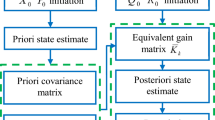
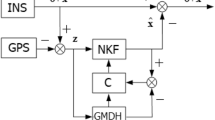
Abstract—
The limitations of Kalman filter (KF) have motivated researchers to consider alternative methods of integrating inertial navigation systems (INS) and global navigation satellite systems (GNSS), predominantly based on artificial intelligence (AI). Over the past two decades, a great number of research gained in order to validate the possibility of using AI methods in the field of integrated navigation systems. Different approaches have been proposed for combining AI modules with the other parts of the INS/GNSS system. The article suggests a new classification of the resulting schemes based on the functionality of AI modules in the INS/GNSS system. The paper also provides a brief explanation of each scheme with its advantages and disadvantages. Some aspects that need to be considered in future research in this field are also highlighted.












Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Grewal, M. S., Weill, L. R., and Andrews, A. P. (2007). Global positioning systems, inertial navigation, and integration. John Wiley & Sons.
Farrell, J. and Barth, M. (1999). The global positioning system and inertial navigation (Vol. 61). New York: Mcgraw-hill.
Chiang, K. W., Noureldin, A., and El-Sheimy, N. (2003). Multisensor integration using neuron computing for land-vehicle navigation. GNSS solutions, 6(4), 209-218.
Salychev, O. S. (1998). Inertial systems in navigation and geophysics (pp. 11–98). Moscow, Russia: Bauman MSTU Press.
Jekeli, C. (2012). Inertial navigation systems with geodetic applications. Walter de Gruyter.
Vörsmann, P., Kaschwich, C., Krüger, T., Schnetter, P., and Wilkens, C. S. (2012). MEMS based integrated navigation systems for adaptive flight control of unmanned aircraft—State of the art and future developments. Gyroscopy and Navigation, 3(4), 235–244.
Schwarz, K. P., El-Sheimy, N., and Liu, Z. (1994). Fixing GNSS cycle slips by INS/GNSS–methods and experiences. Proc. KIS94, 265–275.
Angrisano, A. (2010). GNSS/INS integration methods. Dottorato di ricerca (PhD) in Scienze Geodetiche e Topografiche Thesis, Universita’degli Studi di Napoli PARTHENOPE, Naple, 21.
Crassidis, J. L. and Junkins, J. L. (2004). Optimal estimation of dynamic systems. Chapman and Hall/CRC.
Julier, S. J., and Uhlmann, J. K. (2004). Unscented filtering and nonlinear estimation. Proceedings of the IEEE, 92(3), 401–422.
Vanicek, P. and Omerbasic, M. (1999). Does a navigation algorithm have to use a Kalman filter?. Canadian aeronautics and space journal,45(3), 292–296.
Hong, S., Lee, M. H., Chun, H. H., Kwon, S. H., and Speyer, J. L. (2005). Observability of error states in GNSS/INS integration. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 54(2), 731–743.
Tang, Y., Wu, Y., Wu, M., Wu, W., Hu, X., and Shen, L. (2008). INS/GNSS integration: Global observability analysis. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 58(3), 1129–1142.
Cawsey, A. (1997). The essence of artificial intelligence. Prentice Hall PTR.
Symon, H. (1999). Neural networks: a comprehensive foundation.Prentice-Hall.
Jang, J. S. (1993). ANFIS: adaptive-network-based fuzzy inference system. IEEE transactions on systems, man, and cybernetics, 23(3), 665–685.
Eiben, A. E. and Smith, J. E. (2003). Introduction to evolutionary computing (Vol. 53, p. 18). Berlin: Springer.
Giarratano, J. C. and Riley, G. (1989). Expert systems: Principles and programming. Brooks/Cole Publishing Co.
Mitchell, M. (1998). An introduction to genetic algorithms. MIT press.
Uhr, L. and Honavar, V. (Eds.). (1994). Artificial intelligence and neural networks: steps toward principled integration. Academic press.
Wang, X., Li, K., Gao, P., and Wang, W. (2014). Reinforced ultra-tightly coupled GNSS/INS system for challenging environment. Mathematical Problems in Engineering, 2014.
Refan, M. H., Dameshghi, A., and Kamarzarrin, M. (2015). Utilizing hybrid recurrent neural network and genetic algorithm for predicting the pseudo-range correction factors to improve the accuracy of RTDGNSS. Gyroscopy and Navigation, 6(3), 197–206.
El-Sheimy, N., Chiang, K. W., and Noureldin, A. (2006). The utilization of artificial neural networks for multisensor system integration in navigation and positioning instruments. IEEE Transactions on instrumentation and measurement, 55(5), 1606–1615.
Noureldin, A., Osman, A., and El-Sheimy, N. (2003). A neuro-wavelet method for multi-sensor system integration for vehicular navigation. Measurement science and technology, 15(2), 404.
Noureldin, A., El-Shafie, A., and El-Sheimy, N. (2007). Adaptive neuro-fuzzy module for inertial navigation system/global positioning system integration utilising position and velocity updates with real-time cross-validation. IET Radar, Sonar and Navigation, 1(5), 388–396.
Chiang, K. W., Noureldin, A., and El-Sheimy, N. (2008). Constructive neural-networks-based MEMS/ GNSS integration scheme. IEEE transactions on aerospace and electronic systems, 44(2), 582–594.
Fahlman, S. E. and Lebiere, C. (1990). The cascade-correlation learning architecture. In Advances in neural information processing systems (pp. 524–532).
Adusumilli, S., Bhatt, D., Wang, H., Bhattacharya, P., and Devabhaktuni, V. (2013). A low-cost INS/GNSS integration methodology based on random forest regression. Expert Systems with Applications, 40(11), 4653–4659.
