Abstract
Background
Eucommia ulmoides leaves have high medicinal and economic value as a dual-purpose substance for medicine and food. Employing leaves from 13 natural populations of Eucommia ulmoides as research objects, this study reveals the variation patterns of intra-specific and inter-specific trait variation and explores the response of leaf characteristics to geographical and climatic changes, aiming to provide a scientific basis for the efficient utilization of leaf resources and the breeding of superior varieties.
Results
Descriptive statistical analysis and nested analysis of variance showed significant differences in 11 leaf traits of Eucommia ulmoides inter-populations and intra-populations, with an average coefficient of variation of 17.45%. The coefficient of variation for average leaf phenotypic traits is 20.77%, and the leaf phenotypic variation is mainly from the variation intra-populations. Principal component analysis reveals that the cumulative contribution rate of the top three principal components which mainly contributed to the phenotypic variation of Eucommia ulmoides leaves reached 74.98%, which could be sorted into size traits (34.57%), color traits (25.82%) and shape traits (14.58%). In addition, correlation analysis expresses there is a specific co-variation pattern among leaf traits, with a strong connection between shape, size, and color traits. Geographic and climatic distances are significantly correlated, and mantel test and correlation analysis indicate that leaf traits of Eucommia ulmoides are mainly influenced by altitude. With the increase of altitude, the leaves become smaller. Partial correlation analysis shows that after controlling climate factors, the correlation between some characters and geographical factors disappears significantly. Temperature and precipitation have a great influence on the variation of leaf phenotypic traits, and the larger the leaves are in areas with high temperature and heavy rainfall.
Conclusions
These findings contribute to a further understanding of the leaf morphological characteristics of Eucommia ulmoides and the extent to which the environment influences leaf trait variation. They can provide a scientific basis for the protection and application of Eucommia ulmoides leaf resources in the future.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Plant phenotypic traits not only encompass morphological features such as those of leaves, fruits, and seeds but also serve as a direct indicator of genetic variation in plants [1, 2]. Leaves act as vital gateways for water and gas exchange between plants and the external environment. They constitute the primary organs for photosynthesis and transpiration, exerting significant influence on ecological material production, global carbon cycling, and water cycling [3]. Leaf phenotypic traits represent the most intuitive classification characteristics in plant taxonomy, also reflecting a plant’s adaptability to changing growth environments [4]. Variations in leaf morphology directly impact the physiological and biochemical processes in plants, closely correlating with a plant’s efficiency in acquiring and utilizing resources [5]. For instance, elliptical leaves exhibit higher photosynthetic and water use efficiency than lanceolate leaves [6, 7]. Additionally, leaf size can indicate the content of active components within the leaf [8, 9]. Variations in leaf phenotypes not only serve as a crucial metric for gauging genotypic variations but also reveal the patterns and underlying mechanisms of this variation. This lays a foundation for the genetic improvement, introduction, and domestication of plants [10].
Variation in leaf phenotypes is a manifestation of plants adapting to different habitats under selection pressures, reflecting the survival strategies evolved by plants in response to changing environments [11]. In recent years, with increasing attention to global climate change, research on plant leaf traits in response to the environment has gradually expanded [12, 13]. Studies have shown that factors such as temperature, light intensity, precipitation, latitude, longitude, altitude, and soil type have a significant impact on leaf traits [14, 15]. For instance, in regions with warm temperatures, abundant precipitation, and no direct strong sunlight, leaves tend to be larger. Conversely, in cold regions with strong sunlight or in dry or nutrient-poor soils, leaves tend to be smaller to avoid overheating or reduce water loss [16,17,18]. Specific leaf dry weight can reflect the adaptive characteristics of plants in different habitats [19]. Harsh environmental conditions and increasing altitude lead to an increase in specific leaf dry weight, which is detrimental to the growth of plants or communities [20]. To date, research on leaf phenotypic traits has overlooked the importance of intra-species trait variation in community dynamics. The impact of intra-species trait variation on ecosystem function is significant and should not be underestimated [13]. Therefore, conducting a quantitative study on intra-species trait variation along environmental gradients can support the prediction of species responses to climate change and the influence of the environment on trait variation. This has important implications for the breeding of superior plant varieties, conservation of endangered plant resources, and protection of biodiversity [21].
Eucommia ulmoides (E. ulmoides) is a rare and endangered species endemic to China. Due to the presence of various active components in its leaves, bark, and gum, it has become an important economic and industrial raw material tree species in China [22]. The central production areas are located in northwestern Hunan, northern Guizhou, western Guizhou, and northwestern Hubei, among others, covering a wide range of environmental conditions [23]. In response to future climate change, the overall distribution area is shifting towards the northwest and higher latitudes [24]. Therefore, studying the intraspecific variation of Eucommia ulmoides leaves (EULs) can provide deeper insights into its phenotypic differentiation and ecological adaptation. However, current research on EULs mainly focuses on chemical composition [25, 26], pharmacological uses [27, 28], potential distribution predictions [29], and whole-genome association analysis [30], with very little attention to the phenotypic trait variation of EULs. Meng et al. found that 14 leaf phenotypic traits from the Eucommia germplasm resource database showed rich variation (4.57-20.68%) [31]. Wang et al., on the other hand, found higher levels of variation in five leaf phenotypic traits within natural Eucommia populations (20.96-49.00%). In addition, a correlation analysis between leaf phenotypic traits and three climatic factors revealed that annual average temperature and precipitation significantly influenced leaf size [32]. Furthermore, due to the similarity in active components and pharmacological effects between Eucommia leaves and bark, EULs have a wide range of applications [33]. Previous studies have found that the content of isoquercitrin is closely related to leaf length, leaf area, and leaf perimeter [34]. This provides a scientific basis for further research on leaf phenotypic variation and its response to the environment in natural Eucommia populations with richer phenotypic variation.
