Abstract
Background
Heat shock transcription factors (Hsfs) are highly conserved among eukaryote and always play vital role in plant stress responses. Whereas, function and mechanism of Hsfs in maize are limited.
Results
In this study, an HSF gene ZmHsf11, a member of class B Hsfs, was cloned from maize, and it was up-regulated under heat treatment. ZmHsf11 was a nuclear protein with no transcriptional autoactivation activity in yeast. Overexpression of ZmHsf11 gene in Arabidopsis and rice significantly reduced the survival rate under heat shock treatment and decreased ABA sensitivity of transgenic plants. Under heat stress, transgenic rice accumulated more H2O2, increased cell death, and decreased proline content compared with wild type. In addition, RT-qPCR analysis revealed that ZmHsf11 negatively regulated some oxidative stress-related genes APX2, DREB2A, HsfA2e, NTL3, GR and HSP17 under heat stress treatment.
Conclusions
Our results indicate that ZmHsf11 decreases plant tolerance to heat stress by negatively regulating the expression of oxidative stress-related genes, increasing ROS levels and decreasing proline content. It is a negative regulator involved in high temperature stress response.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
As sessile organisms, plants are generally exposed to adverse environments, and high temperature stress has a great impact on their growth, development and reproduction [1]. Under high temperature stress, plants can sense temperature changes and activate cellular signaling and metabolic pathways to adapt to new environmental conditions [2]. This involves the expression of some genes or proteins, including phytohormone or signal transduction-related genes, Ca2+ signaling pathways, reactive oxygen species-related genes, heat shock transcription factors (Hsfs) and heat shock proteins [3,4,5,6,7]. Heat shock transcription factors (Hsfs) play a major role as regulators in the heat stress regulation pathway [8].
Heat shock transcription factors (Hsfs), as major transactivating element in the heat stress signaling pathway, activate the expression of related genes under heat shock and regulate the process of heat stress response in plants [9]. Hsfs were classified into classes A, B and C based on the structural features of DNA binding domain (DBD) and oligomerization domain (OD) and the presence of class-specific motifs [10]. HsfA genes play a key role in heat stress response, and their members can be roughly divided into A1-A9 [11]. In Arabidopsis, four HsfA1s (a/b/d/e) are functionally redundant, and their hsfa1a/b/d triple and hsfa1a/b/d/e quadruple mutants had significantly reduced survival after exposure to HS. Expression of HS-responsive genes, including molecular chaperones and transcription factors, was also impaired, and tolerance to HS stress was greatly in both the triple and quadruple mutants [12]. A temperature-dependent repression (TDR) domain of AtHsfA1d represses the transactivation activity of HsfA1d through interaction with HSP70 and HSP90, overexpression of HsfA1d lacking the TDR domain induces the expression of heat shock proteins and thereby enhancing the high temperature tolerance of Arabidopsis [13]. Overexpression and small RNA interference of HsfA1 in tomato elucidated its heat shock function in vivo [14]. HsfA2 as a regulatory amplifier for a subset of genes in heat response, increasing the expression of the heat responsive genes APX2 and HSP genes, and enhancing the acquired thermotolerance in Arabidopsis [15,16,17]. In tomato, HsfA2 is an essential coactivator of HsfA1a, and maintains pollen thermotolerance by controlling a number of genes with important developmental functions [18]. The sustained accumulation of histone H3 lysine 4 (H3K4) methylation was depended on HSFA2 and highly induced the expression of related genes after heat shock, and the heteromeric complexes containing both HSFA2 and HSFA3 potently promoted transcriptional memory through positively affecting H3K4 hypermethylation [17, 19]. In Arabidopsis, HsfA3 was a heat shock-inducible gene under the regulation of DREB2A, and DREB2A itself was an HS-inducible gene that played a major role in both heat shock and lack of water stress responses [20, 21]. In tomato, HsfA3 can interact with MAP kinase to modulate the response to heat stress [22]. Overexpression of lily HsfA3s in Arabidopsis increased temperature tolerance and salt sensitivity through altered proline catabolism [23]. LlHsfA4 enhanced basal thermotolerance of lily by regulating ROS metabolism [24]. Whereas, HsfA5 specifically interfered with the oligomeric state of HsfA4, thereby interfering with its DNA-binding ability [25]. Overexpression of TaHsfA6b enhanced the heat tolerance of crops through altering the expression of some stress-related genes [26]. AtHsfA8 acted as a redox-sensing transcription factor in stress-responsive transcriptional networks, and AtHsfA9 was regulated by the seed-specific transcription factor ABI3 and was expressed only at later stages of seed development [27,28,29].
Compared with Class A Hsfs, the function of Class B Hsfs is less clear. Class B Hsfs are significantly different from class A in protein structure, including B1-B4. They do not contain nuclear export signaling and activation domains and thus do not have transcriptional activation activity per se [30]. In Arabidopsis, HsfB1 and HsfB2b were found to act as inhibitors of HSR genes in non-stressed cells and during stress recovery, but were necessary for heat stress-induced heat shock protein gene expression under heat stress, hsfb1-hsfb2b knockout mutant exhibited higher basal thermotolerance than wild-type [31, 32]. HsfB1 was a core regulator of the heat stress response and played a dual role as a transcriptional co-activator and general repressor of HsfA1a in tomato [33]. HsfB2b responded to abiotic stress responses of the circadian clock through inhibition of PRR7 [34]. While HsfB3 and HsfB4 had only been reported on cell death in Arabidopsis [35]. Class C Hsfs include C1 and C2. There are few studies on HsfC, such as the overexpression of FaHsfC1b gene improved the heat tolerance of Arabidopsis [36].
Maize, as one of the food and feed crops for agricultural planting, is beneficial to its high yield and high quality under a suitable growing environment [37, 38]. Therefore, it is especially important to study the mechanism of high temperature resistance in maize. The Hsf gene family played an important regulatory role in the response to high temperature stress, but there are few studies on the function of the maize HsfB gene, only the enhanced sensitivity of ZmHsfB1 to salt and drought has been reported [39]. In this study, a member of class B Hsfs from maize known as ZmHsf11 was cloned, and identified its function in response to high temperature stress. We found that high temperature induced the up-regulated expression of ZmHsf11, the protein was localized in the nucleus and had no transcriptional autoactivation activity. Notably, overexpression of ZmHsf11 in Arabidopsis and rice significantly increased the high temperature stress sensitivity and decreased ABA sensitivity of transgenic plants, decreased the expression of oxidative stress-related genes, reduced proline content, and increased H2O2 content in rice, suggesting that ZmHsf11 negatively regulated plant high temperature tolerance.
