Abstract
Background
Lycopene epsilon-cyclase (ε-LCY) is a key enzyme in the carotenoid biosynthetic pathway (CBP) of higher plants. In previous work, we cloned two Ntε-LCY genes from allotetraploid tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum), Ntε-LCY2 and Ntε-LCY1, and demonstrated the overall effect of Ntε-LCY genes on carotenoid biosynthesis and stress resistance. However, their genetic and functional characteristics require further research in polyploid plants.
Results
Here, we used CRISPR/Cas9 to obtain Ntε-LCY2 and Ntε-LCY1 mutants in allotetraploid N.tabacum K326. Ntε-LCY2 and Ntε-LCY1 had similar promoter cis-acting elements, including light-responsive elements. The Ntε-LCY genes were expressed in roots, stems, leaves, flowers, and young fruit, and their highest expression levels were found in leaves. Ntε-LCY2 and Ntε-LCY1 genes responded differently to normal light and high light stress. Both the Ntε-LCY2 and the Ntε-LCY1 mutants had a more rapid leaf growth rate, especially ntε-lcy2-1. The expression levels of CBP genes were increased in the ntε-lcy mutants, and their total carotenoid content was higher. Under both normal light and high light stress, the ntε-lcy mutants had higher photosynthetic capacities and heat dissipation levels than the wild type, and this was especially true of ntε-lcy2-1. The reactive oxygen species content was lower in leaves of the ntε-lcy mutants.
Conclusion
In summary, the expression patterns and biological functions of the Ntε-LCY genes Ntε-LCY1 and Ntε-LCY2 differed in several respects. The mutation of Ntε-LCY2 was associated with a greater increase in the content of chlorophyll and various carotenoid components, and it enhanced the stress resistance of tobacco plants under high light.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Solar radiation provides the energy for plant photosynthesis and growth, but photoinhibition may occur when the plant is subjected to excessively high light [1, 2]. Photosystem II (PSII) has long been considered the most sensitive photosynthetic component to high light in plants, and it is the site of both photoinhibition and photooxidation [3, 4]. Under high light intensity when repair processes can not keep pace with the high D1 degradation rate, light damage accumulates, exacerbating photoinhibition [5, 6]. Photoinhibition can damage PSII, and this damage increases with higher light intensities and longer stress durations [7]. Therefore, the degree of photoinhibition depends on a balance between PSII photodamage and repair. Photoinhibition also leads to photo-oxidation, which drives the accumulation of excess reactive oxygen species (ROS) in the plant. When ROS levels are too high, protein and lipid peroxidation and even DNA damage may occur [8]. Recent studies have shown that ROS act mainly by inhibiting the repair of damaged PSII [9]. Therefore, plants activate various defense mechanisms to reduce the damage caused by high light stress. For example, carotenoids function in photoprotection, antioxidant processes, and light dissipation under high light [10]. Carotenoids protect photosynthetic organs from ROS-mediated damage by dissipating excess light energy under stress conditions [11]. The carotenoid-based lutein cycle is one mechanism by which plants resist photoinhibition [12]; it can increase the heat dissipation capacity of plants, thereby reducing high light damage [13]. The metabolic balance between carotenoid biosynthesis and catabolism is essential for maintaining appropriate carotenoid content and composition in photosynthetic tissues [14].
Cyclization of the end of the carotenoid C40 hydrocarbon chain is an important branch point in the carotenoid biosynthetic pathway (CBP). The lycopene cyclase family is composed of lycopene epsilon-cyclase (ε-LCY) and lycopene beta-cyclase (β-LCY). The ε-LCY enzyme catalyzes only the formation of a δ ring at one end of the lycopene molecule to generate δ-carotene, and a β ring can then be formed at the other end of δ-carotene through the catalysis of β-LCY. δ-carotene finally forms α-carotene, and α-carotene undergoes hydroxylation and other modifications to form lutein in the α branch of the CBP. The β-LCY enzyme can also catalyze the formation of two β rings at both ends of lycopene to generate β-carotene, which is then hydroxylated and epoxidized to generate β-cryptoxanthin, zeaxanthin, antheraxanthin, violaxanthin, neoxanthin, and other carotenoids in the β branch of the CBP. Therefore, the relative activities of ε-LCY and β-LCY directly determine the ratio of α-carotene to β-carotene substrates, and relative flux through the two branches of the CBP has an important influence on the carotenoid composition of higher plants [15,16,17]. To date, the ε-LCY gene has been cloned from a variety of plants and algae, including Arabidopsis, potato, tomato, maize, Chlorella, olive, and others [1, 18, 19].
The ε-LCY gene exists as a single-copy gene in Arabidopsis and maize. It was reported that mutation of ε-LCY in Arabidopsis increased the contents of β-carotene, violaxanthin, zeaxanthin and other substances, but contents of lutein and other products of the α branch decreased [19]. Downregulation of the ε-LCY gene not only increased the carotenoid content of Brassica napus seeds [20] but also improved the salt tolerance of sweet potato transgenic callus by increasing the biosynthesis of β branch carotenoids [21]. The expression level of ε-LCY can significantly affect carotenoid content and composition in higher plants [22]. Under high temperatures, LCY expression determined the ratio of α/β carotene and the content of carotenoids in banana [23]. Mutation of ε-LCY in banana increased the β-carotene content approximatelty six-fold in the fruit pulp; the content of α-carotene and lutein were significantly reduced, but agronomic traits were not significantly affected [24]. These research results show that ε-LCY plays an important role in the regulation of carotenoid composition and stress resistance in plants, although its specific mechanism of action may differ among plant species.
N. tabacum is derived from the hybridization, doubling, and duplication of the ancestral species Nicotiana sylvestris and Nicotiana tomentosiformis. In Nicotiana tabacum, Ntε-LCY is present as two highly homologous copies, Ntε-LCY1 and Ntε-LCY2. The overall effect of Ntε-LCY gene silencing in tobacco was to improve the total carotenoid and chlorophyll contents while increasing the photosynthetic efficiency [22]. Down-regulation of Ntε-LCY gene increased abscisic acid (ABA) levels and enhanced the ability of tobacco to tolerate salt and drought stresses, however, overexpression of Ntε-LCY gene reduced the ability of tobacco to tolerate salt and drought stresses [25]. Ntβ-LCY overexpression mimicked the phenotype of Ntε-LCY gene silencing [26].
The existence of highly homologous genes is a challenging problem for gene functional characterization in polyploid plants. The homologous genes may or may not show strong/weak functional differentiation or temporal and spatial expression differences. Here, we used the model tetraploid plant N. tabacum K326 to investigate the functions of two Ntε-LCY homologs. We characterized the phenotypes and relevant secondary metabolites of ntε-lcy mutants created with CRISPR/Cas9, documented the expression patterns of Ntε-LCY1 and Ntε-LCY2, and analyzed cis-elements in their promoters. Finally, we compared the functional characteristics of Ntε-LCY1 and Ntε-LCY2 under high light stress.