In this study, climate and geographic data were collected from 13 natural populations in the central production area of E. ulmoides, and 11 leaf phenotypic traits were measured for 134 trees. The aim was to investigate the variation in leaf traits and its mechanisms of adaptation to geographic and climatic factors. This study aims to reveal the patterns of variation in leaf phenotypic traits, providing a scientific basis for the selection of superior Eucommia resources, efficient utilization of leaf resources, and practical production.
Results
Leaf morphological variation
Scanning and morphological comparisons were performed on the leaf base, leaf tip, and leaf shape of 134 EULs. The results indicate that there is abundant variation in EULs (Fig. 1). The leaf base has five shapes: heart shape, round shape, truncate shape, cuneate shape and oblique shape (A1-A5). The leaf apex has five types: cuspidate, acute, acuminate, aristate and caudate (B1-B5). The leaf shape has eight types: lanceolate, ovate-lanceolate, ovate-oblanceolate, oblanceolate, round, ovate, oblong, and elliptical (C1-C8).
Leaf phenotypic variation
Descriptive statistical analysis was conducted on leaf traits (Table 1), and the results indicated that all measured traits exhibited varying degrees of variation. The coefficient of variation ranged from 9.00 to 30.88%, with an average of 17.45%. Among them, the chlorophyll reference value (CRV) showed the highest coefficient of variation (30.88%), followed by leaf area (LA) (26.73%) and specific leaf dry weight (SLDW) (20.94%). The lowest coefficient of variation was observed for the blue component of leaves (BC) (9.00%). The coefficient of variation for the 3 leaf colour traits, the red component of leaves (RC) (11.64%), BC (9.00%), and green component of leaves (GC) (13.89%) was lower than that for the other 8 leaf traits.
Overall phenotypic variation of Eucommia ulmoides leaves and differences in leaf traits among 13 natural populations
The nested analysis of variance results showed that the variation in the 11 leaf traits occurs in inter-populations and intra-populations (Table 2). Except for petiole length (PL) and length to width ratio of leaf (LTWR), which showed no significant differences in inter-populations, all other traits exhibited highly significant differences in both inter-populations and intra-populations (p < 0.01). Further multiple comparison analysis (Tables 3 and 4) indicated that the largest values for LA, maximum leaf width (LW), longest leaf length (LL), maximum leaf perimeter (LP), minimum LTWR, maximum SLDW, and highest CRV were observed in the population from Hunan. Among the populations, the Dayongqiao Sub-district (DYQ) population exhibited the widest leaves, with the highest values for LL (155.04 mm), LW (69.55 mm), LA (6242.52 mm2), and LP (436.23 mm). Conversely, the highest LTWR, shortest LL, smallest LP, and lightest leaf colour were observed in the population from Hubei. Specifically, the Hejia town (HJ) population had the shortest leaves (LL = 128.17 mm, LP = 346.56 mm, LA = 4512.37 mm2).
The variance components and phenotypic differentiation coefficients for the 11 leaf traits inter-populations and intra-populations were obtained through variance analysis (Table 2). The results indicate that the intra-population variance accounts for 46.58% of the total variance, while the inter-population variance accounts for 12.65% of the total variance. The phenotypic differentiation coefficient was 4.65-49.93%, with an average of 20.77%. Therefore, the leaf phenotypic diversity among the 13 natural populations of E. ulmoides is primarily attributed to intra-population variation. The trait with the highest phenotypic differentiation coefficient was GC, while the trait with the lowest coefficient was LTWR.
Different letters in the same column indicate significant difference at the 0.05 level. petiole length (PL), leaf length (LL), length to width ratio of leaf (LTWR), leaf width (LW), leaf area (LA), red component of leaf (RC). Lianghe town, Gansu (LH); Wufeng town, Hubei (WF); Hejia town, Hubei (HJ); Donggongsi town, Guizhou (DGS); Zhongshan town, Guizhou (ZS); Jiangya forest farm, Hunan (JYLC); Jinyan town, Hunan (JY); Reshi town, Hunan (RS); Miaoertan town, Hunan (MET); Qianling town, Hunan (QL); Zhexi town, Hunan (ZX); Lean town, Hunan (LA); Dayongqiao Sub-district, Hunan (DYQ).
Different letters in the same column indicate significant difference at the 0.05 level. blue component of leaf (BC), green component of leaf (GC), chlorophyll reference value (CRV), leaf perimeter (LP), specific leaf dry weight (SLDW). The full names corresponding to population abbreviations are the same as those in Table 3.