Results
Identification and sequence analysis of ZmHsf11
A full-length cDNA of ZmHsf11 gene was obtained from maize inbred B73, contained an open reading frame of 1113 bp. This ORF encoded a 370 aa protein with a predicted molecular weight of 39.56 kDa and an isoelectric point of 5.89. Phylogenetic analysis of Hsf gene families of Arabidopsis, rice, sorghum, millet, and maize revealed that ZmHsf11 belongs to the HsfB2 subfamily and is most closely related to ZmHsf03 and SbHsf21 (SbHsfB2b) (Fig. 1A). Multiple sequence alignments indicated that ZmHsf11 exhibited high similarity with other conserved domains of homologous genes in Arabidopsis and other monocots (Fig. 1B). And according to Lin et al., the ZmHsf11 protein contains N-terminal DNA binding domain (DBD), oligomerization domain (OD) and nuclear location signal (NLS), respectively (Fig. 1B) [40]. These results showed that ZmHsf11 was a member of HsfB2 in maize.
Sequence and phylogenetic analyses of ZmHsf11. A Phylogenetic analysis of Hsf gene families in Arabidopsis, rice, sorghum, millet and maize. B Alignment of the amino acid sequence of ZmHsf11 with its homologous proteins in other species. The related protein names are as follows: ZmHsf11, GRMZM2G098696, from Zea mays; AtHsfB2b, NC_003075.7, from Arabidopsis thaliana; OsHsfB2b, LOC_Os08g43334, from Oryza sativa; SiHsfB2b, Seita.6G236100, from Setaria italica and SbHsfB2b, Sobic.007G180300, from Sorghum bicolor
Expression analysis of ZmHsf11 in maize
Numerous studies have shown that Hsf genes played broad and important roles in stress responses. Therefore, to explore the function of ZmHsf11 gene, we studied the expression patterns of ZmHsf11 gene in different tissues and under different stress treatments by RT-qPCR. Different tissues of maize in different growth periods were selected, including root, stem, leave, cornsilk, pistil and tassel. Tissue specific expression analysis showed that ZmHsf11 gene was expressed in all six tissues of maize, but the expression level in stem, cornsilk and pistil of maize was significantly higher than that in other tissues, and the expression level in leave was significantly lower (Fig. 2A). Subsequently, the expression patterns of ZmHsf11 under different stresses were investigated. Under heat treatment, the expression of ZmHsf11 increased first and then decreased (Fig. 2B). The expression of ZmHsf11 was highest at 1 h of heat stress, 85 times higher than that of the untreated group, and then the expression level decreased gradually (Fig. 2B). Under PEG, NaCl and ABA treatments, the expression level of ZmHsf11 gene was basically lower than that of the untreated group (Fig. 2C, D and E). The above results suggested that ZmHsf11 potentially involved in abiotic stress pathways such as HS. However, the mechanism of how it participates in the regulation of these pathways need to be further explored.
Expression patterns of ZmHsf11 in maize. A Tissue specific expression of ZmHsf11 in root, stem, leaf, cornsilk, pistil, tassel. B-E Expression patterns of ZmHsf11 during HS, PEG, NaCl and ABA treatments, respectively. The maize GAPDH gene was used as the internal reference gene for normalization. Data represent means ± SDs of three independent sample replicates. Significant differences (Student’s t test): *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01
Subcellular localization of ZmHsf11
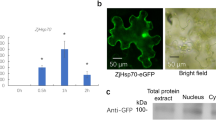
It has been reported that heat shock factor (Hsf) contains a nuclear localization signal (NLS), and ZmHsf11 protein was predicted to be a protein located in the nucleus. To investigate the subcellular localization of ZmHsf11, we constructed fusion proteins containing C-terminal and N-terminal green fluorescent protein (GFP) and GFP control proteins co-transfected with the nuclear localization marker pSAT6:mCherry (RFP):VirD2NLS (mCherry), respectively. The GFP signals were observed only in the nucleus containing ZmHsf11-GFP and GFP-ZmHsf11fusion proteins (Fig. 3B). For GFP control proteins, GFP signals were found throughout the whole cell. The results showed that ZmHsf11 protein was localized in the nucleus.
Transcriptional self-activation activity of ZmHsf11
According to previous reports, ZmHsf11 was a member of the HsfB family without transcriptional self-activation activity. Therefore, the GAL4 system was used to recombine pGBKT7 with ZmHsf11 gene to determine whether it has transcriptional self-activation activity. The yeast containing ZmHsf11 grew well on the defect medium SD/Trp − , but could not grow on the defect medium SD/Trp − His − Ade − /X-α-gal, which was consistent with the negative control, and the growth of the positive control plaque was blue on the defect medium SD/Trp − His − Ade − /X-α-gal (Fig. 4). These results indicated that ZmHsf11 had no transcriptional autoactivation activity in yeast.
Overexpression of ZmHsf11 in Arabidopsis reduces the tolerance to heat stress
To determine the role of ZmHsf11 gene in plant response to heat stress, we transformed ZmHsf11 overexpression vector into Arabidopsis, and obtained three overexpressed Arabidopsis lines (OE1, OE2, OE3) (Fig. S1). The hypocotyls of overexpressed ZmHsf11 lines and wild-type plants were treated with heat shock. The hypocotyls of overexpressed ZmHsf11 lines and wild-type plants were cultured in MS medium at 22 °C for 40 h under dark condition, followed by heat shock at 45 °C for 1 h and dark light recovery at 22 °C for 4 d. After heat treatment, the hypocotyls length of overexpressed ZmHsf11 lines were significantly lower than that of wild-type plants (Fig. 5A and B). To further study whether the overexpressed plants of ZmHsf11 in Arabidopsis were sensitive to heat, 5 d seedlings and 20 d grown seedlings were heat treated, respectively. The results showed that the survival rate of overexpressed plants was significantly lower than that of the wild-type (Fig. 5C, D, E and F). Therefore, these results suggested that overexpression of ZmHsf11 in Arabidopsis reduced the tolerance of Arabidopsis to heat stress.
