Abstract
Background
DNA damage repair is a complex process, which can trigger the development of cancer if disturbed. In this study, we hypothesize a role of variants in the ATM, H2AFX and MRE11 genes in determining breast cancer (BC) susceptibility.
Methods
We examined the whole sequence of the ATM kinase domain and estimated the frequency of founder mutations in the ATM gene (c.5932G > T, c.6095G > A, and c.7630-2A > C) and single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in H2AFX (rs643788, rs8551, rs7759, and rs2509049) and MRE11 (rs1061956 and rs2155209) among 315 breast cancer patients and 515 controls. The analysis was performed using high-resolution melting for new variants and the polymerase chain reaction-restriction fragment length polymorphism (PCR-RFLP) method for recurrent ATM mutations. H2AFX and MRE11 polymorphisms were analyzed using TaqMan assays. The cumulative genetic risk scores (CGRS) were calculated using unweighted and weighted approaches.
Results
We identified four mutations (c.6067G > A, c.8314G > A, c.8187A > T, and c.6095G > A) in the ATM gene in three BC cases and two control subjects. We observed a statistically significant association of H2AFX variants with BC. Risk alleles (the G of rs7759 and the T of rs8551 and rs2509049) were observed more frequently in BC cases compared to the control group, with P values, odds ratios (OR) and 95% confidence intervals (CIs) of 0.0018, 1.47 (1.19 to 1.82); 0.018, 1.33 (1.09 to 1.64); and 0.024, 1.3 (1.06 to 1.59), respectively. Haplotype-based tests identified a significant association of the H2AFX CACT haplotype with BC (P < 0.0001, OR = 27.29, 95% CI 3.56 to 209.5). The risk of BC increased with the growing number of risk alleles. The OR (95% CI) for carriers of ≥ four risk alleles was 1.71 (1.11 to 2.62) for the CGRS.
Conclusions
This study confirms that H2AFX variants are associated with an increased risk of BC. The above-reported sequence variants of MRE11 genes may not constitute a risk factor of breast cancer in the Polish population. The contribution of mutations detected in the ATM gene to the development of breast cancer needs further detailed study.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Cell-cycle checkpoints and DNA damage repair prevent genetic instability and mutagenesis. In response to DNA double-strand breaks, a signaling cascade is initiated: first, the M/R/N complex, consisting of three proteins, MRE11, RAD50 and NBN, acts as a sensor for DNA damage. M/R/N proteins recruit the key signal transducer of DNA damage response: ataxia-telangiectasia mutated (ATM) kinase [1]. Activation of ATM causes cell cycle arrest. ATM phosphorylates several substrates, including histone H2AFX. The phosphorylated form of H2AFX, γ-H2AFX, modulates DNA repair mechanisms by reorganizing chromatin and preventing the separation of broken DNA ends.
Several genes involved in maintaining and monitoring genomic stability have emerged as breast cancer (BC) susceptibility genes. High-throughput methods have allowed identification of variants associated with breast cancer in more than 20 genes involved in DNA damage signaling and repair [2]. BRCA1, BRCA2 and CHEK2 are known breast cancer predisposition genes. Mutations in BRCA1 or BRCA2 have been detected in 20% of families with a history of breast cancer in Poland. Polish founder mutations (5382insC, C61G and 4153delA) are reported to be responsible for nearly 90% of BRCA1 mutations [3, 4]. Furthermore, variants of CHEK2 (1100delC, IVS2 + 1G/A, del5395bp, and I157T), PALB2 (509_510delGA and 172_175delTTGT) and RECQL (c.1667_1667 + 3delAGTA) are also associated with breast cancer in the Polish population. Patients with CHEK2 mutations have a greater-than-25% risk of breast cancer [5, 6]. The presence of PALB2 mutations is associated with increased breast cancer risk (odds ratio [OR] = 4.4, 95% confidence interval [CI] 2.30 to 8.37; P < 0.0001) [7]. Moreover, a mutation in the RECQL gene is associated with a 5.5-fold increase in the risk of breast cancer in Poland [8]. In addition, individuals with certain rare genetic syndromes, such as Peutz-Jeghers (caused by STK11 mutations, where the risk of BC is 45% by the age of 70) or Li-Fraumeni (caused by TP53 mutations, with a BC relative risk of 6.4×), have an increased risk of breast cancer [9, 10].
Pathogenic mutations in BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes explain ~ 30% of the cases of families with a high risk of cancer and ~ 15% of breast cancer familial relative risk [11]. The genetic background of breast cancer is still unknown in some of cases. There are some indications of a potential contribution of other genes involved in the DNA damage response to breast cancer risk, including NBS1, ATM, H2AFX, BRIP1, BARD1, RAD51C and RAD51D [12].
We hypothesize that variants in the ATM, H2AFX and MRE11 genes may modulate a predisposition to breast cancer.
