Abstract
Background
Considering the scarcity of literature data about the predictive capacity of polarization microscopy (PM) in identifying meiotic normality in human in vivo-matured oocytes, the main objective of the present study was to determine whether qualitative analysis of the spindle through PM can predict meiotic normality in fresh in vivo-matured human oocytes.
Methods
Infertile patients undergoing controlled ovarian stimulation to intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI) were selected. Fresh in vivo-matured oocytes were evaluated by PM and, immediately afterward, fixed for confocal microscopy (CM) analysis for evaluation of the spindle and chromosome distribution. We evaluated the percentage of oocytes with meiotic normality and abnormality determined by CM among oocytes with visible and nonvisible spindle and between oocytes with the spindle located at 0° to 60° angle to the first polar body (PB; normal position) and at 60° to 90° angle to the first PB (risky position) according to PM.
Results
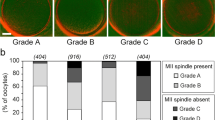
From 23 patients, 73 oocytes were analyzed. There were no significant differences in the percentage of oocytes with meiotic abnormalities among oocytes with visible and nonvisible spindles and among oocytes with the spindle in the normal and risky positions.
Conclusions
Under the conditions tested, qualitative evaluation of the spindle through PM is not consistent with CM analysis and has limited predictive value of meiotic normality in fresh in vivo-matured human oocytes, which needs to be confirmed in larger studies. Our findings make questionable the usefulness of this methodology as a tool for noninvasive oocyte selection for ICSI.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mattson BA, Albertini DF. Oogenesis: chromatin and microtubule dynamics during meiotic prophase. Mol Reprod Dev. 1990; 25(4):374–383.
Albertini DF. Cytoplasmic microtubular dynamics and chromatin organization during mammalian oogenesis and oocyte maturation. Mutat Res. 1992;296(1–2):57–68.
Liu L, Oldenbourg R, Trimarchi JR, Keefe DL. A reliable, noninvasive technique for spindle imaging and enucleation of mammalian oocytes. Nat Biotechnol. 2000;18(2):223–225.
Wang WH, Keefe DL. Prediction of chromosome misalignment among in vitro matured human oocytes by spindle imaging with the PolScope. Fertil Steril. 2002;78(5):1077–1081.
Navarro PA, Liu L, Trimarchi JR, Ferriani RA, Keefe DL. Noninvasive imaging of spindle dynamics during mammalian oocyte activation. Fertil Steril. 2005;83 suppl 1:1197–1205.
Mandelbaum J, Anastasiou O, Levy R, Guerin JF, de Larouziere V, Antoine JM. Effects of cryopreservation on the meiotic spindle of human oocytes. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 2004;113 suppl 1:S17–S23.
Coticchio G, Sciajno R, Hutt K, Bromfield J, Borini A, Albertini DF. Comparative analysis of the metaphase II spindle of human oocytes through polarized light and high-performance confocal microscopy. Fertil Steril. 2010;93(6):2056–2064.
Hu Y, Betzendahl I, Cortvrindt R, Smitz J, Eichenlaub Ritter U. Effects of low O2 and ageing on spindles and chromosomes in mouse oocytes from pre-antral follicle culture. Hum Reprod. 2001;16(4):737–748.
Eichenlaub Ritter U, Shen Y, Tinneberg HR. Manipulation of the oocyte: possible damage to the spindle apparatus. Reprod Biomed Online. 2002;5(2):117–124.
Mullen SF, Agca Y, Broermann DC, Jenkins CL, Johnson CA, Critser JK. The effect of osmotic stress on the metaphase II spindle of human oocytes, and the relevance to cryopreservation. Hum Reprod. 2004;19(5):1148–1154.
Roberts R, Franks S, Hardy K. Culture environment modulates maturation and metabolism of human oocytes. Hum Reprod. 2002;17(11):2950–2956.
