Abstract
Purpose
Recently, the upgrading of in vitro maturation (IVM) of human oocytes as a promising strategy has emerged in assisted reproductive technology (ART). The goal was to evaluate the correlation of the in vitro matured oocytes selected on the basis of the zona pellucida (ZP) birefringence and meiotic spindles (MS) detection with fertilization and subsequent embryo development in ICSI program.
Methods
A total of 168 immature oocytes [germinal vesicle (n = 140) and metaphase I (n = 28)] obtained from patients undergoing oocytes retrieval for ICSI. After in vitro culture for 24–40 h, 112 (67 %) oocytes reached to MII stage. Using a polarized microscopy, the presence of MS and ZP birefringence were assessed in matured oocytes, followed by ICSI performance.
Results
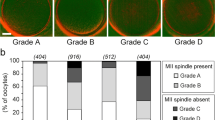
The rates of fertilization in oocytes with spindles (51.3 %) were similar to that of the oocytes without spindles (50.7 %; P = 1.00). Moreover, the fertilization rates in high birefringence (HB) oocytes was not statistically different than oocytes with low birefringence (LB) (P = 0.44). The findings also showed that 64.9 % of the fertilized oocytes developed to embryos, in which 33.3 % were derived from spindle-detected oocytes. Regarding the ZP birefringence, 35.5 % of the embryos were derived from HB oocytes.
Conclusions
There were insignificant relationships between the MS detection and ZP birefringence score with the rates of fertilization and embryo development in IVM oocytes.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Braga DPdAF, Figueira RdCS, Rodrigues D, Madaschi C, Pasqualotto FF, Iaconelli Jr A et al (2008) Prognostic value of meiotic spindle imaging on fertilization rate and embryo development in in vitro-matured human oocytes. Fertil Steril 90:429–433
Hourvitz A, Maman E, Brengauz M, Machtinger R, Dor J (2010) In vitro maturation for patients with repeated in vitro fertilization failure due to “oocyte maturation abnormalities”. Fertil Steril 94:496–501
Omidi M, Khalili MA, Ashourzadeh S, Rahimipour M (2014) Zona pellucida birefringence and meiotic spindle visualisation of human oocytes are not influenced by IVM technology. Reprod Fertil Dev 26:407–413
Lim KS, Chae SJ, Choo CW, Ku YH, Lee HJ, Hur CY et al (2013) In vitro maturation: clinical applications. Clin Exp Reprod Med 40:143–147
Grynberg M, El Hachem H, de Bantel A, Benard J, le Parco S, Fanchin R (2013) In vitro maturation of oocytes: uncommon indications. Fertil Steril 99:1182–1188
Grøndahl C (2008) Oocyte maturation. Basic and clinical aspects of in vitro maturation (IVM) with special emphasis of the role of FF-MAS. Dan Med Bull 55:1–16
Yazdanpanah F, Khalili MA, Eftekhar M, Karimi H (2013) The effect of vitrification on maturation and viability capacities of immature human oocytes. Arch Gynecol Obstet 288:439–444
Son W-Y, Lee S-Y, Yoon S-H, Lim J-H (2007) Pregnancies and deliveries after transfer of human blastocysts derived from in vitro matured oocytes in in vitro maturation cycles. Fertil Steril 87:1491–1493
Li Y, Feng H-L, Cao Y-J, Zheng G-J, Yang Y, Mullen S et al (2006) Confocal microscopic analysis of the spindle and chromosome configurations of human oocytes matured in vitro. Fertil Steril 85:827–832
Rienzi L, Ubaldi FM, Iacobelli M, Minasi MG, Romano S, Ferrero S et al (2008) Significance of metaphase II human oocyte morphology on ICSI outcome. Fertil Steril 90:1692–1700
Khalili MA, Mojibian M, Sultan A-M (2005) Role of oocyte morphology on fertilization and embryo formation in assisted reproductive techniques. Middle East Fertil Soc J 10:72–77
