Abstract
Background
Starch are the main nutritional components of maize (Zea mays L.), and starch pasting properties are widely used as essential indicators for quality estimation. Based on the previous studies, various genes related to pasting properties have been identified in maize. However, the loci underlying variations in starch pasting properties in maize inbred lines remain to be identified.
Results
To investigate the genetic architecture of these traits, the starch pasting properties were examined based on 292 maize inbred lines, which were genotyped with the MaizeSNP50 BeadChip composed of 55,126 evenly spaced, random SNPs. A genome-wide association study (GWAS) implemented in the software package FarmCPU was employed to identify genomic loci for the starch pasting properties. 48 SNPs were found to be associated with pasting properties. Moreover, 37 candidate genes were correlated with pasting properties. Among the candidate genes, GRMZM2G143646 and GRMZM2G166407 were associated with breakdown and final viscosity significantly, and both genes encode PPR (Pentatricopeptide repeat) protein. We used GWAS to explore candidate genes of maize starch pasting properties in this study. The identified candidate genes will be useful for further understanding of the genetic architecture of starch pasting properties in maize.
Conclusion
This study showed a complex regulation network about maize quality trait and starch pasting properties. It may provide some useful markers for marker assisted selection and a basis for cloning the genes behind these SNPs.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Maize (Zea mays L.), one of the most fundamental crops in the world, plays a crucial role in food, feed and industrial production. The natural population of maize shows abundant phenotypic variation and genotypic variation, offering great convenience for studying the relationship between genotype and phenotypic diversity [1]. Determining the allelic variation of important agronomic traits not only helps to analyze the genetic basis of agronomic traits, but also provides effective gene resources and molecular markers for marker assisted selection (MAS) [2].
Developments in association analysis have heightened the need for analyzing the genetic basis of complex quantitative characters [3]. Association analysis based on a natural population and linkage disequilibrium (LD) can directly identify phenotypic variation-related genes by combining the genetic variation of target traits with genetic polymorphism [4, 5]. A wide range of genetic materials can be simultaneously used to examine the associated sites and alleles of most QTL (Quantitative Trait Locus), not limited by the traditional “two-parent range”. The LD attenuates and exists within a very short distance after many reorganizations, which ensures higher location accuracy [6]. With the development of high-throughput sequencing and other biological technology, GWAS have been verified to be a useful approach for identifying genes, alleles or haplotypes related to a certain agronomic traits under complex environments, which is based on the linkage disequilibrium (LD) resulting from the association of target trait and haplotype loci. GWAS has been widely used in maize genetics, which provides many opportunities for further understanding the genetic basis for controlling the occurrence of complex quantitative characters in maize. Liu et al. (2016) identified 4 starch content related SNPs in chromosomes 1, 2, 5, and 77 starch synthesis related genes by using 263 maize inbred lines [7]. According to genome-wide association study (GWAS) based on genotyping of a natural population, a significant SNP for starch content within the ORF region of GRMZM5G852704_T01 colocalized with QTL Qsta9.1 which located in a 1.7 Mb interval on chromosome 9 [8]. Xu et al. (2018) identified 60 quantitative trait nucleotides (QTNs) for starch pasting properties through GWAS for seven pasting properties of maize starch with a panel of 230 inbred lines and 145,232 SNPs [9].
Starch is a polymeric carbohydrate consisting of numerous glucose units joined by glycosidic bonds called polymers. This polysaccharide is produced by most green plants as energy storage. Plants produce starch by first converting glucose 1-phosphate to ADP-glucose using the enzyme glucose-1-phosphate adenylyltransferase. This step requires energy in the form of ATP. The enzyme starch synthase then adds the ADP-glucose via a 1,4-alpha glycosidic bond to a growing chain of glucose residues, liberating ADP and creating amylose. The ADP-glucose is almost certainly added to the non-reducing end of the amylose polymer, as the UDP-glucose is added to the non-reducing end of glycogen during glycogen synthesis [10]. Moreover, many genes have been found to contribute to starch biosynthesis in maize, and are regulated by a complex regulation network [11].
