA:
-
Surrogate variable analysis
- PCA:
-
Principal component analysis
- TFRC:
-
Transferrin receptor
- PH:
-
Pulmonary hypertension
- MCT:
-
Monocrotaline
- RVSP:
-
Right ventricular systolic pressure
- RVH:
-
Right ventricular hypertrophy
- EVG:
-
Elastin van gieson
- qRT:
-
PCR-Quantitative Reverse Transcription Polymerase Chain Reaction
- RIPA:
-
Radioimmunoprecipitation assay
- PVDF:
-
Polyvinylidene Fluoride
- GAPDH:
-
Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate Dehydrogenase
- ELISA:
-
Enzyme-Linked immunosorbent assay
- SEM:
-
Standard error of mean
- BMI:
-
Body mass index
- 6MWD:
-
6-minute walk distance
- NT:
-
proBNP-N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide
- mPAP:
-
Mean pulmonary arterial pressure
- PVR:
-
Pulmonary vascular resistance
- IPAH:
-
Idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension
- DO:
-
Disease Ontology
- KEGG:
-
Kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes
- DOSE:
-
Disease ontology semantic and enrichment analysis
References
McGoon MD, Benza RL, Escribano-Subias P, Jiang X, Miller DP, Peacock AJ, Pepke-Zaba J, Pulido T, Rich S, Rosenkranz S, et al. Pulmonary arterial hypertension: epidemiology and registries. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2013;62:D51–59.
Farber HW, Miller DP, Poms AD, Badesch DB, Frost AE, Muros-Le Rouzic E, Romero AJ, Benton WW, Elliott CG, McGoon MD, Benza RL. Five-year outcomes of patients enrolled in the REVEAL Registry. Chest. 2015;148:1043–54.
Tang B, Pan Z, Yin K, Khateeb A. Recent advances of Deep Learning in Bioinformatics and Computational Biology. Front Genet. 2019;10:214.
Orlov YL, Anashkina AA, Klimontov VV, Baranova AV. Medical Genetics, Genomics and Bioinformatics Aid in understanding Molecular mechanisms of Human diseases. Int J Mol Sci 2021, 22.
Qin Y, Yan G, Qiao Y, Wang D, Tang C. Identification of hub genes based on integrated analysis of single-cell and microarray transcriptome in patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension. BMC Genomics. 2023;24:788.
Zhou X, Liang B, Lin W, Zha L. Identification of MACC1 as a potential biomarker for pulmonary arterial hypertension based on bioinformatics and machine learning. Comput Biol Med. 2024;173:108372.
Wang T, Zheng X, Li R, Liu X, Wu J, Zhong X, Zhang W, Liu Y, He X, Liu W, et al. Integrated bioinformatic analysis reveals YWHAB as a novel diagnostic biomarker for idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension. J Cell Physiol. 2019;234:6449–62.
Yang Z, Zhou L, Ge H, Shen W, Shan L. Identification of autophagy-related biomarkers in patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension based on bioinformatics analysis. Open Med (Wars). 2022;17:1148–57.
Langfelder P, Horvath S. WGCNA: an R package for weighted correlation network analysis. BMC Bioinformatics. 2008;9:559.
Elinoff JM, Mazer AJ, Cai R, Lu M, Graninger G, Harper B, Ferreyra GA, Sun J, Solomon MA, Danner RL. Meta-analysis of blood genome-wide expression profiling studies in pulmonary arterial hypertension. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2020;318:L98–111.
Mura M, Cecchini MJ, Joseph M, Granton JT. Osteopontin lung gene expression is a marker of disease severity in pulmonary arterial hypertension. Respirology. 2019;24:1104–10.
Zhao YD, Chu L, Lin K, Granton E, Yin L, Peng J, Hsin M, Wu L, Yu A, Waddell T, et al. A biochemical Approach to understand the pathogenesis of Advanced Pulmonary arterial hypertension: metabolomic profiles of Arginine, Sphingosine-1-Phosphate, and Heme of Human Lung. PLoS ONE. 2015;10:e0134958.
Risbano MG, Meadows CA, Coldren CD, Jenkins TJ, Edwards MG, Collier D, Huber W, Mack DG, Fontenot AP, Geraci MW, Bull TM. Altered immune phenotype in peripheral blood cells of patients with scleroderma-associated pulmonary hypertension. Clin Transl Sci. 2010;3:210–8.