Methods
Study population
We collected blood samples from 315 non-selected female patients diagnosed with breast cancer. A total of 515 anonymous blood samples were used as a control population. The control group consisted of individuals attending for a screening check-up in hospital or were healthy blood donors with no history of medical illness. Patients were eligible for present study if they revealed no mutations in BRCA1, BRCA2 and CHEK2 genes. The baseline characteristics of the patients are shown in Table 1. The mean age of patients was 53 years (range 26–76 years). Invasive ductal carcinoma was the most common subtype of cancer (n = 191, 60.6%). Most of the tumors were II and undetermined grade (n = 91, 28.9%, n = 75, 23.8%, respectively). ER/PgR status was available for majority of our BC patients. The study was conducted with the approval of the Central Ethical Committee of the Ministry of Health in Poland, in accordance with the tenets of the Declaration of Helsinki (Decision no. 949/16). All patients signed informed consent forms.
Genotyping and mutation screening
Genomic DNA was extracted from whole blood samples using a PureGene DNA isolation kit in accordance with the manufacturer’s protocols (Gentra Systems).
The ATM mutations analysis was done using a combination of different methods. Polymerase chain reaction-restriction fragment length polymorphism (PCR-RFLP) was used to detect c.5932G > T, c.6095G > A and c.7630-2A > C mutations. PCR-RFLP analysis was performed using the restriction enzymes MseI, BfaI and AluI, respectively. The c.7630-2A > C mutation abolishes an AluI site. Digestion with AluI of the PCR product without the mutation gives four fragments (143, 70, 61 and 7 base pair (bp)), whereas the PCR product with mutation only three bands are observed (213, 61 and 7 bp). The c.5932G > T mutation creates an MseI restriction site. After digestion with MseI, a 232 bp PCR product produces three bands: 159, 40 and 33 in patients with the mutation, while c.6095G > A disrupts the BfaI site. After digestion with BfaI, a 234 bp PCR product without mutation shows two bands, 127 and 107 bp, and the PCR product of alleles with this mutation remains undigested. PCR products were digested with 10 U of restriction enzymes by overnight incubation at 37 °C. The restriction fragments were resolved on 3% agarose gel.
The sequence of the ATM kinase domain was analyzed using high-resolution melting (HRM). The primer sequences are listed in Supplement 1. The primers encompass a kinase domain sequence of ATM between codons 2712–2962. The PCR cycling and HRM analysis were done on CFX96 BioRad instruments. HRM was performed using a Type-it® HRM™ PCR kit (Qiagen, Crawley, UK) following the manufacturer’s instructions. The cycling protocol was as follows: 45 cycles of 95 °C for 10 s, 59 °C for 10 s, and 72 °C for 20 s; 1 cycle of 95 °C for 1 min; and a melt from 60 °C to 90 °C for all assays. For the melt, the temperature was increased at the rate of 0.2 °C/s. All reactions were carried out in duplicate.
Furthermore, selected variants of H2AFX and MRE11 (rs7759, rs8551, rs643788, rs2509049, rs1061956 and rs2155209) were genotyped using TaqMan® SNP genotyping assays (Life Technologies, Carlsbad, California) and CFX96 BioRad instruments. Four SNPs, rs643788, rs8551, rs7759 and rs2509049, are located in the far promoter region of the H2AFX gene -1654C > T, -1420C > T, −1187A > G, and -417C > T, respectively. The PCR was performed with HOT FIREPol Probe qPCR Mix Plus (no ROX) in accordance with the manufacturer’s instructions (Solis Biodyne, Tartu, Estonia). The PCR thermal cycling was as follows: initial denaturation at 95 °C for 15 min. and next 40 cycles of 95 °C for 15 s and 60 °C for 60 s. As a quality control measure, negative controls and approximately 5% of the samples were genotyped in duplicate to check genotyping accuracy.
The genotypes of selected samples and newly detected ATM variants were confirmed by direct sequencing.
Nucleotide positions were determined according to the standard reference sequences for ATM NM_000051.3, whereby mutation numbering uses the ‘A’ of the ATG initiation codon as + 1. The reference sequence for H2AFX used NC_000011.10, and for MRE11 NC_000011.9.
Statistical analysis
All statistical analysis was undertaken using GraphPad Prism 5.0 software (GraphPad, La Jolla, CA, USA). The genotype frequencies of each SNP were tested for deviation from the Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium (HWE) amongst the controls. This was done by comparing the observed genotype frequencies with the expected frequencies using a Chi-squared test. The ORs and 95% CIs were calculated to assess BC risk. We considered P < 0.05 to be significant for all analyses. P values were corrected using Benjamini-Hochberg adjustment. Linkage disequilibrium (LD) measures (Lewontin’s D’ and the r2 coefficient) between SNPs were calculated using Haploview 4.2 software (Daly Lab, USA). Haplotype frequencies were compared among patients and controls (using the Chi-squared test). The statistical power analyses were determined using free available Power and Sample Size Calculator.
Cumulative genetic risk score
SNPs showing significant association with BC were included in the cumulative genetic risk score (CGRS) analysis. Genotypes were coded as 0, 1 or 2, indicating the number of risk alleles in the genotype. Both unweighted (uwCGRS) and weighted (wCGRS) CGRS were calculated. In an unweighted approach, coded genotypes were counted to create a CGRS (therefore, the range of possible scores for three SNPs was 0 to 6). In a weighted approach, all the scores of the coded genotypes were multiplied by the log(OR) estimated for each risk allele in the current study. A weighted risk score is the sum of the multiplied results for each SNP and scaled by a factor of 3/∑wi, where wi = log(OR) (the logarithm of the odds ratio) for the ith SNP and i = 3 [13]. The effect of unweighted and weighted CGRSs on BC was calculated using logistic regression analysis. A t-test was applied to compare the average and mode values of uwCGRS and wCGRS between the BC and control groups.