Principal component analysis of the 11 leaf traits
The principal component analysis (PCA) results indicate that the first three principal components have eigenvalues greater than 1, and together, they account for 74.98% of the total variation in the EULs traits (Table 5). This suggests that the first three principal components can explain a significant portion of the variation in the EULs traits. For the first principal component, traits such as LP (0.958), LA (0.957), LL (0.932), and LW (0.866) had relatively large positive eigenvectors. These traits are primarily associated with leaf size. For the second principal component, the positive eigenvectors for RC, GC, and BC were all higher than 0.9. These traits are primarily associated with leaf colour. For the third principal component, the positive eigenvector for the LTWR was the largest, indicating that it primarily reflected leaf shape. As shown in Fig. 2, the vector lengths of the means of the Reshi town, Hunan (RS), Jinyan town, Hunan (JY), Lean town, Hunan (LA), Zhexi town, Hunan (ZX), Jiangya forest farm, Hunan (JYLC), and Dayongqiao Sub-district, Hunan (DYQ) populations along the PC1 axis were relatively large. Among the populations, the DYQ population had the longest vector along the PC1 axis.
Correlations between leaf phenotypic traits
The correlation analysis of the 11 leaf traits (Fig. 3b) revealed that out of the 55 pairs of relationships examined, 18 pairs exhibited a very significant correlation (p ≤ 0.01), while 5 pairs showed a significant correlation (p ≤ 0.05). Among them, 6 traits related to leaf shape and size (LTWR, LL, LP, LW, LA, and PL), as well as 3 traits related to leaf colour (GC, RC, and BC), exhibited an extremely significant positive correlation. PL and LW show a significant positive correlation. LW and LTWR exhibited a highly significant negative correlation. SLDW was significantly negatively correlated with BC and GC.
Correlation between leaf traits and correlation between leaf traits and climate. a Correlations between 11 leaf traits and climatic factors. b Correlations among leaf traits. Green color represents negative correlation, orange color represents positive correlation, and the darker the color, the stronger the correlation
Effects of geographical factors on the phenotypic traits of leaves
The mantel test results indicated a significant correlation between altitude and leaf traits (p < 0.05), while latitude and longitude did not show significant correlations with the traits (Table 6). The correlation analysis revealed a significant positive correlation between longitude and various traits (LW, LA, SLDW, and LL). Latitude was significantly negatively correlated with LW, LA, RC, BC, and GC and significantly positively correlated with SLDW. Altitude exhibited a significant negative correlation with LW, LA, LP, LL, SLDW, and GC (Tables 7 and 8). Both the mantel test and correlation analysis results showed the predominant influence of altitude on Eucommia leaf traits.
Geographical distance showed a significant correlation with climatic distance (r = 0.78, p = 0.001). After controlling for climatic factors, some significant relationships between leaf traits and geographical factors disappeared (Tables 7 and 8). Regarding the relationships between latitude, longitude, and SLDW, a significant correlation persisted after controlling for the influence of precipitation. In the case of the relationships between altitude and leaf traits, after controlling for climatic factors, it was found that the significant correlations of SLDW, LL, and GC disappeared. However, after controlling for the influence of precipitation, a significant negative correlation with LW and LA was still observed. Furthermore, after controlling for the influence of temperature, a significant negative correlation with LP still existed.
Effects of climatic factors on leaf phenotypic traits
The mantel test results indicated significant correlations between climate and leaf traits (p < 0.01) (Table 6). The correlation analysis revealed that temperature and precipitation had a significant impact on leaf traits (Fig. 3a). For instance, LA, LP, LL, and LW decreased with an increase in mean diurnal range (BIO2) and isothermality (BIO3) but increased with an increase in annual mean temperature (BIO1), mean temperature of wettest quarter (BIO8), mean temperature of driest quarter (BIO9), precipitation of wettest quarter (BIO16), precipitation of warmest quarter (BIO18), and precipitation of coldest quarter (BIO19). RC and GC were positively correlated with BIO9, BIO16, BIO18, and BIO19. RC, GC, and BC were negatively correlated with BIO2 and BIO3. SLDW was positively correlated with temperature annual range (BIO7). Among individual climate factors, seven variables explained a significant portion of the leaf trait variation: BIO1, BIO2, BIO16, and BIO19 explained variation in seven leaf traits, while BIO3 and BIO9 explained variation in eight leaf traits.
Discussion
Leaf phenotypic variation
Studying the correlations between various leaf traits is beneficial for understanding the adaptive strategies of leaves in different environments [35]. In this study, traits characterizing leaf size, including LL, LTWR, LP, LA, LW, and PL, showed a significant positive correlation (Fig. 3b). As leaves grow larger, plants need to acquire more light energy, hence requiring longer petioles to reduce mutual shading within the individual [36]. However, both LW and LTWR exhibited a highly significant negative correlation while SLDW showed a significant negative correlation with BC and GC. These negative correlations reflect the trade-off strategies employed by plants in different environments [37].
