Abstract
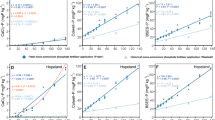
The influence of polyelectrolyte-based soil conditioners on the qualitative and quantitative composition of soil organic matter (SOM) was studied for two soils: sandy Dystric Arenosol (Aric) with 1% of C and silt loamy Abruptic Luvisol (Siltic, Cutanic) with 2% of C. The investigated polymer formulations included a synthetic polycation poly(diallyldimethylammonium chloride) (PDADMAC), a humic-based polyanion (commercial humic product Lignohumate, LH), and an interpolyelectrolyte complex (IPEC) prepared from PDADMAC and LH. In laboratory experiments, soils were treated with polymers and the composition of SOM was analyzed and compared with the control. The effect of polyelectrolytes on the molecular weight distribution and amphiphilic properties of SOM was evaluated using low-pressure size-exclusion chromatography and reversed-phase hydrophobic interaction chromatography. It was shown that the effect of polyelectrolytes differs depending both on the chemical nature and composition of polymers’ functional groups and on the soil properties. Polyanionic LH promoted mobilization of labile humic fractions, whereas polycationic PDADMAC was adsorbed in non-labile fractions. Positively charged IPEC occupied an intermediate position increasing the yield of mobile fractions only in sandy soil. The weighted average molecular weight of SOM slightly decreased with the application of all the polymers. The impact of IPEC on the distribution of hydrophobic and hydrophilic fractions depended on the native humus properties. In clay loam, it increased the proportion of the hydrophilic fraction, whereas in sandy soil the proportion of hydrophobic fractions was higher. Soil organic matter in the sandy low-humus soil provided more distinct effects of polymer application. In contrast, in a more humified loamy soil, polymers were immobilized by binding with the soil organomineral matrix and their effect on the SOM was weak.





Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
A. M. Akimkhan, “Adsorption of polyacrylic acid and polyacrylamide on montmorillonite,” Russ. J. Phys. Chem. 87, 1875–1880 (2013).
V. V. Demidov, I. G. Panova, P. S. Shul’ga, L. O. Il’yasov, and A. A. Yaroslavov, “Anti-erosion properties of chernozem treated with polyelectrolyte complexes based on potassium humates,” in Proceedings of the International Scientific-Practical Conf. “Problems and Prospects of Scientific-Innovative Support of Agroindustrial Regional Complexes” (Moscow State Univ., Moscow, 2019), pp. 503–507.
A. G. Zavarzina, N. G. Vanifatova, and A. A. Stepanov, “Fractionation of humic acids according to their hydrophobicity, size, and charge-dependent mobility by the salting-out method,” Eurasian Soil Sci. 41, 1294–1301 (2008).
V. A. Izumrudov, B. Kh. Mussabayeva, Zh. S. Kassymova, A. N. Klivenko, and L. K. Orazzhanova, “Interpolyelectrolyte complexes: advances and prospects of application,” Russ. Chem. Rev. 88, 1046–1062 (2019).
V. A. Kabanov, “Polyelectrolyte complexes in solution and in bulk,” Russ. Chem. Rev. 74, 3–20 (2005).
L. L. Shishov, V. D. Tonkonogov, I. I. Lebedeva, and M. I. Gerasimova, Classification and Diagnostic System of Russian Soils (Oikumena, Smolensk, 2004) [in Russian].
A. Kullmann, Synthetische Bodenverbesserungsmittel (VEB Deutscher Landwirtschaftsverlag, Berlin, 1972; Kolos, Moscow, 1982).
G. N. Kurochkina and D. L. Pinsky, “Influence of preadsorbed polyelectrolytes on hydrophobic properties of synthetic aluminosilicates,” Russ. J. Phys. Chem. 84, 81–89 (2010).
G. N. Kurochkina and D. L. Pinskii, “Development of a mineralogical matrix at the adsorption of polyelectrolytes on soil minerals and soils,” Eurasian Soil Sci. 45, 1057–1067 (2012).
E. Yu. Milanovskii, E. V. Shein und A. A. Stepanov, “Lyophilic-lyophobic properties of organic matter and soil structure,” Pochvovedenie, No. 6, 122–126 (1993).
L. K. Orazzhanova, Zh. S. Kassymova, B. Kh. Mussabayeva, and A. N. Klivenko, “Soil structuring in the presence of the chitosan–polyacrylic acid interpolymer complex,” Eurasian Soil Sci. 53, 1773–1781 (2020).
D. S. Orlov and E. Yu. Milanovskii, “Gel chromatography in soil science: possibilities and limitations of the method,” in Modern Physical and Chemical Methods of Soil Studies (Moscow State Univ., Moscow, 1987), p. 94.
I. G. Panova, L. O. Ilyasov, and A. A. Yaroslavov, “Polycomplex formulations for the protection of soils against degradation,” Polym. Sci., Ser. C 63, 237–248 (2021).