Overexpression of ZmHsf11 in Arabidopsis reduced the heat stress tolerance. A Hypocotyl phenotype under heat stress. B Hypocotyl length statistics. C Seedling phenotype under heat stress. D Seeding survival statistics. E Grown seedling phenotype under heat stress. F Grown seedling survival statistics. All the values are means (± SDs) from three independent experiments. Significant differences (Student’s t test): *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01
Overexpression of ZmHsf11 in rice reduces the tolerance to heat stress
To further study the effect of ZmHsf11 on plant heat sensitivity, we continued to overexpress ZmHsf11 gene in rice and obtained three transgenic positive rice lines (OE1, OE2, OE3) (Fig. S2). Firstly, seed germination experiments were performed under normal and heat stress condition. After germinating under heat stress treatment for 3 d and recovery at 28 °C for 5 d, plant height was measured to assess the thermotolerance of transgenic and wild-type rice at germination stage. Seeds germinated under 28 °C for 8 d were applied as control. Results showed under control condition, the plant height of only OE1 rice was significantly lower than that of wild-type rice. Whereas, with HS treatment, the plant height of three transgenic plants were significantly lower than that of wild-type plants, indicating that overexpression of ZmHsf11 gene increased the sensitivity of rice plants to heat stress during germination (Fig. S3). To further investigate the sensitivity of overexpression rice to high temperature, we performed heat treatment for transgenic plants at the seedling stage. Under normal conditions, there was no significant difference between transgenic and wild-type plant seedlings. Overexpression and wild-type rice lines grown at 28 °C for 15 d were heat-treated at 45 °C for 22 h, and after 20 d recovery at 28 °C, showed that the relative survival rate of overexpressed rice lines was significantly lower than that of wild-type plants (Fig. 6A and B). Considering that stress can lead to ROS accumulation in plants, we studied H2O2 levels in wild-type and transgenic plants under heat treatment by DAB staining, H2O2 content and GSH content determination. Under normal conditions, there was no significant difference in H2O2 content between wild-type and transgenic plants. Under heat stress, transgenic plants accumulated significantly more H2O2 compared with wild-type (Fig. 6C, E and F). Heat stress can lead to cell membrane damage and cell death to some extent. Trypan blue staining experiments showed increased cell death in transgenic plants compared with wild type under heat stress (Fig. 6D). In addition, we also tested the Proline (PRO) content of the wild-type and transgenic plants, and the Proline (PRO) content of the transgenic plants was significantly lower than that of the wild type under heat treatment (Fig. 6G). Under heat stress, photosynthetic attributes such as photosynthetic rate and stomatal conductance decreased. The results found that the net photosynthetic rate and stomatal conductance of the transgenic plants were lower than those of the wild-type after heat treatment, but there was no significant difference. (Fig. S4). The above results were consistent with the previous results of Arabidopsis, indicating that overexpression of the ZmHsf11 gene reduced the tolerance of rice plants to high temperature stress.
Overexpression of ZmHsf11 in rice reduced the heat stress tolerance. A The phenotypes of wild-type and overexpression of ZmHsf11 in rice under 45 °C 22 h. B Survival statistics. C DAB staining of the rice leaves. (CT: 28 °C; HS: 45 °C 22 h; CK: 10 mM NaHPO4). D Trypan blue staining of the rice leaves. (NC: room temperature; PC: 95 °C; HS: 45 °C). E–G The H2O2, GSH and proline contents were measured of the rice leaves after heat treatment. Data are means ± SDs of three independent sample replicates. Significant differences (Student’s t test): *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01
Overexpression of ZmHsf11 in transgenic plants reduce sensitivity to ABA stress
The plant hormone ABA plays an important role in the response of plants to abiotic stresses such as high temperature. To investigate whether ZmHsf11 is involved in regulating plant thermal sensitivity through the ABA pathway, we treated seed germination of ZmHsf11 overexpressed Arabidopsis and rice plants with 0.75 µM and 10 µM ABA concentrations, respectively. The results showed that the seed germination rate of ZmHsf11 gene in Arabidopsis overexpressed lines was higher than that of wild-type, and the plant height of overexpressed rice lines was significantly higher than that of wild-type, indicating that ZmHsf11 gene possibly regulated plant heat stress response by participating in the ABA pathway (Figs. S5 and 7).
Reduced ABA sensitivity of ZmHsf11 in rice. A Growth performance of wild-type and transgenic rice grown in sterile water containing 10 μM ABA concentrations after 10 d. B Measurements of plant heights of wild-type and ZmHsf11 transgenic seedlings. Data are means ± SDs (n = 10). Significant differences (Student’s t test): **, P < 0.01
Expression analysis of stress-related genes of ZmHsf11 in transgenic rice
To further explore the functional molecular mechanism of ZmHsf11 under heat stress, we detected the expression of oxidative stress related genes DREB2A, HsfA2e, NTL3, HSP17, HSP18, GR, APX2 and Rab7 under heat stress by RT-qPCR assays. Under normal growth conditions, there was no significant difference in the expression of these genes between ZmHsf11 overexpressed and wild-type rice. However, under heat treatment, the expression levels of APX2, DREB2A, HsfA2e, NTL3, GR and HSP17 in transgenic rice were significantly lower than those in wild-typerice (Fig. 8). The transcription levels of the other 2 genes (HSP18 and Rab7) were not significantly changed (data not shown). These results indicated that ZmHsf11 negatively regulated oxidative stress-related genes APX2, DREB2A, HsfA2e, NTL3, GR and HSP17 under heat stress.
Discussion
Plant responds to varied environmental stresses through complex signaling networks, and heat shock transcription factors (Hsfs) play a crucial role in plant response to abiotic stresses. Class A Hsfs contained AHA activation domain at the C-terminus and have been reported as positive regulators of stress tolerance [10, 41]. However, class B Hsfs contained a BRD inhibitory domain at the C-terminus and no AHA activation domain, and were identified as negative regulators of stress tolerance [42]. For example, HsfB1 and HsfB2b had inhibitory activity and negatively regulated stress tolerance in Arabidopsis and soybean [32, 43]. In maize, current studies have reported that there were few Hsf gene members, such as class A members ZmHsf01, ZmHsf05 and ZmHsf06 that were tolerance under abiotic stress, and a class B member ZmHsf08 that was sensitivity to salt and drought [39, 44,45,46]. In this study, we reported the characterization of ZmHsf11, a member of class B Hsfs in maize. Our data suggested that ZmHsf11 was probably a negative regulator involved in high temperature stress tolerance.
Phylogenetic tree analysis showed that ZmHsf11 shared homology with HsfB2 members of other species (Fig. 1A), revealing that ZmHsf11 belonged to the HsfB2 subfamily. Multiple alignment of the amino acid sequences of ZmHsf11 and other homologous proteins found that ZmHsf11 contained a conserved DNA binding domain (DBD), an intermediate oligomerization domain (OD) and a nuclear localization signal (NLS), lacked nuclear export signal (NES) and activation domain (AHA) (Fig. 1B). This may lead to changes in its structure and function, thus acting as a negative regulator in the opposite function of class A members. The structure was further verified by yeast transcriptional autoactivation assay and protoplast transient expression subcellular localization experiment. The absence of its AHA domain made the gene lack transcriptional autoactivation activity, and the presence of NLS allowed the gene to localize in the nucleus (Figs. 3 and 4). The above results revealed that ZmHsf11 was a highly conserved Hsf protein that possibly needed to interact with other proteins to activate its transcriptional ability.
