Abstract
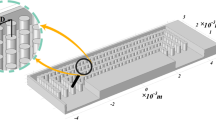
In this paper, the numerical study of the thermal efficiency of a micro-heatsink (MHS) with nanofluid flow of water and alumina has been done. The heatsink (HS) is designed to cool an electronic component. Four different wall models have been studied in MHS. By changing the inlet velocity, the volume percentage of nanoparticles for different HS models, the values of heat transfer coefficient, thermal resistance, temperature uniformity and FOM have been studied. The equations are discretized using the volume control method, and FLUENT software is used for simulation. The results of the study demonstrated that in the case that pin fins were tangential, the lowest temperature and thermal resistance, as well as the best temperature uniformity occurred on the contact surface of the MHS and microchip. Some of the models proposed in this article had better thermal performance compared to similar HSs and could reduce the temperature of microchips to lower levels and improve the performance of electronic devices. Finally, it is suggested that the geometry of connected fin pins be used as heatsink walls.












Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- C p :
-
Specific heat \((\mathrm{J}/\mathrm{kg}.\mathrm{K})\)
- d :
-
Diameter of the NPs (nm)
- D:
-
Distance between fin center (m)
- FOM:
-
Figure of Merit
- H:
-
Heat transfer coefficient \((W/{m}^{2}.K)\)
- HS:
-
Heat sink
- K:
-
Thermal conductivity \((W/m.K)\)
- MHS:
-
Micro-heatsink
- NF:
-
Nanofluid
- \(p\) :
-
Pressure \((Pa)\)
- PP:
-
Pumping power (W)
- \(q\mathrm{^{\prime}}\mathrm{^{\prime}}\) :
-
Heat flux (W/m2)
- \(\dot{Q}\) :
-
Volumetric flow (m3/s)
- R:
-
Thermal resistance (m2.K/W)
- T:
-
Temperature (K)
- V:
-
Velocity (m/s
- Φ:
-
Solid volume fraction
- Θ:
-
Temperature uniformity (m2.K/W)
- Μ:
-
Dynamic viscosity \((kg/m.s)\)
- Ρ:
-
Density (\(kg{/m}^{3})\)
- ∆P:
-
Pressure difference
- Ave:
-
Average
- eff:
-
Effective
- f:
-
Pure fluid
- In:
-
Inlet
- m:
-
Average fluid temperature
- Max:
-
Maximum temperatures on the bottom surface of the MHS
- Mid:
-
Average temperature of the bottom of the MHS
- Min:
-
Minimum temperatures on the bottom surface of the MHS
- Nf:
-
Nanofluid
- Out:
-
Outlet
- P:
-
Solid nanoparticle
References
A. Mohammed Adham, N. Mohd-Ghazali, R. Ahmad, Thermal and hydrodynamic analysis of microchannel heat sinks: a review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 21, 614–622 (2013)
J.F. Tullius, R. Vajtai, Y. Bayazitoglu, A review of cooling in microchannels. Heat Transf. Eng. 32(7–8), 527–54 (2011)
W. Nakayama, Thermal management of electronic equipment: a review of technology and research topics. Appl. Mech. Rev. 47, 1847–1868 (1986)
A.H. Pordanjani, S. Aghakhani, M. Afrand, B. Mahmoudi, O. Mahian, S. Wongwises, An updated review on application of nanofluids in heat exchangers for saving energy. Energy Convers. Manag. 198, 111886 (2019)
A.H. Pordanjani et al., Nanofluids: physical phenomena, applications in thermal systems and the environment effects-a critical review. J. Clean. Prod. 320, 128573 (2021)
S.S. Murshed, C.N. De Castro, A critical review of traditional and emerging techniques and fluids for electronics cooling. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 78, 821–833 (2017)
S. Chingulpitak, S. Wongwises, A review of the effect of flow directions and behaviors on the thermal performance of conventional heat sinks. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 81, 10–18 (2015)
S. Aghakhani, A.H. Pordanjani, M. Afrand, M. Sharifpur, J.P. Meyer, Natural convective heat transfer and entropy generation of alumina/water nanofluid in a tilted enclosure with an elliptic constant temperature: applying magnetic field and radiation effects. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 174, 105470 (2020)
S. Aghakhani, A.H. Pordanjani, A. Karimipour, A. Abdollahi, M. Afrand, Numerical investigation of heat transfer in a power-law non-Newtonian fluid in a C-Shaped cavity with magnetic field effect using finite difference lattice Boltzmann method. Comput. Fluids 176, 51–67 (2018)
A.H. Pordanjani, S. Aghakhani, Numerical investigation of natural convection and irreversibilities between two inclined concentric cylinders in presence of uniform magnetic field and radiation. Heat Transf. Eng. 2021, 1–21 (2021)
M. Afrand, S. Farahat, A.H. Nezhad, G. Ali Sheikhzadeh, F. Sarhaddi, 3-D numerical investigation of natural convection in a tilted cylindrical annulus containing molten potassium and controlling it using various magnetic fields. Int. J. Appl. Electromagn. Mech. 46(4), 809–821 (2014)
