Abstract
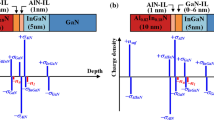
We try to theoretically analyze the reported experimental data of the Al x In1–x N/AlN/GaN heterostructures grown by MOCVD and quantitatively investigate the effects of AlGaN buffers and the GaNchannel thickness on the electrical transport properties of these systems. Also, we obtain the most important effective parameters of the temperature-dependent mobility in the range 35–300 K. Our results show that inserting a 1.1 μm thick Al0.04Ga0.96N buffer enhances electron mobility by decreasing the effect of phonons, the interface roughness, and dislocation and crystal defect scattering mechanisms. Also, as the channel thickness increases from 20 nm to 40 nm, the electron mobility increases from 2200 to 2540 cm2/(V s) and from 870 to 1000 cm2/(V s) at 35 and 300 K respectively, which is attributed to the reduction in the dislocation density and the strain-induced field. Finally, the reported experimental data show that inserting a 450 nm graded AlGaN layer before an Al0.04Ga0.96N buffer causes a decrease in the electron mobility, which is attributed to the enhancement of the lateral size of roughness, the dislocation density, and the strain-induced field in this sample.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
H. Morkoc, Handbook of Nitride Semiconductor and Devices (Wiley, Berlin, 2008). Vols. I–III.
J. Kuzmik, IEEE Electron Device Lett. 22, 510 (2001).
J. Kuzmik, Semicond. Sci. Technol. 17, 540 (2002).
R. Tülek, A. Ilgaz, S. Gökden, A. Teke, M. K. Öztürk, M. Kasap, S. Özçelik, E. Arslan, and E. Özbay, J. Appl. Phys. 105 (1), 013707 (2009).
A. Koukitu, Y. Kumagai, and H. Seki, Phys. Status Solidi A 180, 115 (2000).
M. Gonschorek, J.-F. Carlin, E. Feltin, M. A. Py, N. Grandjean, Appl. Phys. Lett. 89, 062106 (2006).
J. Xue, J. Zhang, W. Zhang, L. Li, F. Meng, M. Lu, J. Ning, and Y. Hao, J. Cryst. Growth 343, 110 (2012).
O. Kelekci, P. Tasil, S. S. Cetin, M. Kasap, S. Ozcelik, and E. Ozbay, Curr. Appl. Phys. 12 (6), 1600 (2012).
O. Katz, D. Mistele, B. Meyler, G. Bahir, and J. Salzman, IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 52, 146 (2005).
M. T. L. Tansley, in Properties of Group III Nitrides, Ed. by J. H. Edgar, Electronic Materials Information Service (EMIS) Data Reviews Series (INSPEC, London, 1994). No. 11, pp. 35–40.
S. Gokden, Chin. J. Phys. 46, 145 (2008).
H. Harima, J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 14, R967 (2002).
A. Kasic, M. Schubert, Y. Saito, G. Wagner, and Y. Nanishi, Phys. Rev. B: Condens. Matter 65, 115206/1 (2002).
M. Levinshtein, S. Rumyantsev, and M. Shur, Properties of Advanced Semiconductor Materials: GaN, AlN, InN, BN, SiC, SiGe (Wiley, New York, 2001).
B. K. Ridley, J. Phys. C: Solid State Phys. 15, 5899 (1982).
K. Lee, M. S. Shur, T. J. Drummond, and H. Morkoc, J. Appl. Phys. 54, 11 (1983).
P. K. Basu and B. R. Nag, Phys. Rev. B: Condens. Matter 22, 4849 (1980).
P. J. Price, Ann. Phys. (New York) 133, 217 (1981).
P. J. Price, J. Vac. Sci. Technol. 19, 599 (1981).
K. Hess, Appl. Phys. Lett. 35, 484 (1979).
C. T. Sah, T. H. Ning, and L. L. Tscopp, Surf. Sci. 32, 561 (1972).
S. Das Sarma and F. Stern, Phys. Rev. B: Condens. Matter 32, 8442 (1985).
J. H. Davies, The Physics of Low-Dimensional Semiconductors (Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 1998).
D. Zanato, S. Gokden, N. Balkan, and W. J. Schaff, Semicond. Sci. Technol. 19, 427 (2004).
U. Panner, H. Rucker, and I. N. Yassievich, Semicond. Sci. Technol. 13, 709 (1998).
B. K. Ridley, B. E. Foutz, and L. F. Eastman, Phys. Rev. B: Condens. Matter 61, 16862 (2000).
M. J. Kearney and A. L. Horrel, Semicond. Sci. Technol. 13, 174 (1998).
H. Tang, W. Kim, A. Botchkarev, G. Popovici, F. Hamdani, and H. Morkoc, Solid-State Electron. 42, 839 (1998).
H. Morkoç and Ümit Özgür, Zinc Oxide: Fundamentals, Materials and Device Technology (Wiley, New York, 2009).
I. Vurgaftman, J. R. Meyer, and L. R. Ram-Mohan, J. Appl. Phys. 89, 5815 (2001).
A. U. Sheleg and V. A. Savastenko, Izv. Akad. Nauk SSSR, Neorg. Mater. 15, 1598 (1979).
C. S. Gallinat, G. Koblmuller, F. Wu, and J. S. Speck, J. Appl. Phys. 107, 053517 (2010).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The article is published in the original.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Amirabbasi, M. The role of AlGaN buffers and channel thickness in the electronic transport properties of Al x In1–x N/AlN/GaN heterostructures. J. Exp. Theor. Phys. 122, 159–164 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1063776115130075
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1063776115130075