Abstract
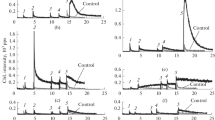
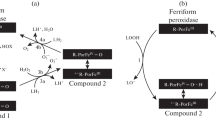
The destruction of cytochrome c during its catalysis of the lipoperoxidase reaction, which causes the impairment of mitochondrial membranes in living cells and the release of various pro-apoptotic factors into the cytosol, was studied. Spectrophotometric analysis showed a much more intense destruction of cytochrome c when hydrogen peroxide was added in the presence of tetraoleylcardiolipin at protein : cardiolipin ratios of 1 : 30 and 1 : 60, which were optimal for the formation of a cytochrome c complex with cardiolipin, compared to the sample in which only hydrogen peroxide and cytochrome c were present. In the second case, the destruction of the porphyrite group of heme took the form of a linear function, while in the presence of cardiolipin the dependence was clearly exponential; upon addition of a lipid substrate, phosphatidic acid, the value of the first-order rate constant of the cytochrome c destruction increased. It is proposed that the rapid destruction of cytochrome c during its catalysis of the lipoperoxidase reaction is an evolutionarily developed mechanism for preventing the spontaneous initiation of apoptosis.




Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Yu. A. Vladimirov, E. V. Proskurnina, and A. V. Alekseev, Biochemistry (Moscow) 78 (10), 1086 (2013).
M. Li, A. Mandal, V. A. Tyurin, et al., Structure 27, 806 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.str.2019.02.007
I. I. Vlasova, Molecules 23 (10), 2561 (2018). https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23102561
A. Mandal, C. L. Hoop, M. DeLucia, et al., Biophys. J. 109, 1873 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bpj.2015.09.016
N. A. Belikova, Y. A. Vladimirov, A. N. Osipov, et al., Biochemistry 45, 4998 (2006).
P. G. Furtmuller, W. Jantschko, M. Zederbauer, et al., Jpn. J. Infect. Dis. 57, 830 (2004).
J. N. Rodriguez-Lopez, D. J. Lowe, J. Hernandez-Ruiz, et al., J. Am. Chem. Soc. 123, 11838 (2001).
L. A. Romodin, S. V. Shangin, Yu. A. Vladimirov, et al., Izv. Mezhd. Akad. Agrarn. Obraz., No. 42-1, 118 (2018).
Yu. A. Vladimirov, E. V. Proskurnina, D. Yu. Izmailov, et al., Biochemistry (Moscow) 71 (9), 998 (2006).
C. Dallacosta, E. Monzani, and L. Casella, J. Biol. Inorg. Chem. 8, 770 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00775-003-0478-z
L. A. Romodin, M. F. Trifonova, N. P. Lysenko, and S. A. Bekuzarova, RF Patent No. 2720807 (May 13, 2020).
Funding
The experiments whose results are presented in this paper were supported by the Russian Foundation for Basic Research, project no. 18-015-00491 Study of the mechanism of reactions of free radical formation in the membranes of cells and mitochondria catalyzed by the cytochrome c complex with anionic lipids (Cyt−AL).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
All authors of this article declare that they have no conflict of interest regarding the materials presented in the work.
COMPLIANCE WITH ETHICAL STANDARDS
This article does not contain a description of the studies performed by the authors with the participation of humans or using animals as experimental objects.
Additional information
Translated by E. Puchkov
Abbreviations: CytC, cytochrome c; PA, phosphatidic acid; TOCL, tetraoleylcardiolipin; CytC−TOCL, complex of cytochrome c with tetraoleylcardiolipin.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Romodin, L.A., Vladimirov, Y.A. & Lysenko, N.P. The Destruction of Cytochrome c in a Complex with Cardiolipin during Catalysis of Lipid Peroxidation. BIOPHYSICS 66, 59–64 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0006350921010085
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0006350921010085