Abstract
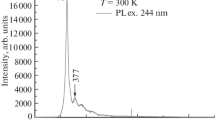
The effect of the Er3+-ion excitation type on the photoluminescence spectra of crystalline ZnO(ZnO〈Ce, Yb, Er〉) films is determined in the cases of resonant (λ = 532 nm, Er3+-ion transition from 4S3/2, 2H11/2 levels to 4I15/2) and non-resonant (λ = 325 nm, in the region near the ZnO band-edge emission) excitation. It is shown that resonant excitation gives rise to lines with various emission intensities, characteristic of the Er3+-ion intracenter 4f transition with λ = 1535 nm when doping crystalline ZnO films with three rare-earth ions (REIs, Ce, Yb, Er) or with two impurities (Ce, Er) or (Er, Yb), independently of the measurement temperature (T = 83 and 300 K). The doping of crystalline ZnO films with rare-earth impurities (Ce, Yb, Er) leads to the efficient transfer of energy to REIs, a consequence of which is the intense emission of an Er3+ ion in the IR spectral region at λmax = 1535 nm. The kick-out diffusion mechanism is used upon the sequential introduction of impurities into semiconductor matrices and during the postgrowth annealing of the ZnO films under study. The crystalline ZnO films doped with Ce, Yb, Er also exhibit intense emission in the visible spectral region at room temperature, which makes them promising materials for optoelectronics.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zinc Oxide Bulk. Thin Films and Nanostructures Processing, Properties and Applications, Ed. by C. Jagadish and S. Pearton (Elsevier, Amsterdam, 2006).
D. C. Look, J. Electron. Mater. 35, 1299 (2006).
Z. L. Wang, Appl. Phys. A: Mater. Sci. Proc. (2007). doi: 10.1007/s00339-007-3942-8
P. M. Parthangal, R. E. Cavicchi, and M. R. Zachariah, Nanotechnology 17, 3786 (2006).
H. J. Lozukowski and W. M. Jadwisienczak, Phys. Status Solidi B 1, 18 (2007).
A. Thurber, G. L. Beausolbel, G. A. Alanko, J. J. Andhel, M. S. Jones, L. M. Jonson, C. B. Hanna, D. A. Tenne, and A. Punnose, J. Appl. Phys. 109, 07C305 (2011).
A. A. Kaminskii and B. M. Antipenko, Multilevel Functional Schemes of the Crystal Lasers (Nauka, Moscow, 1989), p. 199 [in Russian].
D. L. Dexter, J. Chem. Phys. 21, 836 (1953).
Handbook of Laser Science and Technology, Ed. by M. J. Weber (CRC Press, Boca Raton, 1982), Vol. 1.
R. Sh. Malkovich, Mathematics of Diffusion in Semiconductors (Nauka, Leningrad, 1999), p. 175 [in Russian].
M. M. Mezdrogina, M. V. Eremenko, S. M. Golubenko, and S. N. Razumov, Phys. Solid State 54, 1235 (2012).
G. Brauer, W. Anwand, et al., Phys. Rev. B 79, 115212 (2009); U. Ozgur et al., J. Appl. Phys. 98, 041301 (2005).
S. Iwan, S. Bambang, J. L. Zhao, S. T. Tan, H. M. Fan, L. Sun, S. Zhang, H. H. Ryu, and S. W. Sun, Physica B 407, 2721 (2012).
H. Zhou, T. Komori, M. Yoshino, and M. Morinaga, Appl. Phys. Lett. 86, 041107 (2005).
X. M. Duan, C. Stampfl, M. M. M. Bilek, and D. R. McKenzzie, Phys. Rev. B 79, 235208 (2009).
J. P. Suchet, Physical Chemistry of Semiconductors (Dunod, Paris, 1962; Metallurgiya, Moscow, 1969).
X. Liu, Y. Teng, Y. Zhuang, J. Xie, Y. Qiao, G. Dong, D. Chen, and J. Qiu, Opt. Lett. 34, 3505 (2009).
J. X. Meng, K. W. Chea, Zh. Pu. Shi, and J. Q. Li, Appl. Phys. Lett. 91, 151107 (2007).
M. Ishi, Sh. Komuro, T. Morikawa, and Y. Aoyagi, J. Appl. Phys. 89, 3679 (2001).
M. M. Mezdrogina, G. N. Mosina, E. I. Terukov, and I. N. Trapeznikova, Semiconductors 35, 684 (2001).
Peterson, Ch. H. Brimont, M. Gallot, G. Shrenber, C. Uplag-Bullet, C. Collins, and A. Dinia, J. Appl. Phys. 107, 123522 (2010).
M. M. Mezdrogina, M. V. Eremenko, E. I. Terukov, and Yu. V. Kozhanova, Semiconductors 46, 901 (2012).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © M.M. Mezdrogina, M.V. Eremenko, A.N. Smirnov, V.N. Petrov, E.I. Terukov, 2015, published in Fizika i Tekhnika Poluprovodnikov, 2015, Vol. 49, No. 8, pp. 1016–1023.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mezdrogina, M.M., Eremenko, M.V., Smirnov, A.N. et al. Emission intensity of the λ = 1.54 μm line in ZnO films grown by magnetron sputtering, diffusion doped with Ce, Yb, Er. Semiconductors 49, 992–999 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1063782615080138
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1063782615080138