Abstract
Background
Cases of colonization or infection caused by Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) are frequently reported in people who work with animals, including veterinary personnel. The aim of this study was to determine the prevalence of MRSA colonization among veterinary professionals. A total of 134 nasal swabs from healthy attendees of a veterinary conference held in the Czech Republic were tested for presence of MRSA. The stains were further genotypically and phenotypically characterized.
Results
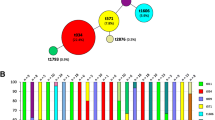
Nine isolated MRSA strains were characterized with sequence type (ST), spa type (t) and Staphylococcal Cassette Chromosome mec type. Five different genotypes were described, including ST398-t011-IV (n = 5), ST398-t2330-IV (n = 1), ST398-t034-V (n = 1), ST225-t003-II (n = 1) and ST4894-t011-IV (n = 1). The carriage of the animal MRSA strain was confirmed in 8 cases, characteristics of one strain corresponded to the possible nosocomial origin. Among animal strains were described three spa types (t011, t034, t2330) belonging into one dominating clonal complex spa-CC11.
Conclusion
According to our results, the prevalence of nasal carriage of MRSA in veterinary personnel is 6.72%. Although we described an increase compared to the results of previous study (year 2008), the prevalence in the Czech Republic is still remaining lower than reported from neighboring countries. Our results also indicate that healthcare - associated MRSA strains are still not spread among animals.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus) is a common bacterium adapted to the human host, persistently colonizing the nasal mucosa of 30%, and transiently present in up to 70% of healthy people [1]. Carriers of Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) are infrequent (0.2%) in people with no previous contact with healthcare [2]. The prevalence is higher among healthcare workers, in Europe it shows geographic dependence, and differs from < 1% in northern countries up to > 40% in Southern and Western Europe [3]. Colonization increases the risk of subsequent infection by fourfold [4]. Under eligible conditions colonizing MRSA strains may cause purulent skin and soft tissue infection or serious pneumonia. Animals, mainly livestock were described as MRSA reservoirs [5]. The livestock-associated strains (LA-MRSA) adapted to animal hosts [6]. After frequent and close contact with an MRSA-positive animal, humans can be colonized by these bacteria, but rarely become infected [7]. Not only farmers and livestock breeders, but also veterinary personnel are at higher risk of acquiring MRSA as shown previously.
The aim of this study was to determine the prevalence of MRSA colonization among veterinary professionals attending a veterinary conference for mixed animal practice and to characterize these strains genotypically and phenotypically (determine their antibiotic resistance profiles).
Results
Of the 134 attendees who agreed to be tested, 119/134 (88.8%) were veterinarians, 6/134 (4.4%) were pharmacists/researchers and 5/134 (3.7%) were veterinary school students; all confirmed animal contact. Among these healthy volunteers various age groups ranging from 22 to 69 years (median 35.5; mean age 37.6) were represented. With regard to type of practice, 76/134 (57%) worked in small-animal practice, 57/134 (42.3%) in mixed practice, and 1/134 (0.7%) worked with livestock only. The other characteristics are summarized in Table 1.
Staphylococcus intermedius/pseudintermedius, a common pathogen in dogs and cats, was identified in 2/134 swabs (1.5%). S. aureus was confirmed in 40/134 samples (29.9%), of which 9/40 (6.72%) were MRSA strains all carrying mecA gene. Overall, in this study group there were more women (88/134, 66%) than men (46/134, 34%).
Nine isolated MRSA strains were characterized with sequence type (ST), spa type (t) and staphylococcal cassette chromosome mec (SCCmec). Five genotypes were described, including ST398-t011-IV (n = 5), ST398-t2330-IV (n = 1), ST398-t034-V (n = 1), ST225-t003-II (n = 1) and ST4894-t011-IV (n = 1). To determine the clonal relatedness of the isolates, Based Upon Repeat Pattern (BURP) analysis was performed according to the assigned spa types. Spa type t011 was determined as a founder of the cluster spa-CC11. Spa t2330 and t034 belonged to the same aforementioned cluster, while the isolate with spa type t003 was singleton. In accordance with their spa and SCCmec type, the strains showed a typical antibiotic resistance profile. Except for the one spa type t003, the isolates were resistant to tetracycline, and strains t011, t2330 were additionally resistant to gentamicin and ciprofloxacin (Table 2).
