Abstract
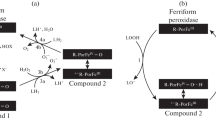
In the present work, the recorded kinetics of chemiluminescence enhanced by coumarin 334 indicated that the complexes of cytochrome c (Cyt) with anionic lipids (Cyt-AL), such as cardiolipin (CL) and phosphatidic acid (PA), when added to mitochondrial and cytoplasmic membranes, are capable of catalysing reactions of lipid free radical formation. The effect of Cyt-CL complex was studied on mitochondria isolated from the liver of male Wistar rats and male outbred mice, as well as on erythrocytes isolated from the blood of male Wistar rats. It was shown that complex Cyt-PA exerts a peroxidase effect similar to the effect produced by Cyt-CL. Upon exposure to Cyt-CL, the formation of free radicals was more prominent in mitochondrial ghosts (mitochondria subjected to freeze-thawing and washed by several precipitation–resuspension cycles) than in intact mitochondria. This suggests that Cyt-CL does not pass through biological membranes: even if it penetrates into them, it probably gets stuck in the phospholipid bilayer. Thus, the previously discovered cytotoxic effect of Cyt-CL on cancer cells is most likely due to peroxidation of the cytoplasmic membrane, but not of the inner membrane of mitochondria.





Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Skulachev V.P. 1996. Why are mitochondria involved in apoptosis? Permeability transition pores and apoptosis as selective mechanisms to eliminate superoxide-producing mitochondria and cell. FEBS Lett. 397 (1), 7–10.
Skulachev V.P. 2000. Mitochondria in the programmed death phenomena; A principle of biology: “It is better to die than to be wrong”. IUBMB Life. 49 (5), 365–373.
Vladimirov Y.A. 2002. The loss of barrier properties by inner and outer mitochondrial membranes, necrosis and apoptosis. Biol. Membrany (Rus.).19, 356–377.
Hunter D.R., Haworth R.A. 1979. The Ca2+-induced membrane transition in mitochondria. I. The protective mechanisms. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 195 (2), 453–459.
Hunter D.R., Haworth R.A. 1979. The Ca2+-induced membrane transition in mitochondria. III. Transitional Ca2+ release. Arch Biochem. Biophys. 195 (2), 468–477.
Korkina L.G., Sorokovoy V.I., Vladimirov Y.A. 1973. Accumulation of Ca2+ in mitochondrial membranes and Ca2+-induced membrane damage studied with chlorotetracycline as a fluorescent probe. Studia Biophysica. 3, 177–192.
Brustugun O.T., Fladmark K., Døskeland S., Orrenius S., Zhivotovsky B. 1998. Apoptosis induced by microinjection of cytochrome C is caspase-dependent and is inhibited by Bcl-2. Cell Death Differ.5 (8), 660–668.
Zhivotovsky B., Orrenius S., Brustugun O.T., Doskeland S.O. 1998. Injected cytochrome c induces apoptosis. Nature. 391 (6666), 449–450.
Green D.R., Llambi F. 2015. Cell death signaling. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 7 (12), a006080.
Green D.R. 2011. Means to an end: Apoptosis and other cell death mechanisms. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press.
Green D.R., Kroemer G. 2004. The pathophysiology of mitochondrial cell death. Science. 305 (5684), 626–629.
Brustugun O.T., Fladmark K.E., Doskeland S.O., Orrenius S., Zhivotovsky B. 1998. Apoptosis induced by microinjection of cytochrome c is caspase-dependent and is inhibited by Bcl-2. Cell Death Differ. 5 (8), 660–668.
Kroemer G., Reed J.C. 2000. Mitochondrial control of cell death. Nat. Med. 6 (5), 513–519.
Belikova N.A., Vladimirov Y.A., Osipov A.N., Kapralov A.A., Tyurin V.A., Potapovich M.V., Basova L.V., Peterson J., Kurnikov I.V., Kagan V.E. 2006. Peroxidase activity and structural transitions of cytochrome c bound to cardiolipin-containing membranes. Biochemistry. 45 (15), 4998–5009.