I. G. Panova, D. D. Khaidapova, L. O. Ilyasov, A. A. Kiushov, A. B. Umarova, A. V. Sybachin, and A. A. Yaroslavov, “Polyelectrolyte complexes of potassium humates and poly(dialyldimethylammonium chloride) for fixing sand soil,” Polym. Sci., Ser. B 61, 698–703 (2019).
L. A. Pozdnyakov, A. L. Stepanov, M. E. Gasanov, M. V. Semenov, O. S. Yakimenko, I. K. Suada, I. N. Rai, and N. M. Shchegolkova, “Effect of lignohumate on soil biological activity on the Bali Island, Indonesia,” Eurasian Soil Sci. 53, 653–660 (2020).
A. V. Smagin, N. B. Sadovnikova, and E. I. Nikolaeva, “Thermodynamic analysis of the effect of strongly swelling polymer hydrogels on the physical state of soil and sediment samples,” Eurasian Soil Sci. 47, 78–88 (2014).
A. A. Stepanov, “Separation and characterization of amphiphilic humic acid fractions,” Moscow Univ. Soil Sci. Bull. 63, 125–129 (2008).
O.A. Trubetskoi and O.E. Trubetskaya, “Reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatography of the stable electrophoretic fractions of soil humic acids,” Eurasian Soil Sci. 48, 148–156 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1134/S106422931502012X
I. K. Khabirov and R. R. Saifullin, “The influence of high-molecular water-soluble polymers on the agrophysical properties of soils and the productivity of agricultural crops after they implementation,” Izv. Orenb. Gos. Agrar. Univ. 74 (6), 8–11 (2018).
O. S. Yakimenko and V. A. Terekhova, “Humic preparations and the assessment of their biological activity for certification purposes,” Eurasian Soil Sci. 44, 1222–1230 (2011).
O. S. Yakimenko, D. A. Gruzdenko, A. A. Stepanov, M. A. Butylkina, A. A. Kiushov, and I. G. Panova, “Polyelectrolytes for the construction of artificial soils,” Polym. Sci., Ser. C 63, 249–255 (2021).
S. Behera and P.A. Mahanwar, “Superabsorbent polymers in agriculture and other applications: a review,” Polym.-Plast. Technol. Mater. 59 (4), 341–356 (2020).
M. Curcio and N. Picci, “Polymer in agriculture: a review,” Am. J. Agric. Biol. Sci. 3 (1), 299–314 (2008).
Y. Deng, J. B. Dixon, and G. N. White, “Adsorption of polyacrylamide on smectite, illite, and kaolinite,” Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 70 (1), 297–304 (2006).
A. Ertani, O. Francioso, V. Tugnoli, V. Righi, and S. Nardi, “Effect of commercial lignosulfonate-humate on Zea mays L. metabolism,” J. Agric. Food Chem. 59, 11940–11948 (2011).
Z. S. Kassymova, L. K. Orazzhanova, A. N. Klivenko, B. K. Mussabayeva, and D. K. Aserzhanov, “Preparation and properties of interpolymer complexes capable of soil structuring,” Russ. J. Appl. Chem. 92 (2), 208–217 (2019).
A. Klivenko, L. Orazzhanova, B. Mussabayeva, G. Yelemessova, and Z. Kassymova, “Soil structuring using interpolyelectrolyte complexes of water-soluble polysaccharides,” Polym. Adv. Technol. 31 (12), 3292–3301 (2020).
D. A. Laird, “Bonding between polyacrylamide and clay mineral surfaces,” Soil Sci. 162 (11), 826–832 (1997).
E. V. Lasareva, A. M. Parfenova, and N. A. Azovtseva, “Formation of soil aggregates via clay flocculation with organic polyelectrolytes,” Biointerface Res. Appl. Chem. 10 (4), 5765–5771 (2020).
S. H. Lee, M. C. Shin, S. J. Choi, J. H. Shin, and L. S. Park, “Improvement of flocculation efficiency of water treatment by using polymer flocculants,” Environ. Technol. 19 (4), 431–436 (1998).
A. I. Mamedov, A. Tsunekawa, N. Haregeweyn, M. Tsubo, H. Fujimaki, T. Kawai, B. Kebede, T. Mulualem, G. Abebe, A. Wubet, and G. J. Levy, “Soil structure stability under different land uses in association with polyacrylamide effects,” Sustainability 13 (3), 1407 (2021).
T. Nishimura, T. Yamamoto, S. Suzuki, and M. Kato, “Effect of gypsum and polyacrylamide application on erodibility of an acid Kunigami Mahji soil,” Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 51 (5), 641–644 (2005).
F. Novak, M. Sestauberova, and R. Hrabal, “Structural features of lignohumic acids,” J. Mol. Struct. 1093, 179–185 (2015).
D. C. Olk, D. L. Dinnes, J. R. Scoresby, C. R. Callaway, and J. W. Darlington, “Humic products in agriculture: potential benefits and research challenges-a review,” J. Soils Sediments 18 (8), 2881–2891 (2018).