Khalili MA, Nottola SA, Shahedi A, Macchiarelli G (2013) Contribution of human oocyte architecture to success of in vitro maturation technology. Iran J Rep Med 11:1–10
Cohen Y, Malcov M, Schwartz T, Mey-Raz N, Carmon A, Cohen T et al (2004) Spindle imaging: a new marker for optimal timing of ICSI? Hum Reprod 19:649–654
Korkmaz C, Sakinci M, Tekin YB, Ercan CM (2014) Do quantitative birefringence characteristics of meiotic spindle and zona pellucida have an impact on implantation in single embryo transfer cycles? Archiv Gynecol Obstet 289:433–438
Madaschi C, Aoki T, de Almeida Ferreira Braga DP, de Cássia Sávio Figueira R, Francisco LS, Iaconelli Jr A et al (2009) Zona pellucida birefringence score and meiotic spindle visualization in relation to embryo development and ICSI outcomes. Reprod Biomed Online 18:681–686
Wang W, Meng L, Hackett R, Keefe D (2001) Developmental ability of human oocytes with or without birefringent spindles imaged by Polscope before insemination. Hum Reprod 16:1464–1468
Familiari G, Heyn R, Relucenti M, Sathananthan H (2007) Structural changes of the zona pellucida during fertilization and embryo development. Front Biosci 13:6730–6751
Omidi M, Khalili MA, Nahangi H, Ashourzadeh S, Rahimipour M (2013) Does women’s age influence zona pellucida birefringence of metaphase ΙΙ oocytes in in vitro maturation program? Iran J Rep Med 11:823
Organization WH (2010) WHO laboratory manual for the examination and processing of human semen. Cambridge University Press
Halvaei I, Khalili MA, Razi MH, Nottola SA (2012) The effect of immature oocytes quantity on the rates of oocytes maturity and morphology, fertilization, and embryo development in ICSI cycles. J Assist Reprod Genet 29:803–810
Nazari S, Khalili M, Esmaielzadeh F, Mohsenzadeh M (2011) Maturation capacity, morphology and morphometric assessments of human immature oocytes after vitrification and in vitro maturation. Iran J Rep Med 9:209–216
Chian R-C, Buckett WM, Tan S-L (2004) In-vitro maturation of human oocytes. Reprod Biomed Online 8:148–166
Eftekhar M, Khalili MA, Aflatoonian A, Esfandiari N (2012) Successful pregnancy following a novel endometrial preparation in a PCOS patient undergoing IVM: a case report. J Assist Reprod Genet 29:335–336
Lanzendorf SE (2006) Developmental potential of in vitro—and in vivo—matured human oocytes collected from stimulated and unstimulated ovaries. Fertil Steril 85:836–837
Shahedi A, Khalili MA, Soleimani M, Morshedizad S (2013) Ultrastructure of in vitro matured human oocytes. Iran Red Crescent Med J 15(12):e7379. doi:10.5812/ircmj.7379
Wang W-H, Keefe DL (2002) Prediction of chromosome misalignment among in vitro matured human oocytes by spindle imaging with the PolScope. Fertil Steril 78:1077–1081
Braga DPdAF, Figueira RdCS, Queiroz P, Madaschi C, Iaconelli Jr A, Borges Jr E (2010) Zona pellucida birefringence in in vivo and in vitro matured oocytes. Fertil Steril 94:2050–2053
Montag M, Schimming T, Köster M, Zhou C, Dorn C, Rösing B et al (2008) Oocyte zona birefringence intensity is associated with embryonic implantation potential in ICSI cycles. Reprod Biomed Online 16:239–244
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Dr. Nasim Tabibnejad for her English editing of the manuscript.
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ashourzadeh, S., Khalili, M.A., Omidi, M. et al. Noninvasive assays of in vitro matured human oocytes showed insignificant correlation with fertilization and embryo development. Arch Gynecol Obstet 292, 459–463 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00404-015-3644-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00404-015-3644-y