Methods
Plant growth conditions and high light treatment
Seeds of allotetraploid tobacco K326 were provided by the Zhengzhou Tobacco Research Institute. CRISPR/Cas9 mutants of K326 (ntε-lcy2-1, ntε-lcy2-2, ntε-lcy1-1, and ntε-lcy1-2) and wild-type (WT) plants were used as the experimental materials. Plants were grown in a greenhouse with a photosynthetic photon flux density (PAR) of 80–250 μmol m−2 s−1 and a 16-h light/8-h dark photoperiod. The temperature was 25 ± 2 °C, and the relative humidity was 60 ± 2%. Samples used for tissue expression analysis were obtained from 5-month-old wild-type tobacco plants. In other experiments, tobacco plants grown for 45 days were exposed to normal light (PAR = 80–250 μmol m−2 s−1) or high light (PAR = 440–1000 μmol m−2 s−1) for 2 h. Tobacco leaf samples in the same part were frozen in liquid nitrogen immediately before use, and additional samples were stored at − 80℃.
Sequences and bioinformatics analyses of Ntε-LCY genes from N. tabacum
The coding sequences (CDSs) of the target genes (Ntε-LCY2 and Ntε-LCY1) and of homologous genes from Nicotiana sylvestris and Nicotiana tomentosiformis were downloaded from the China Tobacco Genome Database v4.0 (http://10.6.0.76/). The CDSs of Ntε-LCY1 and Ntε-LCY2 were used as blastn queries to search for Solanum tuberosum and Solanum lycopersicum homologs in the website (https://phytozome.jgi.doe.gov/). These ε-LCY protein sequences were aligned by ClustalW, the neighbor-joining trees were constructed by using MEGA7 with 1000 replicates of bootstrap [27]. Conserved domains were identified in the predicted ε-LCY proteins using MEME 4.12.0 software (parameters: -mod anr -nmotifs 12 -minw 6 -maxw 30) (http://meme-suite.org/tools/meme) [28]. The homology of CDSs were visually inspected with DNAMAN software, and cis-acting elements were identified in the 3000-bp promoter regions upstream of Ntε-LCY1 and Ntε-LCY2 using PlantCARE (http://bioinformatics.psb.ugent.be/webtools/plantcare/html/) [29]. The I-TASSER program was used to predict the spatial structures, active sites, and ligand-binding sites of Ntε-LCY1 and Ntε-LCY2 proteins (https://zhanglab.ccmb.med.umich.edu/cgi-bin/itasser_submit.cgi) [30].
Construction of gene editing vectors and identification of homozygous Ntε-LCY mutants
The design of target sites and detection primers and the construction of CRISPR/Cas9 vectors for Ntε-LCY2 and Ntε-LCY1 were carried out according to the Mutation Sites Based Specific Primers Polymerase Chain Reaction (MSBSP-PCR) method [31]. Exon and intron sequence information for the Ntε-LCY2 and Ntε-LCY1 genes was downloaded from the China Tobacco Genome Database, and target sites were identified using CRISPR Multi Targeter (http://www.multicrispr.net/index.html) based on the multiple PAM (NGG or CCN) sites. We selected optimal sgRNA sequences close to the 5' end of the Ntε-LCY2 and Ntε-LCY1 CDSs. Appropriate primers were designed ~ 150 bp upstream and downstream of the target site to detect the position and sequence of gene editing in Ntε-LCY2 and Ntε-LCY1 transgenic lines (Table S2).
Next, the pSHE401 vector was modified to enable the precise mutation of Ntε-LCY2 and Ntε-LCY1 [31]. The Ntε-LCY2 and Ntε-LCY1 recombinant vectors were transformed individually into tobacco callus, and T0 transgenic-positive plants were identified based on the presence of the kanamycin resistance gene sequence using kanamycin gene primers (Table S2). Their seeds were harvested, T1 generation plants were obtained. The mutation sites of the gene-editing positive plants were identified. using the MSBSP-PCR method [31]. The procedure was as follows:If first round of PCR reaction produced amplified products (Primers used: Ntε-LCY1/2-F + Ntε-LCY1/2-R), and the second round of PCR reaction produced no amplified products (Primers used: Ntε-LCY1/2-Target + Ntε-LCY1/2-R) (Table S2), and then picked 100 µL of positive bacterial solution and sent them to Beijing Tsingke Biotechnology Co., Ltd. for bacterial solution sequencing verification, and used Geneious software to check the sequence results, Finally Ntε-LCY1 and Ntε-LCY2 homozygous mutant lines were identified.
Phenotypic observations of the Ntε-LCY mutants
To minimize the influence of off-target gene editing effects, two separate T2 homozygous mutant lines for each gene were used for phenotypic observations and analysis. The maximum length and maximum width of the third true leaf (L3) from the top of WT and ntε-lcy2-1, ntε-lcy2-2, ntε-lcy1-1, and ntε-lcy1-2 mutant plants were measured with a ruler (12 plants per genotype). The phenotypes of WT, ntε-lcy2-1, and ntε-lcy1-1 plants were photographed.
Measurement of chlorophyll a and chlorophyll b contents
Chlorophyll a and chlorophyll b contents were measured as described in [32].
Extraction and quantitative analysis of carotenoids
Fresh, freeze-dried tobacco leaves were ground into powder with a ball mill (30 Hz, 1 min). An appropriate amount of internal standard was added to 50 mg of the ground sample, and carotenoids were extracted with a mixture (1:1:2, v/v/v) of n-hexane, acetone, and ethanol that contained 0.01% BHT (g/mL). The extract was vortexed for 20 min at room temperature. After repeating the extraction, the supernatant was collected by centrifugation, then evaporated to dryness under nitrogen flow and reconstituted in a 3:1 mixture (v/v) of methanol and MTBE. Finally, the solution was filtered through a 0.22-μm filter and analyzed by high performance liquid chromatography-photo diode array detection-mass spectrometry (HPLC–DAD-MS) method with atmospheric pressure chemical ionization (APCI) mode for qualitative [33]. Analyst 1.6.3 software was used to process the mass spectrometry data. The integrated peak area ratios of all samples were entered into the standard curve equation, and the absolute contents of various carotenoids in the actual samples were calculated.
Total RNA extraction and quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR)
Total RNA was extracted from leaf tissue of ntε-lcy2-1, ntε-lcy1-1, and WT plants using the Spin Column Plant Total RNA Purification Kit (Shenggong, China), and cDNA was synthesized from the extracted RNA using TransScript One-Step gDNA Removal and cDNA Synthesis SuperMix (Transgen, China), and the RNA/cDNA quality was checked using a ultra-versus spectrophotometer. qRT-PCR was performed using Super Real PreMix Plus (Tiangen, China) on a Light Cycler 480 II system (Roche, Switzerland). The 2−∆∆Ct method was used to calculate relative gene expression [34], using the 26 s RNA gene as an internal reference. The qRT-PCR primers for the Ntε-LCY genes and related genes in the CBP were designed with Primer-BLAST software [35] and are listed in Table S3.
Measurement of chlorophyll fluorescence parameters
Chlorophyll fluorescence parameters were measured using an Imaging-PAM-MAXI chlorophyll fluorescence meter (Walz, Germany) between 9:00 a.m. and 11:00 a.m. The chlorophyll fluorometer was connected to a computer, and ImagingWin software (Walz, Germany) was used for data acquisition. The experimental protocol followed that described in [36].
