Abstract
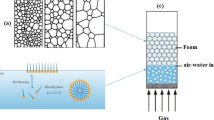
In this paper, we investigated two types of silicas obtained by the sol-gel synthesis (silica 1) and solgel synthesis of endotemplates (fructose) (silica 2). In the first phase of work, the surface characteristics of the synthesized silicas were evaluated. Area measurement and pore volume of silica samples showed that the surface of silica 2 had a narrow slitlike pores, and the pore size was 3.15–3.17 nm. Thermochemical studies of silica showed that the content of hydroxyl groups per 1 g of silica was greater in the case of silica synthesized by endotemplate technology. The obtained data on the texture parameters and chemical activity of the surface were used in the study of systems containing surfactant and silica in aqueous media. Common for particles of synthesized silica is that the form of particles in the solutions remains spherical and the zeta potential decreases. Moreover, the neutralization of the surface charge of silica 2 takes place to a greater extent than the neutralization of the charge on the surface of particles of silica 1. The greatest practical interest may be the pre-foaming solution with the addition of silica 2, because the maximum lifetime was recorded in this solution.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Frolova, A.M., Chukhleb, M.A., Drobot, A.V., Krokhmal’, A.P., Boichenko, A.P., and Loginova, L.P., Production of fine monolithic layers of inorganic sorbent by sol-gel synthesis, Vestn. Kharkovsk. Nats. Univ., Khim., 2008, no. 820, no. 16 (39), pp. 160–167.
Parfenyuk, E., Aleshin, N., Antsiferova, Yu., and Sotnikova, N., Transport nanosystem for the immune correction of macrophage functions in endometriosis, Nanoindustriya, 2012, vol. 1, no. 31, pp. 58–64.
Chew, T.-L., Ahmad, A.L., and Bhatia, S., Ordered mesoporous silica (OMS) as an adsorbent and membrane for separation of carbon dioxide (CO2), Adv. Colloid Interface Sci., 2010, vol. 153, pp. 43–57.
Derkach, S.R. and Zotova, K.V., Rheology of food emulsions, Vestn. Mosk. Gos. Tekh. Univ., 2012, vol. 15, no. 1, pp. 84–95.
Binks, B.P. and Rodrigues, J.A., synergistic interaction in emulsions stabilized by a mixture of silica, Langmuir, 2007, vol. 23, pp. 3626–3636.
Shabanova, N.A. and Sarkisov, P.D., Osnovy zol’-gel’ tekhnologii nanodispersnogo kremnezema (Fundamentals of Sol-Gel Technology of Nanodispersed Silica), Moscow: Akademkniga, 2004.
Shüth, F., Endo- and exotemplating to create high-surface- area inorganic materials, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2003, vol. 42, pp. 3604–3622.
Beck, J.S., Vartuli, J.C., Kennedy, G.J., Kresge, C.T., Roth, W.J., and Schramm, S.E., Molecular or supramolecular templating: Defining the role of surfactant chemistry in the formation of microporous and mesoporous molecular sieves, Chem. Mater., 1994, vol. 6, pp. 1816–1821.
Gonzenbach, U.T., Studart, A.R., Tervoort, E., and Gauckler, L.J., Stabilization of foams with inorganic colloidal particles, Langmuir, 2006, vol. 22, pp. 10983–10988.
Erasov, V.S., Pletnev, M.Yu., and Pokidko, B.V., Stability and rheology of foams containing microbial polysaccharide and particles of silica and bentonite clay, Colloid J., 2015, vol. 77, no. 5, pp. 614–621.
Colloidal Silica: Fundamentals and Applications, Surfactant Science, Bergna, H.E., and Roberts, W.O., Eds., Boca Raton: CRC, 2005, vol. 131. https://books.google.ru/ books?id=xZ0nNHdFCKsC&printsec=frontcover&hl=ru#v=onepage&q&f=false.
Babicka, F., Groppa, S., and Kätzelb, U., Manuel Vorbau dynamic light scattering of dispersed fumed silica aggregates, Powder Technol., 2012, vol. 217, pp. 39–45. doi 10.1016/j.powtec.2011.10.064
Stober, W., Fink, A., and Bohn, E., Controlled growth of monodisperse silica spheres in micron size range, Colloid Interface Sci. 1968, no. 26, pp. 62–69.
Taratanov, N.A., Lebedeva, N.Sh., and Potemkina, O.V., The silica dioxide modification for creation of doublepurpose fire extinguishing compositions, Pozhary Chrezvychainye Situatsii: Predotvrashchenie, Likvidatsiya, 2016, no. 1, pp. 66–70.
Sing, K.S.W., Reporting physisorption data for gas/solid systems with special reference to the determination of surface area and porosity (recommendations 1984), Pure Appl. Chem., 1985, vol. 57, no. 4, pp. 603–619.
NIST Chemistry WebBook. http://webbook.nist.gov/ chemistry/.
Zhuravlev, L.T., The surface chemistry of amorphous silica. Zhuravlev model, Colloids Surf., A, 2000, vol. 173, pp. 1–38.
Zhuravlev, L.T. and Potapov, V.V., Density of silanol groups on the surface of silica precipitated from a hydrothermal solution, Russ. J. Phys. Chem. A, 2006, vol. 80, no. 7, pp. 1119–1128.
Lisichkin, G.V. and Fadeev, A.Y., Khimiya privitykh poverhnostnykh soedinenii (Chemistry of Grafted Surface Compounds), Moscow: Fizmatlit, 2003.
Dorcheh, A.S. and Abbasi, M.H., Silica aerogel: Synthesis, properties, and characterization, J. Mater. Process. Technol., 2008, vol. 199, nos. 1–3, pp. 10–26.
Ek, S., Root, A., Peussa, M., et al., Determination of the hydroxyl group content in silica by thermogravimetry and a comparison with 1 H MAS NMR results, Thermochim. Acta, 2001, vol. 379, pp. 201–212.
Binks, B.P., Particles as surfactants-similarities and differences, Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci., 2002, vol. 7, nos. 1–2, pp. 21–41.
Vignati, E., Piazza, R., and Lockhart, T.P., Pickering emulsions: Interfacial tension, colloidal layer morphology, and trapped-particle motion, Langmuir, 2003, vol. 19, pp. 6650–6656.
Binks, B.P. and Horozov, T.S., Aqueous foams stabilized solely by silica nanoparticles, Angew. Chem., 2005, vol. 117, pp. 3788–3791.
Lepori, L. and Gianni, P., Partial molar volumes of ionic and nonionic organic solutes in water: A simple additivity scheme based on the intrinsic volume approach, J. Solution Chem., 2000, vol. 29, no. 5, pp. 405–447.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © N.Sh. Lebedeva, N.A. Taratanov, E.V. Barinova, O.V. Potemkina, 2017, published in Perspektivnye Materialy, 2017, No. 5, pp. 45–55.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lebedeva, N.S., Taratanov, N.A., Barinova, E.V. et al. Effect of supplementation different hydrophobic silicas on the stability of foams. Inorg. Mater. Appl. Res. 8, 727–733 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1134/S2075113317050148
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S2075113317050148