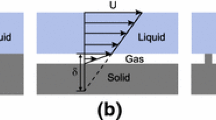
Abstract.
An extremely thin gas film was found between a sphere and a free surface when the sphere impacted onto a water pool. That might influence the generation and evolution of water entry cavity. However, it is quite difficult to be captured through normal numerical and experimental tests. In this work, by using a finite element method we investigate the water entry of a hydrophobic sphere with gas viscosity artificially increased. The air film rupture in the early stage, contact line dynamics on a curved solid surface, and air pocket formation are investigated. The numerical results reveal that the lifetime of the gas film can be predicted by a viscous squeezing flow model qualitatively well. That relates to the fact that the gas film is much thinner than the diameter of the sphere, even when the gas viscosity is 100 times as large as the liquid one. However, inviscid flow can be found in the most part of the liquid bulk. The free surface profile (or the gas film profile) is then determined by the impact speed, namely the Weber number. More importantly, after the “gas” film ruptures at the bottom of the sphere, a contact line is generated. The contact line retracts along the sphere's surface, and the retracting speed fulfils \( U_{MCL}\propto T^{-1/2}\) law generally. This implies that the retracting process of the gas film is dominated by the inertia-capillary balance, rather than simply by the visco-capillary.
Graphical abstract

Similar content being viewed by others
References
A.M. Worthington, R.S. Cole, Philos. Trans. R. Soc. London, Ser. A 189, 137 (1897)
A.M. Worthington, R.S. Cole, Philos. Trans. R. Soc. London, Ser. A 194, 175 (1900)
A. May, J. Appl. Phys. 22, 1219 (1951)
A. May, J. Appl. Phys. 23, 1362 (1952)
V. Duclaux, F. Caillé, C. Duez, C. Ybert, L. Bocquet, C. Clanet, J. Fluid Mech. 591, 1 (2007)
J. Aristoff, J.W.M. Bush, J. Fluid Mech. 619, 45 (2009)
C. Duez, C. Ybert, C. Clanet, L. Bocquet, Nat. Phys. 3, 180 (2007)
M.H. Zhao, X.P. Chen, Q. Wang, Sci. Rep. 4, 5376 (2014)
D. Quéré, Annu. Rev. Mater. Res. 38, 71 (2008)
F.C. Yang, X.P. Chen, P. Yue, Phys. Fluids 30, 012106 (2018)
H. Ding, B.Q. Chen, H.R. Liu, C.Y. Zhang, P. Gao, X.Y. Lu, J. Fluid Mech. 783, 504 (2015)
M. Do-Quang, G. Amberg, Phys. Fluids 21, 022102 (2009)
M. Do-Quang, G. Amberg, Math. Comput. Simul. 80, 1664 (2010)
H. Yan, Y. Liu, J. Kominarczuk, D.K.P. Yue, J. Fluid Mech. 641, 441 (2009)
M. Greenhow, Appl. Ocean Res. 10, 191 (1988)
S. Gaudet, Phys. Fluids 10, 2489 (1998)
J.O. Marston, I.U. Vakarelski, S.T. Throddsen, J. Fluid Mech. 680, 660 (2011)
A.L. Biance, C. Clanet, D. Quéré, Phys. Rev. E 69, 016301 (2004)
T. Tran, H. de Maleprade, C. Sun, D. Lohse, J. Fluid Mech. 726, R3 (2013)
K. Langley, E.Q. Li, S.T. Thoroddsen, J. Fluid Mech. 813, 647 (2017)
C. Josserand, S. Thoroddsen, Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 48, 365 (2016)
B.C.W. Tan, J.H.A. Vlaskamp, P. Denissenko, P.J. Thomas, J. Fluid Mech. 790, 33 (2016)
P. Yue, J.J. Feng, C. Liu, J. Shen, J. Fluid Mech. 515, 293 (2004)
P. Yue, C. Zhou, J.J. Feng, C.F. Ollivier-Gooch, H.H. Hu, J. Comput. Phys. 219, 47 (2006)
P. Yue, C. Zhou, J.J. Feng, J. Fluid Mech. 645, 279 (2010)
C. Huh, S.G. Mason, J. Colloid Interface Sci. 60, 11 (1977)
J.M. Aristoff, T.T. Truscott, A.H. Techet, J.W.M. Bush, Phys. Fluids 22, 032102 (2010)
A.A. Korobkin, V.V. Pukhnach, Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 20, 159 (1998)
D. Battistin, A. Iafrati, J. Fluids Struct. 17, 643 (2003)
A. Iafrati, A.A. Korobkin, Phys. Fluids 16, 2214 (2004)
C. Geuzaine, J.F. Remacle, Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 79, 1309 (2009)
X. Chen, S. Mandre, J.J. Feng, Phys. Fluids 18, 092103 (2006)
A.G. Petrov, I.S. Kharlamova, Eur. J. Mech. B/Fluids 48, 40 (2014)
D.Y.C. Chan, E. Klaseboer, R. Manica, Soft Matter 7, 2235 (2011)
J. Eggers, J.R. Lister, H.A. Stone, J. Fluid Mech. 401, 293 (1999)
T.S. Chan, S. Srivastava, A. Marchand, B. Andreotti, L. Biferale, F. Toschi, J.H. Snoeije, Phys. Fluids 25, 074105 (2013)
M. Liu, X.P. Chen, Eur. Phys. J. E 41, 92 (2018)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
The EPJ Publishers remain neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, FC., Chen, XP. & Yue, P. The influences of “gas” viscosity on water entry of hydrophobic spheres. Eur. Phys. J. E 42, 34 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1140/epje/i2019-11795-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1140/epje/i2019-11795-9