There were two different groups of tobacco seedlings, one exposed to normal light (PAR = 80 μmol m−2 s−1), one exposed to high light (PAR = 440 μmol m−2 s−1) for 2 h. ImagingWin software was used to measure six areas of individual leaves, and five sets of leaves were measured for each genotype. Chlorophyll fluorescence parameters were calculated as follows: maximum photosynthetic efficiency of PSII (Fv/Fm) = (Fm − F0)/Fm, and non-photochemical quenching (NPQ) = (Fm-Fm')/Fm' [37].
Measurement of O2 − and H2O2 content
We analyzed the O2− content using the nitroblue tetrazolium (NBT) staining method. First, we added 5 mg of NBT to 50 mL 25 mM Hepes buffer solution and then added 50 μL 0.1% Triton X-100 to make a 0.1 mg/mL NBT solution. We used a punch to obtain tobacco leaf discs having a diameter of 0.5 cm from the same part of each plant. We immersed all the samples in the NBT dye solution, stained them for 24 h at 28℃ in the dark, removed the dye solution, added 80% ethanol, and placed the samples in a boiling water bath for 3 min. We removed the 80% ethanol, added absolute ethanol, and kept the samples in the boiling water bath for another 3 min. If necessary, these steps were repeated until no green color remained. We added absolute ethanol to the completely decolorized samples and photographed them under a microscope (Smartzoom5, Zeiss, Germany). H2O2 content was measured following the manufacturer’s instructions of a hydrogen peroxide kit (Suzhou Comin, China) based on absorbance at 415 nm measured with a microplate reader (Multiskan GO, Thermo Scientific, USA). We confirm that all materials and methods were performed in accordance with the relevant guidelines/regulations/legislation in China.
Statistical analysis
All experiments included at least three independent technical and biological replicates, and data are expressed as the mean ± standard error of the mean (SEM). All data analyses and processing were performed using Microsoft Excel and GraphPad Prism 5 software (GraphPad Software, Inc. USA). Data for each experiment were compared among WT, ntε-lcy2-1, and ntε-lcy1-1 lines using one- or two-way ANOVA and Tukey’s post-hoc test (*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001).
Results
Sequences and bioinformatics analyses of Ntε-LCY genes from N. tabacum
To investigate the genetic basis for potential functional differentiation between Ntε-LCY2 and Ntε-LCY1, we analyzed their phylogenetic relationships, conserved domains, and homology to related genes in Solanaceae species. MEME analysis of their predicted amino acid sequences showed that Ntε-LCY2 and Ntε-LCY1 were highly conserved and had similarities and differences in their conserved motifs. Both Ntε-LCY2 and Ntε-LCY1 contained motifs 9, 5, 1, 8, 11, 10, 12, 2, 4, and 6, but Ntε-LCY2 contained motif 3 and Ntε-LCY1 contained motif 7. The CDS of Ntε-LCY2 is 1497 bp in length and encodes 498 amino acids, whereas that of Ntε-LCY1 was 1431 bp in length and encoded 476 amino acids. The coding sequence of the ε-LCY gene in both ancestral species was 1431 bp in length and encoded 476 amino acids. One ε-LCY gene was identified in tomato (Solanum lycopersicum, Sly) and potato (Solanum tuberosum, Stu). In both cases, its coding sequence was 1584 bp in length and encoded 528 amino acids. The homology of the Ntε-LCY2 and Ntε-LCY1 CDSs was 87.95%. The phylogenetic relationships, conserved domains, and percent homologies of Ntε-LCY2, Ntε-LCY1, and related Solanaceae genes are presented in Fig. S1a. Although Ntε-LCY2 and Ntε-LCY1 proteins had very similar predicted structures, ligand binding sites, and enzyme active sites, there were some differences. For example, Ntε-LCY2 had a predicted F280 active site in motif 3 and a Y465 active site in motif 6, but these were absent in Ntε-LCY1. These differences may be related to the functional characteristics of Ntε-LCY2 and Ntε-LCY1 proteins (Fig. S1a–b).
The 3000-bp promoter regions of Ntε-LCY2 and Ntε-LCY1 contained a number of conserved motifs, such as ARE, MBS, ABRE, and AE-box. The unique motifs in the Ntε-LCY2 promoter were TGA-element, CA-motif, GA-motif, TCT-motif, chs-CMA1a, and chs-CMA2a. The unique motifs in the Ntε-LCY1 promoter were TC-rich repeats, HD-Zip1, AT1-motif, ACE, G-box, and LTR. Both promoters contained light response elements, consistent with a potential function in protection against high light stress (Table S1).
Phenotypes of Ntε-LCY mutants generated by CRISPR/Cas9-mediated editing
To investigate the functions of the Ntε-LCY genes, we used CRISPR/Cas9-mediated editing to generate mutants of Ntε-LCY2 and Ntε-LCY1 using the MSBSP-PCR method [31]. Four lines (ntε-lcy2-1, ntε-lcy2-2, ntε-lcy1-1, and ntε-lcy1-2) produced amplification products of ~ 300 bp in the first round of PCR and produced no amplification products in the second round, indicating that Ntε-LCY2 and Ntε-LCY1 homozygous mutants had been generated successfully (Fig. S2). Corresponding bacterial liquid was successfully sequenced and verified (Fig. S3; Fig. 1a–b). Sequence alignment showed that the target site of Ntε-LCY2 was located between 478 and 496 bp from the 5′ to the 3′ end. ntε-lcy2-1 contained a homozygous 17-bp base substitution between 478 and 494 bp, and ntε-lcy2-2 contained a homozygous 1-bp deletion at 492 bp (Fig. 1a). The target site of Ntε-LCY1 was between 172 and 191 bp from the 5′ to the 3′ end. ntε-lcy1-1 contained a homozygous 1-bp deletion at 187 bp, and ntε-lcy1-2 contained a homozygous 1-bp insertion at 188 bp (Fig. 1b).
Identification and phenotypic analysis of homozygous Ntε-LCY mutants. a–b Sequence analysis of Ntε-LCY2 and Ntε-LCY1 homozygous mutant strains generated by CRISPR/Cas9; the red font indicates the gene editing area. c Tissue expression patterns of Ntε-LCY2 and Ntε-LCY1 in roots, stems, leaves, flowers and young fruit by qRT-PCR. Data are presented as the mean ± standard error of the mean (SEM) of three independent experiments (n = 3; two-way ANOVA; Tukey’s post-hoc test). d–e Maximum length and width of the third true leaf (L3) of five tobacco materials (WT, ntε-lcy2-1, ntε-lcy2-2, ntε-lcy1-1, and ntε-lcy1-2). Data are presented as the mean ± SEM of at least 12 plants. Scale bar = 1 cm (n = 12 *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01; one-way ANOVA; Tukey’s post-hoc test). f Phenotypes of three lines (WT, ntε-lcy2-1, and nt ε-lcy1-1), and the interval of each two plants is 15 cm
Ntε-LCY2 and Ntε-LCY1 genes were weakly expressed in roots, stems, flowers, and young fruit; the highest transcript levels were detected in leaves, which were then used for subsequent gene functional analyses (Fig. 1c). Notably, Ntε-LCY2 and Ntε-LCY1 had similar expression patterns in all tissues. There was therefore no evidence for temporal or spatial expression differences, although functional differentiation could not be ruled out.