The MRSA carriers reported contact with large farm animals (pigs, cattle, horses, sheep) only in 3/9 cases, the frequent contact stated one of them, in the remaining 2 cases the contact was less frequent. Interestingly, all of them reported regular frequent contact with small animals (daily 8/9, weekly 1/9). The statistical analysis (Fisher test) did not show a significant association between the carriage of MRSA and the frequent contact with small animals.
Discussion
MRSA is an important pathogen not only for humans, but also for small animals or livestock and colonization itself brings the risk of future infection. The higher prevalence of MRSA carriage in veterinary personnel has been proven by multiple studies all over the world. The rates in Europe vary from 0.7–19.2% [8, 9]. Traditionally, high prevalence data come from countries with well-developed livestock production, such as Netherlands, Denmark or Germany [10,11,12]. Type of veterinary practice, frequency of contact with animals, time since exposure and the study design itself are factors leading to international differences in prevalence rates. There is a lack of data describing the situation in the Czech Republic. A study of similar design performed in the Czech Republic in 2008 revealed 0.7% (2/280) colonization of veterinary personnel attending the conference [8], but the strains were rather not animal-related and the rate corresponded with expected community colonization rates [13]. According to our results, the prevalence of nasal carriage of MRSA in veterinary personnel in our country has increased to 6.72% [9/134, 95% exact Confidence Interval (CI) (3.12, 12.37)].
The most prevalent livestock-associated MLST type in Europe is ST398, we confirmed dominance of this clone also in the Czech Republic. Animal related MRSA strains belonged to spa t011, t034 and t2330. The first two are ranked as the most common spa types in European conditions together with t108 and t567 [14]. Moreover, an isolate spa t034 was confirmed in a veterinarian from neighboring country (Slovakia), who was in contact with both companion animals and livestock. Spa t034 had high prevalence among pigs originated from Slovakia [15]. All animal strains showed typical resistance to tetracycline, an antibiotic frequently used in food animal production [16].
The strain ST225-t003-II was a singleton and differed from others in antibiotic susceptibility profile. It had been previously described as predominant in hospitals in the Czech Republic, central Germany, and western Poland [17]. Carrier of this strain did not confirm any contact with the healthcare facility or residence with a healthcare worker in the 30-day period before screening, however, we could not rule out the possibility of contact before the 30-day period questioned. We could not exclude that the strain could possibly have originated from companion animals [18].
MRSA carriage or infections were described mostly in farm animals, such as pigs [19], cattle [20], sheep [21], horses [22] or poultry [23]. Transmission to humans has been documented, mostly after prolonged, repeated and close contact with a colonized animal [24] or through a contaminated vehicle such as meat [25] or dairy products [26]. Several studies confirmed the presence of MRSA ST398 in pigs, goats, cow and sheep and their meat and milk products in the Czech Republic [27,28,29,30]. The strains isolated from pigs and pork meat belonged to ST398, whereas the strains from cattle were multiple ST types with the spa type t011 and t034 detected most frequently [31].
All colonized veterinarians stated frequent contact with small animals, and regular contact with livestock concerned only three of them. Therefore the sporadic finding of S. intermedius/ pseudintermedius in our test group is surprising. Their sharing between pets and humans has been well documented [32]. S. aureus is not a typical commensal bacterium in companion animals, being described in less than 10% and even lower (0.7%) in the case of MRSA carriage [33, 34]. MRSA isolates circulating in dogs and cats belong mostly to nosocomial clones often identified in humans [18]. This indicates that MRSA isolated in companion animals may originate in humans and those animals are a reservoir for possible human re-infection [35]. We observed, MRSA carriage in veterinary personnel was primarily associated with contact with small animals. Its statistical significance has not been confirmed, the frequency of positive finding is too low to be generalized.
Conclusion
This study showed increasing prevalence of MRSA carriage in veterinary personnel with confirmed presence of both animal and nosocomial strains. Attention should be given to the increased colonization rates in this occupational group, especially on admission to hospitalization. Occupational history should be supplemented in clinical practice with a statement about contact with animals. This risk factor should not be underestimated before surgical procedures because of the undeniably higher occurrence of infectious complications in these individuals and MRSA screening should be provided.