Leek JT, Johnson WE, Parker HS, Jaffe AE, Storey JD. The sva package for removing batch effects and other unwanted variation in high-throughput experiments. Bioinformatics. 2012;28:882–3.
Ito K, Murphy D. Application of ggplot2 to Pharmacometric Graphics. CPT Pharmacometrics Syst Pharmacol. 2013;2:e79.
Yu G, Wang LG, Han Y, He QY. clusterProfiler: an R package for comparing biological themes among gene clusters. Omics. 2012;16:284–7.
Yu G, Wang LG, Yan GR, He QY. DOSE: an R/Bioconductor package for disease ontology semantic and enrichment analysis. Bioinformatics. 2015;31:608–9.
Galiè N, Humbert M, Vachiery JL, Gibbs S, Lang I, Torbicki A, Simonneau G, Peacock A, Vonk Noordegraaf A, Beghetti M, et al. 2015 ESC/ERS guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of pulmonary hypertension: the Joint Task Force for the diagnosis and treatment of pulmonary hypertension of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) and the European Respiratory Society (ERS): endorsed by: Association for European Paediatric and Congenital Cardiology (AEPC), International Society for Heart and Lung Transplantation (ISHLT). Eur Heart J. 2016;37:67–119.
Ruopp NF, Cockrill BA. Diagnosis and treatment of pulmonary arterial hypertension: a review. JAMA. 2022;327:1379–91.
Pi H, Xia L, Ralph DD, Rayner SG, Shojaie A, Leary PJ, Gharib SA. Metabolomic signatures Associated with Pulmonary arterial hypertension outcomes. Circ Res. 2023;132:254–66.
Bousseau S, Sobrano Fais R, Gu S, Frump A, Lahm T. Pathophysiology and new advances in pulmonary hypertension. BMJ Med. 2023;2:e000137.
Boucly A, Tu L, Guignabert C, Rhodes C, De Groote P, Prévot G, Bergot E, Bourdin A, Beurnier A, Roche A et al. Cytokines as prognostic biomarkers in pulmonary arterial hypertension. Eur Respir J 2023, 61.
Hojda SE, Chis IC, Clichici S. Biomarkers in pulmonary arterial hypertension. Diagnostics (Basel) 2022, 12.
Lin W, Tang Y, Zhang M, Liang B, Wang M, Zha L, Yu Z. Integrated Bioinformatic Analysis reveals TXNRD1 as a Novel Biomarker and potential therapeutic target in idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension. Front Med (Lausanne). 2022;9:894584.
Li A, He J, Zhang Z, Jiang S, Gao Y, Pan Y, Wang H, Zhuang L. Integrated Bioinformatics Analysis reveals marker genes and potential therapeutic targets for pulmonary arterial hypertension. Genes (Basel) 2021, 12.
Fillebeen C, Charlebois E, Wagner J, Katsarou A, Mui J, Vali H, Garcia-Santos D, Ponka P, Presley J, Pantopoulos K. Transferrin receptor 1 controls systemic iron homeostasis by fine-tuning hepcidin expression to hepatocellular iron load. Blood. 2019;133:344–55.
Weber RA, Yen FS, Nicholson SPV, Alwaseem H, Bayraktar EC, Alam M, Timson RC, La K, Abu-Remaileh M, Molina H, Birsoy K. Maintaining Iron Homeostasis is the key role of lysosomal acidity for cell proliferation. Mol Cell. 2020;77:645–e655647.
Heath JL, Weiss JM, Lavau CP, Wechsler DS. Iron deprivation in cancer–potential therapeutic implications. Nutrients. 2013;5:2836–59.
Crescenzi E, Leonardi A, Pacifico F. Iron Metabolism in Cancer and Senescence: a Cellular Perspective. Biology (Basel) 2023, 12.
Weber S, Parmon A, Kurrle N, Schnutgen F, Serve H. The clinical significance of Iron Overload and Iron Metabolism in Myelodysplastic Syndrome and Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Front Immunol. 2020;11:627662.
Kobak KA, Radwanska M, Dziegala M, Kasztura M, Josiak K, Banasiak W, Ponikowski P, Jankowska EA. Structural and functional abnormalities in iron-depleted heart. Heart Fail Rev. 2019;24:269–77.