Our previous studies revealed that silencing of Ntε-LCY led to higher leaf carotenoid content, and carotenoids have essential roles in plant development. We therefore collected basic phenotypic data on the WT and Ntε-LCY mutant lines. At the four-leaf stage, WT, ntε-lcy2-1, ntε-lcy2-2, ntε-lcy1-1, and ntε-lcy1-2 plants differed significantly in the maximum length and width of the third true leaf (L3). L3 leaf length and width were largest in the ntε-lcy2 lines, somewhat lower in the ntε-lcy1 lines, and smallest in the WT plants (Fig. 1d–e). We therefore used leaf tissues from WT, ntε-lcy2-1, and ntε-lcy1-1 plants in subsequent research. When the ntε-lcy2-1 and ntε-lcy1-1 mutants had four leaves, the fourth leaves of the WT plants were not always visible. Leaves grew larger and more rapidly in ntε-lcy2-1, suggesting that mutation of Ntε-LCY2 led to more plant benefits (Fig. 1f).
The accumulation of carotenoids was enhanced in the leaves of Ntε-LCY mutants
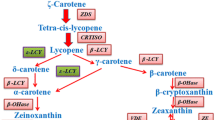
To better understand the effect of Ntε-LCY mutation on the CBP (Fig. 2a) and on the leaf phenotype of Ntε-LCY mutants, we examined the content of different carotenoids in the ntε-lcy2-1 and ntε-lcy1-1 mutants by high performance liquid chromatography-photo diode array detection-mass spectrometry (HPLC–DAD-MS) method with atmospheric pressure chemical ionization (APCI) mode [33]. The ntε-lcy2-1 mutants showed the highest carotenoid levels, followed by the ntε-lcy1-1 mutants and the WT plants, consistent with the leaf phenotype data. Among the main types of carotenoids, α-carotene and β-cryptoxanthin contents were significantly higher in the Ntε-LCY mutants, especially in the leaves of ntε-lcy2-1 (Fig. 2c). The contents of phytoene, zeaxanthin, and β-carotene were also somewhat higher in the Ntε-LCY mutants (Fig. 2c–d). The lutein content of ntε-lcy2-1 was significantly higher than that of ntε-lcy1-1 and WT (Fig. 2d), and the zeinoxanthin content was clearly higher in the Ntε-LCY mutants than in the WT (Fig. 2f). There were no significant differences in antheraxanthin or violaxanthin content among the genotypes (Fig. 2c–e).
Mutation of Ntε-LCY affects the carotenoid and chlorophyll contents of leaves. a Diagram of the carotenoid biosynthetic pathway (CBP). Target genes studied in this experiment are printed in red. Isopentenyl diphosphate (IPP), dimethylallyl diphosphate (DMAPP), geranylgeranyl diphosphate (GGPP), phytoene synthase (PSY), phytoene desaturase (PDS), ζ-carotene desaturase (ZDS), carotenoid isomerase (CRTISO), β-lycopenecyclase (β-LCY), β-carotene hydroxylase (β-OHase), violaxanthin deepoxidase (VDE), zeaxanthin epoxidase (ZE), and neoxanthin synthase (NXS) are shown. b–f Relative carotenoid and chlorophyll levels in WT and Ntε-LCY mutant strains. Chlorophyll a, Chlorophyll b, phytoene, α-carotene, β-cryptoxanthin, zeaxanthin, antheraxanthin, lutein, β-carotene, violaxanthin, neoxanthin, γ-carotene, and zeinoxanthin are shown. Data are presented as the mean ± SEM of three independent experiments (n = 3, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001; two-way ANOVA, Tukey’s post-hoc test)
Chlorophyll a (Chl a) and Chlorophyll b (Chl b) contents were also much higher in the Ntε-LCY mutants. Chlorophyll content showed the same trend as leaf growth and carotenoid content: highest in ntε-lcy2-1, followed by ntε-lcy1-1 and the WT. Together, these data suggested that mutation of Ntε-LCY genes indeed enhanced the accumulation of carotenoids and chlorophylls. Ntε-LCY2 mutation promoted carotenoid and chlorophyll accumulation to a greater extent than Ntε-LCY1 mutation, suggesting that the homologs exhibited strong and weak functional differentiation.
Ntε-LCY2 mutation has stronger effects than Ntε-LCY1 mutation on carotenoid biosynthesis
The products of most CBP enzymes were present at higher levels in the ntε-lcy2-1 and ntε-lcy1-1 mutants. The first CBP product, phytoene, is crucial for the regulation of the entire pathway. However, the contents of lutein and β-carotene, the main carotenoid components in N. tabacum, were also clearly increased in the mutants. We next examined the expression levels of genes that encoded CBP enzymes. qRT-PCR results showed that the expression levels of phytoene synthase (PSY), phytoene desaturase (PDS), ζ-carotene desaturase (ZDS), carotenoid isomerase (CRTISO), β-lycopene cyclase (β-LCY), β-carotene hydroxylase (β-OHase), violaxanthin deepoxidase (VDE), zeaxanthin epoxidase (ZE), and neoxanthin synthase (NXS) genes were upregulated in ntε-lcy plants under normal growing conditions. Their expression patterns showed the same trend: highest in ntε-lcy2-1, followed by ntε-lcy1-1, and lowest in the WT. Notably, the expression levels of β-LCY, ZE, and NXS were significantly higher in ntε-lcy plants than in the WT. However, the expression level of VDE was lower in Ntε-LCY mutants than in the WT under normal conditions (Fig. 3).
Relative expression of upstream and downstream genes related to the Ntε-LCY branch of the CBP after exposuring to normal light (photon flux density (PAR) = 250 μmoL m−2 s−1) and high light ( photon flux density (PAR) = 1000 μmoL m−2 s−1) for 2 h. Phytoene synthase (PSY), phytoene desaturase (PDS), ζ-carotene desaturase (ZDS), carotenoid isomerase (CRTISO), β-lycopenecyclase (β-LCY), β-carotene hydroxylase (β-OHase), violaxanthin deepoxidase (VDE), zeaxanthin epoxidase (ZE), and neoxanthin synthase (NXS) are shown. Data are presented as the mean ± SEM of three independent experiments (n = 3, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001; two-way ANOVA, Tukey’s post-hoc test)
Carotenoids can protect the photosystems from photodamage and photoinhibition under high light stress. To gain insights into the biological effects of Ntε-LCY mutation, we used qRT-PCR to examine the expression of CBP enzyme genes in WT, ntε-lcy2-1, and ntε-lcy1-1 after a 2 h exposure to high light. Under high light stress, the relative expression levels of PSY, PDS, ZDS, β-OHase, VDE, and NXS were strongly upregulated in ntε-lcy mutants compared to their expression under normal growing conditions. The genotypes showed the same trend from high (ntε-lcy2-1) to low (WT). By contrast, the relative expression of CRTISO was significantly upregulated in ntε-lcy2-1 but downregulated in ntε-lcy1-1 and the WT. The relative expression of β-LCY was significantly downregulated in ntε-lcy1-1 and WT plants but only slightly affected by high light stress in ntε-lcy2-1. Finally, the relative expression of ZE was downregulated in the Ntε-LCY mutants and the WT under high light stress. Together, these results demonstrate that Ntε-LCY2 mutation produces stronger effects than Ntε-LCY1 mutation on carotenoid biosynthesis and the photosynthetic system.