Results
ATM variants in BC patients
In the group studied, we found six changes (five in the BC patients and two in the control group) in the functional domain of the ATM gene (c.6067G > A, c.6095G > A (twice), c.8187A > T, c.8314G > A, c.6083A > G and c.8787-55C > T). In the BC cases, three were known mutations: c.6095G > A, c.8187A > T and c.6067G > A. The patient with the c.6067G > A mutation was also a carrier of the NBN Ile171Val mutation. Moreover, c.8787-55C > T was found in a homozygous state. We detected two mutations in the control group: c.6095G > A and c.8314G > A.Deleterious consequences of all detected changes were scored using the following tools: SIFT, PolyPhen2 and MutationTaster Phylop. All these algorithms estimate the pathogenic effects of SNPs on protein in different ways. SIFT calculates score based on multiple sequence alignments. PolyPhen2 predicts the possible effects using multiple sequence alignments, 3D protein structures and residue contact information from secondary structure. Mutation taster Phylop evaluates disease-causing potential of sequence alterations comprising many aspects: evolutionary conservation, splice-site changes, loss of protein features and changes that might affect the amount of mRNA. The pathogenic effects on ATM were confirmed if more than two analysis indicated damaging consequences. The details are presented in Table 2.
SIFT algorithm ranges from 0 to 1. The amino acid substitution is predicted damaging is the score is ≤0.05, and tolerated if the score is > 0.05; PolyPhen 2 algorithm ranges from 0 to 1. possibly damaging and probably damaging (> 0.5) or benign (< 0.5); Mutation taster Phylop algorithm evaluates disease-causing potential of sequence alterations comprising evolutionary conservation, splice-site changes, loss of protein features and changes that might affect the amount of mRNA.
H2AFX and MRE11 genotype and allele distributions among patients and controls
The genotype and allele frequencies are summarized in Tables 3 and 4. The observed genotype frequencies of the six polymorphisms referred to above were all in agreement with the HWE in the control subjects (the P values for the H2AFX HWE were as follows: 0.32, 0.82, 0.08 and 0.72; for the MRE11 HWE, the P values were: 0.84 and 0.59). For the H2AFX polymorphisms, the logistic regression analysis revealed that the rs7759 GG and rs8551 TT were significantly increased among breast cancer patients compared to the rs7759 AA and rs8551 CC genotypes, respectively (rs7759 GG versus AG: adjusted OR = 1.94, 95% CI 1.14 to 3.28; P = 0.042, after Benjamini-Hochberg correction; rs8551 CC versus TT, OR = 1.82, 95% CI 1.18 to 2.80; P = 0.034, after Benjamini-Hochberg correction). The significant association was also found between the H2AFX rs7759 polymorphism and cancer risk under the heterozygous co-dominant model (AA versus AG): OR = 1.73, 95% CI 1.28 to 2.33; P = 0.024, after Benjamini-Hochberg correction and under the dominant genetic model (AA versus AG + GG): OR = 1.76, 95% CI 1.32 to 2.34; P = 0.0016, after Benjamini-Hochberg correction. The G allele at rs7759 was significantly more prevalent in BC cases compared to the controls (OR = 1.47, 95% CI 1.19 to 1.82; P = 0.0018, after Benjamini-Hochberg correction). Otherwise, there were no differences at rs8551 under the dominant genetic model (CC versus CT + TT): OR = 1.37, 95% CI 1.021 to 1.83; P = 0.0357, or under the heterozygous co-dominant model (CC versus CT): OR = 1.26, 95% CI 0.93 to 1.71; P = 0.14. We observed that the frequency of the T allele of rs8551 was higher in BC patients than in the controls (OR = 1.33, 95% CI 1.09 to 1.64; P = 0.018, after Benjamini-Hochberg correction). There were no differences in the occurrences of the TC, CC and TC + CC genotypes at rs643788 and the CT, TT and CT + TT genotypes at rs2509049 between the BC cases and the controls. On the other hand, the T allele in rs2509049 was significantly higher in BC patients compared to controls: OR = 1.3, 95% CI 1.06 to 1.59; P = 0.024, after Benjamini-Hochberg correction. For the two MRE11 variants, there were no statistically significant differences in genotype and allele frequencies between the BC patients and the controls at rs1061956 or rs2155209.
Frequency of H2AFX promoter haplotypes and risk of breast cancer
To determine the combined effects of the four promoter H2AFX SNPs, we generated haplotypes based on the observed genotypes (Fig. 1). For H2AFX SNPs, the construction of haplotypes revealed the presence of seven haplotypes in BC patients and eight haplotypes in the control group. In both groups, the most frequent H2AFX haplotype was CACC, without any risk variant allele (54.4% in BC patients and 61.4% in the control group). We also observed haplotypes that only presented in particular groups: TGTC in BC cases and TGCT and CATC in the control group. This observation could be related to the small size of the study group. Haplotypes with a frequency lower than 1% were not considered for further analysis. Haplotypes are presented in Table 5. When the CACC haplotype was used as the reference, CACT haplotype was associated with an increased risk of breast cancer. The difference in the frequency distribution of haplotype between the BC cases and controls was statistically significant (P < 0.0001 for CACT: OR = 27.29, 95% CI 3.56 to 209.5).
