Abstract
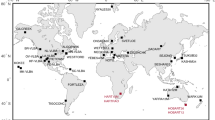
The International astrogeodetic standard IERS Conventions (2010) contains a model of the diurnal and semidiurnal variations in Earth rotation parameters (ERPs), the pole coordinates and the Universal Time, arising from lunisolar tides in the world ocean. This model was constructed in the mid-1990s through a global analysis of Topex/Poseidon altimetry. The goal of this study is to try to estimate the parameters of this model by processing all the available VLBI observations on a global network of stations over the last 35 years performed within the framework of IVS (International VLBI Service) geodetic programs. The complexity of the problemlies in the fact that the sought-for corrections to the parameters of this model lie within 1 mm and, thus, are at the limit of their detectability by all currently available methods of ground-based positional measurements. This requires applying universal software packages with a high accuracy of reduction calculations and a well-developed system of controlling the simultaneous adjustment of observational data to analyze long series of VLBI observations. This study has been performed with the QUASAR software package developed at the Institute of Applied Astronomy of the Russian Academy of Sciences. Although the results obtained, on the whole, confirm a high accuracy of the basic model in the IERS Conventions (2010), statistically significant corrections that allow this model to be refined have been detected for some harmonics of the ERP variations.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
T. Artz, L. Bernhard, A. Nothnagel, P. Steigenberger, and S. Tesmer, J. Geod. 86, 221 (2012); doi:10.1007/s00190-011-0512-9.
A. M. Finkelstein, A. V. Ipatov, E. A. Skurikhina, I. F. Surkis, S. G. Smolentsev, and L. V. Fedotov, Astron. Lett. 38, 394 (2012).
V. S. Gubanov, Sov. Astron. 13, 529 (1969).
V. S. Gubanov, Generalized Least-Squares Method. Theory and Applications to Astrometry (Nauka, St. Petersburg, 1997) [in Russian].
V. S. Gubanov and S. L. Kurdubov, Pis’ma Astron. Zh. 41(5) (2015), (in press).
S. L. Kurdubov, Tr. IPA RAN 14, 138 (2006).
G. Petit and B. Luzum, IERS Techn. Note, No. 36 (2010).
R. D. Ray, D. J. Steinberg, B. F. Chao, et al., Science 264 (1994).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © V.S. Gubanov, S.L. Kurdubov, 2015, published in Pis’ma v Astronomicheskiĭ Zhurnal, 2015, Vol. 41, No. 5, pp. 248–254.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gubanov, V.S., Kurdubov, S.L. Influence of ocean tides on the diurnal and semidiurnal earth rotation variations from VLBI observations. Astron. Lett. 41, 225–231 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1063773715050047
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1063773715050047