Material and methods
Study population
We addressed attendees of the veterinary conference VETclasses 2017, held in Hradec Kralove, Czech Republic, 23. - 24. 9. 2017. The target groups were both small-animal and livestock practitioners. Among 436 participants, there were 334 practicing veterinarians, and 102 nurses, technicians and other personnel involved in industry or research. Most of them were from the Czech Republic, but a few representatives from Slovakia and Belgium were also represented. Total of 134 volunteers agreed to be screened, which is approximately 3% of the practicing veterinarians in Czech Republic. According to the Chamber of Veterinary Surgeons of the Czech Republic, there were 4205 private veterinarians registered, which forms the majority of practicing professionals in the Czech Republic (accessed 26 August 2019). In our country small animal veterinary practitioners make up 70%, the rest are involved in mixed animal practice, livestock specialized veterinarians have minimal representation. The Ethics Committee of the Faculty Hospital in Hradec Kralove gave permission to carry out the study on human volunteers.
Sample collection
Bilateral nasal swab specimens (~ 1 cm into each nostril) were collected with sterile cotton-tipped swabs, stored in transport medium (Copan Transystem®) and transported immediately for laboratory processing. The sample collection was voluntary and anonymous, and additional data were obtained: demographic data, data on exposure to animals or a hospital environment, place of work, job description, type of clinical practice (small animals, mostly dogs, cats or large animals, horses, pigs, ruminants), known exposure to an MRSA positive-animal, previous hospitalization within 30 days, residence with a healthcare worker. The questionnaire was developed for the purposes of this study (Additional file 1).
Bacterial strains
Nasal swabs were cultured for 18 h on Sheep Blood Agar (Oxoid™ Columbia Blood Agar Base, Thermo Scientific™) and chromogenic agar MRSA Select™ (Bio-Rad). S. aureus was identified morphologically, identification was confirmed by Matrix-Assisted Laser Desorption/Ionization Time of Flight Mass Spectrometry (MALDI-TOF MS, Bruker Microflex LT™, Bruker Daltonics). MRSA was detected by cefoxitin resistance [36] and confirmed by detection of mecA and mecC genes by PCR [37].
Antibiotic susceptibility testing
Testing and evaluation of Minimal Inhibitory Concentrations (MIC) in MRSA strains was performed by broth microdilution method according to standard ISO 20776-1 [38]. Susceptibility to erythromycin, clindamycin, linezolid, chloramphenicol, tetracycline, ciprofloxacin, trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole, gentamicin and vancomycin was tested.
Spa typing and Based upon repeat pattern (BURP) analysis
The typing was performed with primers spa-1113f (5’TAA AGA CGA TCC TTC GGT C − 3′) and spa-1514r (5′-CAG CAG TAG TGC CGT TTG CTT -3′) [39]. The software Ridom StaphType™ (ver. 2.2.1; Ridom GmbH) was used for sequence and BURP analysis. Resulting clonal clusters (spa-CCs) were composed of ≥2 related spa types and clustered only if their cost value was ≤4 and had at least 5 repeats [40]. The algorithm counts with repeat duplication, deletion and point mutation when assessing if different spa types are related.
Multilocus Sequence Typing (MLST) was performed as described previously [41]; the allele types and the resulting STs were assigned using software BioNumerics (ver.7.0; Applied Maths).
SCCmec typing
The SCCmec types were identified using multiplex PCR based on identification of specific genes within J regions of particular cassettes (I to V) as described previously [42].
Statistical analysis
The statistical analyses (Confidence Interval, Fisher test) was performed using NCSS 11 Statistical Software (2016). NCSS, LLC. Kaysville, Utah, USA, ncss.com/software/ncss.
Availability of data and materials
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article.