Starch pasting properties are a critical index for measuring the quality of starch and have an important effect on the application and processing of starch. Therefore, understanding the pasting properties of starch is an important basis for its application [9]. The peak viscosity of starch is determined by the friction between starch granules after water swelling and the increase in viscosity, which reflects the expansibility of starch. The trough viscosity is due to the bursting of starch granules after the expansibility reaches its limit, reflecting the shear resistance of starch at high temperatures. The final viscosity is due to the further increase in viscosity caused by the movement of water molecules surrounding in amylose and amylopectin; this property reflects the hardness of starch at room temperature. Breakdown represents the change in the stability, reflecting the shear resistance of starch at high temperatures. Setback reflects the aging degree of starch. The pasting properties of starch are closely related to the molecular size of amylose and the branching chain length of amylopectin [12].
At present, the study of maize starch is mainly focused on the analysis and evaluation of applied quality, and traditional QTL mapping is used to locate related genes [13, 14]. However, the mapping interval is relatively large. To date, few works have performed a GWAS of starch pasting properties and discovered candidate genes. In this study, a genome-wide association study was performed based on a MaizeSNP50 BeadChip composed of 55,126 and the phenotypic data of 292 maize inbred lines. The aims of this study were to detect pasting properties related genes in maize, and to provide an important theoretical basis for maize quality breeding.
Results
Phenotypic variations analysis and genome-wide association study of quality traits
The quality traits in maize are under the control of many factors. In this study, the statistical results of the phenotype of quality traits are listed in Tables 1 and 2. In the four environments, the average protein contents were 11.52%, 11.01%, 11.87%, and 11.34%. The average starch contents were 70.46%, 71.54%, 70.24%, and 70.63%. The average oil contents were 4.54%, 4.35%, 4.35% and 4.35%. The data pertaining to each trait approximately followed a normal distribution, and the absolute values of the kurtosis and skewness among these environments were less than 1; thus, the phenotypic data were suitable for GWAS and further analysis. In the four environments, there was a significant positive correlation between protein content and oil content, except at Luoyang; starch content showed a significant negative correlation with protein content and oil content. The heritability of protein, starch and oil content were 82.73%, 85.82% and 80.69%, respectively.
In order to find the quality traits related SNPs (Single Nucleotide Polymorphism), the genotype data of the 25,331 SNPs and the phenotypic data of the 292 maize inbred lines were used for genome-wide association study. The analysis identified 26 SNPs at the P < 10–4 level, based on the FarmCPU methods (Fig. 1) [15]. In the four different environments, 8, 11 and 7 SNPs were identified to correlate to protein, starch and oil content, respectively. PZE_106054189 at Bin6.04 detected in 2015Luoyang and 2016Jiaozhou was correlated with starch content. PZE_108135907 and PZE_109032161 correlated with protein and starch content were detected at Bin8.09 and Bin9.03, respectively. PZE_105086878, PZE_106067078, SYN3414 and PZE_106054189 correlated with starch and oil content were detected at Bin5.04, Bin6.01 and Bin6.04, respectively (Table 3).
Genome-wide association study of starch content
In order to identify the SNPs related to starch content, the genome-wide association study was carried out through the phenotype data from four different environments. The result showed that 37 SNPs were related to starch content under four environments. 9 and 8 SNPs were identified in 2015 at Luoyang and Qingzhou respectively. 6 and 14 SNPs were identified at Jiaozhou in 2016 and 2017 respectively. In addition, the two SNPs, PZE_108135907 and PZE_109032161, were both detected to be related to starch content and protein content. Based on the gene annotation of MaizeGDB database [16], the identified SNPs that related to starch content were related to various metabolism pathways or signaling pathways.