The analysis of variation in eleven leaf phenotypic traits of E. ulmoides revealed coefficients of variation (CV) ranging from 9.00 to 30.88%, with an average of 17.45% (Table 1). These values are similar to those found in studies on Acer mono Maxim (18.07%) [38] and Davidiain volucrata (16.22%) [39]. Notably, in this study, we observed the highest CV for the CRV (30.88%), followed by leaf area (26.73%). This differs from the findings of Meng et al., where leaf area exhibited the highest CV (20.68%) and CRV showed the lowest CV (4.57%) [31]. Chlorophyll is a green pigment in plants, and its content directly influences photosynthesis [40]. The concentration of chlorophyll is primarily influenced by atmospheric and soil factors [41]. This variation in the CRV may be attributed to the more diverse natural habitats of the E. ulmoides populations studied here compared to those in the germplasm resource base. This increased habitat diversity likely contributed to the observed higher variation in the CRV.
In this study, rich variation was observed in traits representing leaf size (Table 1), which aligns with previous findings on leaf variation within natural populations of E. ulmoides [32]. Leaf size directly influences a plant’s ability to capture light and acquire carbon [42], and it can also reflect the content of active components within the leaf [8, 9]. Additionally, morphological scans of E. ulmoides leaves revealed a diverse range of variations in leaf quality traits, particularly the leaf base, the leaf tip, and leaf shape (Fig. 1). Among these, leaf shape exhibits the highest degree of variation, encompassing eight distinct types, including lanceolate, ovate, elliptic, and inverse lanceolate forms and others. Changes in leaf shape provide a visual representation of the plant’s adaptation to environmental shifts; for instance, oval-shaped leaves exhibit higher photosynthetic efficiency and water use efficiency than lanceolate leaves [6, 7]. As E. ulmoides serves both medicinal and dietary purposes, further research is needed to ascertain whether leaf shape and size can serve as indicators of the content of active components within EULs.
Sources of leaf phenotypic variation
The 11 leaf phenotypic traits of E. ulmoides exhibit significant variations both intra- and inter-populations (Table 2), which is consistent with findings for Litsea coreana Levl. var. sinensis [10] and Carpinus tschonoskii [43]. The average coefficient of variation for leaf phenotypic traits across the 13 E. ulmoides populations was 20.77%, which is lower than that of Tetracentron sinense (46.69%) [44] and Phoebe chekiangensis (Lauraceae) (41.43%) [45] but higher than that of Azadirachta indica (11.89%) [46]. In comparison with these other woody plants, E. ulmoides populations show a moderate degree of leaf phenotypic variation, with most attributable to intra-population variation. Hamrick et al. suggested that outcrossing plants can mitigate the impact of genetic drift on genetic structure, facilitating the maintenance of low levels of genetic differentiation inter-populations [47]. E. ulmoides is a dioecious plant. From the 1950s to the late 1980s, traditional bark harvesting for medicinal purposes led to severe over-exploitation of E. ulmoides resources, resulting in their current scarcity and fragmented distribution [48]. Consequently, cross-pollination between populations of E. ulmoides is relatively challenging, thereby providing conditions conducive to genetic differentiation inter-populations.
Under natural conditions, E. ulmoides seedlings take 7–8 years to flower, resulting in limited seed production [49]. E. ulmoides seeds face persistent challenges such as low germination rates, poor seedling development, and a loss of germination capacity in the second year [50]. This leads to slow self-renewal intra-populations, promoting genetic differentiation intra-populations. Field investigations have revealed that E. ulmoides populations are widely distributed, primarily in mountainous areas, which increases the difficulty of inter-population pollination. Additionally, E. ulmoides fruits are relatively heavy (with a weight of 4.24–13.42 g per hundred seeds) [32], making long-distance seed dispersal challenging. Some populations show high plant density, intensifying genetic exchange intra-populations and thereby increasing the level of differentiation intra-populations. Consequently, intra-population variation serves as the primary source of leaf variation in E. ulmoides populations.
Relationship between leaf phenotype and environmental factors
In this study, the mantel test results revealed significant correlations between altitude and leaf traits (Table 6). Traits representing leaf size, such as LW, LA, and LP, decreased with increasing altitude (Tables 7 and 8), consistent with Ternstroemia lineata [14] and Salix triandra L. [51]. In high-altitude, low-temperature environments, smaller leaves incur lower respiration and transpiration costs, reducing the plant’s maintenance expenditure [52]. Additionally, at higher altitudes, regions experience higher wind speeds, and smaller leaves are more wind-resistant than larger leaves [22]. This aligns with the results of the PCA (Fig. 2), where populations in lower-altitude regions (RS, JY, LA, ZX, JYLC, and DYQ) had larger leaves than populations in higher-altitude regions (ZS, LH, WF, DGS, HJ, QL), with plants in DYQ exhibiting the largest leaves. The results of multiple analyses also corroborate this conclusion (Tables 3 and 4). Furthermore, latitude and longitude show no significant correlation with the traits, indicating that the 11 leaf phenotypic traits do not exhibit a consistent geographic variation pattern along latitudinal and longitudinal gradients.
Climate has a significant impact on the leaf phenotypic traits (p < 0.01). LA, LP, LL, and LW are positively correlated with BIO1, BIO8, BIO9, BIO16, BIO18, and BIO19, indicating that in regions with higher temperatures and greater precipitation, leaves tend to be larger (Fig. 3a). This finding is consistent with those for Litsea coreana var. sinensis [10] and Tetracentron sinense Oliv [15]. Larger leaves have thicker boundary layers, which slow sensible heat exchange with the surrounding air. [16]. All leaves cool themselves through transpirational water loss. When water supply is insufficient, plants reduce leaf area to minimize water consumption and prevent the leaf surface from becoming excessively hot [18, 53]. Therefore, in regions with lower altitudes, higher temperatures, and higher precipitation, the leaves of E. ulmoides tend to be larger.