Kagan V.E., Gleiss B., Tyurina Y.Y., Tyurin V.A., Elenstrom-Magnusson C., Liu S.X., Serinkan F.B., Arroyo A., Chandra J., Orrenius S., Fadeel B. 2002. A role for oxidative stress in apoptosis: Oxidation and externalization of phosphatidylserine is required for macrophage clearance of cells undergoing Fas-mediated apoptosis. J. Immunol. 169 (1), 487–499.
Kagan V.E., Borisenko G.G., Serinkan B.F., Tyurina Y.Y., Tyurin V.A., Jiang J., Liu S.X., Shvedova A.A., Fabisiak J.P., Uthaisang W., Fadeel B. 2003. Appetizing rancidity of apoptotic cells for macrophages: Oxidation, externalization, and recognition of phosphatidylserine. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell Mol. Physiol. 285 (1), L1–17.
Kagan V.E., Borisenko G.G., Tyurina Y.Y., Tyurin V.A., Jiang J., Potapovich A.I., Kini V., Amoscato A.A., Fujii Y. 2004. Oxidative lipidomics of apoptosis: Redox catalytic interactions of cytochrome c with cardiolipin and phosphatidylserine. Free Radic. Biol. Med.37 (12), 1963–1985.
Kagan V.E., Tyurin V.A., Jiang J., Tyurina Y.Y., Ritov V.B., Amoscato A.A., Osipov A.N., Belikova N.A., Kapralov A.A., Kini V. 2005. Cytochrome c acts as a cardiolipin oxygenase required for release of proapoptotic factors. Nat. Chem. Biol. 1 (4), 223–232.
Kimelberg H.K., Papahadjopoulos D. 1971. Interactions of basic proteins with phospholipid membranes. Binding and changes in the sodium permeability of phosphatidylserine vesicles. J. Biol. Chem. 246 (4), 1142–1148.
Brown L.R., Wuthrich K. 1977. A spin label study of lipid oxidation catalyzed by heme proteins. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 464 (2), 356–369.
Brown L.R., Wuthrich K. 1977. NMR and ESR studies of the interactions of cytochrome c with mixed cardiolipin-phosphatidylcholine vesicles. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 468 (3), 389–410.
Quinn P.J., Dawson R.M. 1969. Interactions of cytochrome c and [14C]-carboxymethylated cytochrome c with monolayers of phosphatidylcholine, phosphatidic acid and cardiolipin. Biochem. J.115 (1), 65–75.
Rytomaa M., Kinnunen P.K. 1994. Evidence for two distinct acidic phospholipid-binding sites in cytochrome c. J. Biol. Chem. 269 (3), 1770–1774.
Rytomaa M., Kinnunen P.K. 1995. Reversibility of the binding of cytochrome c to liposomes. Implications for lipid–protein interactions. J. Biol. Chem. 270 (7), 3197–3202.
Sinibaldi F., Howes B.D., Piro M.C., Polticelli F., Bombelli C., Ferri T., Coletta M., Smulevich G., Santucci R. 2010. Extended cardiolipin anchorage to cytochrome c: A model for protein-mitochondrial membrane binding. J. Biol. Inorg. Chem.15 (5), 689–700.
Vladimirov Y.A., Proskurnina E.V., Izmailov D.Y., Novikov A.A., Brusnichkin A.V., Osipov A.N., Kagan V.E. 2006. Mechanism of activation of cytochrome C peroxidase activity by cardiolipin. Biochemistry (Mosc.). 71 (9), 989–997.
Vladimirov Y.A., Proskurnina E.V., Izmajlov D.Y. 2011. Kinetic chemiluminescence as a method for study of free radical reactions. Biophysics (Mosc.). 56 (6), 1055–1062.
Muenzner J., Pletneva E.V. 2014. Structural transformations of cytochrome c upon interaction with cardiolipin. Chem. Phys. Lipids. 179, 57–63.
Muenzner J., Toffey J.R., Hong Y., Pletneva E.V. 2013. Becoming a peroxidase: Cardiolipin-induced unfolding of cytochrome c.J. Phys. Chem. B.117 (42), 12878–12886.
Mohammadyani D., Yanamala N., Samhan-Arias A.K., Kapralov A.A., Stepanov G., Nuar N., Planas-Iglesias J., Sanghera N., Kagan V.E., Klein-Seetharaman J. 2018. Structural characterization of cardiolipin-driven activation of cytochrome c into a peroxidase and membrane perturbation. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Biomembr. 1860 (5), 1057–1068.