Phenotypic variations analysis and genome-wide association study of starch pasting properties
The statistical results concerning the phenotype of starch pasting properties are listed in Tables 4 and 5. The data for each trait approximately follow a normal distribution, and the absolute values of the kurtosis and skewness among these environments were less than 1. In the four environments, significant positive correlations were observed between any two parameters among PV, TV, BD, FV, and SB; PT was positively correlated with PTP; and BD was negatively correlated with PT and PTP. The heritability values of PV, TV, BD, FV, SB, PT and PTP were 87.98%, 82.14%, 80.45%, 87.98%, 87.56%, 80.24% and 89.43%, respectively.
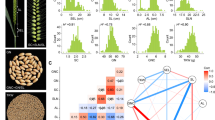
In order to find the SNPs that related to starch pasting properties, data of 25,331 SNPs and starch pasting properties were used based on the FarmCPU software. Significantly correlated SNPs were identified at the P < 10–4 level, and the candidate genes were identified (Fig. 2). A total of 48 SNPs correlated with pasting properties were detected in the four environments: 5, 7, 6, 9, 8, 8 and 5 SNPs for PV, TV, BD, FV, SB, PT and PTP, respectively. PZE_101122760, PZE_103046325, PZE_104089684, PZE_106039028, SYN26334 and PZE_110040421 were correlated with FV and SB; PZE_103091447 and PZE_105156016 were correlated with PV and TV; PZE_103096842 was correlated with PV and FV; and PZE_106067257 was correlated with TV and FV (Table 6).
GO analysis of candidate genes
Based on the genome-wide association study results, 26 and 37 candidate genes were found to be related to starch content and starch pasting properties respectively (Tables 7 and 8). In order to gain insights into the functions of the identified candidate genes, Gene Ontology term enrichment analysis was performed through ShinyGO database [17]. For starch content, the annotated results were classified into two parts: biological process (16 categories) and molecular function (20 categories) (Fig. 3). The results showed that, in biological process, the fold enrichment of triglyceride biosynthetic process, neutral lipid biosynthetic process, acylglycerol biosynthetic process reach to 631, 553, 552 respectively. In addition, the diacylglycerol O-acyltransferase activity (the fold enrichment reached to 1104) was one of the most enriched categories of molecular function. For starch pasting properties, 64 biological process related categories and 18 molecular function related categories were identified (Fig. 4). In biological process, the fold enrichment of positive regulation of biological process, positive regulation of cellular process, positive regulation of cellular metabolic process, positive regulation of nitrogen compound metabolic process is 816, 900, 711, 691 respectively. Moreover, the fold enrichment of ligase activity, actin binding, identical protein binding is 642, 164, 99 respectively in molecular function.
Discussion
Starch or amylum is a polymeric carbohydrate consisting of numerous glucose units joined by glycosidic bonds [18]. This polysaccharide is produced by most plants for energy storage. In plants, the extra glucose is changed into starch which is more complex than the glucose produced by plants. Starch biosynthesis is a complex process in plants. Starch is produced by first converting glucose 1-phosphate to ADP-glucose using the enzyme glucose-1-phosphate adenylyltransferase in plant. The starch synthase then adds the ADP-glucose via a 1,4-alpha glycosidic bond to a growing chain of glucose residues, liberating ADP and creating starch. Starch content in maize kernels is a complex process [19]. In this study, the heritability of starch, protein and oil content were 85.82%, 82.73% and 80.69% respectively. It indicates the important role of genotypes in expression of traits and maize breeding. Identification of the key genes related to the variation in starch content and pasting properties can help to understand the genetic background of starch quantity and maize kernels quality and expand its application. In addition, the starch content and pasting properties SNPs we found in this study can provide some useful markers for maize marker-assisted selection.
In this study, we identified 37 SNPs and 26 candidate genes for starch content through GWAS analysis in the 292 inbred lines. In addition, 48 SNPs correlated with pasting properties were detected. The GO analysis indicated that some carbohydrate metabolism related processes, such as triglyceride, neutral, acylglycerol biosynthetic process, have an important influence on starch content. Consistent with previous studies, many carbohydrate metabolism related QTLs or genes participate in starch metabolism [20,21,22,23].