Studies have shown that Hsfs are involved in a variety of abiotic stress pathways and ABA-mediated stress pathways. Overexpression of FaHsfA2c in tall fescue enhanced the tolerance of plants to heat stress through inducing high expression of heat stress-related genes in vivo and enhancing photosynthesis ability [47]. And overexpression of ZmHsf04 enhanced tolerance to heat and salt stress in transgenic Arabidopsis [48]. The HsfA6b in Arabidopsis enhanced plant tolerance to heat, salt and drought stress through an ABA-mediated pathway [49]. The MdHSFA8a promoted the accumulation of flavonoids and removed reactive oxygen species, thus improving the drought tolerance of plants [50]. Arabidopsis HsfB1 and HsfB2b regulated the expression of the defensin gene Pdf1.2 a/b in plants and significantly enhanced the disease resistance of hsfb1-hsfb2b double mutants [31]. In this study, we observed the expression levels of ZmHsf11 under different abiotic stresses and ABA hormone treatment, and the expression patterns of ZmHsf11 in different tissues were surveyed. Like other members of Hsfs, ZmHsf11 was also strongly induced by heat stress, but the expression level gradually decreased with increasing heat treatment time (Fig. 2B). However, the expression of ZmHsf11 was inhibited under NaCl, PEG and ABA treatments (Fig. 2C, D and E). Therefore, the results showed that ZmHsf11 potentially involved in different biological processes as a negative regulator of Hsfs in plants. The expression level of ZmHsf11 gene in maize was identified by tissue expression pattern, and it was found that ZmHsf11 gene was highly expressed in stem, cornsilk and pistil (Fig. 2A), which may indicate that ZmHsf11 gene was involved in plant growth and development and regulated reproductive organs tissue response to heat stress.
To determine the function of ZmHsf11 gene in plant responses to heat stress, ZmHsf11 gene was overexpressed in Arabidopsis and rice. Compared with wild-type, overexpression of ZmHsf11 gene reduced the tolerance of transgenic plants to heat stress (Figs. 5 and 6A, B and S3). This may be related to the accumulation of ROS in plants after heat stress [51]. Reactive oxygen species (ROS) play a key role in plant adaptation to abiotic stress [52]. ROS increases in cells, causing oxidative damage to cell membranes, proteins, RNA and DNA molecules, and even oxidative damage to cells [53]. Therefore, regulation of ROS under high temperature stress is crucial. Proline acts as an important antioxidant, reducing oxidative damage under stressful conditions [54]. In this study, the transgenic rice accumulated more H2O2 after heat treatment (Fig. 6C, E and F), while the proline content was significantly lower than that of the wild-type (Fig. 6G). Meanwhile, heat stress can cause cell membrane damage and cell death to a certain extent. Trypan blue staining showed that the cell death of transgenic plants increased significantly under heat stress (Fig. 6D). Therefore, these results explained that ZmHsf11 may play a negative regulatory role in plant response to heat stress. ABA signaling pathway has been reported to be related to abiotic stresses such as drought, salt, and high temperature [55, 56]. In this study, the inducible expression pattern analysis showed that ZmHsf11 had a similar expression trend to heat shock and ABA (Fig. 2B and E), and the ZmHsf11 transgenic plants were also less sensitive to ABA during seed germination (Fig. 7 and Fig. S4). These results probably revealed the tandem of abiotic stresses such as high temperature and ABA, thereby regulating the homeostasis in plants under stress conditions. This speculation remains to be explored by further experiments.
To elucidate the potential molecular mechanism of the reduced heat tolerance in plants overexpressing ZmHsf11, we investigated the expression of some oxidative stress-related genes DREB2A, HsfA2e, NTL3, HSP17, HSP18, GR, APX2 and Rab7 in rice. DREB gene played a positive role in the expression of drought, high salt and low temperature responsive genes [57]. OsHsfA2e enhanced heat and salt tolerance in transgenic plants [58]. OsNTL3 regulated the expression of genes involved in ER protein folding and other processes, thereby regulating plant heat tolerance [59]. Overexpression of OsHsp17 and OsHsp18 enhanced the resistance of rice to abiotic stress [60, 61]. OsGR increased the thermotolerance of yeast strains [62]. APX2 was a pleiotropic protein involved in H2O2 homeostasis, chloroplast protection, maintenance of plant configuration and fertility [63]. Overexpression of OsRab7 gene improved the drought and heat tolerance of rice, and thus increased rice yield [64]. Under heat stress, the expression levels of APX2, DREB2A, HsfA2e, NTL3, GR and HSP17 were decreased in transgenic rice, suggesting that ZmHsf11 may negatively regulate oxidative stress-related genes (Fig. 8). These results indicated that ZmHsf11 negatively regulated the heat stress response by inhibiting the expression levels of oxidative stress-related genes.
Conclusions
A maize HsfB2 member, ZmHsf11, was cloned and characterized.. Overexpression of ZmHsf11 gene in Arabidopsis and rice reduced plant tolerance to heat stress through negatively regulating the expression of oxidative stress-related genes, and this was also associated with the accumulation of ROS levels and the reduction of proline content.
Materials and methods
Plant materials and stress treatments
Maize B73 inbred lines were germinated and grown for 14 d in a greenhouse with a 16/8 h light/dark at 28 ℃/24 ℃, then treated with 42 ℃, 200 mM NaCl, 20% PEG6000 and 100 µM ABA. Samples were taken at 0 h, 1 h, 3 h, 6 h, 12 h and 24 h for each treatment. Meanwhile, root, stem and leaf samples were taken, and cornsilk, pistil and tassel were taken respectively when they grew to the flowering stage, three plants of each sample are mixed for sampling and quick-frozen with liquid nitrogen, stored at -80 ℃ for RNA extraction.
Zhonghua11 used for transgenic rice was consistent with the maize growth greenhouse. The Columbia type used for transgenic Arabidopsis was grown at 22 ℃/20 ℃ with a 16/8 h light/dark. Arabidopsis seeds were grown and identified on MS medium, and seedlings were then transferred to a mixture of peat and vermiculite at 14 d.
Cloning and sequence analysis of ZmHsf11
In the plant genome database website (https://phytozome.jgi.doe.gov/pz/portal.html), the full-length CDS sequence and amino acid sequence of the maize ZmHsf11 gene were obtained. The amino acid sequences of the ZmHsf11 homologous genes were obtained from the NCBI website (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/). The amino acid sequence of ZmHsf11 was analyzed by ExPASy website (https://web.expasy.org/protparam/), and the sequences of ZmHsf11 and its homologous genes were compared by DNAMAN software [65]. Amino acid sequences of the Hsf gene families in Arabidopsis, rice, sorghum, millet and maize were obtained using the Phytozome (https://phytozome-next.jgi.doe.gov/pz/portal.html) and Pfam websites (http://pfam.xfam.org/). The phylogenetic tree was constructed by NJ method using MEGA X software, and bootstrap analysis was performed, with a total of 1000 replicates [66]. According to the obtained full-length cDNA sequence of ZmHsf11, specific primers for the ZmHsf11 gene were designed using Primer5 software, and the full-length ZmHsf11 gene was amplified by PCR assay. The PCR product was purified and cloned into the pEASY-Blunt simple vector for sequencing. Primers for ZmHsf11-F and ZmHsf11-R were shown in Supplementary Table S1.