Cumulative genetic risk score
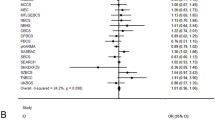
All H2AFX variants that showed a significant association with BC were included in the CGRS analysis. The risk alleles were defined as G for rs7759 and T for rs8551 and rs2509049. The average (± standard deviation [SD]) of the cumulative risk scores among the two groups studied were similar (for BC 2.37 ± 2.06 and for the control group 2.01 ± 1.88), although mode values were different for the BC and control groups, at 3 and 0 respectively. Individuals were stratified into three groups according to the number of risk alleles: carrying ≤ two (reference group), three, and ≥ four alleles. The risk of BC increased with the number of alleles and was statistically significant for three alleles (P = 0.019) and ≥ four alleles (P = 0.014) compared to ≤ two risk alleles. ORs (95% CI) for carriers of three and ≥ four risk alleles were 1.46 (1.06 to 2.01) and 1.71 (1.11 to 2.62), respectively (Fig. 2). The ORs calculated in unweighted and weighted CGRS analysis were similar, which is probably connected to the low number of risk alleles and small sample size. We also compared a clinical data between patients with high cumulative genetic risk score (≥4 risk alleles) and all BC patients. The detailed clinical parameters of BC patients with high cumulative genetic risk score (≥4 risk alleles) are shown in Table 6.
Statistical power analysis
The post-hoc analysis revealed that the statistical power of our study for analyses of the differences in distribution of alleles at loci rs7759, rs8551 and rs2509049 (OR: 1.3 to 1.47 for the three H2AFX SNPs with a frequency of 0.28 to 0.35) between BC patients and controls ranged between 71 and 94%. This means that the study had enough power to detect an association of the H2AFX gene in BC group, in the case-control analysis.
Discussion
Our previous studies focused on the hypothesis that M/R/N gene polymorphisms are associated with the risk of different cancers. We showed that the germline p.Ile171Val mutation in NBN, one of the M/R/N genes, may be considered a risk factor in the development of solid malignant tumors, including breast cancer, larynx and colorectal cancer or acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) [14,15,16,17]. Heterozygous carriers of the NBN c.657del5 mutation have an increased risk of malignant tumor development, especially of breast, prostate, colon and rectal cancers [18]. We also demonstrated that RAD50 gene mutations are not a risk factor of familial and sporadic breast cancer in the Polish population [19].
In this case-control study, we investigated the relationships between other variants in ATM, H2AFX and MRE11 genes and risk of breast cancer.
It has been shown that heterozygous ATM mutations cause increased risk of malignancy. Female relatives of ataxia-telangiectasia cases have increased risk of breast cancer [20, 21]. Moreover, numerous epidemiological studies have indicated the contribution of ATM variants to breast cancer [22,23,24,25,26]. A few recurring mutations in the ATM gene have been detected in Polish ataxia-telangiectasia patients. Three of the mutations, c.6095G > A, c.7630-2A > C and c.5932G > T, were the most frequent [27, 28]. A mutation at position 5932 creates a stop codon and changes a GAA codon, specifying glutamine, into a UAA. A second mutation at position 6095 is the substitution of the last nucleotide of exon 43 and changes guanine to adenine. This mutation results in the deletion of exon 43, caused by defective splicing. The last mutation alters the splice-acceptor site at − 2 from exon 54 and results in a deletion of this exon beginning at codon 2544. Therefore, in this study, we investigated the frequency and spectrum variants of the kinase domain in the ATM gene in a series of women with breast cancer.
There are a few studies regarding associations between breast cancer development and the ATM gene mutation in the Polish population. Bogdanova et al. showed that the c.5932G > T mutation is a predisposing breast cancer susceptibility variant in populations in Belarus, Russia, Ukraine and Poland [29]. In another study, two protein-truncating mutations in the ATM gene were found in two Polish probands with breast cancer without founder mutations in BRCA1, CHEK2 or NBS1. In that study, both patients with ATM mutations also had another truncating mutation, in the PALB2 and XRCC2 genes, respectively [30].
In the coding sequence of the ATM kinase domain in our study, we detected five mutations in the 830 samples in both the BC and control groups. One of the mutations, which presented in two BC patients, is the founder mutation (c.6095G > A) observed in Polish ataxia-telangiectasia patients. The rest of the detected variants were single nucleotide changes: c.6067G > A, p.Gly2023Arg; c.8314G > A, p.Gly2772Arg; c.8187A > T, p.Gln2729His; c.8787-55C > T and c.6083A > G; Q2028R. Using SIFT and PolyPhen and Mutation taster Phylop algorithms to predict the possible impact of the amino acid changes on ATM function, we confirmed that three of the missense variants (c.6067G > A, c.8187A > T, c.8314G > A) were classified as probably being damaging mutations/ disease causing. All these algorithms estimate a functional effect of SNPs in different ways. Accordingly, the pathogenic effects of ATM gene variants were confirmed if more than two analyses indicated demanding consequences.