Ntε-LCY2 and Ntε-LCY1 genes showed different light response patterns
Given that Ntε-LCY mutation could strongly induce carotenoid-related gene expression and increase carotenoid and chlorophyll levels, we further analyzed the expression of the two Ntε-LCY genes under normal light and high light stress using qRT-PCR. Under normal light conditions, the relative expression of Ntε-LCY2 was significantly higher in WT than in ntε-lcy1-1. In fact, the relative expression of Ntε-LCY2 in ntε-lcy1-1 was almost zero. After 2 h of high light exposure, the expression of Ntε-LCY2 was upregulated in both WT and ntε-lcy1-1, but its expression was still significantly higher in WT. This result indicated that the expression of Ntε-LCY2 is inhibited in the ntε-lcy1-1 mutant and that high light induces Ntε-LCY2 expression (Fig. 4a). However, high light exposure repressed the expression of Ntε-LCY1, and Ntε-LCY1 expression was also inhibited in the ntε-lcy2-1 mutant (Fig. 4b). Under normal light conditions, the relative expression of Ntε-LCY1 was higher in WT than in ntε-lcy2-1. After 2 h of high light exposure, the relative expression of Ntε-LCY1 was downregulated in both WT and ntε-lcy2-1 (Fig. 4b). Therefore, expression of Ntε-LCY1 or Ntε-LCY2 was repressed by the mutation of its homolog. The two genes also showed contrasting responses to high light stress: high light induced Ntε-LCY2 expression but repressed Ntε-LCY1 expression, perhaps owing to differences in their promoter cis-elements. These results suggested that Ntε-LCY2 may have a more important function in α-carotene biosynthesis, as both Ntε-LCY2 transcripts and lutein accumulated to a greater extent in response to high light stress (Fig. 4).
Ntε-LCY2 and Ntε-LCY1 genes have different light response patterns in leaves. a Response pattern of Ntε-LCY2 in WT and ntε-lcy1-1 lines after exposure to normal light (PAR = 250 μmoL m−2 s−1) and high light (PAR = 1000 μmoL m−2 s−1) for 2 h measured by qRT-PCR. b Response pattern of Ntε-LCY1 in WT and ntε-lcy2-1 lines after exposuring to normal light (PAR = 250 μmoL m−2 s−1) and high light (PAR = 1000 μmoL m−2 s−1) for 2 h measured by qRT-PCR. (n = 3, *p < 0.05; two-way ANOVA, Tukey’s post-hoc test)
The photosynthetic apparatus was protected in Ntε-LCY mutants under high light stress, especially in ntε-lcy2
To gain insight into the biological effects of Ntε-LCY mutation, we examined the photosynthetic parameters of 45-day-old WT, ntε-lcy2-1, and ntε-lcy1-1 seedlings after exposuring to high light stress for 2 h. Under normal light conditions, the maximum photochemical efficiency of PSII (Fv/Fm) was significantly higher in Ntε-LCY mutant plants than in the WT. However, there was no clear difference in Fv/Fm between ntε-lcy2-1 and ntε-lcy1-1. After a 2 h exposure to high light stress, Fv/Fm was lower in all genotypes, but it was higher in the Ntε-LCY mutant plants than in the WT plants, especially in the ntε-lcy2-1 mutant (Fig. 5a).
Effect of high light stress on photosynthetic parameters of detached leaves of Ntε-LCY mutant plants. a Effect of a 2-h exposure to normal light or high light stress on the leaf maximum photochemical efficiency of PSII (Fv/Fm) in Ntε-LCY mutant plants. b Non-photochemical quenching of chlorophyll fluorescence (NPQ) in detached leaves of Ntε-LCY mutant plants exposed to high light stress for 2 h. The photon flux density (PAR) of normal light was 80 μmoL m−2 s−1, and that of high light was 440 μmoL m−2 s−1. Data are presented as the mean ± SEM of four independent experiments (n = 4, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01; two-way ANOVA, Tukey’s post-hoc test)
We next examined non-photochemical quenching (NPQ) in 45-day-old WT, ntε-lcy2-1, and ntε-lcy1-1 seedlings after exposuring to high light stress for 2 h (Fig. 5b). Under normal light conditions, NPQ was higher in the Ntε-LCY mutant plants than in the WT plants, and NPQ was significantly higher in ntε-lcy2-1 plants than in WT and ntε-lcy1-1 plants. After a 2 h exposure to high light stress, NPQ increased significantly in all genotypes; it was the highest in the ntε-lcy2-1 plants, followed by ntε-lcy1-1 and WT plants. These data indicated that photosynthetic capacity and heat dissipation capacity were higher in Ntε-LCY mutant plants than in WT plants regardless of light level, consistent with their enhanced accumulation of carotenoids and chlorophylls.Ntε-LCY2 mutation promoted the accumulation of carotenoids in the β-carotene branch of the CBP, thereby promoting light stress adaptation. In particular, lutein wss essential for NPQ, and the higher lutein content of ntε-lcy2-1 can be seen in Fig. 2d. Together, these results showed that Ntε-LCY mutations, especially mutation of Ntε-LCY2, directed the metabolic flux toward β-carotene biosynthesis and improved photosynthetic efficiency in tetraploid N. tabacum.
Mutation of Ntε-LCY2 and Ntε-LCY1 reduced ROS accumulation in tobacco leaves under normal and high light stress conditions
Given the higher carotenoid accumulation and photosynthetic efficiency of the ntε-lcy mutants, we next examined their O2− and hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) contents after a 2 h exposure to high light stress. Both ntε-lcy2-1 and ntε-lcy1-1 showed lighter nitroblue tetrazolium staining than the WT under normal light conditions, and the degree of staining did not differ significantly between ntε-lcy2-1 and ntε-lcy1-1. After a 2 h exposure to high light, the depth of blue staining was highest in the WT, followed by ntε-lcy1-1 and ntε-lcy2-1 (Fig. 6a). Mutation of Ntε-LCY2 and Ntε-LCY1 genes reduced the accumulation of O2− in tobacco leaves under normal and high light conditions.
The mutation of Ntε-LCY genes reduced the accumulation of reactive oxygen species in leaves to different extents after exposure to normal light or high light stress in WT, ntε-lcy2-1, and ntε-lcy1-1 lines. a In situ O2− production in 1-cm leaf discs by NBT staining (n = 12). b Total H2O2 content of WT and ntε-lcy lines after exposuring to normal light or high light stress. Data are presented as the mean ± SEM of three independent experiments (n = 3, *p < 0.05; two-way ANOVA, Tukey’s post-hoc test)
Similarly, the H2O2 content was lower in ntε-lcy2-1 and ntε-lcy1-1 than in WT under normal light conditions, and it was lowest in ntε-lcy1-1. However, after a 2 h high light exposure, H2O2 content was highest in WT, followed by ntε-lcy1-1 and ntε-lcy2-1 (Fig. 6b). H2O2 accumulation did not change significantly in ntε-lcy2-1 or WT under high light, but it increased significantly in ntε-lcy1-1 (Fig. 6b). These results suggested that Ntε-LCY2 and Ntε-LCY1 mutation reduced the production and/or enhanced the scavenging of H2O2 in tobacco leaves under normal and high light conditions. Overall, the mutation of Ntε-LCY2 and, to a lesser extent, Ntε-LCY1 increased carotenoid accumulation, improved the maximum efficiency of PSII and NPQ, and reduced the accumulation of ROS.
