Abstract
Background
Gordonia terrae is a rare cause of clinical infections, with only 23 reported cases. We report the first case of peritoneal dialysis-related peritonitis caused by Gordonia terrae in mainland China.
Case presentation
A 52-year-old man developed peritoneal dialysis-related peritonitis and received preliminary antibiotic treatment. After claiming that his symptoms had been resolved, the patient insisted on being discharged (despite our recommendations) and did not receive continued treatment after leaving the hospital. A telephone follow-up with the patient’s relatives revealed that the patient died 3 months later. Routine testing did not identify the bacterial strain responsible for the infection, although matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry identified the strain as Gordonia rubropertincta. However, a 16S rRNA sequence analysis using an isolate from the peritoneal fluid culture revealed that the responsible strain was actually Gordonia terrae. Similar to this case, all previously reported cases have involved a delayed diagnosis and initial treatment failure, and the definitive diagnosis required a 16S rRNA sequence analysis. Changes from an inappropriate antibiotic therapy to an appropriate one have relied on microbiological testing and were performed 7–32 days after the initial treatment.
Conclusions
The findings from our case and the previously reported cases indicate that peritoneal dialysis-related peritonitis caused by Gordonia terrae can be difficult to identify and treat. It may be especially challenging to diagnose these cases in countries with limited diagnostic resources.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Gordonia terrae is a gram-positive, coccoid to bacillary, weakly acid-fast bacterium that was initially isolated from soil and is a rare cause of clinical infection. Unfortunately, the Gordonia spp. are not identifiable using Gram staining of clinical specimens, and definitive identification may require the use of a 16S rRNA sequence analysis. We report the first case of peritoneal dialysis-related peritonitis caused by Gordonia terrae in mainland China. Matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry initially identified the responsible strain as Gordonia rubropertincta, although definitive identification was achieved using a 16S rRNA sequence analysis. To the best of our knowledge, only 23 similar cases have been reported in the English literature (Table 1).
Case presentation
Medical history of the patient
A 52-year-old man was diagnosed with uraemia at a local hospital in February 2013. He was treated using haemodialysis while in the hospital and with peritoneal dialysis after discharge. His serum creatinine concentration was 1000 μmol/L, showing two reduced renal volume. The patient was also diagnosed with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, grade 3 hypertension (high-risk), and cardiac insufficiency. Starting in June 2015, the patient reported experiencing epigastric pain during the peritoneal dialysis, which was exacerbated during inspiration, relieved during dialysis fluid removal, and absent during non-dialysis periods. The dialysis fluids were smooth and accompanied by floccule.
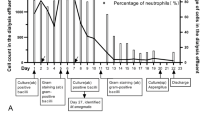
On November 17, 2015, the patient experienced bloody ascites, swelling of both lower limbs, and asthma after playing sports and was admitted to our hospital. A physical examination revealed a body temperature of 38.0 °C, a respiratory rate of 22 breaths/min, a pulse of 110 beats/min, and blood pressure of 130/63 mmHg. The patient showed clear consciousness, but he exhibited facial signs of chronic anaemia, distension of the jugular vein, barrel chest, mild swelling of both lower limbs, wheezing in both lungs, an expanded heart boundary on two sides, abdominal wall tension, positive pressure at the navel, and no rebound tenderness. Laboratory testing revealed a white blood cell count of 3.4 × 109/L, a procalcitonin level of 2.69 ng/mL, a B-type natriuretic peptide level of 460 pg/mL, a prothrombin time of 14.5 s, and a D-dimer level of 2,127 ng/mL. Routine testing of the peritoneal fluid revealed a slightly muddy appearance with a specific gravity of 1.018, weak positive results in the Rivalta test, a white blood cell count of 510 × 106/L (mononuclear cells: 40%, multinuclear cells: 60%), a red blood cell count of 2,980 × 106/L, and positive results for coagulability.
The patient’s peritoneal fluid was submitted for culturing, and the patient received initial treatment using intravenous cefazolin, which was changed to intraperitoneal ceftazidime and vancomycin on November 19. On November 23, the patient’s body temperature was 36.5 °C. He reported that his chest congestion and stomach ache were relieved, and the dialysis fluid appeared smooth and clear. The patient and his relatives insisted that he be discharged, despite our informing them that the culture results were incomplete, the infection might not be controlled, and the patient might experience recurrence of the peritonitis and septicopyaemia. Unfortunately, a telephone follow-up with the patient’s relatives revealed that he had not received continued treatment after his discharge and had died in February 2016. The cause of death was multiorgan failure.