However, one functional study indicated that c.8314G > A, p.Gly2772Arg is only a missense variant, which does not interfere with ATM kinase activity and radiosensitivity [31]. However, we cannot exclude the possibility that this mutation has an impact on the interaction between ATM and other proteins. Mutation c.6067G > A was observed in a patient from Brazil with sporadic breast cancer. In that case, the tumor was diagnosed at the age of 45 and was defined as clinical stage II [32]. In our case tumor was diagnosed at the age of 49 and the pathologic stage of tumor was defined as T2N1M0. The c.8187A > T variant was identified in one case of familial prostate cancer [33]. Moreover, our patient with c.6067G > A was also a carrier of the NBN p.Ile171Val mutation. It is difficult to conclude which changes are pathogenic because the p.Ile171Val variant has been connected with ALL, breast, larynx and colorectal cancer, and multiple primary tumors of the head and neck [34,35,36,37]. On the other hand, Dzikiewicz-Krawczyk et al. indicated that the heterozygous p.Ile171Val mutation does not significantly impair nibrin function and, therefore, p.Ile171Val does not play a crucial role in tumorigenesis [38].
In the above-mentioned results and in data previously presented by Cybulski et al., it was observed that some of the BC patients with detected ATM variants also had other changes in different genes involved in DNA damage repair [30]. This evidence suggests that, in some BC cases, the development of breast cancer can be linked with the accumulation of variants in DNA damage repair genes.
In addition, we found two polymorphic variants: c.6083A > G, Gln2028Arg and the intronic variant, c.8787-55C > T, which was found in a homozygous state. These two variants do not play a role in the development of breast cancer.
In the second part of our case-control study, six potentially functional SNPs were genotyped in two other genes, H2AFX and MRE11, connected with the DNA damage response signaling cascade. We selected SNPs in H2AFX and MRE11 genes based on observations from previous reports [39,40,41,42]. Four SNPs, rs643788, rs8551, rs7759 and rs2509049, are located in the far promoter region of the H2AFX gene -1654C > T, -1420C > T, −1187A > G, and -417C > T, respectively. Two of SNPs, rs8551 and rs7759, are also located in the 3′UTR of other gene, DPAGT1. While, the rs643788 causes an amino acid change in DPAGT1 protein. This substitution converts isoleucine into valine (I393V). The I393V variant was predicted as tolerated by SIFT and benign by PolyPhen2. DPAGT1 gene encodes an enzyme that catalyzes the first step in the dolichol-linked oligosaccharide pathway for glycoprotein biosynthesis. However, we did not find any evidences that I393V variant has pathogenic effect on DPAGT1 protein or is associated with an increased risk of cancer.
The MRE11 variants, rs1061956 (*442A > G) and rs2155209 (*2501A > G), are located in non-coding DNA sequences: the three prime untranslated region (3’UTR) of the gene. A functional study of polymorphisms in the H2AFX distal promoter showed a possible regulatory impact of two SNPs. Studies, based on gel shift assays, revealed that the rs643788 C allele disrupts a consensus sequence for a Yin Yang 1 transcription factor binding site. Moreover, the probe with rs2509049 C allele binds more strongly to an undefined protein complex than the rs2509049 T allele. On the other hand, it has been shown no differential binding by gel shift assay for rs8551 and rs7759 probes. It is not excluded that these SNPs may have an impact on binding only under specific conditions [43]. A few studies have indicated that SNPs in the promoter region of H2AFX are associated with cancer risk. Lu et al. found significant associations between minor variant genotypes of four SNPs (rs643788, rs8551, rs7759 and rs7350) and haplotypes with minor alleles in the promoter region of H2AFX and risk of breast cancer. Age at onset of breast cancer significantly decreased as the number of variant alleles in the H2AFX promoter region increased [44]. Furthermore, Novik et al. indicated the protective effect of the rs2509049 TT genotype in non-Hodgkin lymphoma [41].
Our findings suggest that there is a potential link between an increased risk of breast cancer and two H2AFX SNPs: rs8551 and rs7759. Likewise, comparing the allele frequency of rs7759, rs8551 and rs2509049 SNPs, we observed a statistically significant higher prevalence of the minor alleles in BC cases in comparison with the control group. However, the haplotype analysis of all the H2AFX polymorphisms studied showed no association of haplotypes with minor/major alleles with increased risk of breast cancer. We only observed significant differences in the distributions of haplotype consisting of CACT alleles between the BC cases and controls.
We also identified a cumulative effect of three SNPs in the H2AFX promoter locus. The risk of breast cancer escalated with an increased number of risk alleles. The comparison of clinical data between two groups, BC patients with high cumulative genetic risk score (≥4 risk alleles) and BC patients with < 4 risk alleles, showed that high CGRS is not correlated with age of diagnosis (53 vs 54 yrs.), T stage and histological subtype of breast cancer. We observed differences in tumor grade among two groups. In patients with high cumulative genetic risk score, grades of tumor were shifted towards moderate and poor differentiation (% of tumor grades G1 vs G2 + G3, 0% vs 64.8% in patients with high cumulative genetic risk score; 12.7% vs 41% in BC patients with < 4 risk alleles). We found increased numbers of patients with high cumulative genetic risk score with negative ER status (59.2% vs 24.6%) and PgR status (54.9% vs 25.4%), in comparison to all BC cases.