Discussion
Homologous genes with high sequence similarity are always present in the genomes of polyploid plants and may show similar or contrasting expression patterns. Owing to gene sequence variation and genome recombination, the functions of homologous genes may change through differentiation, silencing, gain of new function, etc. They may exhibit functional differentiation, strong and weak functional differentiation, and/or spatiotemporal expression differences. During molecular breeding, it is crucial to precisely delineate the functional differentiation of homologs so that the more effective gene can be selected. ε-LCY is located at the branch point of the α and β branches of the CBP and therefore directly determines the ratio of α-carotene to β-carotene. There are two ε-LCY genes in the N. tabacum K326 genome, Ntε-LCY1 and Ntε-LCY2. The two genes had similar expression patterns in different tissues; both had the highest expression in leaves (Fig. 1c), suggesting that they functioned in tobacco leaf growth and development, consistent with the findings of Shi et al. [22]. There were four points of difference between the two homologs. First, bioinformatic predictions indicated that Ntε-LCY1 and Ntε-LCY2 had two different amino acids in the enzyme active site, which may contribute to differences in their enzyme activities (Fig. S1a–b). Second, their promoters contained some unique cis-elements (Table S1). Third, high light stress induced the expression of Ntε-LCY2 but repressed the expression of Ntε-LCY1, perhaps owing to their different promoter cis-elements. Fourth, Ntε-LCY2 mutation produced stronger effects than Ntε-LCY1 mutation on the regulation of carotenoid biosynthesis and photosynthetic parameters. Together, these differences between Ntε-LCY2 and Ntε-LCY1 were consistent with classical strong and weak functional differentiation.
The biological function of ε-LCY is different from that of other genes in the CBP [20, 22, 24]. Mutation of ε-OHase in Arabidopsis caused a decrease in lutein content; β-carotene content did not increase significantly, but the contents of violaxanthin and zeaxanthin, which are located downstream of β-carotene, did increase [26]. The CRTISO mutant in Arabidopsis accumulated large amounts of lycopene and had lower contents of lutein, β-carotene, violaxanthin, and zeaxanthin. Chlorophyll a and chlorophyll b contents were also lower, and the content of violaxanthin decreased slightly [38]. Mutation of β-OHase in Arabidopsis caused a decrease in lutein, β-carotene, violaxanthin, and zeaxanthin and an increase in α-carotene content [39]. Unlike the former genes, the silencing of PSY, PDS, β-LCY, and VDE caused the photobleaching of different plant organs and/or significant declines in photosynthetic efficiency and stress resistance [40,41,42,43,44,45].Therefore, it would be helpful to study the functional differentiation of homologous genes in allotetraploid tobacco.
The overall effect of downregulating or silencing tobacco Ntε-LCY is to increase total carotenoid and chlorophyll contents, photosynthetic efficiency, and levels of the stress response hormone ABA. Ntε-LCY silencing can also enhance plant tolerance to salt, drought, and other environmental stresses [22, 25]. Our results showed that the mutation of Ntε-LCY2 and Ntε-LCY1 increased the chlorophyll (Fig. 2b) and carotenoid (Fig. 2c–f) contents, decreased photoinhibition (Fig. 5), and reduced the accumulation of ROS (Fig. 6). Therefore, the tolerance of tobacco plants to high light stress appeared to be improved. Ntε-LCY2 and Ntε-LCY1 mutation increased the contents of chlorophyll a, chlorophyll b, α-carotene, β-carotene, β-cryptoxanthin, and lutein to varying degrees (Fig. 2b–d). The contents of β-cryptoxanthin and lutein were up to 2.15 times and 1.79 times higher in ntε-lcy2-1 than in ntε-lcy1-1 (Fig. 2c–d). Likewise, a previous study in banana reported that β-carotene content increased up to six-fold when ε-LCY was edited, but the α-carotene and lutein contents were decreased [24]. NPQ reflects the photoprotective ability of plants; it dissipates excess energy from the photosynthetic electron transport chain and reduces ROS accumulation [46]. Xanthophylls and lutein play an important role in the photoprotection of PSII [47]. Ntε-LCY2 mutation increased plant carotenoid accumulation, thereby protecting the photosynthetic apparatus and reducing ROS accumulation to a greater extent than Ntε-LCY1 mutation.
Our results demonstrated that the mutation of Ntε-LCY2 or its homologs in other plants can be conveniently achieved through CRISPR/Cas9-mediated genome editing or other mutagenesis technology.
Availability of data and materials
Sequence data of the genes described in this article can be found in supplementary information files, The authors affirm that all data generated or analysed during this study are included in this published article [and its supplementary information files].
Abbreviations
- CBP:
-
Carotenoid biosynthetic pathway
- CDSs:
-
Coding sequences
- PSII:
-
Photosystem II
- Fv/Fm:
-
Maximum photosynthetic efficiency of PSII
- PAR:
-
Photosynthetic photon flux density
- NPQ:
-
Non-photochemical quenching
- NBT:
-
Nitroblue tetrazolium
- ROS:
-
reactive oxygen species
- H2O2 :
-
Hydrogen peroxide
- ABA:
-
Abscisic acid
- Nsyε-LCY :
-
Nicotiana sylvestris
- Ntomε-LCY :
-
Nicotiana tomentosiformis
- Stuε-LCY :
-
Solanum tuberosum
- Slyε-LCY :
-
Solanum lycopersicum
- qRT-PCR:
-
Quantitative real-time PCR
- IPP:
-
Isopentenyl diphosphate
- DMAPP:
-
Dimethylallyl diphosphate
- GGPP:
-
Geranylgeranyl diphosphate
- PSY :
-
Phytoene synthase
- PDS :
-
Phytoene desaturase
- ZDS :
-
ζ-Carotene desaturase
- CRTISO :
-
Carotenoid isomerase
- ε-LCY :
-
Lycopene epsilon-cyclase
- β-LCY :
-
Lycopene beta-cyclase
- β-OHase :
-
β-Carotene hydroxylase
- VDE :
-
Violaxanthin deepoxidase
- ZE:
-
Zeaxanthin epoxidase
- NXS:
-
neoxanthin synthase
References
Diretto G, Tavazza R, Welsch R, Pizzichini D, Mourgues F, Papacchioli V, Beyer P, Giuliano G. Metabolic engineering of potato tuber carotenoids through tuber-specific silencing of lycopene epsilon cyclase. BMC PLANT BIOL. 2006;6:13.
Oquist G, Anderson JM, McCaffery S, Chow WS. Mechanistic differences in photoinhibition of sun and shade plants. Planta. 1992;188(3):422–31.