Quantitative real‑time PCR and semi real‑time PCR analysis
Total RNA was extracted by Trizol method using RNA isolater Total RNA Extraction Reagent (Vazyme R401-01), and cDNA for RT-qPCR was synthesized using HiScript III RT SuperMix for qPCR (+ gDNA wiper) (Vazyme R323-01), cDNA for RT-PCR was synthesized using HiScript III 1st Strand cDNA Synthesis Kit (+ gDNA wiper) (Vazyme R312-01). RT-qPCR was performed using AceQ qPCR SYBR Green Master Mix (Vazyme Q111-02) on the LightCycler480 instrument (Roche). The GAPDH and Actin genes were used as internal control for maize. The relative expression level was calculated using the 2−ΔΔCT method [67]. All the primers used for RT-qPCR were listed in Supplementary Table S1.
Subcellular localization of the ZmHsf11 protein
The coding sequence of ZmHsf11 gene without terminator was linked into p1305-GFP vector by double digestion method (Xba I/Sma I). And the coding sequence of ZmHsf11 gene was ligated into pCUB-GFP vector by homologous recombination method, and primers are shown in Supplementary Table S1. The p1305-ZmHsf11-GFP, pCUB-GFP- ZmHsf11 recombinant plasmids and p1305-GFP and pCUB-GFP empty vectors were co-transformed into protoplasts together with the nuclear localization signal plasmid pSAT6:mCherry (RFP):VirD2NLS by transient transformation technology. After culturing in the dark at 28 °C for 18 h, the protoplasts were observed by laser scanning microscopy (LSM800, Carl Zeiss, Jena, Germany).
Transcriptional self-activation activity assay in yeast
The coding sequence of the ZmHsf11 gene was homologous recombined into the pGBKT7 vector using EcoR I restriction enzyme and ClonExpress II One Step Cloning Kit (Vazyme C112-01), and primers are shown in Supplementary Table S1. The recombinant plasmid pGBKT7-ZmHsf11 was transformed into yeast strain Y2H Gold by PEG/LiAc method. Positive control was pGBKT7-53 and pGADT7-T, and negative control was pGBKT7 vector. The transformed yeast cells were serially diluted on SD/Trp − and SD/Trp − Leu − Ade − /X-α-Gal plates, respectively, and the yeast cells were grown at 30 °C in the dark for 3 d.
Generation of ZmHsf11 transgenic plants
To construct the overexpression vector, the coding sequence of ZmHsf11 gene was linked to the p1301a vector (modified in this experiment) by double digestion method (Kpn I/Pst I) to obtain the recombinant plasmid p1301a-ZmHsf11. The recombinant plasmid was transferred into Arabidopsis and rice by agrobacterium-mediated method to obtain transgenic T0 generation plants. Transgenic T1 generation plants were screened by hygromycin, GUS staining and semi real‑time PCR assays to obtain multiple positive lines. Three of the overexpressing Arabidopsis and rice lines (OE1, OE2, OE3) were selected and cultured to obtain T3 homozygous overexpression plants for subsequent experiments.
Heat stress tolerance assays
The seeds of T3 generation of three overexpressed strains and wild-type of Arabidopsis were placed on MS plates and sealed. Each plate was placed vertically, wrapped with tin foil, and grown in the dark at 22 °C/20 °C for 2 d. Then, heat treatment at 45 °C for 1 h in an artificial climate box in the dark, then wrapped it with tin foil, and placed in greenhouse for dark growth for 3–4 d. The hypocotyl length of different strains was observed and statistical data were obtained.
The seeds of T3 generation of three overexpressed strains and wild-type of Arabidopsis were placed on MS plates and sealed. Each plate was placed horizontally with 36 seeds at each plant point. The seeds were grown at 22 °C /20 °C for 5 d in a 16/8 h, light/dark greenhouse, used a water bath at 42 °C for 55 min, cooled to room temperature, and then put it back in the greenhouse for about 3 d to observe the survival rate of seedlings of different lines and make statistics.
Three Arabidopsis overexpression lines T3 generation seeds and wild-type were grown in MS plate at 22 °C/20 °C, 16/8 h, light/dark greenhouse for 10 d, and then transplanted to pots with vermiculite: black soil = 2: 1, continued to grow for 10 d, used artificial climate chamber, under 45 °C light conditions, 6.5 h treatment, replaced in the greenhouse for 4–5 d to recover cultivation, observed the survival rate of seedlings of different lines, and statistical data.
The seeds of the T3 generation of the three overexpressed rice lines and the wild-type seeds of Zhonghua 11 were fully swollen and placed in a moderate heat treatment at 35 °C for 3 d and a recovery at 28 °C for 5 d. The plant height of rice seeds of different lines was measured by a ruler.
The seeds of the T3 generation of the three overexpression lines of rice and the wild-type seeds of Zhonghua11 were transplanted into small round pots after 8 d of germination, which were placed in a 28 °C/24 °C, 16/8 h, light/dark greenhouse for 15 d. In an artificial climate box, under the light condition of 45 °C, treated for 22 h, and then placed in the greenhouse to resume cultivation for 20 d. The survival rate of rice seedlings of different lines was observed and the statistics were collected.
Physiological analysis of plants in response to heat stress
The 15-day-old rice seedlings were heat-treated at 45 °C for 22 h, and the physiological features of overexpression and wild-type rice were determined respectively. The same parts of untreated and heat-treated rice leaves were taken for DAB and trypan blue staining, as described by Zhang et al. [68]. And the contents of hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), reduced glutathione (GSH) and proline (PRO) were determined according to the protocol of Nanjing Jiancheng Bioengineering Institute. Net photosynthetic rate and stomatal conductance were measured using a photosynthesis instrument CIRAS-3.
ABA sensitivity analysis
The vernalized Arabidopsis seeds were sown on MS medium containing 0.75 μM ABA, with 36 seeds in each plant line, and placed in the Arabidopsis greenhouse, grown for 8 d. The germination status of seeds was observed, and the germination rate was calculated. Sterilized rice seeds were cultured in sterile water at 30 °C for 2 d in the dark. Then, rice seeds of the same size were selected and continued to be cultured in sterile water containing 10 μM ABA in a greenhouse at 28 °C for 8 d. The heights of different lines were measured and the data were counted.
Analysis of stress-related genes regulated by ZmHsf11
The expression levels of oxidative stress-related genes DREB2A, HsfA2e, NTL3, HSP17, HSP18, GR, APX2 and Rab7 in overexpressed and wild-type rice lines were analyzed by RT-qPCR experiments. For the overexpression line OE1 and wild-type rice, samples were taken at 45 °C for 0 h, 1 h and 3 h, respectively. The other steps were the same as above.
Availability of data and materials
All data generated or analysed during this study are included in this published article and its supplementary information files.
However, the sequence data in this study can also be accessed at https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/gene/?term=GRMZM2G098696.
In addition, all databases used in this study are open for public and the links are as follows:
Phytozome: https://data.jgi.doe.gov/refine-download/phytozome?q=Arabidopsis+thaliana
ExPASy: https://web.expasy.org/cgi-bin/protparam/protparam1?A0A804NZV2@noft@.