In this paper, two other SNPs from a subsequent gene involved in the DNA repair process, the MRE11 gene, were investigated. Choudhury et al. demonstrated the MRE11 3’UTR SNP to be associated with bladder cancer risk. However, the authors noticed a marginal increase in risk of bladder cancer for rs2155209 (OR = 1.54, 95% CI 1.13 to 2.08; P = 0.01) in individuals homozygous for the C allele compared to those carrying the common TT or TC genotype [42]. The carrier state of at least one rare 3’UTR variant of MRE11 was significantly associated with worse cancer-specific survival among patients with muscle-invasive bladder cancer [45]. In this report, there is a lack of association of MRE11 polymorphisms with breast cancer patients from Poland. Neither the rs2155209 nor the rs1061956 SNP showed statistically significant differences in the frequencies of genotypes.
Conclusion
The current data suggest that H2AFX variants are significantly associated with BC. The risk of BC increased with the number of the risk alleles (G of rs7759, T of rs8551 and T of rs2509049) carried. The above-reported sequence variants of the MRE11 gene may not constitute a risk factor of breast cancer in the Polish population. The contribution of mutations detected in the ATM gene to the development of breast cancer needs further detailed study.
Abbreviations
- ATM:
-
Ataxia-telangiectasia mutated
- CGRS:
-
Cumulative genetic risk score
- H2AFX:
-
H2A histone family, member X
- HRM:
-
High-resolution melting
- HWE:
-
Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium
- LD:
-
Linkage disequilibrium
- M/R/N:
-
Mre11/Rad50/NBN
- MRE11:
-
Homolog, double-strand break repair nuclease
- PCR-RFLP:
-
Polymerase chain reaction-restriction fragment length polymorphism
- SNP:
-
Single nucleotide polymorphism
References
Lavin MF. ATM and the Mre11 complex combine to recognize and signal DNA double-strand breaks. Oncogene. 2007;26(56):7749–58.
Bogdanova N, Helbig S, Dork T. Hereditary breast cancer: ever more pieces to the polygenic puzzle. Hered Cancer Clin Pract. 2013;11(1):12.
Gorski B, Jakubowska A, Huzarski T, Byrski T, Gronwald J, Grzybowska E, Mackiewicz A, Stawicka M, Bebenek M, Sorokin D, et al. A high proportion of founder BRCA1 mutations in polish breast cancer families. Int J Cancer. 2004;110(5):683–6.
Gorski B, Byrski T, Huzarski T, Jakubowska A, Menkiszak J, Gronwald J, Pluzanska A, Bebenek M, Fischer-Maliszewska L, Grzybowska E, et al. Founder mutations in the BRCA1 gene in polish families with breast-ovarian cancer. Am J Hum Genet. 2000;66(6):1963–8.
Bak A, Janiszewska H, Junkiert-Czarnecka A, Heise M, Pilarska-Deltow M, Laskowski R, Pasinska M, Haus O. A risk of breast cancer in women - carriers of constitutional CHEK2 gene mutations, originating from the north - Central Poland. Hered Cancer Clin Pract. 2014;12(1):10.
Cybulski C, Wokolorczyk D, Jakubowska A, Huzarski T, Byrski T, Gronwald J, Masojc B, Deebniak T, Gorski B, Blecharz P, et al. Risk of breast cancer in women with a CHEK2 mutation with and without a family history of breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2011;29(28):3747–52.
Cybulski C, Kluzniak W, Huzarski T, Wokolorczyk D, Kashyap A, Jakubowska A, Szwiec M, Byrski T, Debniak T, Gorski B, et al. Clinical outcomes in women with breast cancer and a PALB2 mutation: a prospective cohort analysis. Lancet Oncol. 2015;16(6):638–44.
Cybulski C, Carrot-Zhang J, Kluzniak W, Rivera B, Kashyap A, Wokolorczyk D, Giroux S, Nadaf J, Hamel N, Zhang S, et al. Germline RECQL mutations are associated with breast cancer susceptibility. Nat Genet. 2015;47(6):643–6.
Hearle N, Schumacher V, Menko FH, Olschwang S, Boardman LA, Gille JJ, Keller JJ, Westerman AM, Scott RJ, Lim W, et al. Frequency and spectrum of cancers in the Peutz-Jeghers syndrome. Clin Cancer Res. 2006;12(10):3209–15.
Ruijs MW, Verhoef S, Rookus MA, Pruntel R, van der Hout AH, Hogervorst FB, Kluijt I, Sijmons RH, Aalfs CM, Wagner A, et al. TP53 germline mutation testing in 180 families suspected of li-Fraumeni syndrome: mutation detection rate and relative frequency of cancers in different familial phenotypes. J Med Genet. 2010;47(6):421–8.
Couch FJ, Nathanson KL, Offit K. Two decades after BRCA: setting paradigms in personalized cancer care and prevention. Science. 2014;343(6178):1466–70.