Breiman, L. (2001). Random forests. Machine learning, 45(1), 5–32.
Moré, J. J. (1978). The Levenberg-Marquardt algorithm: implementation and theory. In Numerical analysis (pp. 105–116). Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg.
Sharaf, R., Noureldin, A., Osman, A., and El-Sheimy, N. (2005). Online INS/GNSS integration with a radial basis function neural network. IEEE Aerospace and Electronic Systems Magazine, 20(3), 8–14.
Sharaf, R. and Noureldin, A. (2007). Sensor integration for satellite-based vehicular navigation using neural networks. IEEE transactions on neural networks, 18(2), 589–594.
Taha, M. R., Noureldin, A., and El-Sheimy, N. (2001, March). Improving INS/GNSS positioning accuracy during GNSS outages using fuzzy logic. In Proceedings of the 16th International Technical Meeting of the Satellite Division of The Institute of Navigation (ION GNSS/GNSS 2003) (pp. 499–508).
Bezdek, J. C. (1981). Objective function clustering. In Pattern recognition with fuzzy objective function algorithms (pp. 43–93). Springer, Boston, MA.
Noureldin, A., El-Shafie, A., and Taha, M. R. (2007). Optimizing neuro-fuzzy modules for data fusion of vehicular navigation systems using temporal cross-validation. Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence, 20(1), 49–61.
Hasan, A. M., Samsudin, K., Ramli, A. R., and Azmir, R. S. (2011). Automatic estimation of inertial navigation system errors for global positioning system outage recovery. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part G: Journal of Aerospace Engineering, 225(1), 86–96.
Hasan, A. M., Samsudin, K., and Ramli, A. R. (2011). Optimizing of ANFIS for estimating INS error during GNSS outages. Journal of the Chinese Institute of Engineers, 34(7), 967–982.
Kennedy, J. (2010). Particle swarm optimization. Encyclopedia of machine learning, 760–766.
Hou, H., and El-Sheimy, N. (2001, March). Inertial sensors errors modeling using Allan variance. In Proceedings of the 16th International Technical Meeting of the Satellite Division of the Institute of Navigation (ION GNSS/GNSS 2003) (pp. 2860–2867).
Goodall, C., Syed, Z., and El-Sheimy, N. (2006, September). Improving INS/GNSS navigation accuracy through compensation of Kalman filter errors. In IEEE Vehicular Technology Conference (pp. 1–5). IEEE.
Abdel-Hamid, W., Noureldin, A., and El-Sheimy, N. (2007). Adaptive fuzzy prediction of low-cost inertial-based positioning errors. IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems, 15(3), 519–529.
Noureldin, A., Karamat, T. B., Eberts, M. D., and El-Shafie, A. (2009). Performance enhancement of MEMS-based INS/GNSS integration for low-cost navigation applications. IEEE Transactions on vehicular technology, 58(3), 1077–1096.
Xu, Z., Li, Y., Rizos, C., and Xu, X. (2010). Novel hybrid of LS-SVM and Kalman filter for GNSS/INS integration. The Journal of Navigation, 63(2), 289–299.
Vapnik, V. (1998). The support vector method of function estimation. In Nonlinear Modeling (pp. 55–85). Springer, Boston, MA.
Chen, X., Shen, C., Zhang, W. B., Tomizuka, M., Xu, Y., and Chiu, K. (2013). Novel hybrid of strong tracking Kalman filter and wavelet neural network for GNSS/INS during GNSS outages. Measurement,46(10), 3847–3854.
Boutayeb, M. and Aubry, D. (1999). A strong tracking extended Kalman observer for nonlinear discrete-time systems. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 44(8), 1550–1556.
Zhang, J., Walter, G. G., Miao, Y., and Lee, W. N. W. (1995). Wavelet neural networks for function learning. IEEE transactions on Signal Processing, 43(6), 1485–1497.
Wang, X., Chen, J. X., and Ni, W. (2015, July). A hybrid prediction method and its application in the distributed low-cost INS/GNSS integrated navigation system. In 2015 18th International Conference on Information Fusion (Fusion) (pp. 1205–1212). IEEE.
Wang, J. J., Wang, J., Sinclair, D., and Watts, L. (2007). Neural network aided Kalman filtering for integrated GNSS/INS geo-referencing platform. In Proc. 5th Int. Symp. Mobile Mapping Technol (pp. 1–6).
Chen, L. and Fang, J. (2014). A hybrid prediction method for bridging GNSS outages in high-precision POS application. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 63(6), 1656–1665.
Jingsen, Z., Wenjie, Z., Bo, H., and Yali, W. (2016, July). Integrating Extreme Learning Machine with Kalman Filter to Bridge GNSS Outages. In 2016 3rd International Conference on Information Science and Control Engineering (ICISCE) (pp. 420–424). IEEE.
Huang, G. B., Wang, D. H., and Lan, Y. (2011). Extreme learning machines: a survey. International journal of machine learning and cybernetics, 2(2), 107–122.
Yao, Y., Xu, X., Zhu, C., and Chan, C. Y. (2017). A hybrid fusion algorithm for GNSS/INS integration during GNSS outages. Measurement, 103, 42–51.
Yao, Y. and Xu, X. (2017). A RLS-SVM aided fusion methodology for INS during GNSS outages. Sensors, 17(3), 432.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nader Al Bitar, Gavrilov, A. & Khalaf, W. Artificial Intelligence Based Methods for Accuracy Improvement of Integrated Navigation Systems During GNSS Signal Outages: An Analytical Overview. Gyroscopy Navig. 11, 41–58 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1134/S2075108720010022
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S2075108720010022