Abbreviations
- Hsf:
-
Heat shock transcription factor
- ABA:
-
Abscisic acid
- ROS:
-
Reactive oxygen species
- H2O2 :
-
Hydrogen peroxide
- GSH:
-
Glutathione
References
Lippmann R, Babben S, Menger A, Delker C, Quint M. Development of Wild and Cultivated Plants under Global Warming Conditions. Curr Biol. 2019;29(24):R1326–38.
Mittler R, Finka A, Goloubinoff P. How do plants feel the heat? Trends Biochem Sci. 2012;37(3):118–25.
Atkinson NJ, Urwin PE. The interaction of plant biotic and abiotic stresses: from genes to the field. J Exp Bot. 2012;63(10):3523–43.
Qu AL, Ding YF, Jiang Q, Zhu C. Molecular mechanisms of the plant heat stress response. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2013;432(2):203–7.
Katano K, Honda K, Suzuki N. Integration between ROS Regulatory Systems and Other Signals in the Regulation of Various Types of Heat Responses in Plants. Int J Mol Sci. 2018;19(11):3370.
Cortleven A, Leuendorf JE, Frank M, Pezzetta D, Bolt S, Schmulling T. Cytokinin action in response to abiotic and biotic stresses in plants. Plant Cell Environ. 2019;42(3):998–1018.
Albertos P, Dundar G, Schenk P, Carrera S, Cavelius P, Sieberer T, Poppenberger B. Transcription factor BES1 interacts with HSFA1 to promote heat stress resistance of plants. EMBO J. 2022;41(3): e108664.
Ohama N, Sato H, Shinozaki K, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K. Transcriptional Regulatory Network of Plant Heat Stress Response. Trends Plant Sci. 2017;22(1):53–65.
Kotak S, Larkindale J, Lee U, von Koskull-Doring P, Vierling E, Scharf KD. Complexity of the heat stress response in plants. Curr Opin Plant Biol. 2007;10(3):310–6.
Nover L, Bharti K, Doring P, Mishra SK, Ganguli A, Scharf KD. Arabidopsis and the heat stress transcription factor world: how many heat stress transcription factors do we need? Cell Stress Chaperones. 2001;6(3):177–89.
Scharf KD, Berberich T, Ebersberger I, Nover L. The plant heat stress transcription factor (Hsf) family: structure, function and evolution. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012;1819(2):104–19.
Yoshida T, Ohama N, Nakajima J, Kidokoro S, Mizoi J, Nakashima K, Maruyama K, Kim JM, Seki M, Todaka D, et al. Arabidopsis HsfA1 transcription factors function as the main positive regulators in heat shock-responsive gene expression. Mol Genet Genomics. 2011;286(5–6):321–32.
Ohama N, Kusakabe K, Mizoi J, Zhao H, Kidokoro S, Koizumi S, Takahashi F, Ishida T, Yanagisawa S, Shinozaki K, et al. The Transcriptional Cascade in the Heat Stress Response of Arabidopsis Is Strictly Regulated at the Level of Transcription Factor Expression. Plant Cell. 2016;28(1):181–201.
Mishra SK, Tripp J, Winkelhaus S, Tschiersch B, Theres K, Nover L, Scharf KD. In the complex family of heat stress transcription factors, HsfA1 has a unique role as master regulator of thermotolerance in tomato. Genes Dev. 2002;16(12):1555–67.
Schramm F, Ganguli A, Kiehlmann E, Englich G, Walch D, von Koskull-Doring P. The heat stress transcription factor HsfA2 serves as a regulatory amplifier of a subset of genes in the heat stress response in Arabidopsis. Plant Mol Biol. 2006;60(5):759–72.
Charng YY, Liu HC, Liu NY, Chi WT, Wang CN, Chang SH, Wang TT. A heat-inducible transcription factor, HsfA2, is required for extension of acquired thermotolerance in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2007;143(1):251–62.
Lamke J, Brzezinka K, Altmann S, Baurle I. A hit-and-run heat shock factor governs sustained histone methylation and transcriptional stress memory. EMBO J. 2016;35(2):162–75.
Fragkostefanakis S, Mesihovic A, Simm S, Paupiere MJ, Hu Y, Paul P, Mishra SK, Tschiersch B, Theres K, Bovy A, et al. HsfA2 Controls the Activity of Developmentally and Stress-Regulated Heat Stress Protection Mechanisms in Tomato Male Reproductive Tissues. Plant Physiol. 2016;170(4):2461–77.
Friedrich T, Oberkofler V, Trindade I, Altmann S, Brzezinka K, Lamke J, Gorka M, Kappel C, Sokolowska E, Skirycz A, et al. Heteromeric HSFA2/HSFA3 complexes drive transcriptional memory after heat stress in Arabidopsis. Nat Commun. 2021;12(1):3426.
Sakuma Y, Maruyama K, Qin F, Osakabe Y, Shinozaki K, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K. Dual function of an Arabidopsis transcription factor DREB2A in water-stress-responsive and heat-stress-responsive gene expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006;103(49):18822–7.
Schramm F, Larkindale J, Kiehlmann E, Ganguli A, Englich G, Vierling E, von Koskull-Doring P. A cascade of transcription factor DREB2A and heat stress transcription factor HsfA3 regulates the heat stress response of Arabidopsis. Plant J. 2008;53(2):264–74.
Link V, Sinha AK, Vashista P, Hofmann MG, Proels RK, Ehness R, Roitsch T. A heat-activated MAP kinase in tomato: a possible regulator of the heat stress response. FEBS Lett. 2002;531(2):179–83.
Wu Z, Liang J, Wang C, Zhao X, Zhong X, Cao X, Li G, He J, Yi M. Overexpression of lily HsfA3s in Arabidopsis confers increased thermotolerance and salt sensitivity via alterations in proline catabolism. J Exp Bot. 2018;69(8):2005–21.
Wang C, Zhou Y, Yang X, Zhang B, Xu F, Wang Y, Song C, Yi M, Ma N, Zhou X, et al. The Heat Stress Transcription Factor LlHsfA4 Enhanced Basic Thermotolerance through Regulating ROS Metabolism in Lilies (Lilium Longiflorum). Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(1):572.
Baniwal SK, Chan KY, Scharf KD, Nover L. Role of heat stress transcription factor HsfA5 as specific repressor of HsfA4. J Biol Chem. 2007;282(6):3605–13.
Poonia AK, Mishra SK, Sirohi P, Chaudhary R, Kanwar M, Germain H, Chauhan H. Overexpression of wheat transcription factor (TaHsfA6b) provides thermotolerance in barley. Planta. 2020;252(4):53.
Giesguth M, Sahm A, Simon S, Dietz KJ. Redox-dependent translocation of the heat shock transcription factor AtHSFA8 from the cytosol to the nucleus in Arabidopsis thaliana. FEBS Lett. 2015;589(6):718–25.