Byrnes GB, Southey MC, Hopper JL. Are the so-called low penetrance breast cancer genes, ATM, BRIP1, PALB2 and CHEK2, high risk for women with strong family histories? Breast Cancer Res. 2008;10(3):208.
Zurawek M, Fichna M, Fichna P, Skowronska B, Dzikiewicz-Krawczyk A, Januszkiewicz D, Nowak J. Cumulative effect of IFIH1 variants and increased gene expression associated with type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2015;107(2):259–66.
Ziolkowska-Suchanek I, Mosor M, Wierzbicka M, Rydzanicz M, Baranowska M, Nowak J. The MRN protein complex genes: MRE11 and RAD50 and susceptibility to head and neck cancers. Mol Cancer. 2013;12(1):113.
Kaluzna EM, Rembowska J, Ziolkowska-Suchanek I, Swiatek-Koscielna B, Gabryel P, Dyszkiewicz W, Nowak JS. Heterozygous p.I171V mutation of the NBN gene as a risk factor for lung cancer development. Oncol Lett. 2015;10(5):3300–4.
Mosor M, Ziolkowska I, Pernak-Schwarz M, Januszkiewicz-Lewandowska D, Nowak J. Association of the heterozygous germline I171V mutation of the NBS1 gene with childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Leukemia. 2006;20(8):1454–6.
Nowak J, Mosor M, Ziolkowska I, Wierzbicka M, Pernak-Schwarz M, Przyborska M, Roznowski K, Plawski A, Slomski R, Januszkiewicz D. Heterozygous carriers of the I171V mutation of the NBS1 gene have a significantly increased risk of solid malignant tumours. Eur J Cancer. 2008;44(4):627–30.
Ziolkowska I, Mosor M, Nowak J. Regional distribution of heterozygous 657del5 mutation carriers of the NBS1 gene in Wielkopolska province (Poland). J Appl Genet. 2006;47(3):269–72.
Mosor M, Ziolkowska-Suchanek I, Roznowski K, Baranowska M, Januszkiewicz-Lewandowska D, Nowak J. RAD50 gene mutations are not likely a risk factor for breast cancer in Poland. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2010;123(2):607–9.
Swift M, Morrell D, Massey RB, Chase CL. Incidence of cancer in 161 families affected by ataxia-telangiectasia. N Engl J Med. 1991;325(26):1831–6.
Thompson D, Duedal S, Kirner J, McGuffog L, Last J, Reiman A, Byrd P, Taylor M, Easton DF. Cancer risks and mortality in heterozygous ATM mutation carriers. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2005;97(11):813–22.
Renwick A, Thompson D, Seal S, Kelly P, Chagtai T, Ahmed M, North B, Jayatilake H, Barfoot R, Spanova K, et al. ATM mutations that cause ataxia-telangiectasia are breast cancer susceptibility alleles. Nat Genet. 2006;38(8):873–5.
Broeks A, Braaf LM, Huseinovic A, Schmidt MK, Russell NS, van Leeuwen FE, Hogervorst FB. Van 't veer LJ: the spectrum of ATM missense variants and their contribution to contralateral breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2008;107(2):243–8.
Goldgar DE, Healey S, Dowty JG, Da Silva L, Chen X, Spurdle AB, Terry MB, Daly MJ, Buys SM, Southey MC, et al. Rare variants in the ATM gene and risk of breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. 2011;13(4):R73.
Bernstein JL, Haile RW, Stovall M, Boice JD Jr, Shore RE, Langholz B, Thomas DC, Bernstein L, Lynch CF, Olsen JH, et al. Radiation exposure, the ATM gene, and contralateral breast cancer in the women's environmental cancer and radiation epidemiology study. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2010;102(7):475–83.
Gonzalez-Hormazabal P, Bravo T, Blanco R, Valenzuela CY, Gomez F, Waugh E, Peralta O, Ortuzar W, Reyes JM, Jara L. Association of common ATM variants with familial breast cancer in a south American population. BMC Cancer. 2008;8:117.
Podralska MJ, Stembalska A, Slezak R, Lewandowicz-Uszynska A, Pietrucha B, Koltan S, Wigowska-Sowinska J, Pilch J, Mosor M, Ziolkowska-Suchanek I, et al. Ten new ATM alterations in polish patients with ataxia-telangiectasia. Mol Genet Genomic Med. 2014;2(6):504–11.
Mitui M, Bernatowska E, Pietrucha B, Piotrowska-Jastrzebska J, Eng L, Nahas S, Teraoka S, Sholty G, Purayidom A, Concannon P, et al. ATM gene founder haplotypes and associated mutations in polish families with ataxia-telangiectasia. Ann Hum Genet. 2005;69(Pt 6):657–64.
Bogdanova N, Cybulski C, Bermisheva M, Datsyuk I, Yamini P, Hillemanns P, Antonenkova NN, Khusnutdinova E, Lubinski J, Dork T. A nonsense mutation (E1978X) in the ATM gene is associated with breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2009;118(1):207–11.
Cybulski C, Lubinski J, Wokolorczyk D, Kuzniak W, Kashyap A, Sopik V, Huzarski T, Gronwald J, Byrski T, Szwiec M, et al. Mutations predisposing to breast cancer in 12 candidate genes in breast cancer patients from Poland. Clin Genet. 2015;88(4):366–70.