Huang W, Yang YJ, Hu H, Zhang SB. Moderate Photoinhibition of Photosystem II Protects Photosystem I from Photodamage at Chilling Stress in Tobacco Leaves. FRONT PLANT SCI. 2016;7:182.
Critchley C, Smillie RM: Leaf Chlorophyll Fluorescence as an Indicator of High Light Stress (Photoinhibition) in Cucumis sativus L. Funct Plant Biol. 1981;8. https://www.publish.csiro.au/fp/PP9810133.
Yamamoto Y, Hori H, Kai S, Ishikawa T, Ohnishi A, Tsumura N, Morita N. Quality control of Photosystem II: reversible and irreversible protein aggregation decides the fate of Photosystem II under excessive illumination. FRONT PLANT SCI. 2013;4:433.
Aro EM, Virgin I, Andersson B. Photoinhibition of Photosystem II. Inactivation, protein damage and turnover. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1993;1143(2):113–34.
Brestic M, Zivcak M, Kunderlikova K, Allakhverdiev SI. High temperature specifically affects the photoprotective responses of chlorophyll b-deficient wheat mutant lines. PHOTOSYNTH RES. 2016;130(1–3):251–66.
Zhang QY, Wang LY, Kong FY, Deng YS, Li B, Meng QW. Constitutive accumulation of zeaxanthin in tomato alleviates salt stress-induced photoinhibition and photooxidation. Physiol Plant. 2012;146(3):363–73.
Nishiyama Y, Murata N. Revised scheme for the mechanism of photoinhibition and its application to enhance the abiotic stress tolerance of the photosynthetic machinery. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2014;98(21):8777–96.
Dong C, Qu G, Guo J, Wei F, Gao S, Sun Z, Jin L, Sun X, Rochaix J, Miao Y, et al. Rational design of geranylgeranyl diphosphate synthase enhances carotenoid production and improves photosynthetic efficiency in Nicotiana tabacum. Sci Bull. 2022;67(3):315–27.
Han H, Li Y, Zhou S. Overexpression of phytoene synthase gene from Salicornia europaea alters response to reactive oxygen species under salt stress in transgenic Arabidopsis. Biotechnol Lett. 2008;30(8):1501–7.
Niyogi KK, Shih C, Soon CW, Pogson BJ, Dellapenna D, Bjorkman O. Photoprotection in a zeaxanthin- and lutein-deficient double mutant of Arabidopsis. Photosynth Res. 2001;67(1–2):139–45.
Demmig-Adams B, Adams WW. Photoprotection and Other Responses of Plants to High Light Stress. Ann Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol. 1992;43(1):599–626.
Beisel KG, Jahnke S, Hofmann D, Koppchen S, Schurr U, Matsubara S. Continuous turnover of carotenes and chlorophyll a in mature leaves of Arabidopsis revealed by 14CO2 pulse-chase labeling. Plant Physiol. 2010;152(4):2188–99.
Chettry U, Chrungoo NK. A multifocal approach towards understanding the complexities of carotenoid biosynthesis and accumulation in rice grains. Brief Funct Genomics. 2020;19(4):324–35.
Liang MH, Liang ZC, Chen HH, Jiang JG. The bifunctional identification of both lycopene beta- and epsilon-cyclases from the lutein-rich Dunaliella bardawil. Enzyme Microb Technol. 2019;131:109426.
Domonkos I, Kis M, Gombos Z, Ughy B. Carotenoids, versatile components of oxygenic photosynthesis. Prog Lipid Res. 2013;52(4):539–61.
Bai L, Kim EH, Dellapenna D, Brutnell TP. Novel lycopene epsilon cyclase activities in maize revealed through perturbation of carotenoid biosynthesis. Plant J. 2009;59(4):588–99.
Cunningham FJ, Pogson B, Sun Z, McDonald KA, DellaPenna D, Gantt E. Functional analysis of the beta and epsilon lycopene cyclase enzymes of Arabidopsis reveals a mechanism for control of cyclic carotenoid formation. Plant Cell. 1996;8(9):1613–26.
Yu B, Lydiate DJ, Young LW, Schafer UA, Hannoufa A. Enhancing the carotenoid content of Brassica napus seeds by downregulating lycopene epsilon cyclase. Transgenic Res. 2008;17(4):573–85.
Kim SH, Kim YH, Ahn YO, Ahn MJ, Jeong JC, Lee HS, Kwak SS. Physiol Plant. 2013;147(4):432–42.
Shi Y, Wang R, Luo Z, Jin L, Liu P, Chen Q, Li Z, Li F, Wei C, Wu M, et al. Molecular cloning and functional characterization of the lycopene epsilon-cyclase gene via virus-induced gene silencing and its expression pattern in Nicotiana tabacum. Int J Mol Sci. 2014;15(8):14766–85.
Fu X, Cheng S, Feng C, Kang M, Huang B, Jiang Y, Duan X, Grierson D, Yang Z. Lycopene cyclases determine high alpha-/beta-carotene ratio and increased carotenoids in bananas ripening at high temperatures. Food Chem. 2019;283:131–40.
Kaur N, Alok A, Shivani, Kumar P, Kaur N, Awasthi P, Chaturvedi S, Pandey P, Pandey A, Pandey AK, et al. CRISPR/Cas9 directed editing of lycopene epsilon-cyclase modulates metabolic flux for beta-carotene biosynthesis in banana fruit. Metab Eng. 2020;59:76–86.
Shi Y, Liu P, Xia Y, Wei P, Li W, Zhang W, Chen X, Cao P, Xu Y, Jin L, et al. Downregulation of the lycopene ε-cyclase gene confers tolerance to salt and drought stress in Nicotiana tabacum. Acta Physiol Plant. 2015;37(10):210.
Tian L, Musetti V, Kim J, Magallanes-Lundback M, DellaPenna D. The Arabidopsis LUT1 locus encodes a member of the cytochrome p450 family that is required for carotenoid epsilon-ring hydroxylation activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004;101(1):402–7.
Tamura K: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis using Maximum Likelihood, Evolutionary Distance, and Maximum Parsimony Methods. Mol Biol Evol. 2011;28. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21546353/.
Bailey TL, Boden M, Buske FA, Frith M, Grant CE, Clementi L, Ren J, Li WW, Noble WS. MEME SUITE: tools for motif discovery and searching. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009;37(Web Server issue):W202–8.
Lescot M, Dehais P, Thijs G, Marchal K, Moreau Y, Van de Peer Y, Rouze P, Rombauts S. PlantCARE, a database of plant cis-acting regulatory elements and a portal to tools for in silico analysis of promoter sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002;30(1):325–7.
Yang J, Zhang Y. I-TASSER server: new development for protein structure and function predictions. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015;43(W1):W174–81.
Guo J, Li K, Jin L, Xu R, Miao K, Yang F, Qi C, Zhang L, Botella JR, Wang R, et al. A simple and cost-effective method for screening of CRISPR/Cas9-induced homozygous/biallelic mutants. Plant Methods. 2018;14:40.
Zagari N, Sandoval-Ibanez O, Sandal N, Su J, Rodriguez-Concepcion M, Stougaard J, Pribil M, Leister D, Pulido P. SNOWY COTYLEDON 2 Promotes Chloroplast Development and Has a Role in Leaf Variegation in Both Lotus japonicus and Arabidopsis thaliana. Mol Plant. 2017;10(5):721–34.
