Abstract
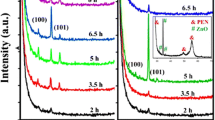
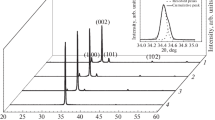
Well aligned 1D ZnO nanostructures are important for optoelectronic and nanoscale electronic devices. In this report, 1D ZnO nanorods were synthesized by very simple, low cost, low temperature hydrothermal process. An effect of concentration, growth time, growth temperature, seed layer annealing, and seed layer thickness was investigated. The synthesized ZnO nanorods were characterized by scanning and transmission electron microscopies, X-ray diffraction, Raman and ultraviolet–visible spectroscopies. Growth parameters were found to influence strongly on the morphology, orientation, diameter, length, and density of the ZnO nanorod arrays. The growth temperature 80–90°C, seed layer annealing at 300–400°C, growth time 3 h, 0.025 M precursor concentration, and 0.2–0.3 M seed layer solution concentrations are more favorable conditions for better orientation and excellent crystallinity of the ZnO nanorods.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
U. Ozgur, Y. I. Alivov, C. Liu, et al., J. Appl. Phys. 98, 041301 (2005).
C. F. Klingshin, Chem. Phys. Chem. 8, 782 (2007).
S. Ranwa, P. K. Kulriya, V. K. Sahu, et al., Appl. Phys. Lett. 105, 213103 (2014).
Z. L. Wang, ACS Nano 2, 1987 (2008).
L. E. Greene, M. Law, D. H. Tan, et al., Nano Lett. 5, 1231 (2005).
J. Elias, R. Tena-Zaera, and C. Lévy-Clément, Thin Solid Films 515, 8553 (2007).
H. Ghayour, H. R. Rezaie, Sh. Mirdamadi, and A. A. Nourbakhsh, Vacuum 86, 101 (2011).
L. W. Ji, M. Peng, J. S. Wu, et al., J. Phys. Chem. Solids 70, 1359 (2009).
C. Li, G. Fang, J. Li, et al., J. Phys. Chem. C 112, 990 (2008).
G. Amin, M. H. Asif, A. Zainelabdin, et al., J. Nanomater. 2011, 269692 (2011).
R. A. Laudise and A. A. Ballman, J. Phys. Chem. 64, 688 (1960).
Y. W. Heo, V. Varadarajan, M. Kaufman, et al., Appl. Phys. Lett. 81, 3046 (2002).
X. Liu, X. Wu, H. Cao, and R. P. H. Chang, J. Appl. Phys. 95, 3141 (2004).
C. K. Xu, G. D. Xu, Y. K. Liu, and G. H. Wang, Solid State Commun. 122, 175 (2002).
B. Q. Cao, M. Lorenz, A. Rahm, et al., Nanotechnology 18, 455707 (2007).
S. Kim, M. C. Jeong, B. Y. Oh, et al., J. Cryst. Growth 290, 485 (2006).
D. Lin, H. Wu, and W. Pan, Adv. Mater. 19, 3968 (2007).
Z. Zhang, M. Lu, H. Xu, and W. S. Chin, Chem. Eur. J. 13, 632 (2007).
Y. W. Wang, L. D. Zhang, G. Z. Wang, et al., J. Cryst. Growth 234, 171 (2002).
S. Xu and S. L. Wang, Nano Res., 4 (11), 1013 (2011).
H. Zhang, D. R. Yang, Y. Y. Ma, et al., J. Phys. Chem. B 110, 827 (2006).
P. C. Chang and J. G. Lu, IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 55, 2977 (2008).
S. Xu, Y. Wei, M. Kirkham, et al., J. Amer. Chem. Soc. 130,14958 (2008).
K. Govender, D. S. Boyle, P. B. Kenway, and P. O’Brien, J. Mater. Chem. 14, 2575 (2004).
S. Xu, N. Adiga, S. Ba, et al., ACS Nano 3, 1803 (2009).
P. Yang, H. Yan, S. Mao, et al., Adv. Funct. Mater. 12, 323 (2002).
M. Jiao, D. H. Nguyen, V. D. Nguyen, et al., J. Sci. Res. Rep. 9 (5), 1 (2016).
V. Strano, R. G. Urso, M. S. Scuderi, et al., J. Phys. Chem. C 118, 28189 (2014).
Q. Zhang, S. J. Liu, and S. H. Yu, J. Mater. Chem. 19, 191 (2009).
S. N. Heo, F. Ahmed, and B. H. Koo, Ceram. Intern. 40, 5467 (2014).
S. A. Morin, M. J. Bierman, J. Tong, and S. Jin, Science 328, 476 (2010).
R. T. R. Kumar, E. McGlynn, C. McLoughlin, et al., Nanotechnology 18, 215704 (2007).
K. H. Kim, K. Utashiro, Y. Abe, and M. Kawamura, Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 9, 2080 (2014).
K. Umar, B. Karunagaran, E. K. Suh, and Y.B. Hahn, Nanotechnology 17, 4072 (2006).
H. Sun, M. Luo, W. Weng, et al., Nanotechnology 19, 395602 (2008).
A. Kushaha, H. Kalita, and M. Aslam, Int. J. Math., Comput., Phys., Electr. Comput. Engin. 7 (2), 203 (2013).
S. Fujihara, C. Sasaki, and T. Kimura, J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 21, 2109 (2010).
C. Jagadish and S. J. Pearton, Zinc Oxide Bulk, Thin Films, and Nanostructures (Elsevier, New York, 2006).
B. Ha, H. Ham, and C. J. Lee, J. Phys. Chem. Solids 69, 2453 (2008).
A. K. Pal and D. G. Mohan, Appl. Surf. Sci. 333, 244 (2015).
H. A. Wahab, A. A. Salama, A. A. E-Saeid, et al., Results Phys. 3, 46 (2013).
M. Ahmed and S. R. Dafeh, Chin. Phys. B. 24, 117203 (2015).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The article is published in the original.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kamruzzaman, M., Zapien, J.A. Effect of Temperature, Time, Concentration, Annealing, and Substrates on ZnO Nanorod Arrays Growth by Hydrothermal Process on Hot Plate. Crystallogr. Rep. 63, 456–471 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1063774518030112
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1063774518030112