Abstract
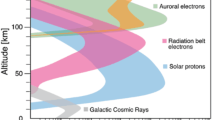
The mechanisms of the influence of various energetic particles on the atmosphere and their consideration by modern models are discussed. The types of energetic particles considered are galactic cosmic rays, auroral electrons, solar protons, and electrons precipitating into the atmosphere from outer radiation belt. The effects of these particles on the ozone layer and climate are illustrated using observational data and model calculations. The influence of galactic cosmic rays is noticeable only in the troposphere at southern latitudes, whereas a strong but short-term destruction of ozone by episodic solar protons have no effect at climatic time scales. Thus, the main influence on the long-term ozone layer variability is exerted by energetic electrons. Changing ozone contents lead to changing heating rates, temperature, and structure of stratospheric circulation, which in turn affects wave processes and climate. Simulation of these processes requires the use of complex numerical models that include all necessary processes and their interaction in the atmosphere from the surface to the upper thermosphere.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
E. Rozanov, L. Callis, M. Schlesinger, et al., Geophys. Rev. Lett. 32, L14811 (2005). doi 10.1029/2005GL023041
A. Seppälä, C. E. Randall, M. A. Clilverd, et al., J. Geophys. Res. 114, A10312 (2009). doi 10.1029/2008JA014029
I. A. Mironova, K. L. Aplin, F. Arnold, et al., Space Sci. Rev. 194, 1 (2015). doi 10.1007/s11214-015-0185-4
C. E. Randall, V. L. Harvey, C. S. Singleton, et al., J. Geophys. Res. 112, D8308 (2007). doi 10.1029/2006JD007696
B. Funke, A. Baumgaertner, M. Calisto, et al., Atmos. Chem. Phys. 11, 9089 (2011).
M. E. Andersson, P. T. Verronen, C. J. Rodger, et al., Nat. Commun. 5, 5197 (2014). doi 10.1038/ncomms6197
C. H. Jackman, D. R. Marsh, D. E. Kinnison, et al., Atmos. Chem. Phys. 16, 5853 (2016). doi 10.5194/acp-16-5853-2016
E. Rozanov, M. Calisto, T. Egorova, et al., Surv. Geophys. 33, 483 (2012).
K. Kodera and Y. Kuroda, J. Geophys. Res. 107, D24.4749 (2002). doi 10.1029/2002JD002224
J. Kidston, A. A. Scaife, S. C. Hardiman, et al., Nat. Geosci. 8, 433 (2015). doi 10.1038/NGEO2424
J. G. Anet, E. V. Rozanov, S. Muthers, et al., Geophys. Rev. Lett. 40, 4420 (2013). doi 10.1002/grl.50806
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © E.V. Rozanov, 2018, published in Khimicheskaya Fizika, 2018, Vol. 37, No. 8, pp. 73–78.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rozanov, E.V. Effect of Precipitating Energetic Particles on the Ozone Layer and Climate. Russ. J. Phys. Chem. B 12, 786–790 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1990793118040152
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1990793118040152