Bacteria culture and identification
On November 19, 2015, the patient’s peritoneal fluid was aseptically collected into aerobic blood culture bottles (BD, USA) and sent to a clinical laboratory, where it was cultured using the BactecTM 9120 blood culture system (BD, USA). After culturing for 51.76 h, a positive result was observed, and the culture fluid was directly smeared to identify gram-positive bacilli. The fluid was also transferred to blood agar (Zhengzhou Autobio) and chocolate agar plates (Tianjin Jinzhang), which were incubated at 35 °C with 5% CO2. There were no visible colonies after 24 h of culturing, although both plates exhibited small light-brown colonies after 48 h of culturing. The colonies were positive in the catalase test. After 72 h on the chocolate agar plate and 6 days on the blood agar plate, the colonies were dry, cracked, elevated, and light brown in colour (Figs. 1 and 2). Figures 3 and 4 show that the colonies were confirmed to be gram-positive bacilli with positive, weak acid-fast staining. Additional testing using the MicrolexLT/SH mass spectrometer (Bruker) identified the strain as G. rubropertincta with a score of 1.702. However, a 16S rRNA sequence analysis was also performed at the Shanghai Sangon Company, using the following primers: 27 F (5′-GAGTTTGATCCTGGCTCAG-3′) and 1492R (5′-AAGGAGGTGATCCAGCCGCA-3′) [1]. After Blast alignment, we observed that the bacteria were 99% similar to the sequence of G. terrae EY-T12 (GenBank: KR476419.1). The phylogenetic tree of the 20160601 isolate is shown in Fig. 5.
Antimicrobial susceptibility test
An antimicrobial susceptibility testing was performed using the E-test (Zhengzhou Autobio), in which in the McFarland and M-H plates (Tianjin Jinzhang) are adjusted to 0.5 and incubated at 35 °C with 5% CO2 for 48 h. The results from the patient described in this report and from those in previous studies are summarized in Table 2. The strains in the previous studies were also tested using the E-test after 48 h of incubation. The isolate from the present report was resistant to ceftazidime and susceptible to penicillin, ampicillin, amikacin, erythromycin, ceftriaxone, imipenem, gentamicin, and vancomycin.
Discussion
The Gordonia genus includes 29 species, including G. bronchialis, G. aichiensis, G. rubropertincta, G. sputi, and G. terrae, which are associated with human disease [2]. G. terrae is an aerobic bacillus that grows slowly (a culture time of >48 h is needed) and is most frequently identified in the environment. However, G. terrae also infects patients with reduced immune status and causes brain abscesses, duct-associated blood infections, and cholecystitis and nephrapostasis after transplantation [3–6]. Lai et al. retrospectively identified 7 G. terrae strains from among 15 Gordonia strains from 9 cases of infection at a Taiwanese university hospital (1997–2008), and all infected patients had a reduced immune status [7].
Unfortunately, Gordonia, Rhodococcus, Nocardia, and Mycobacterium are all actinomycetes and can easily be misidentified during smear microscopic analysis and biochemical testing. In addition, G. terrae can metabolize rhamnose and produce acid, but cannot metabolize raffinose, which may increase the likelihood of confusing it with Rhodococcus. Nocardia can generate aerial hyphae on blood agar plates and provide positive results during lysozyme resistance testing, while Mycobacterium might also be confused with G. terrae based on its production of mycolic acid during high-performance liquid chromatography [8]. Therefore, the definitive identification of these bacteria should be performed using 16S rRNA sequence analysis.
Peritoneal dialysis is the main therapy for patients with end-stage renal failure, although patients with a reduced immune status may easily experience peritonitis. A 15-year retrospective analysis of infectious peritonitis associated with peritoneal dialysis in China revealed that the identification rate of gram-positive bacilli increased from 0% during 1990–2000 to 5.6% during 2001–2005 [9]. In addition, four cases of peritoneal dialysis-related peritonitis involved bacilli found to be gram-positive on the third day of culturing, with 3 cases that involved G. terrae. However, identification of G. terrae took 7–32 days, and the antibiotics were subsequently changed from cefazolin to vancomycin [10]. In the present case, the patient’s peritoneal fluid was confirmed as being gram-positive after 51.76 h of culturing, although 15 days were required to complete the definitive identification of the bacteria, which prevented us from adjusting the patient’s antibiotic treatment because he had been discharged before we obtained the definitive identification. The mass spectrometry results correctly identified the isolate as Gordonia, although it incorrectly identified the species. Thus, although mass spectrometry is convenient and rapid, it may not be able to accurately identify rare bacterial strains. After we confirmed the isolate’s identity using 16S rRNA sequencing, we contacted the mass spectrometry engineer and reconstructed spectrograms for the species.
Interestingly, we have not found any evidence regarding the appropriate antibiotic therapy for Gordonia. Johnson et al. reported that G. terrae is sensitive to most antibiotics (including β-lactams, glycopeptides, and carbapenems), although the treatment course is too long for patients with peritonitis [11]. For example, the previous reports regarding G. terrae indicated that at least 3 weeks of vancomycin therapy were needed to prevent secondary infections. Therefore, clinicians should carefully consider the development of secondary peritonitis in patients with peritoneal dialysis caused by G. terrae. In addition, efforts should be made to rapidly and definitively identify the responsible strain in order to facilitate effective therapy.