Vladimirov Y.A., Nol’ Y.T., Volkov V.V. 2011. Protein–lipid nanoparticles that determine whether cells will live or die. Crystallography Reports. 56 (4), 553–559.
Vladimirov Y.A., Proskurnina E.V., Alekseev A.V. 2013. Molecular mechanisms of apoptosis. Structure of cytochrome c-cardiolipin complex. Biochemistry (Mosc.). 78 (10), 1086–1097.
Proskurnina E.V., Proskurnin M.A., Alekseev A.V., Galimova V.R., Vladimirov Yu.A. 2018. Determination of the composition of the complex of cytochrome c with cardiolipin by means of spectrophotometry and dark-linse spectrometry. Tekhnologii zhivykh sistem (Rus.). 3, 27–32.
Demin E.M., Proskurnina E.V., Vladimirov Y.A. 2008. Antioxidant effects of dihydroquercetin and rutin in peroxidase reactions catalyzed by cytochrome c.Moscow University Chemistry Bulletin. 63 (5), 297–302.
Proskurnina E.V., Alekseev A.V., Demin E.M., Izmailov D.Y., Vladimirov Y.A. 2013. Cyt-CL complex: Peroxidase activity and role in lipid peroxidation. FEBS J.280 (SI Suppl.1), 264.
Vladimirov Y.A., Demin E.M., Proskurnina E.V., Osipov A.N. 2009. Lipoperoxide radical production during oxidation of cardiolipin in the complex with cytochrome c. Biochem. (Mosc.).Suppl. Series A: Membr. Cell Biol. 3 (4), 479–489.
Folch J., Lees M., Sloane Stanley G.H. 1957. A simple method for the isolation and purification of total lipides from animal tissues. J. Biol. Chem. 226 (1), 497–509.
Vikulina A.S., Alekseev A.V., Proskurnina E.V., Vladimirov Y.A. 2015. The complexs of cytochrome c with cardiolipin in non-polar environment. Biochemistry (Mosc.). 80 (10), 1298–1302.
Vladimirov G.K., Vikulina A.S., Volodkin D.V., Vladimirov Y.A. 2018. Structure of the complex of cytochrome C with cardiolipin in non-polar environment. Chem. Phys. Lipids.214, 35–45
Vladimirov G.K., Remenshchikov V.E., Nesterova A.M., Volkov V.V., Vladimirov Y.A. 2019. Comparison of the size and properties of the cytochrome c/cardiolipin nanospheres in a sediment and non-polar medium. Biochemistry (Mosc.).84 (8), 923–30.
Vladimirov Y.A., Sharov V.S., Driomina E.S., Reznitchenko A.V., Gashev S.B. 1995. Coumarin derivatives enhance the chemiluminescence accompanying lipid peroxidation. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 18 (4), 739–745.
Kapralov A.A., Yanamala N., Tyurina Y.Y., Castro L., Samhan-Arias A., Vladimirov Y.A., Maeda A., Weitz A.A., Peterson J., Mylnikov D., Demicheli V., Tortora V., Klein-Seetharaman J., Radi R., Kagan V.E. 2011. Topography of tyrosine residues and their involvement in peroxidation of polyunsaturated cardiolipin in cytochrome c/cardiolipin peroxidase complexes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1808 (9), 2147–2155.
Chance B. 1949. The properties of the enzyme–substrate compounds of horse-radish and lacto-peroxidase. Science. 109 (2826), 204–208.
Chance B., Higgins J. 1952. Peroxidase kinetics in coupled oxidation; an experimental and theoretical study. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 41 (2), 432–441.
Furtmuller P.G., Jantschko W., Zederbauer M., Jakopitsch C., Arnhold J., Obinger C. 2004. Kinetics of interconversion of redox intermediates of lactoperoxidase, eosinophil peroxidase and myeloperoxidase. Jpn. J. Infect. Dis. 57 (5), S30–31.
Hannun Y.A. 1997. Apoptosis and the dilemma of cancer chemotherapy. Blood. 89 (6), 1845–1853.