Abbreviations
- arc :
-
Carbamate kinase
- aro :
-
Shikimate dehydrogenase
- BURP:
-
Based upon repeat pattern
- CC:
-
Clonal complex
- CI:
-
Confidence interval
- CIP:
-
Ciprofloxacin
- CLI:
-
Clindamycin
- CXT:
-
Cefoxitin
- ERY:
-
Erythromycin
- GEN:
-
Gentamicin
- glp :
-
Glycerol kinase
- gmk :
-
Guanylate kinase
- LA-MRSA:
-
Livestock-associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus
- MALDI-TOF MS:
-
Matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time of flight mass spectrometry
- MIC:
-
Minimal inhibitory concentrations
- MLST:
-
Multilocus sequence typing
- MRSA:
-
Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus
- PCR:
-
Polymerase chain reaction
- pta :
-
Phosphate acetyltransferase
- S. aureus :
-
Staphylococcus aureus
- SCCmec :
-
Staphylococcal Cassette Chromosome mec
- spa-CCs:
-
spa clonal clusters
- ST:
-
Sequence type
- t:
-
spa type
- TET:
-
Tetracycline
- tpi :
-
Triosephosphate isomerase
- yqi :
-
Acetyle coenzyme A acetyltransferase
References
von Eiff C, Becker K, Machka K, Stammer H, Peters G. Nasal carriage as a source of Staphylococcus aureus bacteremia. N Engl J Med. 2001;344:11–6. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJM200101043440102.
Salgado CD, Farr BM, Calfee DP. Community-acquired methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus: a meta-analysis of prevalence and risk factors. Clin Infect Dis. 2003;36:131–9. https://doi.org/10.1086/345436.
Tiemersma EW, Bronzwaer SL, Lyytikäinen O, Degener JE, Schrijnemakers P, Bruinsma N, et al. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in Europe, 1999-2002. Emerg Infect Dis. 2004;10(9):1627–34. https://doi.org/10.3201/eid1009.040069.
Safdar N, Bradley EA. The risk of infection after nasal colonization with Staphylococcus Aureus. Am J Med. 2008;121:310–5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amjmed.2007.07.034.
Witte W, Strommenger B, Stanek C, Cuny C. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus ST398 in humans and animals. Central Europe Emerg Infect Dis. 2007;13:255–8. https://doi.org/10.3201/eid1302.060924.
Fitzgerald JR. Human origin for livestock-associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. MBio. 2012;3:e00082–12. https://doi.org/10.1128/mBio.00082-12.
Cuny C, Wieler LH, Witte W. Livestock-Associated MRSA: The Impact on Humans. Antibiot (Basel). 2015;4:521–43. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics4040521.
Zemlickova H, Fridrichova M, Tyllova K, Jakubu V, Machova I. Carriage of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in veterinary personnel. Epidemiol Infect. 2009;137:1233. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0950268809002015.
Cuny C, Abdelbary MMH, Köck R, Layer F, Scheidemann W, Werner G, et al. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus from infections in horses in Germany are frequent colonizers of veterinarians but rare among MRSA from infections in humans. One Health (Amsterdam). 2016;2:11–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.onehlt.2015.11.004.
Wulf MWH, Sørum M, van Nes A, Skov R, Melchers WJG, Klaassen CHW, et al. Prevalence of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus among veterinarians: an international study. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2008;14:29–34. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-0691.2007.01873.x.
Moodley A, Nightingale EC, Stegger M, Nielsen SS, Skov RL, Guardabassi L. High risk for nasal carriage of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus among Danish veterinary practitioners. Scand J Work Environ Health. 2008;34:151–7 http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18470441.
Cuny C, Nathaus R, Layer F, Strommenger B, Altmann D, Witte W. Nasal colonization of humans with methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) CC398 with and without exposure to pigs. PLoS One. 2009;4:e6800. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0006800.
Melter O, de Sousa AM, Urbaskova PJ, et al. Update on the major clonal types of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in the Czech Republic. Clin Microbiol. 2003;41(11):4998–5005.
Frana TS, Beahm AR, Hanson BM, Kinyon JM, Layman LL, Karriker LA, et al. Isolation and characterization of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus from pork farms and visiting veterinary students. PLoS One. 2013;8:e53738. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0053738.
Huang E, Gurzau AE, Hanson BM, Kates AE, Smith TC, Pettigrew MM, et al. Detection of livestock-associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus among swine workers in Romania. J Infect Public Health. 2014;7:323–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jiph.2014.03.008.
Vanderhaeghen W, Hermans K, Haesebrouck F, Butaye P. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) in food production animals. Epidemiol Infect. 2010;138:606. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0950268809991567.