Conclusions
The present case is the first report of an peritoneal dialysis-related peritonitis caused by Gordonia terrae in mainland China. The findings from our case and the previously reported cases indicate that peritoneal dialysis-related peritonitis caused by Gordonia terrae can be difficult to identify and treat. It may be especially challenging to diagnose these cases in countries with limited diagnostic resources. In addition, resistance to the antimicrobial agents were observed in isolates from the present patient as well as previous reports.
References
Suzuki MT, Giovannoni SJ. Bias caused by template annealing in the amplification of mixtures of 16S rRNA genes by PCR. Appl Envron Microbiol. 1996;62:625–30.
Blanc V, Dalle M, Markarian A, Debunne MV, Duplay E, Rodriguez-Nava V, et al. Gordonia terrae: a difficult-to-diagnose emerging pathogen? J Clin Microbiol. 2007;45:1076–7.
Drancourt M, McNeil MM, Brown JM, Lasker BA, Maurin M, Choux M, et al. Brain abscess due to Gordona terrae in an immunocompromised child: case report and review of infections caused by G. terrae. Clin Infect Dis. 1994;19:258–62.
Pham AS, Dé I, Rolston KV, Tarrand JJ, Han XY. Catheter-related bacteremia caused by the nocardioform actinomycete Gordonia terrae. Clin Infect Dis. 2003;36:524–7.
Gil-Sande E, Brun-Otero M, Campo-Cerecedo F, Esteban E, Aguilar L, García-de-Lomas J. Etiological misidentification by routine biochemical tests of bacteremia caused by Gordonia terrae infection in the course of an episode of acute cholecystitis. J Clin Microbiol. 2006;44:2645–7.
Nicodemo AC, Odongo FC, Doi AM, Sampaio JL. Gordonia terrae kidney graft abscess in a renal transplant patient. Transpl Infect Dis. 2014;16:681–6.
Lai CC, Wang CY, Liu CY, Tan CK, Lin SH, Liao CH, et al. Infections caused by Gordonia species at a medical centre in Taiwan, 1997 to 2008. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2010;16:1448–53.
Imran M, Livesley P, Bell G, Pai P, Neal T, Anijeet H. Gordona: A rare cause of peritoneal dialysis peritonitis. Perit Dial Int. 2012;32:344–6.
Guo Q-Y, Chen L, Yang X, Yang N-S, Feng M, Jiang Z-P, et al. Characteristics of infecting pathogens and their antimicrobial susceptibilities in peritoneal dialysis related peritollitis: report of related episodes in a medical center over fifteen years. Chin J Nephrol. 2006;12:719–24.
Ma TK, Chow KM, Kwan BC, Lee KP, Leung CB, Li PK, et al. Peritoneal-dialysis related peritonitis caused by Gordonia species: report of four cases and literature review. Nephrology. 2014;19:379–83.
Johnson JA, Onderdonk AB, Cosimi LA, Yawetz S, Lasker BA, Bolcen SJ, et al. Gordonia bronchialis bacteremia and pleural infection: case report and review of the literature. J Clin Microbiol. 2011;49:1662–6.
Drancourt M, Pelletier J, Cherif AA, Raoult D. Gordona terrae central nervous system infection in an immunocompetent patient. J Clin Microbiol. 1997;35:379–82.
Bakker XR, Spauwen PH, Dolmans WM. Mycetoma of the hand caused by Gordona terrae: a case report. J Hand Surg (Br). 2004;29:188–90.
Grisold AJ, Roll P, Hoenigl M, Feierl G, Vicenzi-Moser R, Marth E. Isolation of Gordonia terrae from a patient with catheter-related bacteraemia. J Med Microbiol. 2007;56:1687–8.
Zardawi IM, Jones F, Clark DA, Holland J. Gordonia terrae-induced suppurative granulomatous mastitis following nipple piercing. Pathology. 2004;36:275–8.
Zampella JG, Kwatra SG, Kazi N, Aguh C. Madura foot caused by Gordonia terrae misdiagnosed as Nocardia. Australas J Dermatol. 2016;7.
Aoyama K, Kang Y, Yazawa K, Gonoi T, Kamei K, Mikami Y. Characterization of clinical isolates of Gordonia species in Japanese clinical samples during 1998–2008. Mycopathologia. 2009;168:175–8.
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Funding
Not applicable.
Availability of data and materials
The near-complete length GenBank 16S rRNA sequences for Gordonia terrae, which support the conclusions of this report, are included as Additional file 1.
Authors’ contributions
CRH and YY conceived and designed the experiments. ZYL and CRH collected the information regarding the case and contributed to the data acquisition, analysis, and interpretation. CRH, ZYL, and YY wrote and revised the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Consent for publication
Written informed consent was obtained from the patient’s family member for publication of this case report and the accompanying images.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The experimental protocols were approved by the institutional review board of Shanxi Dayi Hospital.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional file
Additional file 1:
16S rRNA sequence analysis. (DOCX 58 kb)
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated.
About this article
Cite this article
Hou, C., Yang, Y. & Li, Z. A Chinese patient with peritoneal dialysis-related peritonitis caused by Gordonia terrae: a case report. BMC Infect Dis 17, 179 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12879-017-2283-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12879-017-2283-2