Inbaraj BS, Lu H, Hung CF, Wu WB, Lin CL, Chen BH. Determination of carotenoids and their esters in fruits of Lycium barbarum Linnaeus by HPLC-DAD-APCI-MS. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2008;47(4–5):812–8.
Schmittgen TD, Livak KJ. Analyzing real-time PCR data by the comparative C(T) method. Nat Protoc. 2008;3(6):1101–8.
Ye J, Coulouris G, Zaretskaya I, Cutcutache I, Rozen S, Madden TL. Primer-BLAST: a tool to design target-specific primers for polymerase chain reaction. BMC Bioinformatics. 2012;13:134.
Lu C, Qiu N, Wang B, Zhang J. Salinity treatment shows no effects on photosystem II photochemistry, but increases the resistance of photosystem II to heat stress in halophyte Suaeda salsa. J Exp Bot. 2003;54(383):851–60.
Hura T, Hura K, Grzesiak M, Rzepka A. Effect of long-term drought stress on leaf gas exchange and fluorescence parameters in C3 and C4 plants. Acta Physiol Plant. 2007;29(2):103–13.
Park H, Kreunen SS, Cuttriss AJ, DellaPenna D, Pogson BJ. Identification of the carotenoid isomerase provides insight into carotenoid biosynthesis, prolamellar body formation, and photomorphogenesis. Plant Cell. 2002;14(2):321–32.
Kim J, DellaPenna D. Defining the primary route for lutein synthesis in plants: the role of Arabidopsis carotenoid beta-ring hydroxylase CYP97A3. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006;103(9):3474–9.
Parada R, Royo C, Gadaleta A, Colasuonno P, Marcotuli I, Matus I, Castillo D, de Camargo AC, Araya-Flores J, Villegas D, et al. Phytoene synthase 1 (Psy-1) and lipoxygenase 1 (Lpx-1) Genes Influence on Semolina Yellowness in Wheat Mediterranean Germplasm. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(13):4669.
Pola W, Sugaya S, Photchanachai S. Influence of Postharvest Temperatures on Carotenoid Biosynthesis and Phytochemicals in Mature Green Chili (Capsicum annuum L.). Antioxidants (Basel). 2020;9(3):203.
Shi Y, Guo J, Zhang W, Jin L, Liu P, Chen X, Li F, Wei P, Li Z, Li W. Cloning of the Lycopene β-cyclase Gene in Nicotiana tabacum and Its Overexpression Confers Salt and Drought Tolerance. Int J Mol Sci. 2015;16(12):30438–57.
Fantini E, Falcone G, Frusciante S, Giliberto L, Giuliano G. Dissection of tomato lycopene biosynthesis through virus-induced gene silencing. Plant Physiol. 2013;163(2):986–98.
Moreno JC, Pizarro L, Fuentes P, Handford M, Cifuentes V, Stange C. Levels of lycopene beta-cyclase 1 modulate carotenoid gene expression and accumulation in Daucus carota. PLoS ONE. 2013;8(3):e58144.
Gao S, Han H, Feng HL, Zhao SJ, Meng QW. Overexpression and suppression of violaxanthin de-epoxidase affects the sensitivity of photosystem II photoinhibition to high light and chilling stress in transgenic tobacco. J Integr Plant Biol. 2010;52(3):332–9.
Ruban AV. Nonphotochemical Chlorophyll Fluorescence Quenching: Mechanism and Effectiveness in Protecting Plants from Photodamage. Plant Physiol. 2016;170(4):1903–16.
Jahns P, Holzwarth AR. The role of the xanthophyll cycle and of lutein in photoprotection of photosystem II. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012;1817(1):182–93.
Acknowledgements
We thank Professor Baoming Tian, Associate professors Gongyao Shi, Gangqiang Cao and Zhengqing Xie of Zhengzhou University for their help in the study.
Funding
This work is supported by grants from the Natural Science Foundation of Henan Province (182300410053/902018AS0010 to RW) and the Tobacco Genome Science Project (110202101042 (JY-19)/2022530000241007, 110202102033, 110202001030 (JY-13) and 902018AA0120.2). The funding bodies had no role in the design of the study; collection, analysis, or interpretation of data; or manuscript writing.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
RW, FW, and JG conceptualized the study; WS and RW performed the data curation; RW and CD performed the formal data analysis; RW and LJ acquired the funding; WS and SG organized the methodology; WS, SG, LJ, FL, and PW downloaded and used the software; RW supervised the research; WS, SG, FW, CD, and JH contributed to different experiments and performed experimental validation; RW, WS, and FW wrote the paper. All authors approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Additional file 1.
Ntε-LCY1 and Ntε-LCY2 related sequences.
Additional file 2: Figure S1.
Sequences and phylogenetic analysis of thelycopene epsilon-cyclase genes in Nicotianatobacum. a Phylogenetic tree andconserved domain analysis of amino acid sequences from Solanaceae species. N. tabacum (Ntε-LCY1), N. tabacum (Ntε-LCY2), Nicotianasylvestris (Nsyε-LCY), Nicotiana tomentosiformis (Ntomε-LCY), Solanum tuberosum (Stuε-LCY),and Solanum lycopersicum (Slyε-LCY) sequences are shown. b Spatial structures, ligand binding sites, andenzyme active sites of Ntε-LCY2 (497 amino acids) and Ntε-LCY1 (475 amino acids) from N.tobacumpredicted with the I-TASSER program. Figure S2. Screening gelelectrophoresis of homozygous mutants of Ntε-LCY2and Ntε-LCY1. a ntε-lcy2-1 homozygousmutant line with two rounds of PCR verification. b ntε-lcy2-2 homozygousmutant line with two rounds of PCR verification. c ntε-lcy1-1 homozygousmutant line with two rounds of PCR verification. d ntε-lcy1-2 homozygousmutant line with two rounds of PCR verification. M, DL2000 DNA marker. FigureS3. Sequencing verification results of bacterial liquidcorresponding to two rounds of PCR reactions for Ntε-LCY2 and Ntε-LCY1homozygous mutant lines. a Partialpeak diagram of WT and two homozygous mutant linesof Ntε-LCY2 (ntε-lcy2-1, ntε-lcy2-2) b Partial peak diagram of WT and twohomozygous mutant lines of Ntε-LCY1 (ntε-lcy1-1, ntε-lcy1-2). Table S1. cis-acting elementsin Ntε-LCY gene promoters (3000 bpupstream of the start codon) identified using PlantCARE online software.Important motifs and their functions are shown to highlight similarities anddifferences among the Ntε-LCYhomologs. Table S2. The primers and targetsequences used to construct the CRISPR/Cas9 vectors for Ntε-LCY2 and Ntε-LCY1 and identify the resulting mutants. Table S3. The primers used for quantitative real-time PCR(qRT-PCR) analysis.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
About this article
Cite this article
Song, W., Wei, F., Gao, S. et al. Functional characterization and comparison of lycopene epsilon-cyclase genes in Nicotiana tabacum. BMC Plant Biol 22, 252 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-022-03634-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-022-03634-5