I. G. Panova, A. V. Sybachin, V. V. Spiridonov, K. Kydralieva, Sh. Jorobekova, A. B. Zezin, and A. A. Yaroslavov, “Non-stoichiometric interpolyelectrolyte complexes: promising candidates for protection of soils,” Geoderma 307, 91–97 (2017).
I. G. Panova, V. V. Demidov, P. S. Shulga, L. O. Ilyasov, M. A. Butilkina, and A. A. Yaroslavov, “Interpolyelectrolyte complexes as effective structure-forming agents for chernozem soil,” Land Degrad. Dev. 32, 1022–1033 (2021).
I. Panova, A. Drobyazko, V. Spiridonov, A. Sybachin, K. Kydralieva, S. Jorobekova, and A. Yaroslavov, “Humic-based interpolyelectrolyte complexes for antierosion protection of soil: model investigation,” Land Degrad. Dev. 30, 337–347 (2019).
I. G. Panova, D. D. Khaydapova, L. O. Ilyasov, A. B. Umarova, and A. A. Yaroslavov, “Polyelectrolyte complexes based on natural macromolecules for chemical sand/soil stabilization,” Colloids Surf., A 590, 124504 (2020).
I. V. Perminova, “From green chemistry and nature-like technologies towards ecoadaptive chemistry and technology,” Pure Appl. Chem. 91 (5), 851–864 (2019).
F. Puoci, F. Iemma, U. G. Spizzirri, G. Cirillo, M. Curcio, and N. Picci, “Polymer in agriculture: a review,” Am. J. Agric. Biol. Sci. 3 (1), 299–314 (2008).
A. Saha, S. Sekharan, and U. Manna, “Superabsorbent hydrogel (SAH) as a soil amendment for drought management: a review,” Soil Tillage Res. 204, 104736 (2020).
A. Sikder, A. K. Pearce, S. J. Parkinson, R. Napier, and R. K. O’Reilly, “Recent trends in advanced polymer materials in agriculture related applications,” ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 3 (3), 1203–1217 (2021).
A. Smagin, I. Panova, L. Ilyasov, K. Ogawa, Y. Adachi, and A. Yaroslavov, “Water retention in sandy substrates modified by cross-linked polymeric microgels and their complexes with a linear cationic polymer,” J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 138 (31), 50754 (2021).
K. Suada, N. Rai, W. Budiasa, G. N. Santosa, N. Sunarta, G. M. Adnyana, and O. Yakimenko, “Effect of lignohumate on yield and quality of rice in a paddy field in Bali, Indonesia,” Voda: Khim. Ekol., No. 5, 3–11 (2017).
X. Tian, H. Fan, J. Wang, J. Ippolito, Y. Li, S. Feng, M. An, F. Zhang, and K. Wang, “Effect of polymer materials on soil structure and organic carbon under drip irrigation,” Geoderma 340, 94–103 (2019).
O. Trubetskaya, O. Trubetskoj, and C. Richard, “Hydrophobicity of electrophoretic fractions of different soil humic acids,” J. Soils Sediments 132, 84–89 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gexplo.2013.06.00
O. A. Trubetskoj, C. Richard, G. Guyot, G. Voyard, and O. Trubetskaya, “Analysis of electrophoretic soil humic acids fractions by reversed-phase high performance liquid chromatography with on-line absorbance and fluorescence detection,” J. Chromatogr. A 1243, 62–68 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2012.04.043
A. B. Volikov, V. A. Kholodov, N. A. Kulikova, O. I. Philippova, S. A. Ponomarenko, E. V. Lasareva, A. M. Parfyonova, K. Hatfield, and I. V. Perminova, “Silanized humic substances act as hydrophobic modifiers of soil separates inducing formation of water-stable aggregates in soils,” Catena 137, 229–236 (2016).
O. Yakimenko, A. Stepanov, S. Patsaeva, D. Khundzhua, O. Osipova, and O. Gladkov, “Formation of humic-like substances during the technological process of Lignohumate® synthesis as a function of time,” Separations 8 (7), 1–13 (2021).
A. B. Zezin, S. V. Mikheikin, V. B. Rogacheva, M. F. Zansokhova, A. V. Sybachin, and A. A. Yaroslavov, “Polymeric stabilizers for protection of soil and ground against wind and water erosion,” Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 226, 17–23 (2015).
Funding
This study was supported by the Interdisciplinary Scientific and Educational School of the Lomonosov Moscow State University “Future Planet and Global Environmental Changes.” Soil analyses were carried out according to state assignment no. 121040800154-8.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Translated by D. Konyushkov
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yakimenko, O.S., Ziganshina, A.R., Stepanov, A.A. et al. Effect of Polyelectrolytes on Soil Organic Matter in Model Experiments. Eurasian Soil Sc. 55, 988–997 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1064229322070134
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1064229322070134