Kotak S, Vierling E, Baumlein H, von Koskull-Doring P. A novel transcriptional cascade regulating expression of heat stress proteins during seed development of Arabidopsis. Plant Cell. 2007;19(1):182–95.
Tejedor-Cano J, Prieto-Dapena P, Almoguera C, Carranco R, Hiratsu K, Ohme-Takagi M, Jordano J. Loss of function of the HSFA9 seed longevity program. Plant Cell Environ. 2010;33(8):1408–17.
Kotak S, Port M, Ganguli A, Bicker F, von Koskull-Doring P. Characterization of C-terminal domains of Arabidopsis heat stress transcription factors (Hsfs) and identification of a new signature combination of plant class A Hsfs with AHA and NES motifs essential for activator function and intracellular localization. Plant J. 2004;39(1):98–112.
Kumar M, Busch W, Birke H, Kemmerling B, Nurnberger T, Schoffl F. Heat shock factors HsfB1 and HsfB2b are involved in the regulation of Pdf1.2 expression and pathogen resistance in Arabidopsis. Mol Plant. 2009;2(1):152–65.
Ikeda M, Mitsuda N, Ohme-Takagi M. Arabidopsis HsfB1 and HsfB2b act as repressors of the expression of heat-inducible Hsfs but positively regulate the acquired thermotolerance. Plant Physiol. 2011;157(3):1243–54.
Fragkostefanakis S, Simm S, El-Shershaby A, Hu Y, Bublak D, Mesihovic A, Darm K, Mishra SK, Tschiersch B, Theres K, et al. The repressor and co-activator HsfB1 regulates the major heat stress transcription factors in tomato. Plant Cell Environ. 2019;42(3):874–90.
Kolmos E, Chow BY, Pruneda-Paz JL, Kay SA. HsfB2b-mediated repression of PRR7 directs abiotic stress responses of the circadian clock. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014;111(45):16172–7.
Zhu X, Thalor SK, Takahashi Y, Berberich T, Kusano T. An inhibitory effect of the sequence-conserved upstream open-reading frame on the translation of the main open-reading frame of HsfB1 transcripts in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell Environ. 2012;35(11):2014–30.
Zhuang L, Cao W, Wang J, Yu J, Yang Z, Huang B. Characterization and Functional Analysis of FaHsfC1b from Festuca arundinacea Conferring Heat Tolerance in Arabidopsis. Int J Mol Sci. 2018;19(9):2702.
Wang H, Gu L, Zhang X, Liu M, Jiang H, Cai R, Zhao Y, Cheng B. Global transcriptome and weighted gene co-expression network analyses reveal hybrid-specific modules and candidate genes related to plant height development in maize. Plant Mol Biol. 2018;98(3):187–203.
Dong Q, Xu Q, Kong J, Peng X, Zhou W, Chen L, Wu J, Xiang Y, Jiang H, Cheng B. Overexpression of ZmbZIP22 gene alters endosperm starch content and composition in maize and rice. Plant Sci. 2019;283:407–15.
Wang J, Chen L, Long Y, Si W, Cheng B, Jiang H. A Novel Heat Shock Transcription Factor (ZmHsf08) Negatively Regulates Salt and Drought Stress Responses in Maize. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(21):11922.
Lin YX, Jiang HY, Chu ZX, Tang XL, Zhu SW, Cheng BJ. Genome-wide identification, classification and analysis of heat shock transcription factor family in maize. BMC Genomics. 2011;12:76.
Baniwal SK, Bharti K, Chan KY, Fauth M, Ganguli A, Kotak S, Mishra SK, Nover L, Port M, Scharf KD, et al. Heat stress response in plants: a complex game with chaperones and more than twenty heat stress transcription factors. J Biosci. 2004;29(4):471–87.
Czarnecka-Verner E, Pan S, Salem T, Gurley WB. Plant class B HSFs inhibit transcription and exhibit affinity for TFIIB and TBP. Plant Mol Biol. 2004;56(1):57–75.
Bian XH, Li W, Niu CF, Wei W, Hu Y, Han JQ, Lu X, Tao JJ, Jin M, Qin H, et al. A class B heat shock factor selected for during soybean domestication contributes to salt tolerance by promoting flavonoid biosynthesis. New Phytol. 2020;225(1):268–83.
Zhang H, Li G, Hu D, Zhang Y, Zhang Y, Shao H, Zhao L, Yang R, Guo X. Functional characterization of maize heat shock transcription factor gene ZmHsf01 in thermotolerance. PeerJ. 2020;8: e8926.
Li GL, Zhang HN, Shao H, Wang GY, Zhang YY, Zhang YJ, Zhao LN, Guo XL, Sheteiwy MS: ZmHsf05, a new heat shock transcription factor from Zea mays L. improves thermotolerance in Arabidopsis thaliana and rescues thermotolerance defects of the athsfa2 mutant. Plant Sci 2019, 283:375–384.
Li HC, Zhang HN, Li GL, Liu ZH, Zhang YM, Zhang HM, Guo XL. Expression of maize heat shock transcription factor gene ZmHsf06 enhances the thermotolerance and drought-stress tolerance of transgenic Arabidopsis. Funct Plant Biol. 2015;42(11):1080–91.
Wang X, Huang W, Liu J, Yang Z, Huang B. Molecular regulation and physiological functions of a novel FaHsfA2c cloned from tall fescue conferring plant tolerance to heat stress. Plant Biotechnol J. 2017;15(2):237–48.
Jiang YL, Zheng QQ, Chen L, Liang YN, Wu JD: Ectopic overexpression of maize heat shock transcription factor gene ZmHsf04 confers increased thermo and salt-stress tolerance in transgenic Arabidopsis. Acta Physiologiae Plantarum 2018, 40(1).
Huang YC, Niu CY, Yang CR, Jinn TL. The Heat Stress Factor HSFA6b Connects ABA Signaling and ABA-Mediated Heat Responses. Plant Physiol. 2016;172(2):1182–99.
Wang N, Liu W, Yu L, Guo Z, Chen Z, Jiang S, Xu H, Fang H, Wang Y, Zhang Z, et al. HEAT SHOCK FACTOR A8a Modulates Flavonoid Synthesis and Drought Tolerance. Plant Physiol. 2020;184(3):1273–90.
Suzuki N, Katano K. Coordination Between ROS Regulatory Systems and Other Pathways Under Heat Stress and Pathogen Attack. Front Plant Sci. 2018;9:490.
Choudhury FK, Rivero RM, Blumwald E, Mittler R. Reactive oxygen species, abiotic stress and stress combination. Plant J. 2017;90(5):856–67.
Mittler R. Oxidative stress, antioxidants and stress tolerance. Trends Plant Sci. 2002;7(9):405–10.
Liu J, Wang YS. Proline metabolism and molecular cloning of Am P5CS in the mangrove Avicennia marina under heat stress. Ecotoxicology. 2020;29(6):698–706.