M. Afrand, S. Farahat, A.H. Nezhad, G.A. Sheikhzadeh, F. Sarhaddi, Numerical simulation of electrically conducting fluid flow and free convective heat transfer in an annulus on applying a magnetic field. Heat Transf. Res. 45(8), 749–766 (2014)
J. Choi, M. Jeong, J. Yoo, M. Seo, A new CPU cooler design based on an active cooling heatsink combined with heat pipes. Appl. Thermal Eng. 44, 50–56 (2012)
M.W. Alam et al., CPU heat sink cooling by triangular shape micro-pin-fin: Numerical study. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 112, 104455 (2020)
L. Yang, J.N. Huang, M. Mao, W. Ji, Numerical assessment of Ag-water nano-fluid flow in two new microchannel heatsinks: Thermal performance and thermodynamic considerations. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 110, 104415 (2020)
Y. Wang, K. Zhu, Z. Cui, J. Wei, Effects of the location of the inlet and outlet on heat transfer performance in pin fin CPU heat sink. Appl. Thermal Eng. 151, 506–513 (2019)
N. Zhao, L. Guo, C. Qi, T. Chen, X. Cui, Experimental study on thermo-hydraulic performance of nanofluids in CPU heat sink with rectangular grooves and cylindrical bugles based on exergy efficiency. Energy Convers. Manag. 181, 235–246 (2019)
D. Kim et al., Convective heat transfer characteristics of nanofluids under laminar and turbulent flow conditions. Curr. Appl. Phys. 9(2), e119–e123 (2009)
V.L. Vinodhan, K.S. Rajan, Computational analysis of new microchannel heat sink configurations. Energy Convers. Manag. 86, 595–604 (2014)
Z. Zhang, L. Feng, H. Liu, L. Wang, S. Wang, Z. Tang, Mo 6+–P 5+ co-doped Li 2 ZnTi 3 O 8 anode for Li-storage in a wide temperature range and applications in LiNi 0.5 Mn 1.5 O 4/Li 2 ZnTi 3 O 8 full cells. Inorg. Chem. Front. 9(1), 35–43 (2022)
L. Yang et al., Rapid sintering method for highly conductive Li7La3Zr2O12 ceramic electrolyte. Ceram. Int. 46(8), 10917–10924 (2020)
F. Meng, D. Wang, P. Yang, G. Xie, Application of sum of squares method in nonlinear H∞ control for satellite attitude maneuvers. Complexity 2019, 5124108 (2019)
G. Wang, D. Liu, S. Fan, Z. Li, J. Su, High-k erbium oxide film prepared by sol-gel method for low-voltage thin-film transistor. Nanotechnology 32(21), 215202 (2021)
T. Gao et al., Carbon fiber reinforced polymer in drilling: from damage mechanisms to suppression. Compos. Struct. 286, 115232 (2022)
S. Mu et al., Molecular grafting towards high-fraction active nanodots implanted in N-doped carbon for sodium dual-ion batteries. Natl. Sci. Rev. 8(7), p.nwaa178 (2021)
J. Zhang et al., Pd/PANI/Ti composite electrocatalyst with efficient electrocatalytic performance: synthesis, characterization, stability, kinetic studies, and degradation mechanism. J. Alloys Compd. 902, 163723 (2022)
Q. Yin et al., Effects of physicochemical properties of different base oils on friction coefficient and surface roughness in MQL milling AISI 1045. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf.-Green Technol. 8(6), 1629–1647 (2021)
T. Gao et al., Mechanics analysis and predictive force models for the single-diamond grain grinding of carbon fiber reinforced polymers using CNT nano-lubricant. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 290, 116976 (2021)
Z. Duan et al., Milling force model for aviation aluminum alloy: academic insight and perspective analysis. Chin. J. Mech. Eng. 34(1), 1–35 (2021)
H.W. Xian, N.A.C. Sidik, G.J.J.O.T.A. Najafi, Recent state of nanofluid in automobile cooling systems. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 135(2), 981–1008 (2019)
Y.-M. Chu, M. Ibrahim, T. Saeed, A.S. Berrouk, E.A. Algehyne, R. Kalbasi, Examining rheological behavior of MWCNT-TiO2/5W40 hybrid nanofluid based on experiments and RSM/ANN modeling. J. Mol. Liq. 333, 115969 (2021)
M. Ibrahim, T. Saeed, Y.M. Chu, H.M. Ali, G. Cheraghian, R. Kalbasi, Comprehensive study concerned graphene nano-sheets dispersed in ethylene glycol: experimental study and theoretical prediction of thermal conductivity. Powder Technol. 386, 51–59 (2021)
L. Tang et al., Biological stability of water-based cutting fluids: progress and application. Chin. J. Mech. Eng. 35(1), 3 (2022)
Z. Zhang, M. Sui, C. Li, Z. Zhou, B. Liu, Y. Chen, Z. Said, S. Debnath, S. Sharma, Residual stress of grinding cemented carbide using MoS2 nano-lubricant. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2022, 1–15 (2022)
