Abstract
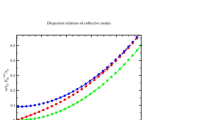
The low-energy modes of a spin-imbalanced superfluid Fermi gas in the Bardeen-Cooper-Schrieffer (BCS) side are studied. The gas is assumed to be sufficiently dilute so that the pairing of atoms can be considered effective only in s-wave between fermions of different internal state. The order parameter at equilibrium is determined by the mean-field approximation, while the properties of the collective modes are calculated within a Gaussian approximation for the fluctuations of the order parameter. In particular we investigate the effects of asymmetry between the populations of the two different components and of temperature on the frequency and damping of collective modes. It is found that the temperature does not much affect the frequency and the damping of the modes, whereas an increase of the imbalance shifts the frequency toward lower values and enhances the damping sensitively. Besides the Bogoliubov-Anderson phonons, we observe modes at zero frequency for finite values of the wave-number. These modes indicate that an instability develops driving the system toward two separate phases, normal and superfluid.
Graphical abstract

Similar content being viewed by others
References
L. Radzihovsky, D.E. Sheehy, Rep. Prog. Phys. 73, 076501 (2010)
K.B. Gubbels, H.T.C. Stoof, Phys. Rep. 525, 255 (2013)
G. Bighin, G. Mazzarella, L. Dell’Anna, L. Salasnich, J. Phys. B 47, 195302 (2014)
P.-A. Pantel, D. Davesne, M. Urban, Phys. Rev. A 90, 053629 (2014)
P.-A. Pantel, D. Davesne, M. Urban, Phys. Rev. A 94, 019901 (2016)
I. Boettcher, J. Braun, T.K. Herbst, J.M. Pawlowski, D. Roscher, C. Wetterich, Phys. Rev. A 91, 013610 (2015)
D. Roscher, J. Braun, J.E. Drut, Phys. Rev. A 91, 053611 (2015)
S. Dutta, E.J. Mueller, Phys. Rev. A 94, 063627 (2016)
M. Zwierlein, A. Schirotzek, C.H. Schunck, W. Ketterle, Science 311, 492 (2006)
G.B. Partridge, W. Li, R.I. Kamar, Y.-A. Liao, R.G. Hulet, Science 311, 503 (2006)
G.B. Partridge, W. Li, Y.-A. Liao, R.G. Hulet, M. Haque, H.T.C. Stoof, Phys. Rev. Lett. 97, 190407 (2006)
Y. Shin, M.W. Zwierlein, C.H. Schunck, A. Schirotzek, W. Ketterle, Phys. Rev. Lett. 97, 030401 (2006)
Y. Shin, C.H. Schunck, A. Schirotzek, W. Ketterle, Nature 451, 689 (2008)
N. Navon, S. Nascimbene, F. Chevy, C. Salomon, Science 328, 729 (2010)
B.A. Olsen, M.C. Revelle, J.A. Fry, D.E. Sheehy, R.G. Hulet, Phys. Rev. A 92, 063616 (2015)
G. Sarma, J. Phys. Chem. Solids 24, 1029 (1963)
S. Giorgini, L.P. Pitaevskii, S. Stringari, Rev. Mod. Phys. 80, 1215 (2008)
R.B. Diener, R. Sensarma, M. Randeria, Phys. Rev. A 77, 023626 (2008)
S.N. Klimin, J. Tempere, P.A. Devreese, J. Low Temp. Phys. 165, 261 (2011)
A.I. Larkin, Yu.N. Ovchinnikov, Zh. Eksp. Teor. Fiz. 47, 1136 (1964) [Sov. Phys. JETP 20, 762 (1965)]
P. Fulde, R.A. Ferrell, Phys. Rev. 135, A550 (1964)
A. Altland, B. Simons, Condensed matter field theory (Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 2007)
F. Matera, M.F. Wagner, Eur. Phys. J. D 69, 158 (2015)
J.R. Engelbrecht, M. Randeria, C.A.R. Sá de Melo, Phys. Rev. B 55, 15153 (1997)
C.J. Pethick, H. Smith, Bose-Einstein condensation in dilute gases (Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 2004)
J.W. Negele, H. Orland, Quantum many-particle systems (Addison-Wesley, New York, 1987)
P. Nozières, Le Problème à N Corps (Dunod, Paris, 1963)
D. Pines, P. Nozières, The theory of quantum liquids (W.A. Benjamin, New York, 1966)
E. Abrahams, T. Tsuneto, Phys. Rev. 152, 416 (1966)
J.E. Baarsma, K.B. Gubbels, H.T.C. Stoof, Phys. Rev. A 82, 013624 (2010)
F.F. Abraham, Phys. Rep. 53, 93 (1979)
F. Matera, A. Dellafiore, Phys. Rev. C 62, 044611 (2000)
P. Chomaz, M. Colonna, J. Randrup, Phys. Rep. 389, 263 (2004)
Y. Ohashi, A. Griffin, Phys. Rev. A 67, 063612 (2003)
M. Urban, P. Schuck, Phys. Rev. A 73, 013621 (2006)
H. Heiselberg, Phys. Rev. A 73, 013607 (2006)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Matera, F., Wagner, M.F. Low-energy modes of spin-imbalanced Fermi gases in BCS phase. Eur. Phys. J. D 71, 293 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1140/epjd/e2017-80156-0
Received:
Revised:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1140/epjd/e2017-80156-0