Battaglia DE, Goodwin P, Klein NA, Soules MR. Influence of maternal age on meiotic spindle assembly in oocytes from naturally cycling women. Hum Reprod. 1996;11(10):2217–2222.
Van Blerkom J, Henry G. Oocyte dysmorphism and aneuploidy in meiotically mature human oocytes after ovarian stimulation. Hum Reprod. 1992;7(3):379–390.
Jones KT, Lane SI. Chromosomal, metabolic, environmental, and hormonal origins of aneuploidy in mammalian oocytes. Exp Cell Res. 2012;318(12):1394–1399.
Miyara F, Aubriot FX, Glissant A, et al. Multiparameter analysis of human oocytes at metaphase II stage after IVF failure in nonmale infertility. Hum Reprod. 2003;18(7):1494–1503.
Yu Y, Yan J, Liu ZC, et al. Optimal timing of oocyte maturation and its relationship with the spindle assembly and developmental competence of in vitro matured human oocytes. Fertil Steril. 2011;96(1):73–8 e1.
Heindryckx B, De Gheselle S, Lierman S, Gerris J, De Sutter P. Efficiency of polarized microscopy as a predictive tool for human oocyte quality. Hum Reprod. 2011;26(3):535–544.
Korkmaz C, Cinar O, Akyol M. The relationship between meiotic spindle imaging and outcome of intracytoplasmic sperm injection: a retrospective study. Gynecol Endocrinol. 2011;27(10): 737–741.
Petersen CG, Oliveira JB, Mauri AL, et al. Relationship between visualization of meiotic spindle in human oocytes and ICSI outcomes: a meta-analysis. Reprod Biomed Online. 2009;18(2): 235–243.
Tomari H, Honjou K, Nagata Y, Horiuchi T. Relationship between meiotic spindle characteristics in human oocytes and the timing of the first zygotic cleavage after intracytoplasmic sperm injection. J Assist Reprod Genet. 2011;28(11):1099–1104.
Hyun CS, Cha JH, Son WY, Yoon SH, Kim KA, Lim JH. Optimal ICSI timing after the first polar body extrusion in in vitro matured human oocytes. Hum Reprod. 2007;22(7):1991–1995.
Dib LA, Araujo MC, Giorgenon RC, Ferriani RA, Navarro PA. Apparently matured oocytes injected in telophase I have worse outcomes from assisted reproduction. Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2012;34(5):203–208.
Montag M, Koster M, van der Ven K, van der Ven H. Gamete competence assessment by polarizing optics in assisted reproduction. Hum Reprod Update. 2011;17(5):654–666.
Barcelos ID, Vieira RC, Ferreira EM, Martins WP, Ferriani RA, Navarro PA. Comparative analysis of the spindle and chromosome configurations of in vitro-matured oocytes from patients with endometriosis and from control subjects: a pilot study. Fertil Steril. 2009;92(5):1749–1752.
Dib LA, Araujo MC, Giorgenon RC, Romao GS, Ferriani RA, Navarro PA. Noninvasive imaging of the meiotic spindle of in vivo matured oocytes from infertile women with endometriosis. Reprod Sci. 2013;20(4):456–462.
Moon JH, Hyun CS, Lee SW, Son WY, Yoon SH, Lim JH. Visualization of the metaphase II meiotic spindle in living human oocytes using the Polscope enables the prediction of embryonic developmental competence after ICSI. Hum Reprod. 2003; 18(4):817–820.
Fang C, Tang M, Li T, et al. Visualization of meiotic spindle and subsequent embryonic development in in vitro and in vivo matured human oocytes. J Assist Reprod Genet. 2007;24(11): 547–551.
Wang WH, Meng L, Hackett RJ, Keefe DL. Developmental ability of human oocytes with or without birefringent spindles imaged by Polscope before insemination. Hum Reprod. 2001;16(7):1464–1468.