Wang W, Deng Z, Hatcher H, Miller LD, Di X, Tesfay L, Sui G, D’Agostino RB Jr., Torti FM, Torti SV. IRP2 regulates breast tumor growth. Cancer Res. 2014;74:497–507.
Alvarez SW, Sviderskiy VO, Terzi EM, Papagiannakopoulos T, Moreira AL, Adams S, Sabatini DM, Birsoy K, Possemato R. NFS1 undergoes positive selection in lung tumours and protects cells from ferroptosis. Nature. 2017;551:639–43.
Greene CJ, Attwood K, Sharma NJ, Gross KW, Smith GJ, Xu B, Kauffman EC. Transferrin receptor 1 upregulation in primary tumor and downregulation in benign kidney is associated with progression and mortality in renal cell carcinoma patients. Oncotarget. 2017;8:107052–75.
Wang Y, Qiu S, Wang H, Cui J, Tian X, Miao Y, Zhang C, Cao L, Ma L, Xu X, et al. Transcriptional Repression of Ferritin Light Chain increases ferroptosis sensitivity in Lung Adenocarcinoma. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021;9:719187.
Wu Y, Zhang S, Gong X, Tam S, Xiao D, Liu S, Tao Y. The epigenetic regulators and metabolic changes in ferroptosis-associated cancer progression. Mol Cancer. 2020;19:39.
Saenz SA, Noti M, Artis D. Innate immune cell populations function as initiators and effectors in Th2 cytokine responses. Trends Immunol. 2010;31:407–13.
Sukhbaatar N, Weichhart T. Iron Regulation: macrophages in control. Pharmaceuticals (Basel) 2018, 11.
Chen F, Fan Y, Hou J, Liu B, Zhang B, Shang Y, Chang Y, Cao P, Tan K. Integrated analysis identifies TfR1 as a prognostic biomarker which correlates with immune infiltration in breast cancer. Aging. 2021;13:21671–99.
Wang Y, Gu LF, Zhao X, Hu C, Chen Q. TFR1 expression in induced sputum is associated with asthma severity. PeerJ. 2022;10:e13474.
Pan Y, Yang J, Dai J, Xu X, Zhou X, Mao W. TFRC in cardiomyocytes promotes macrophage infiltration and activation during the process of heart failure through regulating Ccl2 expression mediated by hypoxia inducible factor-1alpha. Immun Inflamm Dis. 2023;11:e835.
Yaku A, Inagaki T, Asano R, Okazawa M, Mori H, Sato A, Hia F, Masaki T, Manabe Y, Ishibashi T, et al. Regnase-1 prevents pulmonary arterial hypertension through mRNA degradation of Interleukin-6 and platelet-derived growth factor in alveolar macrophages. Circulation. 2022;146:1006–22.
Kojima H, Tokunou T, Takahara Y, Sunagawa K, Hirooka Y, Ichiki T, Tsutsui H. Hypoxia-inducible factor-1 alpha deletion in myeloid lineage attenuates hypoxia-induced pulmonary hypertension. Physiol Rep. 2019;7:e14025.
Klinger JR, Pereira M, Del Tatto M, Brodsky AS, Wu KQ, Dooner MS, Borgovan T, Wen S, Goldberg LR, Aliotta JM, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell Extracellular vesicles Reverse Sugen/Hypoxia Pulmonary hypertension in rats. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2020;62:577–87.
Jia Z, Wang S, Yan H, Cao Y, Zhang X, Wang L, Zhang Z, Lin S, Wang X, Mao J. Pulmonary vascular remodeling in Pulmonary Hypertension. J Pers Med 2023, 13.
Cotroneo E, Ashek A, Wang L, Wharton J, Dubois O, Bozorgi S, Busbridge M, Alavian KN, Wilkins MR, Zhao L. Iron homeostasis and pulmonary hypertension: iron deficiency leads to pulmonary vascular remodeling in the rat. Circ Res. 2015;116:1680–90.
Quatredeniers M, Mendes-Ferreira P, Santos-Ribeiro D, Nakhleh MK, Ghigna MR, Cohen-Kaminsky S, Perros F. Iron Deficiency in Pulmonary arterial hypertension: a deep dive into the mechanisms. Cells 2021, 10.