Scott SP, Bendix R, Chen P, Clark R, Dork T, Lavin MF. Missense mutations but not allelic variants alter the function of ATM by dominant interference in patients with breast cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002;99(2):925–30.
Mangone FR, Miracca EC, Feilotter HE, Mulligan LM, Nagai MA. ATM gene mutations in sporadic breast cancer patients from Brazil. Spring. 2015;4:23.
Leongamornlert D, Saunders E, Dadaev T, Tymrakiewicz M, Goh C, Jugurnauth-Little S, Kozarewa I, Fenwick K, Assiotis I, Barrowdale D, et al. Frequent germline deleterious mutations in DNA repair genes in familial prostate cancer cases are associated with advanced disease. Br J Cancer. 2014;110(6):1663–72.
Roznowski K, Januszkiewicz-Lewandowska D, Mosor M, Pernak M, Litwiniuk M, Nowak J. I171V germline mutation in the NBS1 gene significantly increases risk of breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2008;110(2):343–8.
Ziolkowska I, Mosor M, Wierzbicka M, Rydzanicz M, Pernak-Schwarz M, Nowak J. Increased risk of larynx cancer in heterozygous carriers of the I171V mutation of the NBS1 gene. Cancer Sci. 2007;98(11):1701–5.
Nowak J, Mosor M, Nowicka K, Rembowska J, Januszkiewicz D. Is the NBN gene mutation I171V a potential risk factor for malignant solid tumors in children? J Pediatr Hematol Oncol. 2011;33(6):e248–9.
Cybulski C, Gorski B, Debniak T, Gliniewicz B, Mierzejewski M, Masojc B, Jakubowska A, Matyjasik J, Zlowocka E, Sikorski A, et al. NBS1 is a prostate cancer susceptibility gene. Cancer Res. 2004;64(4):1215–9.
Dzikiewicz-Krawczyk A, Mosor M, Januszkiewicz D, Nowak J. Impact of heterozygous c.657-661del, p.I171V and p.R215W mutations in NBN on nibrin functions. Mutagenesis. 2012;27(3):337–43.
Fan W, Zhou K, Zhao Y, Wu W, Chen H, Jin L, Chen G, Shi J, Wei Q, Zhang T, et al. Possible association between genetic variants in the H2AFX promoter region and risk of adult glioma in a Chinese Han population. J Neuro-Oncol. 2011;105(2):211–8.
Srivastava N, Gochhait S, de Boer P, Bamezai RN. Role of H2AX in DNA damage response and human cancers. Mutat Res. 2009;681(2–3):180–8.
Novik KL, Spinelli JJ, Macarthur AC, Shumansky K, Sipahimalani P, Leach S, Lai A, Connors JM, Gascoyne RD, Gallagher RP, et al. Genetic variation in H2AFX contributes to risk of non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Cancer Epidemiol Biomark Prev. 2007;16(6):1098–106.
Choudhury A, Elliott F, Iles MM, Churchman M, Bristow RG, Bishop DT, Kiltie AE. Analysis of variants in DNA damage signalling genes in bladder cancer. BMC Med Genet. 2008;9:69.
Bretherick KL, Leach S, Brooks-Wilson AR. Functional characterization of genetic polymorphisms in the H2AFX distal promoter. Mutat Res. 2014;766-767:37–43.
Lu J, Wei Q, Bondy ML, Brewster AM, Bevers TB, Yu TK, Buchholz TA, Meric-Bernstam F, Hunt KK, Singletary SE, et al. Genetic variants in the H2AFX promoter region are associated with risk of sporadic breast cancer in non-Hispanic white women aged <or=55 years. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2008;110(2):357–66.
Teo MT, Dyrskjot L, Nsengimana J, Buchwald C, Snowden H, Morgan J, Jensen JB, Knowles MA, Taylor G, Barrett JH, et al. Next-generation sequencing identifies germline MRE11A variants as markers of radiotherapy outcomes in muscle-invasive bladder cancer. Ann Oncol. 2014;25(4):877–83.
Acknowledgments
We are most grateful to all the subjects who participated in this study.
Availability of data and materials
All data generated or analysed during this study are included in this published article and its supplementary information files. Genotyping data described in the manuscript are available from the authors upon request.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conception and design: MP, IZS, MM. Performance of experiments: MP, IZS, MM. Acquisition of DNA samples: AS, KP, MM. Analysis and interpretation of data: MP, MŻ, ADK. Writing, review, and/or revision of the manuscript: MP, IZS, MM, MŻ. Study supervision: JN, RS. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The study was conducted with the approval of the Central Ethical Committee of the Ministry of Health in Poland, in accordance with the tenets of the Declaration of Helsinki (Decision no. 949/16). All patients signed informed consent forms.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated.
About this article
Cite this article
Podralska, M., Ziółkowska-Suchanek, I., Żurawek, M. et al. Genetic variants in ATM, H2AFX and MRE11 genes and susceptibility to breast cancer in the polish population. BMC Cancer 18, 452 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12885-018-4360-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12885-018-4360-3