When we consider the genes identified here and previously identified QTLs or genes for starch content [7, 8, 21, 23,24,25,26,27,28], we note that the identified starch content related genes by different studies are different. This finding could be the result of differences in population size, genetic backgrounds, statistical analysis methods, environmental effects, etc. In addition, some auxin related genes were detected in this study, such as Indole-3-acetic acid amido synthetase GH3.6 [29], rho GTPase-activating protein [30], in accordance with the previous studies that auxin participates in the starch metabolism [31, 32]. These finding indicated a complex regulation network related to starch content, and the starch content could be regulated be different genes under different environments.
In order to investigate the molecular mechanism of starch pasting properties in maize, we further identified locations of associated SNPs for possible candidate genes. In this study, we identified 48 SNPs and 37 genes that correlated with starch pasting properties. According to functional annotations, these candidate genes were primarily categorized in various biological process and molecular function, such as positive regulation of cellular process, positive regulation of cellular metabolic process, positive regulation of nitrogen compound metabolic process, ligase activity, actin binding, identical protein binding etc. The transcription factors included AP2/EREBP, NAC were detected in this study. Some of the candidate genes or their homologous genes are known genes linked to carbohydrate metabolism. For example, ZmNAC34, a maize NAC transcription factor, negatively regulates starch synthesis in rice [33]. WRINKLED1 (WRI1) belongs to AP2/EREBP transcription factor. Its function in dicots for fatty acids synthesis [34].
Conclusions
Our study provides an important extension of maize starch metabolism and starch pasting properties. As a result, 26 and 37 candidate genes were found to be related to starch content and starch pasting properties respectively, indicated a complex regulatory network about regulation of starch content and starch pasting properties in maize. It also indicated that the regulatory network of starch content and starch pasting properties could be different between different environment conditions. This finding reflects the complex nature of maize starch metabolism, which depends on a large number of different environment related genes.
Materials and methods
Plant material and field design
A population composed of 292 maize inbred lines (The maize inbred line were obtained from Qingdao Agricultural University, Table 9) belonging to four subgroups (Lancaster, Lvdahonggu, P group, and Sipingtou) was used for GWAS. The 292 maize inbred lines were grown in three replications at four locations in China, 2015Qingzhou (Shandong Province, 2015QZ), 2015Luoyang (Henan Province, 2015LY) and Jiaozhou (Shandong Province) in 2016 and 2017 (2016JZ and 2017JZ). The materials were arranged in a randomized complete block design, and each inbred line was grown in a single row measuring 3 m in length and 0.6 m in width, with 15 individual plants per row. Five to eight plants in each row were self-pollinated when more than 80% silk appeared. After maturity, the ears were harvested and naturally dried. The dried ears (water content < 14%) of each plot were shelled manually and bulked for kernel composition trait tests. Pasting properties were measured using a Rapid Visco Analyzer (RVA, Model 3D, Perten, Sweden) and analyzed using Thermal Cycle for Windows (TCW) software. The sample suspension of each inbred line was incubated at 50 °C for 1 min; the temperature was increased to 95 °C, maintained for 2.5 min, and finally cooled to 50 °C and maintained for 1 min. Three primary RVA parameters, peak viscosity (PV), trough viscosity (TV), and final viscosity (FV), were obtained from the pasting curve. Two secondary RVA parameters, breakdown (BD = PV − TV) and setback (SB = FV − TV), were calculated from the primary parameters. Peak time (PT) and pasting temperature (PTP) were also recorded. Trait measurements averaged over the three replications were used as the preliminary data.
Analysis of phenotypic data
All analyses were performed using the statistical analysis software package IBM SPSS Statistics 20.0. The broad-sense heritability (H2) was calculated as follows: \({\mathrm{H}}^{2}={\upsigma }_{\mathrm{g}}^{2}/({\upsigma }_{\mathrm{g}}^{2}+{\upsigma }_{\mathrm{gl}}^{2}/\mathrm{n}+{\upsigma }_{\mathrm{e}}^{2}/\mathrm{nr})\), where \({\upsigma }_{\mathrm{g}}^{2}\), \({\upsigma }_{\mathrm{gl}}^{2}\) and \({\upsigma }_{\mathrm{e}}^{2}\) were estimates of genotype, genotype environment interaction and experimental error variances, while n and r were the numbers of environments and replications, respectively [35].