M.H. Esfe, S. Esfandeh, M.K. Amiri, M. Afrand, A novel applicable experimental study on the thermal behavior of SWCNTs (60%)-MgO (40%)/EG hybrid nanofluid by focusing on the thermal conductivity. Powder Technol. 342, 998–1007 (2019)
M.H. Esfe, H.R. Raki, M.R.S. Emami, M. Afrand, Viscosity and rheological properties of antifreeze based nanofluid containing hybrid nano-powders of MWCNTs and TiO2 under different temperature conditions. Powder Technol. 342, 808–816 (2019)
M.H. Esfe, H. Rostamian, S. Esfandeh, M. Afrand, Modeling and prediction of rheological behavior of Al2O3-MWCNT/5W50 hybrid nano-lubricant by artificial neural network using experimental data. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Appl. 510, 625–634 (2018)
R. Ranjbarzadeh, A. Akhgar, S. Musivand, M. Afrand, Effects of graphene oxide-silicon oxide hybrid nanomaterials on rheological behavior of water at various time durations and temperatures: synthesis, preparation and stability. Powd. Technol. 335, 375–387 (2018)
E. Shahsavani, M. Afrand, R. Kalbasi, Using experimental data to estimate the heat transfer and pressure drop of non-Newtonian nanofluid flow through a circular tube: Applicable for use in heat exchangers. Appl. Therm. Eng. 129, 1573–1581 (2018)
M.S. Shadloo, Application of support vector machines for accurate prediction of convection heat transfer coefficient of nanofluids through circular pipes. Int. J. Numer. Methods Heat Fluid Flow 31(8), 2660–2679 (2020)
J. Mustafa, S. Alqaed, R. Kalbasi, "Challenging of using CuO nanoparticles in a flat plate solar collector-energy saving in a solar-assisted hot process stream. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 124, 258–265 (2021)
M.E.H. Attia et al., Sustainable potable water production from conventional solar still during the winter season at Algerian dry areas: energy and exergy analysis. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 145(3), 1215–1225 (2021)
P. Rana, N. Srikantha, T. Muhammad, G. Gupta, Computational study of three-dimensional flow and heat transfer of 25 nm Cu–H2O nanoliquid with convective thermal condition and radiative heat flux using modified Buongiorno model. Case Stud. Therm. Eng. 27, 101340 (2021)
P. Rana, S.A. Shehzad, T. Ambreen, M.M. Selim, Numerical study based on CVFEM for nanofluid radiation and magnetized natural convected heat transportation. J. Molec. Liq. 334, 116102 (2021)
M.-W. Tian, S. Rostami, S. Aghakhani, A.S. Goldanlou, C. Qi, A techno-economic investigation of 2D and 3D configurations of fins and their effects on heat sink efficiency of MHD hybrid nanofluid with slip and non-slip flow. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 189, 105975 (2021)
M.M. Alqarni, E.E. Mahmoud, T. Saeed, V. Ali, M. Ibrahim, Numerical simulation and exergy analysis of a novel nanofluid-cooled heat sink. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 145(3), 1651–1660 (2021)
M. Ibrahim, S. Saleem, Y.-M. Chu, M. Ullah, B. Heidarshenas, An investigation of the exergy and first and second laws by two-phase numerical simulation of various nanopowders with different diameter on the performance of zigzag-wall micro-heat sink (ZZW-MHS). J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 145(3), 1611–1621 (2021)
M. Ibrahim, A.S. Berrouk, E.A. Algehyne, T. Saeed, Y.-M. Chu, Energetic and exergetic analysis of a new circular micro-heat sink containing nanofluid: applicable for cooling electronic equipment. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 145(3), 1547–1557 (2021)
M.M. Alqarni, E.E. Mahmoud, E.A. Algehyne, T. Saeed, A.S. Berrouk, M. Ibrahim, Numerical evaluation of the effect of nano-additive type on the second-law performance of γ-AlOOH nano-fluid flow in a wavy microchannel. Chem. Eng. Commun. 2021, 1–13 (2021)
M. Bahiraei, S. Heshmatian, Thermal performance and second law characteristics of two new microchannel heat sinks operated with hybrid nanofluid containing graphene–silver nanoparticles. Energy Convers. Manag. 168, 357–370 (2018)
M. Bahiraei, A. Monavari, M. Naseri, H. Moayedi, Irreversibility characteristics of a modified microchannel heat sink operated with nanofluid considering different shapes of nanoparticles. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 151, 119359 (2020)
A. Karamoozian, H. Jiang, C.A. Tan, Probability based survey of braking system: a pareto-optimal approach. IEEE Access 8, 128385–128406 (2020)
M. Karami, S. Tashakor, A. Afsari, M. Hashemi-Tilehnoee, Effect of the baffle on the performance of a micro pin fin heat sink. Therm. Sci. Eng. Progr. 14, 100417 (2019)