Rienzi L, Ubaldi F, Martinez F, et al. Relationship between meiotic spindle location with regard to the polar body position and oocyte developmental potential after ICSI. Hum Reprod. 2003; 18(6):1289–1293.
Cohen Y, Malcov M, Schwartz T, et al. Spindle imaging: a new marker for optimal timing of ICSI? Hum Reprod. 2004;19(3): 649–654.
Shen Y, Stalf T, Mehnert C, et al. Light retardance by human oocyte spindle is positively related to pronuclear score after ICSI. Reprod Biomed Online. 2006;12(6):737–751.
Rama Raju GA, Prakash GJ, Krishna KM, Madan K. Meiotic spindle and zona pellucida characteristics as predictors of embryonic development: a preliminary study using PolScope imaging. Reprod Biomed Online. 2007;14(2):166–174.
Madaschi C, de Souza Bonetti TC, de Almeida Ferreira Braga DP, Pasqualotto FF, Iaconelli A Jr, Borges E Jr. Spindle imaging: a marker for embryo development and implantation. Fertil Steril. 2008;90(1):194–198.
Cristina Magli M, Capoti A, Resta S, Stanghellini I, Ferraretti AP, Gianaroli L. Prolonged absence of meiotic spindles by birefringence imaging negatively affects normal fertilization and embryo development. Reprod Biomed Online. 2011;23(6):747–754.
Navarro PA, Liu L, Ferriani RA, Keefe DL. Arsenite induces aberrations in meiosis that can be prevented by coadministration of N-acetylcysteine in mice. Fertil Steril. 2006;85 suppl 1:1187–1194.
Kilani S, Cooke S, Kan A, Chapman M. Are there non-invasive markers in human oocytes that can predict pregnancy outcome? Reprod Biomed Online. 2009;18(5):674–680.
Allworth AE, Albertini DF. Meiotic maturation in cultured bovine oocytes is accompanied by remodeling of the cumulus cell cytoskeleton. Dev Biol. 1993;158(1):101–112.
Ju JC, Jiang S, Tseng JK, Parks JE, Yang X. Heat shock reduces developmental competence and alters spindle configuration of bovine oocytes. Theriogenology. 2005;64(8):1677–1689.
Ferreira EM, Vireque AA, Adona PR, Ferriani RA, Navarro PA. Prematuration of bovine oocytes with butyrolactone I reversibly arrests meiosis without increasing meiotic abnormalities after in vitro maturation. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 2009; 145(1):76–80.
Li Y, Feng HL, Cao YJ, et al. Confocal microscopic analysis of the spindle and chromosome configurations of human oocytes matured in vitro. Fertil Steril. 2006;85(4):827–832.
Olmsted JB, Borisy GG. Characterization of microtubule assembly in porcine brain extracts by viscometry. Biochemistry. 1973; 12(21):4282–4289.
Krendel M, Inoue S. Anaphase spindle dynamics under D2O-enhanced microtubule polymerization. Biol Bull. 1995;189(2): 204–205.
Cooke S, Tyler JP, Driscoll GL. Meiotic spindle location and identification and its effect on embryonic cleavage plane and early development. Hum Reprod. 2003;18(11):2397–2405.
Woodward BJ, Montgomery SJ, Hartshorne GM, Campbell KH, Kennedy R. Spindle position assessment prior to ICSI does not benefit fertilization or early embryo quality. Reprod Biomed Online. 2008;16(2):232–238.
Taylor TH, Chang CC, Elliott T, Colturato LF, Kort HI, Nagy ZP. Effect of denuding on polar body position in in-vitro matured oocytes. Reprod Biomed Online. 2008;17(4):515–519.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dib, L.A., Da Broi, M.G. & Navarro, P.A. Comparative Analysis of the Spindle of Fresh In Vivo-Matured Human Oocytes Through Polarized Light and Confocal Microscopy: A Pilot Study. Reprod. Sci. 21, 984–992 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1177/1933719113519174
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1177/1933719113519174