Abstract
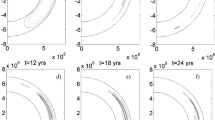
The inverse problem in a spherical shell to find the two-dimensional spatial distributions of the α-effect and differential rotation in a mean-field dynamo model has been solved. The derived distributions lead to the generation of a magnetic field concentrated inside the convection zone. The magnetic field is shown to have no time to rise from the region of maximum generation located in the lower layers to the surface in the polarity reversal time due to magnetic diffusion. The ratio of the maximum magnetic energy in the convection zone to its value at the outer boundary reaches two orders of magnitude or more. This result is important in interpreting the observed stellar and planetary magnetic fields. The proposed method of solving the inverse nonlinear dynamo problem is easily adapted for a wide class of mathematical-physics problems.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
R. Kaiser and A. Tilgner, Phys. Rev. E 63, 37301 (2001).
R. Kaiser, B. J. Schmitt, and F. H. Busse, Geophys. Astrophys. Fluid Dyn. 77, 93 (1994).
A. G. Kosovichev, J. Schou, P. H. Scherrer, R. S. Bogart, R. I. Bush, J. T. Hoeksema, J. Aloise, L. Bacon, et al., Solar Phys. 170, 43 (1997).
F. Krause and K.-H. Rädler, Mean-Field Magnetohydrodynamics and Dynamo Theory (Akademie, Berlin, 1980), p. 271.
W. N. Press, S. A. Teukolsky, W. T. Vetterling, and B. P. Flannery, Numerical Recipes. The Art of Scientific Computing (C++Code), 3rd ed. (Cambridge Univ. Press, Cambridge, 2007), p. 1262.
M. Yu. Reshetnyak, Geomagn. Aeron. 50, 263 (2010).
M. Yu. Reshetnyak, Geomagn. Aeron. 52, 398 (2012).
M. Yu. Reshetnyak, Russ. J. Earth Sci. 15, ES4001 (2015).
M. Yu. Reshetnyak, Astron. Rep. 60, 294 (2016).
G. Rüdiger, L. Kitchatinov, and R. Hollerbach, Magnetic Processes in Astrophysics: Theory, Simulations, Experiments (Willey-VCH, Berlin, 2013), p. 346.
A. A. Ruzmaikin, D. D. Sokolov, and A.M. Shukurov, Magnetic Fields of Galaxies (Nauka, Moscow, 1988; Kluwer, Dordrecht, 1988), p. 280.
R. Simitev, PhD Thesis (Univ. Bayreuth, 2004), p. 182.
J. Simkanin and A. Tilgner, Geophys. Astrophys. Fluid Dyn. 102, 205 (2008).
M. Stix, The Sun: An introduction (Springer, Berlin, 1989), p. 483.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © M.Yu. Reshetnyak, 2016, published in Pis’ma v Astronomicheskii Zhurnal, 2016, Vol. 42, No. 7, pp. 533–539.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Reshetnyak, M.Y. Invisible dynamo in mean-field models. Astron. Lett. 42, 482–487 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1063773716070069
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1063773716070069