Protection and management strategy
Based on the results of this study and considering the current shortage of E. ulmoides resources, the following conservation and management strategies are proposed: (1) Prioritize the protection of high-quality germplasm resources. Using high coefficients of variation and low phenotypic differentiation coefficients as selection criteria for desirable traits is more reliable than other approaches. Additionally, high-quality germplasm resources may be more prevalent in regions with lower altitudes, higher temperatures, and lower precipitation. This could lead to a modification of sampling strategies. (2) E. ulmoides is an endemic monotypic tree species in China with a wide range of adaptability and clear geographical advantages. As the population distribution gradually shrinks, establishing germplasm resource protection through individual transplants is recommended to facilitate gene exchange. (3) Reducing human activities is a crucial measure for strengthening the protection of existing resources and habitats.
Conclusions
The leaf phenotypic variation in different populations of E. ulmoides is abundant, with a diverse range of morphological variations, including in leaf shape. Significant differences in the variation in 11 leaf phenotypic traits existed both in intra- and inter-populations, exhibiting a gradient pattern with respect to altitude. Regarding climatic factors, the leaf phenotypic variation is closely associated with local climate variables such as temperature and precipitation at the sampling sites. The variability in E. ulmoides leaf traits primarily arises from intra-population variation. In the future, the collection of germplasm resources should focus on selecting representative individual samples from populations in low-altitude and warm regions. In summary, E. ulmoides exhibits rich leaf phenotypic variation, showing strong adaptability to different environments. This variation is conducive to expanding its range of adaptation and supports the breeding, utilization, and evaluation of E. ulmoides germplasm resources.
Materials and methods
Plant materials
In September and October 2022, a total of 134 female tree samples were selected from 13 natural populations. The basic information on the populations and sampling sites can be found in Fig. 4; Table 9. Within each population, the distance between sampled trees was set to 30 m to reduce their relatedness. For each tree, 10 fresh and mature leaves without obvious diseases or pests were collected from the middle branches in four directions (east, south, west, and north). These leaves were used for measuring morphological traits [54].
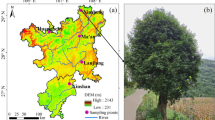
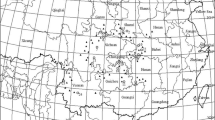
Eucommia ulmoides (E. ulmoides) sampling map. a The gray area in the figure represents the geographical range where the sampling sites of the 13 natural populations of E. ulmoides are located, b Enlarged figure of sampling sites of 8 natural populations of E. ulmoides in Hunan Province, c Adult tree of E. ulmoides natural population. The specific locations are as follows: Lianghe town, Gansu (LH); Wufeng town, Hubei (WF); Hejia town, Hubei (HJ); Donggongsi town, Guizhou (DGS); Zhongshan town, Guizhou (ZS); Jiangya forest farm, Hunan (JYLC); Jinyan town, Hunan (JY); Reshi town, Hunan (RS); Miaoertan town, Hunan (MET); Qianling town, Hunan (QL); Zhexi town, Hunan (ZX); Lean town, Hunan (LA); Dayongqiao Sub-district, Hunan (DYQ). (The maps are created by authors using ArcGIS software)
Collection of environmental data
Geographical data (longitude, latitude, and altitude) of the populations were obtained using GPS 315 (Magellan). Climate data were obtained from WorldClim v2.1 (http://www.worldclim.org/), which provides global meteorological data in raster format [55]. A total of 19 meteorological variables were extracted for the corresponding populations using ArcGIS 10.8. Correlation analysis was performed to remove strongly correlated factors (r2 ≥ 0.9) among the meteorological variables [56]. Finally, 9 climatic factors and 3 geographic factors were selected, and the results are shown in Table 10.
Measurement of leaf phenotype
10 leaves were selected from each tree to measure their 11 phenotypic traits. The LA-S Plant Leaf Image Analyzer (Hangzhou Wanshen Detection Technology Co., Ltd.) was used to measure the following leaf phenotypic traits: LL, LW, LA, RC, BC, GC, CRV, and LP. RGB is a color model that describes colors using the intensities of red, green, and blue primary colors. In this study, the RGB values were used to describe the color characteristics of the leaves [31]. The PL was measured using a vernier caliper. The SLDW is the ratio of leaf dry mass to leaf area. According to the Chinese Pharmacopoeia (2020 edition), fresh leaves were dried to constant weight at low temperature, and then the dry weight of leaves was measured by one-thousandth electronic balance.
Method statement
The investigation and collection of E. ulmoides leaf samples in this study have been approved by the local regulatory authorities. The mature leaves of E. ulmoides were identified by Professor Boru Liao from Jishou university as belonging to the genus Eucommia in the family Eucommiaceae. A voucher specimen has been deposited in the Herbarium of the College of Biology and Environmental Sciences, Jishou university, with voucher number JSU-EU116.