A. Karamoozian, C.A. Tan, L. Wang, M.R. Akbarzadeh, G. Chen, Sensitivity analysis of the equal angle divider mechanism kinematics with the synthesis of the joint gap tolerances. Mech. Based Design Struct. Mach. 46(4), 499–519 (2018)
X. Du et al., Piezo-phototronic effect promoted carrier separation in coaxial p-n junctions for self-powered photodetector. Nano Energy 92, 106694 (2022)
X. Zhang et al., Preparation of PI porous fiber membrane for recovering oil-paper insulation structure. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 31(16), 13344–13351 (2020)
A. Karamoozian, C.A. Tan, L.J.M. Wang, Squeal analysis of thin-walled lattice brake disc structure. Mater. Design 149, 1–14 (2018)
S. Zimmermann, M.K. Tiwari, I. Meijer, S. Paredes, B. Michel, D. Poulikakos, Hot water cooled electronics: exergy analysis and waste heat reuse feasibility. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 55(23), 6391–6399 (2012)
W. A. Khan, M. Yovanovich, and J. Culham, Optimization of microchannel heat sinks using entropy generation minimization method. In: Twenty-second annual ieee semiconductor thermal measurement and management symposium, 2006, pp. 78–86: IEEE
X. Zhang, Y. Tang, F. Zhang, C.-S. Lee, A novel aluminum-graphite dual-ion battery. Adv. Energy Mater. 6(11), 1502588 (2016)
W. Tai et al., Characterization of the receptor-binding domain (RBD) of 2019 novel coronavirus: implication for development of RBD protein as a viral attachment inhibitor and vaccine. Cell. Molec. Immunol. 17(6), 613–620 (2020)
X. Wang, M. Chen, D. Tate, H. Rahimi, S. Zhang, Numerical investigation on hydraulic and thermal characteristics of micro latticed pin fin in the heat sink. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 149, 119157 (2020)
A. Elghool et al., Enhancing the performance of a thermo-electric generator through multi-objective optimisation of heat pipes-heat sink under natural convection. Energy Convers. Manag. 209, 112626 (2020)
Y. Ma, A. Shahsavar, P. Talebizadehsardari, Two-phase mixture simulation of the effect of fin arrangement on first and second law performance of a bifurcation microchannels heatsink operated with biologically prepared water-Ag nanofluid. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 114, 104554 (2020)
K. Khanafer, K. Vafai, A critical synthesis of thermophysical characteristics of nanofluids. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 54(19), 4410–4428 (2011)
M. Bahiraei, S. Heshmatian, Application of a novel biological nanofluid in a liquid block heat sink for cooling of an electronic processor: thermal performance and irreversibility considerations. Energy Convers. Manag. 149, 155–167 (2017)
T. Saravanakumar, D. Senthil Kumar, Performance analysis on heat transfer characteristics of heat SINK with baffles attachment. Int. J. Thermal Sci. 142, 14–19 (2019)
A. Shahsavar, M.M. Baseri, A.A.A.A. Al-Rashed, M. Afrand, Numerical investigation of forced convection heat transfer and flow irreversibility in a novel heatsink with helical microchannels working with biologically synthesized water-silver nano-fluid. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 108, 104324 (2019)
Y. Ma, A. Shahsavar, P. Talebizadehsardari, Two-phase mixture simulation of the effect of fin arrangement on first and second law performance of a bifurcation microchannels heatsink operated with biologically prepared water-Ag nanofluid. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 114, 104554 (2020)
L. Yang, J.-N. Huang, M. Mao, W. Ji, Numerical assessment of Ag-water nano-fluid flow in two new microchannel heatsinks: thermal performance and thermodynamic considerations. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 110, 104415 (2020)
Electricity prices in Europe 2019 by country – Data Eurostat, Graphics – Strom-Report.
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by Deanship of Scientific Research, Majmaah University, Majmaah, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia, under project number R-2022-53.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ibrahim, M., Shah, S.I.A., El-Shorbagy, M.A. et al. Investigation of the effect of wall geometry change on thermal resistance, temperature uniformity and FOM of a micro-heatsink containing nanofluid flow. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 137, 310 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/s13360-022-02469-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/s13360-022-02469-1