Grundmann H, Aanensen DM, van den Wijngaard CC, Spratt BG, Harmsen D, Friedrich AW, et al. Geographic distribution of Staphylococcus aureus causing invasive infections in Europe: a molecular-epidemiological analysis. PLoS Med. 2010;7:e1000215. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pmed.1000215.
Loeffler A, Lloyd DH. Companion animals: a reservoir for methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in the community? Epidemiol Infect. 2010;138:595. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0950268809991476.
Lewis HC, Mølbak K, Reese C, Aarestrup FM, Selchau M, Sørum M, et al. Pigs as source of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus CC398 infections in humans. Denmark Emerg Infect Dis. 2008;14:1383–9. https://doi.org/10.3201/eid1409.071576.
Holmes MA, Zadoks RN. Methicillin Resistant S. aureus in human and bovine mastitis. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia. 2011;16:373–82. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10911-011-9237-x.
Macori G, Giacinti G, Bellio A, Gallina S, Bianchi DM, Sagrafoli D, et al. Molecular Epidemiology of Methicillin-Resistant and Methicillin-Susceptible Staphylococcus aureus in the Ovine Dairy Chain and in Farm-Related Humans. Toxins (Basel). 2017;9. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins9050161.
Haenni M, Châtre P, Dupieux-Chabert C, Métayer V, Bes M, Madec J-Y, et al. Molecular epidemiology of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in horses, cats, and dogs over a 5-year period in France. Front Microbiol. 2017;8:2493. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2017.02493.
Richer A, Sting R, Popp C, Rau J, Tenhagen BA, Guerra B, et al. Prevalence of types of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in Turkey flocks and personnel attending the animals. Epidemiol Infect. 2012;140:2223–32. https://doi.org/10.1017/S095026881200009X.
Graveland H, Wagenaar JA, Bergs K, Heesterbeek H, Heederik D. Persistence of livestock associated MRSA CC398 in humans is dependent on intensity of animal contact. PLoS One. 2011;6:e16830. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0016830.
van Loo IHM, Diederen BMW, Savelkoul PHM, Woudenberg JHC, Roosendaal R, van Belkum A, et al. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in meat products, the Netherlands. Emerg Infect Dis. 2007;13:1753–5. https://doi.org/10.3201/eid1311.070358.
Basanisi MG, La Bella G, Nobili G, Franconieri I, La Salandra G. Genotyping of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) isolated from milk and dairy products in South Italy. Food Microbiol. 2017;62:141–6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fm.2016.10.020.
Vyletelova M, Hanus O, Karpiskova R, Stastkova Z. Occurrence and antimicrobial sensitivity in staphylococci isolated from goat, sheep and cow’s milk. Acta Univ Agric Silvic Mendel Brun. 2011;59:209–14. https://doi.org/10.11118/actaun201159030209.
Bogdanovicova K, Skockova A, Kolackova I, Stastkova Z, Karpiskova R. The bacteriological quality of bulk tank milk in the Czech Republic. Int J Food Nut Sci. 2015;4:7–14. https://doi.org/10.17221/25/2016-cjfs.
Vyletelova M, Vlkova H, Manga I. Occurrence and characteristics of methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus and methicillin resistant coagulase-negative staphylococci in raw milk manufacturing. Czech J Food Sci. 2011;29:11–6.
Klimesova M, Manga I, Nejeschlebova L, Horacek J, Ponizil A. VondruskovaA. Occurrence of Staphylococcus aureus in cattle, sheep, goat, and pig rearing in the Czech Republic. Acta Vet Brno. 2017:86.3–10. https://doi.org/10.2754/avb201786010003.
Kolackova I, Karpiskova R. Characteristics of Methticillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus isolated from food of animal and non-animal origin in retail in the Czech Republic. In Abstract book 4th ASM-ESCMID Conference on Methicillin-resistant Staphylococci in animals: Veterinary and public health implications, Chicago (USA) 2015, 40–41.
Wipler J, Cermakova Z, Hanzalek T, Horakova H, Zemlickova H. Sharing bacterial microbiota between owners and their pets (dogs, cats). Klin Mikrobiol Infekc Lek. 2017;23(2):48–57.
