Abstract.
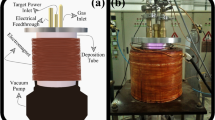
Nickel nanoparticles were prepared by a co-deposition technique via radio frequency plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition (RF-PECVD) and radio frequency (RF) sputtering methods using a Ni target and acetylene gas. To prevent the prepared nanoparticles from agglomeration and in order for the nucleus of the nanocluster to be formed, a DLC film was made as host. We fixed the RF power at 300W and the deposition time at 30min. We prepared four different nickel samples by varying the initial pressure of acetylene gas in the chamber. It is shown as the amount of nickel increases, the electrical resistance decreases where the structure is transformed from a nanoparticle form to a nanocluster form. The nanoclusters have a cone structure, because the initial nanoparticles serve as nuclei for nanoclusters, and deposition is carried out vertically. By applying a magnetic field, it was found that the cluster structure gives a better response to it. The absorbance value at 800nm was improved from 0.5% for the pure nanoparticle sample (#1) to 6.4% for the nanocluster structure (#4). As a result, the nanocluster structure is more suitable for magnetic sensors.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
D.L. Feldheim, A.F. Colby Jr. (Editors), Metal Nanoparticles: Synthesis Characterization and Application (Marcel Dekker, 2002)
S. Ţalu et al., Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 54, 8212 (2015)
M. Kidwai, Nanoparticles in Green Catalysis: Handbook of Green Chemistry (Wiley, 2010)
L.L. Beecroft, C.K. Ober, Chem. Mater. 9, 1302 (1997)
A. Meldrum, L.A. Boatner, C.W. White, Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. B 178, 7 (2001)
G. Schmid, D. Fenske, Phil. Trans. R. Soc. A 368, 1207 (2010)
Y. Chen, D.L. Peng, D. Lin, X. Luo, Nanotechnology 18, 505703 (2007)
W. Szu-Han, C. Dong-Hwang, J. Colloid Interface Sci. 259, 282 (2003)
Wang Sh-Fu et al., Sensors Actuators B 123, 495 (2007)
J. Robertson, Phys. Status Solidi A 205, 2233 (2008)
T. Ghodselahi et al., Surf. Coat. Technol. 202, 2731 (2008)
M. Kataja, T.K. Hakala, A. Julku, M.J. Huttunen, Nat. Commun. 6, 7072 (2015)
J. Robertson, Mater. Sci. Eng. R: Rep. 37, 129 (2002)
M. Ohring, The Materials Science of Thin Films (AcademicPress, Inc, 1992)
M. Spolaore, V. Antoni, M. Bagatin, A. Buffa, Surf. Coat. Technol. 116, 1083 (1999)
R.E.H. Clark, D.H. Reiter (Editors), Nuclear Fusion Research (Springer, 2005)
Y. Kudriavtsev et al., Appl. Surf. Sci. 239, 273 (2005)
A.C. Ferrari, J. Robertson, Phys. Rev. B 63, 121405(R) (2001)
J.A. Creighton, D.J. Eadon, J. Chem. Soc. Faraday Trans. 87, p3881 (1991)
N.F. Mott, E.A. Davis, Electronic Process in Non-crystalline Materials (Clarendon Press, 1979)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ahmadirad, M., Yazdani, A. & Rahimi, K. Effect of magnetic field on Ni nanoclusters prepared via a combined plasma-enhanced chemical vapor deposition and radio frequency sputtering. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 133, 216 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/i2018-12031-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/i2018-12031-1