DNA Extraction and SNP Genotyping
DNA for SNP genotyping was extracted from a seeding of each line by the CTAB method [36]. A total of 55,126 SNPs were selected from the whole maize genome and genotyped with the MaizeSNP50 BeadChip from Pioneer DuPont (U.S). The 25,331 SNPs remaining after excluding SNPs with a missing rate > 20%, heterozygosity > 10% and minor allele frequency (MAF) < 0.05 were used for GWAS.
Association analysis
The SNPs from 292 inbred lines were analyzed with the FarmCPU (Fixed and Random Model Circulating Probability Unification), which used a Fixed Effect Model (FEM) and a Random Effect Model (REM) alternately. The source code of the algorithm (http://zzlab.net/FarmCPU/FarmCPU_functions.txt) was invoked through the R software GAPIT package [Zhu et al. 2018]. The population structure was assessed with unlinked markers (r2 = 0.1) using STRUCTU RE ver. 2.3.4 [37], based on the highest delta K value representing genetic clusters [38].
Candidate genes analysis
Based on the results, SNPs associated with starch pasting properties were identified. In this study, the genome from maize line B73 was used as the reference genome for candidate gene analysis [39, 40]. The genes’ p ‘’ositions and functions were annotated according to MaizeGDB database (http://www.maizegdb.org/)(references) and NCBI database (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/)(references). The ShinyGO database (http://bioinformatics.sdstate.edu/go/) was used to GO analysis of the candidate genes [17].
Availability of data and materials
The datasets generated and/or analyzed during the current study are available in the Figshare repository, https://doi.org/10.6084/m9.figshare.20347005.v1.
References
Yan JB, Warburton M, Crouch J. Association mapping for enhancing maize (Zea mays L.) genetic improvement. Crop Sci. 2011;51:433–49.
Zhang X, Zhang H, Li L, Lan H, Ren Z, Liu D, Wu L, Liu H, Jaqueth J, Li B, Pan G, Gao S. Characterizing the population structure and genetic diversity of maize breeding germplasm in Southwest China using genome-wide SNP markers. BMC Genomics. 2016;17:697.
Jannink J, Bink MC, Jansen RC. Using complex plant pedigrees tomap valuable genes. Trends Plant Sci. 2001;6:337–42.
Zondervan KT, Cardon LR. Thecomplexinterplay among factors that influence allelic association. Nat Rev Genet. 2004;5:9–100.
Tang S, Zhao H, Lu S, Yu L, Zhang G, Zhang Y, Yang QY, Zhou Y, Wang X, Ma W, Xie W, Guo L. Genome- and transcriptome-wide association studies provide insights into the genetic basis of natural variation of seed oil content in Brassica napus. Mol Plant. 2021;14(3):470–87.
Liu HJ, Yan J. Crop genome-wide association study: a harvest of biological relevance. Plant J. 2019;97(1):8–18.
Liu NA, Xue Y, Guo Z, Li W, Tang J. Genome-wide association study identifies candidate genes for starch content regulation in maize kernels. Front Plant Sci. 2016;7:1046.
Lin F, Zhou L, He B, Zhang X, Dai H, Qian Y, Ruan L, Zhao H. QTL mapping for maize starch content and candidate gene prediction combined with co-expression network analysis. Theor Appl Genet. 2019;132(7):1931–41.
Xu Y, Yang T, Zhou Y, Yin S, Li P, Liu J, Xu S, Yang Z, Xu C. Genome-wide association mapping of starch pasting properties in maize using single-locus and multi-locus models. Front Plant Sci. 2018;9:1311.