Statistical analysis
Statistical analysis was performed to calculate the maximum, minimum, mean (\(\stackrel{-}{X}\)), standard deviation (SD), and coefficient of variation (CV) for all 11 phenotypic traits of the leaves. CV was calculated as:
The linear model used for conducting nested analysis of variance for leaf traits is as follows:
where \({\upmu }\) is the overall average, \({\alpha }_{i}\) is the random effective value of the ith population, \({\beta }_{j\left(i\right)}\) is the random effective value of the jth tree in the ith population and \({\epsilon }_{\left(ij\right)n}\) is the experimental error of the ijnth observation value, which is the variation within trees [57].
The formula for calculating the population differentiation coefficient is:
where \({\sigma }_{i}^{2}\) is the variance among populations and \({\sigma }_{j\left(i\right)}^{2}\) is the variance within the population.
After the nested analysis of variance, multiple comparison analysis was conducted using the Duncan method to compare the specific differences in leaf traits inter-populations [58]. Pearson correlation analysis was used to investigate the correlation between leaf phenotypic traits and the influence of climate and geographical factors on leaf trait variation. After controlling climate factors by partial correlation analysis, the correlation between geography and leaf traits was studied. The data were standardized by Z-sore, and the PCA was carried out after the influence of dimensions was eliminated. PCA was used to condense phenotypic traits into several principal components and explore the structure and relationships of leaf traits inter-populations. The data statistics were analyzed using Excel 2016, SPSS 26.0, and R 4.1.3 software.
Availability of data and materials
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Rosique-Esplugas C, Cottrell JE, Cavers S, Whittet R, Ennos RA. Clinal genetic variation and phenotypic plasticity in leaf phenology, growth and stem form in common ash (Fraxinus excelsior L). Forestry. 2022;95(1):83–94.
Thomas CL, Alcock TD, Graham NS, Hayden R, Matterson S, Wilson L, et al. Root morphology and seed and leaf ionomic traits in a Brassica napus L. diversity panel show wide phenotypic variation and are characteristic of crop habit. BMC Plant Biol. 2016;16(1):214.
Chapin FS, Autumn K, Pugnaire F. Evolution of suites of traits in response to environmental-stress. Am Nat. 1993;142:78-S92.
Wright IJ, Ackerly DD, Bongers F, Harms KE, Ibarra-Manriquez G, Martinez-Ramos M, et al. Relationships among ecologically important dimensions of plant trait variation in seven neotropical forests. Ann Bot. 2007;99(5):1003–15.
Ni XF, Sun LJ, Cai Q, Ma SH, Feng YH, Sun YF, et al. Variation and determinants of leaf anatomical traits from boreal to tropical forests in eastern China. Ecol Indic. 2022;140: 108992.
Peppe DJ, Royer DL, Cariglino B, Oliver SY, Newman S, Leight E, et al. Sensitivity of leaf size and shape to climate: global patterns and paleoclimatic applications. New Phytol. 2011;190(3):724–39.
Zeng M. Molecular mechanism of environmental adaptation of heterophylly in Populus euphratica Oliv. Beijing: Beijing Forestry University; 2020.
Guo MQ, Chen XY, Hong SR, Li J, Fan J, Chen XY. The correlation between leaf phenotype diversity and total flavonoids content of overground part of Tetrastigma Hemsleyanum Diels & Gilg. Bull Bot Res. 2022;42(5):876–85.
Zhang CB, Jiang LJ, Chen JZ, Sheng XQ, Tu YH, Yao H. Analysis of tree and leaf phenotypic diversity and saponin content of Sapindus germplasm resources. Mol Plant Breed. 2023. https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail//46.1068.S20230228.0927.004.html.
Yuan GY, Guo QQ, Zhang YQ, Gui Q, Xie N, Luo SQ. Geographical differences of leaf traits of the endangered plant Litsea coreana levl. Var. Sinensis and its relationship with climate. J for Res. 2023;34(1):125–35.
Liu WS, Zheng L, Qi DH. Variation in leaf traits at different altitudes reflects the adaptive strategy of plants to environmental changes. Ecol Evol. 2020;10(15):8166–75.
Yang JH, Li YN, Bu HY, Zhang ST, Qi W. Response of leaf traits of common broad-leaved woody plants to environmental factors on the eastern Qinghai-Xizang Plateau. Chin J Plant Ecol. 2019;43(10):863–76.
Yu X, Ji RX, Li MM, Xia XL, Yin WL, Liu C. Geographical variation in functional traits of leaves of Caryopteris mongholica and the role of climate. Bmc Plant Biol. 2023;23(1):394.
Othón AA, Ken O, César RM, Gerardo R, Santiago RB, Isolda LV. Morphological variation of leaf traits in the Ternstroemia lineata species complex (Ericales: Penthaphylacaceae) in response t o geographic and climatic variation. PeerJ. 2020;8(1):e8307.
Li Y, Li S, Lu XH, Wang QQ, Han HY, Zhang XM, et al. Leaf phenotypic variation of endangered plant Tetracentron Sinense Oliv. And influence of geographical and climatic factors. J for Res. 2021;32(2):623–36.
