Abstract
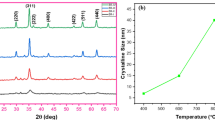
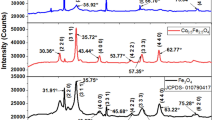
For the first time, under the conditions of in situ oxidative polymerization, a hybrid dispersed magnetic material based on poly-3-amine-7-methylamine-2-methylphenazine (PAMMPh) is obtained in which nanoparticles Fe3O4 are dispersed in an electroactive polymer matrix. According to the results of TEM and SEM, Fe3O4 nanoparticles have sizes of 4 nm < d < 11 nm. Using IR spectroscopy it is established that the chain propagation proceeds via the addition of C–N between 3-amine groups and the para position of phenyl rings relative to nitrogen. The chemical structure, phase composition, and the magnetic and thermal properties of the nanomaterials versus the synthesis conditions are investigated. It is shown that the Fe3O4/PAMMPh nanocomposite material is superparamagnetic and thermally stable.
Similar content being viewed by others

References
R. M. Cornell and U. Schwertmann, The Iron Oxides: Structure, Properties, Reactions, Occurrences, and Uses (VCH, New York, 1996).
D. Y. Godovsky, “Device applications of polymernanocomposites,” Adv. Polym. Sci. 153 (15), 163–205 (2000).
G. P. Karpacheva, “Hybrid magnetic nanocomposites including polyconjugated polymers,” Polym. Sci., Ser. C 58, 131–146 (2016).
X. Lu, Y. Yu, L. Chen, H. Mao, H. Gao, J. Wang, W. Zhang, and Y. Wey, “Aniline dimmer-COOH assisted preparation of well-dispersed polyaniline- Fe3O4 nanoparticles,” Nanotecnology 16, 1660–1665 (2005).
D. Chao, X. Lu, J. Chen, W. Zhang, and Y. Wei, “Anthranilic acid assisted preparation of Fe3O4- poly(aniline-co-o-anthranilic acid) nanoparticles,” J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 102, 1666–1671 (2006).
J. Du, Q. Peng, R. Qiao, W. Chen, C. Xu, Z. Shuai, and M. Gao, “Polyaniline/Fe3O4 nanoparticle composite: synthesis and reaction mechanism,” J. Phys. Chem. B 113, 5052–5058 (2009).
G. Qiu, Q. Wang, and M. Nie, “Polyaniline/Fe3O4 magnetic nanocomposite prepared by ultrasonic irradiation,” J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 102, 2107–2111 (2006).
A. Khan, A. S. Aldwayan, M. Alhoshan, and M. Alsalhi, “Synthesis by in situ chemical oxidative polymerization and characterization of polyaniline/iron oxide nanoparticle composite,” Polym. Int. 59, 1690–1694 (2010).
S. S. Umare and B. H. Shambharkar, “Synthesis, characterization, and corrosion inhibition study of polyaniline- a-Fe2O3 nanocomposite,” J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 127, 3349–3355 (2013).
N. N. Mallikarjuna, S. K. Manohar, P. V. Kulkarni, A. Venkataraman, and T. M. Aminabhavi, “Novel high dielectric constant nanocomposites of polyaniline dispersed with ?-Fe2O3 nanoparticles,” J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 97, 1868–1874 (2005).
M. Bhaumik, T. Y. Leswifi, A. Maity, V. V. Shrinivasu, and M. S. Onyango, “Removal of fluoride from aqueous solution by polypyrrole/Fe3O4 magnetic nanocomposite,” J. Hazard. Mater. 186, 150–159 (2011).
M. Jokar, R. Foroutani, M. H. Safaralizadeh, and K. Farhadi, “Synthesis and characterization of polyaniline/ Fe3O4 magnetic nanocomposite as practical approach for fluoride removal process,” Ann. Res. Rev. Biol. 4, 3262–3273 (2014).
B. H. Shambharkar and S. S. Umare, “Production and characterization of polyaniline/Co3O4 nanocomposite as a cathode of Zn-polyaniline battery,” Mater. Sci. Eng. B 175, 120–128 (2010).
A. Chen, H. Wang, B. Zhao, J. Wang, and X. Li, “Preparation and characterization of Fe3O4/polypyrrole (PPy) composites,” Acta Mater. Compos. Sin. 21, 157–160 (2004).
L. Li, J. Jiang, and F. Xu, “Novel polyaniline- LiNi0.5La0.02Fe1.98O4 nanocomposites prepared via an in situ polymerization,” Eur. Polym. J. 42, 2221–2227 (2006).
L. Li, J. Jiang, and F. Xu, “Synthesis and ferrimagnetic properties of novel Sm-substituted LiNi ferrite-polyaniline nanocomposite,” Mater. Lett. 61, 1091–1096 (2007).
G. D. Prasanna, H. S. Jayanna, and V. Prasad, “Preparation, structural, and electrical studies of polyaniline/ ZnFe2O4 nanocomposites,” J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 120, 2856–2862 (2011).
J. C. Aphesteguy and S. E. Jacobo, “Composite of polyaniline containing iron oxides,” Phys. B (Amsterdam, Neth.) 354, 224–227 (2004).