Martin C, Smith AM. Starch biosynthesis. Plant Cell. 1995;7(7):971.
Zhang X, Xie S, Han J, Zhou Y, Li C, Zhou Z, Wang F, Cheng Z, Zhang J, Hu Y, Hao Z, Li M, Zhang D, Yong H, Huang Y, Weng J, Li X. Integrated transcriptome, small rna, and degradome analysis reveals the complex network regulating starch biosynthesis in maize. BMC Genomics. 2019;20(1):574.
Jane JL, Chen J. Effect of amylose molecular size and amylopectin branch chain length on paste properties of starch. Cereal Chem. 1992;69:60–5.
Hao DR, Xue L, Yuan JH, Zhang ZL, Lu HH, Mao YX, Shi M, Huang X, Zhou G, Chen G. Genetic dissection of starch paste viscosity characteristics in waxy maize revealed by high-density SNPs in a recombinant inbred line population. Mol Breeding. 2017;37:50.
Wang JM, Yang JM, David M, Zhou MX. Mapping of quantitative trait loci controlling barley flour pastingpropertie. Genetica. 2010;138:1191–200.
Kusmec A, Schnable PS. Farm CPU pp efficient large-scale genomewide association studies. Plant Direct. 2018;2(4):e00053.
Portwood JL, Woodhouse MR, Cannon EK, Gardiner JM, Harper LC, Schaeffer ML, Walsh JR, Sen TZ, Cho KT, Schott DA, Braun BL, Dietze M, Dunfee B, Elsik CG, Manchanda N, Coe E, Sachs M, Stinard P, Tolbert J, Zimmerman S, Andorf CM. MaizeGDB 2018: the maize multi-genome genetics and genomics database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019;47(D1):D1146–54.
Ge SX, Jung D, Yao R. ShinyGO: a graphical gene-set enrichment tool for animals and plants. Bioinformatics. 2020;36(8):2628–9.
Compart J, Li X, Fettke J. Starch-A complex and undeciphered biopolymer. J Plant Physiol. 2021;258–259:153389.
Seung D. Amylose in starch: towards an understanding of biosynthesis, structure and function. New Phytol. 2020;228(5):1490–504.
Hu S, Wang M, Zhang X, Chen W, Song X, Fu X, Fang H, Xu J, Xiao Y, Li Y, Bai G, Li J, Yang X. Genetic basis of kernel starch content decoded in a maize multi-parent population. Plant Biotechnol J. 2021;19(11):2192–205.
Dong Y, Zhang Z, Shi Q, Wang Q, Zhou Q, Li Y. QTL identification and meta-analysis for kernel composition traits across three generations in popcorn. Euphytica. 2015;204:649–60.
Wang YZ, Li JZ, Li YL, Wei MG, Li XH, Fu JF. QTL detection for grain oil and starch content and their associations in two connected F2:3 populations in high-oil maize. Euphytica. 2010;174:239–52.
Yang G, Dong Y, Li Y, Wang Q, Shi Q, Zhou Q. Verification of QTL for grain starch content and its genetic correlation with oil content using two connected RIL populations in high-oil maize. PLoS ONE. 2013;8:e53770.
Alves ML, Carbas B, Gaspar D, Paulo M, Brites C, Mendes-Moreira P, Brites CM, Malosetti M, van Eeuwijk F, Vaz Patto MC. Genome-wide association study for kernel composition and flour pasting behavior in wholemeal maize flour. BMC Plant Biol. 2019;19:123.
Cook JP, McMullen MD, Holland JB, Tian F, Bradbury P, Ross-Ibarra J, Buckler ES, Flint-Garcia SA. Genetic architecture of maize kernel composition in the nested association mapping and inbred association panels. Plant Physiol. 2012;158(2):824–34.
Guo Y, Yang X, Chander S, Yan J, Zhang J, Song T, Li J. Identification of unconditional and conditional QTL for oil, protein and starch content in maize. Crop J. 2013;1:34–42.