Leigh A, Sevanto S, Close JD, Nicotra AB. The influence of leaf size and shape on leaf thermal dynamics: does theory hold up under natural conditions? Plant Cell Environ. 2017;40(2):237–48.
Wang CG, He JM, Zhao TH, Cao Y, Wang GJ, Sun B, et al. The smaller the Leaf is, the faster the Leaf Water loses in a Temperate Forest. Front Plant Sci. 2019;10: 58.
Wright IJ, Dong N, Maire V, Prentice IC, Westoby M, Díaz S, et al. Global climatic drivers of leaf size. Science. 2017;357(6354):917–21.
Poorter H, Niinemets Ü, Poorter L, Wright IJ, Villar R. Causes and consequences of variation in leaf mass per area (LMA): a meta-analysis. New Phytol. 2009;182(3):565–88.
Scheepens JF, Frei ES, Stöcklin J. Genotypic and environmental variation in specific leaf area in a widespread Alpine plant after transplantation to different altitudes. Oecologia. 2010;164(1):141–50.
Zhang C, Zeng FP, Zeng ZX, Du H, Su L, Zhang LJ, et al. Impact of selected environmental factors on variation in leaf and branch traits on endangered karst woody plants of southwest China. Forests. 2022;13(7): 1080.
Zhang M, Liang FN, Sun YW, Han F, Zhou Y, Rong YF, et al. Research progress on chemical constituents, pharmacological effects and clinical application of Eucommia ulmoides. Chin Tradit Herb Drugs. 2023;54(14):4740–61.
Du HY, Hu WZ, Yu Y. Report on the development of China’s Eucommia rubber resources and industry. Social Sciences Academic Press (China). 2013. p. 50–96.
Xie SY, Si H, Sun HX, Zhao Q, Li XD, Wang SQ, et al. Predicting the potential distribution of the endangered plant Eucommia ulmoides in China under the background of climate change. Sustainability. 2023;15: 5349.
Zeng M, Long YQ, Zeng J, Yang M, Zhou XR, Zhou RB, et al. Comparison of chemical constituents in different parts of Eucommiae Cortex. Chin Tradit Pat Med. 2023;45(4):1184–94.
Zhang Q, Su YQ, Zhang JF. Seasonal difference in antioxidant capacity and active compounds contents of Eucommia ulmoides Oliver leaf. Molecules. 2013;18(2):1857–68.
Han MF, Zhang LQ, Li YM. Research progress on chemical structures and pharmacological effects of natural aucubin and its derivatives. Chin Tradit Herb Drugs. 2017;48(19):4105–13.
Wang JJ, Qin XM, Gao XX, Zhang B, Wang PY, Hao JQ, et al. Research progress on chemical compounds, pharmacological action, and quality status of Eucommia ulmoides. Chin Tradit Herb Drugs. 2017;48(15):3228–37.
Xie SY, Si HX, Sun HX, Zhao Q, Li XD, Wang SQ, et al. Predicting the potential distribution of the endangered plant Eucommia ulmoides in China under the background of climate change. Sustainability. 2023;15(6):5349.
Liu YC, Peng XX, Lu YB, Wu XX, Chen LW, Feng H. Genome-wide association study reveals the genes associated with the leaf inclusion contents in Chinese medical tree Eucommia ulmoides. Biosci Biotech Bioch. 2021;85(2):233–41.
Meng YD, Du HY, Wang L, Lv GX, Qing J, He F, et al. Diversity analysis of leaf phenotypic traits of Eucommia ulmoides germplasm resources. For Res. 2022;35(5):103–12.
Wang CC, Gong HM, Feng M, Tian CL. Phenotypic variation in leaf, fruit and seed traits in natural populations of Eucommia ulmoides, a relict Chinese endemic tree. Forests. 2023;14(3): 462.
Huang LC, Lyu Q, Zheng WY, Yang Q, Cao G. Traditional application and modern pharmacological research of Eucommia ulmoides Oliv. Chin Med. 2021;16(1):1–26.
Meng YD, Du QX, Du HY, Wang Q, Wang L, Du LY, et al. Analysis of chemotypes and their markers in leaves of core collections of Eucommia ulmoides using metabolomics. Front Plant Sci. 2023;13: 1029907.
Meena ML, Ram RB, Lata R, Sharma SR. Inter-trait association and genetic variability assessment in cabbage under Lucknow conditions. Indian J Hortic. 2014;71(2):202–6.
Migicovsky Z, Swift JF, Helget Z, Klein LL, Ly A, Maimaitiyiming M, et al. Increases in vein length compensate for leaf area lost to lobing in grapevine. Am J Bot. 2022;109(7):1063–73.
Ma XY, Zhou GS, Li G, Wang QL. Quantitative evaluation of the trade-off growth strategies of maize leaves under different drought severities. Water. 2021;13(13): 1852.
Zhang CQ, Ji ZF, Lin LL, Zhao RH, Wang YL. Phenotypic diversity of Acer mono Maxim population. Acta Ecol Sin. 2015;35(16):5343–52.
Zhang TJ, Chen XH, Kang XK, Liu J. Phenotypic diversity of leaf morphologic traits of Davidia involucrata natural populations in Sichuan Province. Chin J Ecol. 2019;38(1):35–43.