M. Wan and J. Li, “Synthesis and electrical-magnetic properties of polyaniline composites,” J. Polym. Sci., A 36, 2799–2805 (1998).
Z. Zhang and M. Wan, “Nanostructures of polyaniline composites containing nano-magnet,” Synth. Met. 132, 205–212 (2003).
G. P. Karpacheva and S. Zh. Ozkan, “Dispersed nanocomposite magnetic material and method of its obtaining,” RF Patent No. 2426188, Byull. Izobret. No. 22 (2011).
I. S. Eremeev, S. Zh. Ozkan, G. P. Karpacheva, and G. N. Bondarenko, “Hybrid dispersed magnetic nanomaterial based on polydiphenylamine-2-carbonic acid and Fe3O4,” Nanotechnol. Russ. 9, 38–44 (2014).
G. P. Karpacheva, S. Zh. Ozkan, I. S. Eremeev, G. N. Bondarenko, E. L. Dzidziguri, and P. A. Chernavskii, “Synthesis of hybrid magnetic nanomaterial based on polydiphenylamine-2-carboxylic acid and Fe3O4 in the interfacial process,” Eur. Chem. Bull. 3, 1001–1007 (2014).
S. Zh. Ozkan, G. P. Karpacheva, E. L. Dzidziguri, P. A. Chernavskii, G. N. Bondarenko, and G. V. Pankina, “Formation features of hybrid magnetic materials based on polyphenoxazine and magnetite nanoparticles,” J. Res. Updates Polym. Sci. 5, 137–148 (2017).
S. Zh. Ozkan, G. P. Karpacheva, G. N. Bondarenko, and Yu. G. Kolyagin, “Polymers based on 3-amine-7-dimethylamine-2-methylphenazine hydrochloride: synthesis, structure, and properties,” Polym. Sci., Ser. B 57, 106–115 (2015).
Yu. V. Karyakin and I. I. Angelov, Pure Chemical Reagents (Khimiya, Moscow, 1974) [in Russian].
S. Zh. Ozkan and G. P. Karpacheva, “Metal-polymer nanocomposite magnetic material based on poly-3-amine-7-methylamine-2-methylphenazine and Fe3O4 nanoparticles and method of its production,” RU Patent No. 2637333 C2, Byull. Izobret. No. 34 (2017).
E. L. Dzidziguri, “Dimensional characteristics of nanopowders,” Nanotechnol. Russ. 4, 857–870 (2009).
P. A. Chernavskii, G. V. Pankina, and V. V. Lunin, “Magnetometric methods of investigation of supported catalysts,” Russ. Chem. Rev. 80, 579–604 (2011).
R. Massart, “Preparation of aqueous magnetic liquids in alkaline and acidic media,” IEEE Trans. Magn. 17, 1247–1248 (1981).
J. Tang, X. Jing, B. Wang, and F. Wang, “Infrared spectra of soluble polyaniline,” Synth. Met. 24, 231–238 (1988).
M. Trchova, J. Prokes, and J. Stejskal, “Infrared spectroscopic study of solid-state protonation and oxidation of polyaniline,” Synth. Met. 101, 840–841 (1999).
N. V. Bhat, D. T. Seshadri, and R. S. Phadke, “Simultaneous polymerization and crystallization of aniline,” Synth. Met. 130, 185–192 (2002).
P. S. Rao, S. Subrahmanya, and D. N. Sathyanarayana, “Inverse emulsion polymerization: a new route for the synthesis of conducting polyaniline,” Synth. Met. 128, 311–316 (2002).
Z. Ping, “In situ FTIR-attenuated total reflection spectroscopic investigations on the base-acid transitions of polyaniline. Base-acid transition in the emeraldine form of polyaniline,” J. Chem. Soc., Faraday Trans. 92, 3063–3067 (1996).
M. I. Ivanovskaya, A. I. Tolstik, D. A. Kotikov, and V. V. Pankov, “The structural characteristics of Zn–Mn ferrite synthesized by spray pyrolysis,” Russ. J. Phys. Chem. A 83, 2081–2086 (2009).
A. Yu. Soloveva, Y. V. Ioni, and S. P. Gubin, “Synthesis of Fe3O4 nanoparticles on the surface of graphene,” Mendeleev Commun. 26, 38–39 (2016).
S. P. Gubin, Yu. A. Koksharov, G. B. Khomutov, and G. Yu. Yurkov, “Magnetic nanoparticles: preparation, structure and properties,” Russ. Chem. Rev. 74, 489–520 (2005).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © S.Zh. Ozkan, G.P. Karpacheva, P.A. Chernavskii, E.L. Dzidziguri, G.N. Bondarenko, G.V. Pankina, 2018, published in Rossiiskie Nanotekhnologii, 2018, Vol. 13, Nos. 3–4.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ozkan, S.Z., Karpacheva, G.P., Chernavskii, P.A. et al. A Hybrid Material Based on Poly-3-Amine-7-Methylamine-2-Methylphenazine and Magnetite Nanoparticles. Nanotechnol Russia 13, 122–129 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1995078018020064
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1995078018020064