Karn A, Gillman JD, Flint-Garcia SA. Genetic Analysis of Teosinte Alleles for Kernel Composition Traits in Maize. G3-Genes Genom Genet. 2017;7(4):1157–64.
Li C, Huang Y, Huang R, Wu Y, Wang W. The genetic architecture of amylose biosynthesis in maize kernel. Plant Biotechnol J. 2018;16(2):688–95.
Aoi Y, Tanaka K, Cook SD, Hayashi KI, Kasahara H. GH3 Auxin-Amido Synthetases Alter the Ratio of Indole-3-Acetic Acid and Phenylacetic Acid in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell Physiol. 2020;61(3):596–605.
Schepetilnikov M, Ryabova LA. Auxin Signaling in Regulation of Plant Translation Reinitiation. Front Plant Sci. 2017;8:1014.
Kabir MR, Nonhebel HM, Backhouse D, Winter G. Expression of key auxin biosynthesis genes correlates with auxin and starch content of developing wheat (Triticum aestivum) grains. Funct Plant Biol. 2021;48(8):802–14.
Zhang D, Zhang M, Liang J. RGB1 Regulates Grain Development and Starch Accumulation Through Its Effect on OsYUC11-Mediated Auxin Biosynthesis in Rice Endosperm Cells. Front Plant Sci. 2021;12: 585174.
Peng X, Wang Q, Wang Y, Cheng B, Zhao Y, Zhu S. A maize NAC transcription factor, ZmNAC34, negatively regulates starch synthesis in rice. Plant Cell Rep. 2019;38(12):1473–84.
Yang J, Tian R, Gao Z, Yang H. Characterization of AtWRI1 in fatty acids and starch synthesis in rice. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 2019;83(10):1807–14.
Knapp SJ, Stroup WW, Ross WM. Exact confidence intervals for heritability on progenymean basis. Crop Sci. 1985;25:192–4.
Yu D, Zhang J, Tan G, Yu N, Wang Q, Duan Q, Qi X, Cheng M, Yan C, Wei Z, Yu Z, Huang W, Li C. An easily-performed high-throughput method for plant genomic DNA extraction. Anal Biochem. 2019;569:28–30.
Zhu XM, Shao XY, Pei YH, Guo XM, Li J, Song XY, Zhao MA. Genetic Diversity and Genome-Wide Association Study of Major Ear Quantitative Traits Using High-Density SNPs in Maize. Front Plant Sci. 2018;9(9):966.
Pritchard JK, Stephens M, Donnelly P. Inference of population structure using multilocus genotype data. Genetics. 2000;155(2):945–59.
Schnable PS, Ware D, Fulton RS, Stein JC, Wei F, Pasternak S, et al. The B73 maize genome: complexity, diversity, and dynamics. Science. 2009;326(5956):1112–5.
Gage JL, Vaillancourt B, Hamilton JP, Manrique-Carpintero NC, Gustafson TJ, Barry K, Lipzen A, Tracy WF, Mikel MA, Kaeppler SM, Buell CB, de Leon N. Multiple maize reference genomes impact the identification of variants by genome-wide association study in a diverse inbred panel. The plant genome. 2019;12(2):180069.
Acknowledgements
Thanks to Prof. Yang Xiaohong from China Agricultural University for proposing revisions and suggestion.
Funding
This work was supported by Crop Varietal Improvement and Insect Pests Control by Nuclear Radiation, National Key Research and Development Program of China (2021YFD1900903), Well-Breed Engineering of Shandong province (2021LZGC022), science and technology commissioner of Tai’an (2021TPY007).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
This research was conceived by XG and XS. Data statistics were analysed by MZ, MW and YP. GWAS and GO analyses were conducted by MW and ZG. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
All methods using plant material were carried out in accordance with relevant guidelines and regulations.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
About this article
Cite this article
Guo, X., Ge, Z., Wang, M. et al. Genome-wide association study of quality traits and starch pasting properties of maize kernels. BMC Genomics 24, 59 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-022-09031-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-022-09031-4