Abstract
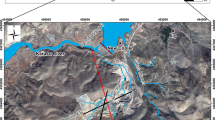
Slope stability accidents are one of the leading causes of destruction at open pit mining operations. Such interception of the seepage water results in the water inflow from the surrounding aquifer towards the mine excavations. In order to design an effective drainage scheme for an open pit mine, prediction of water inflow into the pit is essential. These changes have resulted in some failures and instability problems in different parts of Gol-E-Gohar iron open pit mine. It seems that main parameters which effect the failure and instability of the mine slopes are high pressure of groundwater and system of discontinuities (faults, joins, and bedding planes), which intersect the pit walls. The analysis results indicate that stability of the final pit slopes is sensitive to multi-planar failures and confined water in the walls pit is also a factor adversely affecting the stability. Problems associated with groundwater at the site were also assessed with the analyses of piezometric level and groundwater inflow.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wang, C., Tannant, D.D., and Lilly, P.A., Numerical Analysis of the Stability of Heavily Jointed Rock Slopes Using PFC2D, International Journal of Rock Mechanics & Mining Sciences, 2003, vol. 40, no. 4, pp. 415–424.
Hanna, T.M., Azrag, E.A., and Atkinson, L.C., Use of an Analytical Solution for Preliminary Estimates of Groundwater Inflow tyo a Pit, Mining Engineering, 1994, vol. 46, no. 2, pp. 149–152.
Shevenell, L., Analytical Method for Predicting Filling Rates of Mining Pit Lakes: Example from tghe Getchell Mine, Nevada, Mining Engineering, 2000, vol. 52, no. 3, pp. 53–60.
Singh, R.N. and Atkins A.S., Application of Idealized Analytical Techniques for Prediction of Mine Water Inflow, Journal of Mining Science and Technology, 1985, vol. 2, pp. 131–138.
Singh, R.N. and Atkins, A.S., Analytical Techniques for the Estimation of Mine Water Inflow, International Journal of Mining Engineering, 1985, vol. 3, pp. 65–77.
Marinelli, F. and Niccoli, W.L., Simple Analytical Equations for Estimating Ground Water Inflow to a Mine Pit, Ground Water, 2000, vol. 38, no. 2, pp. 311–314.
Doulati Ardejani, F., Singh, R.N., Baafi, E.Y., and Porter, I., A Finite Element Model to Predict Groundwater Inflow to Surface Mining Excavations, Mine Water and the Environment, 2003, vol. 22 no. 1, pp. 31–38.
McWhorter, D.B., Predicting Groundwater Response to Disturbance by Mining—Selected Problems, Proc. Symp, Surface Mining, Hydrology, Sedimentology, and Reclamation, Univ. KY, Lexington, KY, USA, 1981, pp. 89–95.
Singh, R.N and Reed, S.M., Estimation of Pumping Requirement for a Surface Mining Operation, Proc. Symp. Pumps and Pumping, Nottingham University, England, 1987, pp. 1–24.
Williams, R.E., Winter, G.V., Bloomsburg, G.L., and Ralston, D.R., Mine Hydrology, Port City Press, Inc, Littleton, CO, Soc. Mining. Eng., AIME, 1986.
Domenico, P.A. and Schwartz, F.W., Physical and Chemical Hydrogeology, 1st Ed., John Wiley and Sons, NY, 1990.
Witherspoon, P.A., Y.Wang, J.S., Iwai, K., and Gale, J.E., Validity of Cubic Law for Fluid Flow in a Deformable Rock Fracture, Water Resources Research, 1980, vol. 16, no. 6, pp. 1016–1024.
Harr, M.E., Groundwater and Seepage, McGraw Hill Co., 1962.
Cedergren, H.R., Seepage, Drainage and Flow Nets, John Wiley and Sons, 1967.
González de Vallejo, L.I., Ferrer, L., Ortuño, M., and Oteo, C., Ingeniería Geológica, Pearson Educación, Madrid (in Spanish), 2002.
Sun, J. and Zhao, Z., Effects of Anisotropic Permeability of Fractured Rock Masses on Underground Oil Storage Caverns, Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology, 2010, vol. 25, no. 5, pp. 629–637.
ITASCA Consulting Group, Inc, UDECTM Version 6.0, Distinct Element Modeling of Jointed and Blocky Materials in 2D. Retrieved from 2015.
Kurlenya, M.V., Ecological Problems of Mine Production, Journal of Mining Science, 1993, vol. 28, no. 4, pp. 393–396.
Rogoz, M., Pressing Hydrogeological Problems of Mining in Poland, Journal of Mining Science, 1996, vol. 32, no. 2, pp. 150–157.
Nazarova, L.A., Nazarov, L.A., Dzhamanbaev, M.D., and Chynybaev, M.K., Evolution of Thermohydrodynamic Fields at Tailings Dam at Kumtor Mine, Journal of Mining Science, 2015, vol. 51, no. 1, pp. 17–22.
Doulati Ardejani, F., Singh, R.N., Baafi, E., and Porter, I., A Finite Element Model to Simulate Groundwater Rebound Problems in Backfilled Open Cut Mines, Mine Water and the Environment, 2003, vol. 22, no. 1, pp. 39–44.
Aryafar, A., Ardejani, F.D., Singh, R., and Shokri, B.J., Prediction of Groundwater Inflow and Height of the Seepage Face in a Deep Open Pit Mine Using Numerical Finite Element Model and Analytical Solutions, IMWA Symp. Proc. Water in Mining Environments, Cidu R., Frau F. (Eds.), Cagliari, Italy, 2007, pp. 313–317.
Younger, P.L., and Banwart, S.A., Mine Water: Hydrology, Pollution, Remediation, Kluwer, Dordrecht, 2002.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The article is published in the original.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Moosavi, E., Shirinabadi, R. & Gholinejad, M. Prediction of seepage water pressure for slope stability at the Gol-E-Gohar open pit mine. J Min Sci 52, 1069–1079 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1062739116061601
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1062739116061601