Wang Y, Chang H, Hu S, Lu X, Yuan C, Zhang C, Wang P, Xiao W, Xiao L, Xue GP, et al. Plastid casein kinase 2 knockout reduces abscisic acid (ABA) sensitivity, thermotolerance, and expression of ABA- and heat-stress-responsive nuclear genes. J Exp Bot. 2014;65(15):4159–75.
Huque A, So W, Noh M, You MK, Shin JS. Overexpression of AtBBD1, Arabidopsis Bifunctional Nuclease, Confers Drought Tolerance by Enhancing the Expression of Regulatory Genes in ABA-Mediated Drought Stress Signaling. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(6):2936.
Dubouzet JG, Sakuma Y, Ito Y, Kasuga M, Dubouzet EG, Miura S, Seki M, Shinozaki K, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K. OsDREB genes in rice, Oryza sativa L., encode transcription activators that function in drought-, high-salt- and cold-responsive gene expression. Plant J. 2003;33(4):751–63.
Yokotani N, Ichikawa T, Kondou Y, Matsui M, Hirochika H, Iwabuchi M, Oda K. Expression of rice heat stress transcription factor OsHsfA2e enhances tolerance to environmental stresses in transgenic Arabidopsis. Planta. 2008;227(5):957–67.
Liu XH, Lyu YS, Yang W, Yang ZT, Lu SJ, Liu JX. A membrane-associated NAC transcription factor OsNTL3 is involved in thermotolerance in rice. Plant Biotechnol J. 2020;18(5):1317–29.
Zou J, Liu C, Liu A, Zou D, Chen X. Overexpression of OsHsp17.0 and OsHsp23.7 enhances drought and salt tolerance in rice. J Plant Physiol. 2012;169(6):628–35.
Kuang J, Liu J, Mei J, Wang C, Hu H, Zhang Y, Sun M, Ning X, Xiao L, Yang L: A Class II small heat shock protein OsHsp18.0 plays positive roles in both biotic and abiotic defense responses in rice. Sci Rep 2017, 7(1):11333 .
Kim IS, Kim YS, Yoon HS. Glutathione reductase from Oryza sativa increases acquired tolerance to abiotic stresses in a genetically modified Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain. J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2012;22(11):1557–67.
Wu B, Li L, Qiu T, Zhang X, Cui S. Cytosolic APX2 is a pleiotropic protein involved in H2O2 homeostasis, chloroplast protection, plant architecture and fertility maintenance. Plant Cell Rep. 2018;37(6):833–48.
El-Esawi MA, Alayafi AA: Overexpression of Rice Rab7 Gene Improves Drought and Heat Tolerance and Increases Grain Yield in Rice (Oryza sativa L.). Genes (Basel) 2019, 10(1).
Duvaud S, Gabella C, Lisacek F, Stockinger H, Ioannidis V, Durinx C. Expasy, the Swiss Bioinformatics Resource Portal, as designed by its users. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021;49(W1):W216–27.
Kumar S, Stecher G, Li M, Knyaz C, Tamura K. MEGA X: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis across Computing Platforms. Mol Biol Evol. 2018;35(6):1547–9.
Vandesompele J, De Preter K, Pattyn F, Poppe B, Van Roy N, De Paepe A, Speleman F: Accurate normalization of real-time quantitative RT-PCR data by geometric averaging of multiple internal control genes. Genome Biol 2002, 3(7):RESEARCH0034.
Zhang X, Wang L, Meng H, Wen H, Fan Y, Zhao J. Maize ABP9 enhances tolerance to multiple stresses in transgenic Arabidopsis by modulating ABA signaling and cellular levels of reactive oxygen species. Plant Mol Biol. 2011;75(4–5):365–78.
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Funding
This research was funded by the Ministry of Science and Technology of China (2021YFF1000300) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31771805).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Q.Q, Y.Z., J.Z and L.C conducted the experiments, Q.Q, and Y.Z. analyzed the data and wrote the manuscript, W.S. revised the manuscript, H.J. conceived and supervised the project. All authors contributed to the article and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
All experimental studies on plants were complied with relevant institutional, national, and international guidelines and legislation.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Additional file 1:
Figure 1. Original image of semi-quantitative RT-PCR analysis of ZmHsf11 expression levels in WT, p1301a vector and three T1 transgenic lines in Arabidopsis. Figure 2. Original image of semi-quantitative RT-PCR analysis of ZmHsf11 expression levels in WT and three T1 generation transgenic lines in rice.
Additional file 2:
Figure S1. Identification of ZmHsf11 overexpression positive transgenic Arabidopsis. (A) Schematic representation of a ZmHsf11-containing vector for overexpression transformation. (B) GUS staining of different tissues of positive lines, including seeding, leaf and stem, inflorescence, and silique. (C) Semi-quantitative RT-PCR analysis of ZmHsf11 expression levels in wild-type, p1301a vector and three T1 generation transgenic lines in Arabidopsis. AtActin (AtUBQ5) was used as an internal control. Figure S2. Identification of ZmHsf11 overexpression positive transgenic rice. (A) GUS staining of different tissues of positive lines, including root, stem and leaves. (B) Semiquantitative RT-PCR analysis of ZmHsf11 expression levels in wild-type and three T1 generation transgenic lines in rice. OsActin (OsUBQ5) was used as an internal control. Figure S3. Enhanced heat sensitivity during germination in ZmHsf11 transgenic rice. (A) Seed germination status of wild-type and transgenic plants after treatment at 35 °C for 3 d and recovery at 28 °C for 5 d. (B) Plant height measurements during germination period of wild-type and ZmHsf11 transgenic seeds. Data are mean ± standard deviation (n = 15). **, P < 0.01. Figure S3. Enhanced heat sensitivity during germination in ZmHsf11 transgenic rice. (A) Seed germination status of wild-type and transgenic plants after treatment at 35 °C for 3 d and recovery at 28 °C for 5 d. (B) Plant height measurements during germination period of wild-type and ZmHsf11 transgenic seeds. Data are mean ± standard deviation (n = 15). **, P < 0.01. Figure S4. Physiological indicators of ZmHsf11 transgenic and wild-type rice under heat stress. (A) Net photosynthetic rate. (B) Stomatal conductance. Data are means ± SDs of three independent sample replicates. *, P < 0.05. Figure S5. Reduced ABA sensitivity of ZmHsf11 in Arabidopsis. Growth performance of wild-type and transgenic plants grown on MS medium containing 0.75 μM ABA concentrations after 8 d. Measurements of germination rate of wild-type and ZmHsf11 transgenic seedlings. Data are means ± SDs (n = 36). *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01. Table S1. Primer sequences used in this study.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
About this article
Cite this article
Qin, Q., Zhao, Y., Zhang, J. et al. A maize heat shock factor ZmHsf11 negatively regulates heat stress tolerance in transgenic plants. BMC Plant Biol 22, 406 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-022-03789-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-022-03789-1