Duquette RA, Nuttall TJ. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in dogs and cats: an emerging problem? J Small Anim Pract. 2004;45:591–7 http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15600269. Accessed 16 Jan 2019.
Boost MV, O’Donoghue MM, James A. Prevalence of Staphylococcus aureus carriage among dogs and their owners. Epidemiol Infect. 2008;136:953–64. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0950268807009326.
Bierowiec K, Płoneczka-Janeczko K, Rypuła K. Is the colonisation of Staphylococcus aureus in pets associated with their close contact with owners? PLoS One. 2016;11:e0156052. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0156052.
EUCAST guidelines for detection of resistance mechanisms and specific resistances of clinical and/ or epidemiological importance, version 2.0. 2017. http://www.eucast.org/fileadmin/src/media/PDFs/EUCAST_files/Resistance_mechanisms/EUCAST_detection_of_resistance_mechanisms_170711.pdf. Accessed 22 Oct 2018.
Stegger M, Andersen PS, Kearns A, Pichon B, Holmes MA, Edwards G, et al. Rapid detection, differentiation and typing of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus harbouring either mecA or the new mecA homologue mecALGA251. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2012;18:395–400. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-0691.2011.03715.x.
ISO 20776-1. Clinical laboratory testing and in vitro diagnostic test systems - Susceptibility testing of infectious agents and evaluation of performance of antimicrobial susceptibility test devices - Part 1: Reference method for testing the in vitro activity of antimicrobial agents against rapidly growing aerobic bacteria involved in infectious diseases, 2006. https://www.iso.org/standard/41630.html. Accessed 15 Jan 2018.
DNA Sequencing of the spa gene, version 1.1, 2004. http://www.ridom.de/doc/ Ridom_spa_sequencing.pdf. Accessed 15 Jan 2018.
Strommenger B, Kettlitz C, Weniger T, Harmsen D, Friedrich AW, Witte W. Assignment of Staphylococcus isolates to groups by spa typing, SmaI macrorestriction analysis, and multilocus sequence typing. J Clin Microbiol. 2006;44:2533–40. https://doi.org/10.1128/JCM.00420-06.
Enright MC, Day NP, Davies CE, Peacock SJ, Spratt BG. Multilocus sequence typing for characterization of methicillin-resistant and methicillin-susceptible clones of Staphylococcus aureus. J Clin Microbiol. 2000;38:1008–15 http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10698988.
Milheirico C, Oliveira DC, de Lencastre H. Update to the multiplex PCR strategy for assignment of mec element types in Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2007;51:3374–7. https://doi.org/10.1128/AAC.00275-07.
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to Ian McColl MD, Ph.D. for assistance with the manuscript, to MVDr. Zuzana Cermakova, Ph.D. and to MVDr. Zdenek Hanzalek, Ph.D. for help with organization of sampling at the conference and to RNDr. Eva Cermakova for statistical analysis.
Funding
This work has been supported within the project SVV 260398/2017, which covered the design of the study, sample and data collection and analysis, and interpretation of data.
The writing and submitting of the manuscript has been supported within the project MH CZ – DRO (UHHK, 00179906).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
KN designed the study, led collection of swabs, performed data analysis, and wrote the manuscript. HZ designed the study, contributed to data analysis and drafting of the manuscript. VJ and KP contributed to data analysis and drafting of the manuscript. All authors approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The study was approved by Ethics Committee, University Hospital Hradec Kralove (the written document, reference number 201808 S25P). Each subject gave verbal consent after the nature of the study has been fully explained by the Investigator. Ample time for questions and answers was provided during the consenting process and the verbal consent was formally confirmed, when the subject submitted the questionnaire. The participant’s written consent was not required due to limited time for interaction between researcher and participant. The consent process was recoded using a Record of Consent Form (Interviewee Number, Date, City, Project Explained Yes/No, Signature of Researcher). The Ethics Committee retrospectively approved the procedure of obtaining verbal rather than written consent from study participants.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Additional file 1:
Questionnaire. Questionnaire used to obtain additional data from volunteers in this study.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated.
About this article
Cite this article
Neradova, K., Jakubu, V., Pomorska, K. et al. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in veterinary professionals in 2017 in the Czech Republic. BMC Vet Res 16, 4 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12917-019-2223-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12917-019-2223-z