Croft H, Chen JM, Luo XZ, Bartlett P, Chen B, Staebler RM. Leaf chlorophyll content as a proxy for leaf photosynthetic capacity. Global Change Biol. 2017;23(9):3513–24.
Zheng N, Li SY, Wang XT, Lü SH, Zhao PC, Zang C, et al. Dominance of different plant life forms in the typical steppe evidenced from impacts of environmental factors on chlorophyll. Chin J Plant Ecol. 2022;46(8):951–60.
Milla R, Reich PB. The scaling of leaf area and mass: the cost of light interception increases with leaf size. Proc R Soc Ser B. 2007;274(1622):2109–14.
Zhao RA, Chu XJ, He QQ, Liu W, Zhu ZL. Leaf phenotypic variation in natural populations of Carpinus Tschonoskii in China. J for Res. 2023;34(5):1591–602.
Li S, Gan XH, Han HY, Xu N, Hou ZY, Chen Y, et al. Leaf phenotypic traits of Tetracentron sinense, an endangered plant species. For Res. 2016;29(5):687–97.
Lu YF, Pei NC, Zhu YJ, Bai ZL, Yang AA, Zhang JH, et al. Community structure and leaf trait diversity in a vulnerable species, Phoebechekiangensis (Lauraceae). Chin J Appl Ecol. 2018;29(7):2101–10.
Peng XM, Wu JC, Zheng YX, Zhang YP, Li GQ. Phenotypic variation in cultivated populations of Azadirachta indica in Yunnan, China. Chin J Plant Eco. 2012;36(6):560–71.
Hamrick JL, Godt MJW. Effects of life history traits on genetic diversity in plant species. Philos Trans R Soc B. 1996;351(1345):1291–8.
Chen PL, Wu JY, He SA. The present status and conservation strategies for Eucommia ulmoides Oliv. J Plant Resour Environ. 1992;1(4):6–11.
Wang DW, Li Y, Li ZQ. Identification of a male-specific amplified fragment length polymorphism (AFLP) and a sequence characterized Amplified Region (SCAR) marker in Eucommia ulmoides Oliv. Int J Mol Sci. 2011;12(1):857–64.
Jian CX, Zou D, Duan W, Yang S, Gong YB, Chen LW, et al. Differences in Eucommia ulmoides seed traits and germination ability from different habitats of Sichuan Province. J Northeast for Univ. 2018;46(1):17–20.
Tumpa K, Satovic Z, Vidakovic A, Idzojtic M, Stipetic R, Poljak I. Population variability of almond-leaved willow (Salix triandra L.) based on the leaf morphometry: isolation by distance and environment explain phenotypic diversity. Forests. 2022;13: 420.
Givnish TJ, Burkhardt EL, Happel RE, Weintraub JD. Carnibort in the bromeliad brocchinia-reducta, with a cost-benefit model for the general restriction of canivorous plants to sunny, moist, nutrient-poor habitats. Am Nat. 1984;124(4):479–97.
Wang CS, Wang SP. A review of research on responses of leaf traits to climate change. Chin J Plant Ecol. 2015;39(2):206–16.
Liu JQ, Yin MY, Zuo SY, Yang SB. Phenotypic variations in natural populations of Amygdalus pedunculata. Chin J Plant Ecol. 2017;41(10):1091–102.
Poggio L, Simonetti E, Gimona A. Enhancing the WorldClim data set for national and regional applications. Sci Total Environ. 2018;625:1628–43.
Wang X, Liu JM, Rui X, Xu YY, Zhao GC, Wang LX, et al. Biogeographic divergence in leaf traits of Sapindus mukorossi and Sapindus delavayi and its relation to climate. J for Res. 2021;32(4):1445–56.
Liu ZR, Gao CJ, Li J, Miao YC, Cui K. Phenotypic diversity analysis and superior family selection of industrial raw material forest species-Pinus yunnanensis franch. Forests. 2022;13(4): 618.
Li HG, Wang RZ, Tian ZW, Xu JH, Sun WS, Duan RM, et al. Phenotypic variation and diversity in fruit, leaf, fatty acid, and their relationships to geoclimatic factors in seven natural populations of Malania Oleifera Chun Et S.K. Lee. Forests. 2022;13(10): 1733.
Acknowledgements
All authors would like to thankful to the Jishou university for providing the necessary facilities and resources.
Research involving human participants and/or animals
Not applicable.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (32160388), the open fund project of Key Laboratory of Hunan Forest Products and Chemical Industry Engineering, Jishou University (LCHG2102), and Graduate Research and Innovation Project of Hunan Province (CX20231082).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
CT designed the research; HG, MY and CW conducted the research; HG and MY analyzed the data; HG wrote the paper. All authors have read and agreed to the version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The Eucommia ulmoides leaf materials used in this study were collected with the approval of local regulatory authorities, such as the Jiangya State-owned Forest Farm in Cili country, Hunan province, and the Eucommia ulmoides forest farm in Zunyi city, Guizhou province. All methods were carried out in compliance with local and national regulations.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
About this article
Cite this article
Gong, H., Yang, M., Wang, C. et al. Leaf phenotypic variation and its response to environmental factors in natural populations of Eucommia ulmoides. BMC Plant Biol 23, 562 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-023-04583-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-023-04583-3