Hsu MY, Mina E, Roetto A, Porporato PE. Iron: an essential element of Cancer Metabolism. Cells 2020, 9.
Aldred MA, Comhair SA, Varella-Garcia M, Asosingh K, Xu W, Noon GP, Thistlethwaite PA, Tuder RM, Erzurum SC, Geraci MW, Coldren CD. Somatic chromosome abnormalities in the lungs of patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2010;182:1153–60.
Skikne BS, Flowers CH, Cook JD. Serum transferrin receptor: a quantitative measure of tissue iron deficiency. Blood. 1990;75:1870–6.
Beguin Y. Soluble transferrin receptor for the evaluation of erythropoiesis and iron status. Clin Chim Acta. 2003;329:9–22.
Du Y, Zhang J, Guo K, Yin Y. Identification of potential biomarkers for idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension using single-cell and bulk RNA sequencing analysis. Front Genet. 2024;15:1328234.
Yao X, Jing T, Wang T, Gu C, Chen X, Chen F, Feng H, Zhao H, Chen D, Ma W. Molecular characterization and elucidation of pathways to identify Novel therapeutic targets in pulmonary arterial hypertension. Front Physiol. 2021;12:694702.
Yang X, Wang C, Lin Y, Zhang P. Identification of Crucial Hub Genes and Differential T Cell Infiltration in Idiopathic Pulmonary arterial hypertension using Bioinformatics strategies. Front Mol Biosci. 2022;9:800888.
Pullamsetti SS, Mamazhakypov A, Weissmann N, Seeger W, Savai R. Hypoxia-inducible factor signaling in pulmonary hypertension. J Clin Investig. 2020;130:5638–51.
Zeidan EM, Hossain MA, El-Daly M, Abourehab MAS, Khalifa MMA, Taye A. Mitochondrial regulation of the Hypoxia-Inducible factor in the Development of Pulmonary Hypertension. J Clin Med 2022, 11.
Garcia-Morales LJ, Chen NY, Weng T, Luo F, Davies J, Philip K, Volcik KA, Melicoff E, Amione-Guerra J, Bunge RR, et al. Altered hypoxic-Adenosine Axis and Metabolism in Group III Pulmonary Hypertension. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2016;54:574–83.
Zhang Y, Wang Y. Cell-to-cell crosstalk: a New Insight into Pulmonary Hypertension. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol. 2023;184:159–79.
Fredenburgh LE, Ma J, Perrella MA. Cyclooxygenase-2 inhibition and hypoxia-induced pulmonary hypertension: effects on pulmonary vascular remodeling and contractility. Trends Cardiovasc Med. 2009;19:31–7.
Xing Y, Zhao S, Wei Q, Gong S, Zhao X, Zhou F, Ai-Lamki R, Ortmann D, Du M, Pedersen R et al. A novel piperidine identified by stem cell-based screening attenuates pulmonary arterial hypertension by regulating BMP2 and PTGS2 levels. Eur Respir J 2018, 51.
Funding
This work was supported by grants from the Science and Technology of Jilin Province(YDZJ202301ZYTS525).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
ZHK conceived the study, designed the experiments, acquired the funding and drafted the article. YC performed the bioinformatics analyses, interpreted the data and data analysis. LYH was responsible for conducting the experimental validation, which included qRT-PCR, ELISA and western blotting.All authors ZHK, YC and LYH contributed to revising the manuscript critically for important intellectual content and have given final approval for the version to be published. Each author agrees to be accountable for all aspects of the work in ensuring that questions related to the accuracy or integrity of any part of the work are appropriately investigated and resolved.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The animal study was reviewed and approved by the Ethics Committee of the China-Japan Hospital of Jilin University. Informed consent was obtained from all subjects before the study began. All research procedures were conducted in accordance with the tenets of the Declaration of Helsinki. Ethical approval for research involving human subjects was also obtained from the Ethics Committee of the China-Japan Union Hospital of Jilin University.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License, which permits any non-commercial use, sharing, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if you modified the licensed material. You do not have permission under this licence to share adapted material derived from this article or parts of it. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, C., Liu, YH. & Zheng, HK. Identification of TFRC as a biomarker for pulmonary arterial hypertension based on bioinformatics and experimental verification. Respir Res 25, 296 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12931-024-02928-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12931-024-02928-6