Ghobrial I.M., Witzig T.E., Adjei A.A. 2005. Targeting apoptosis pathways in cancer therapy. CA Cancer J. Clin. 55 (3), 178–194.
Lopez J., Tait S. 2015. Mitochondrial apoptosis: Killing cancer using the enemy within. Br. J. Cancer. 112 (6), 957–962.
Vladimirov Y.A., Sarisozen C., Vladimirov G.K., Filipczak N., Polimova A.M., Torchilin V.P. 2017. The cytotoxic action of cytochrome C/cardiolipin nanocomplex (Cyt-CL) on cancer cells in culture. Pharm. Res. 34 (6), 1264–1275.
Storrie B., Madden E.A. 1990. Isolation of subcellular organelles. Methods Enzymol. 182, 203–225.
Dodge J.T., Mitchell C., Hanahan D.J. 1963. The preparation and chemical characteristics of hemoglobin-free ghosts of human erythrocytes. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 100, 119–130.
Sozarukova M.M. 2017. Neutrophils and erythocytes as sources of free radicals in the blood and albumin as the target of their action. Extended Abstract of Cand. Sci Dissertation (Biol.). RNIMU, Moscow, 2017.
Vladimirov Y.A., Arroyo A., Taylor J.M., Tyurina Y.Y., Matsura T., Tyurin V.A., Kagan V.E. 2000. Quinolizin-coumarins as physical enhancers of chemiluminescence during lipid peroxidation in live HL-60 cells. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 384 (1), 154–162.
Kagan V.E., Bayir H.A., Belikova N.A., Kapralov O., Tyurina Y.Y., Tyurin V.A., Jiang J., Stoyanovsky D.A., Wipf P., Kochanek P.M., Greenberger J.S., Pitt B., Shvedova A.A., Borisenko G. 2009. Cytochrome c/cardiolipin relations in mitochondria: A kiss of death. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 46 (11), 1439–1453.
Vladimirov Y.A. 1996. Intrinsic (low-level) chemiluminescence. In: Free radicals. A practical approach. Eds Punchard N.A. Oxford, New York, Tokyo: Oxford University Press, p. 65–82.
Gryzunov Y.A., Arroyo A., Vigne J.L., Zhao Q., Tyurin V.A., Hubel C.A., Gandley R.E., Vladimirov Y.A., Taylor R.N., Kagan V.E. 2003. Binding of fatty acids facilitates oxidation of cysteine-34 and converts copper–albumin complexes from antioxidants to prooxidants. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 413 (1), 53–66.
Bergstrom C.L., Beales P.A., Lv Y., Vanderlick T.K., Groves J.T. 2013. Cytochrome c causes pore formation in cardiolipin-containing membranes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 110 (16), 6269–6274.
Firsov A.M., Kotova E.A., Korepanova E.A., Osipov A.N., Antonenko Y.N. 2015. Peroxidative permeabilization of liposomes induced by cytochrome c/cardiolipin complex. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1848 (3), 767774.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
The work was supported by the Russian Science Foundation (project no. 17-74-10248).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interests.
All experiments with animals were conducted in accordance with the regulations established by Order of the USSR Ministry of Health of 08/12/1977, no. 755, as well as European Communities Council Directive 1986 (86/609/EEC).
Additional information
Translated by G. Vladimirov
Abbreviations: AL, anionic lipids; C-334, coumarin 334; ChL, chemiluminescence; CytC, cytochrome c; Cyt-AL, cytochrome c complex with anionic lipids; CL, cardiolipin; Cyt-CL, complex cytochrome c with cardiolipin; Cyt-TOCL, a complex of cytochrome c with tetraoleoyl cardiolipin; LOO·, lipoperoxyl radical; LOOH, lipid hydroperoxides; PA, dioleoyl-phosphatidic acid; TOCL, tetraoleoyl cardiolipin.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vladimirov, G.K., Nesterova, A.M., Levkina, A.A. et al. The Dynamics of the Formation of Cytochrome c Complexes with Anionic Lipids and the Mechanism of the Production of Lipid Radicals Catalyzed by These Complexes. Biochem. Moscow Suppl. Ser. A 14, 232–241 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1990747820030137
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1990747820030137